Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex and diverse neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in unique ways. From the varying experiences of identical twins to the differences in brain structure, autism manifests differently in each person.
In this article, we will explore the levels of autism, debunk misconceptions, discuss the importance of understanding the differences, and embrace the concept of neurodiversity. By providing guidance and resources, we aim to empower Parent Advocates to navigate the challenges of raising a child with autism and ensure their well-being.
What is the Autism Spectrum?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a neurodevelopmental condition, displays a wide array of symptoms, strengths, and challenges, varying greatly among individuals. This diversity is highlighted in the case of identical twins, Sam and John Fetters, who despite sharing the same genetic code, exhibit distinct experiences of the autism spectrum.
Sam is a college sophomore and marathon runner, while John attends a special needs school and enjoys Sesame Street. This disparity underscores the complexity and diverse manifestation of autism.
Research has revealed differences in brain structure between those with autism and neurotypical individuals, emphasizing the importance of understanding the disorder's genetic basis. However, the exact cause remains elusive, with no single gene or factor identified as the trigger.
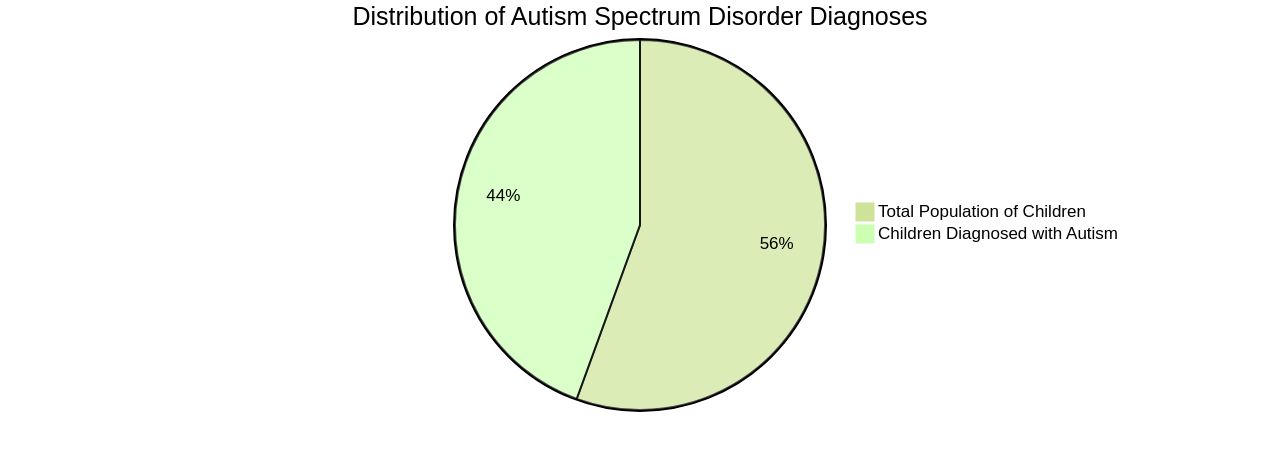
It's crucial to debunk misinformation around autism, such as attributing it to vaccines, parenting styles, or nutrition. The prevalence of autism has significantly increased, with recent statistics showing 1 in every 36 children diagnosed with the condition, up from 1 in 125 in 2004.
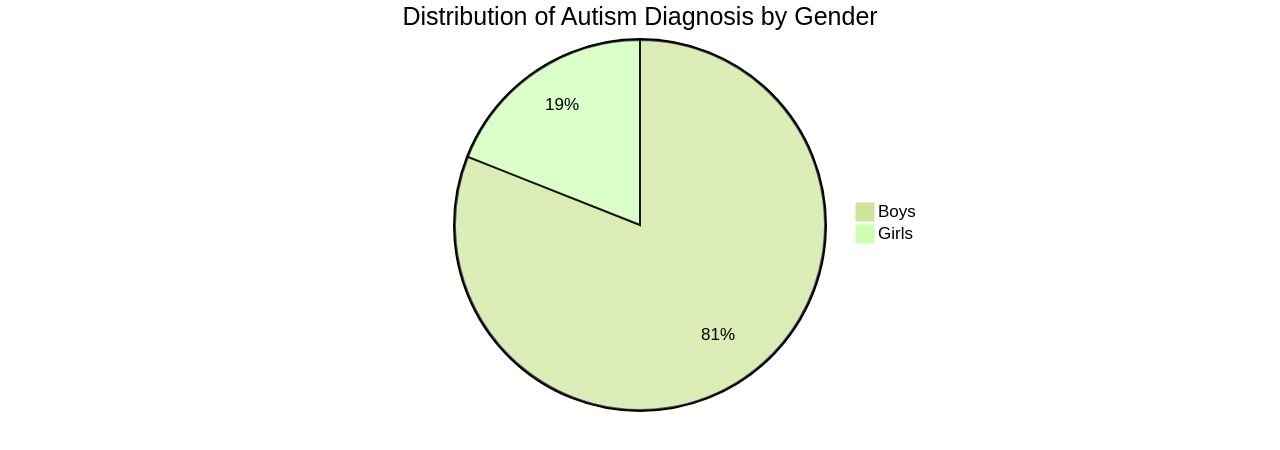
Boys are approximately four times more likely to be diagnosed than girls, and children diagnosed by age 4 are fifty times more likely to receive services. However, disparities exist, with children of color often receiving diagnoses later than their white counterparts due to potential barriers such as stigma, lack of access to healthcare, or language barriers. Autism is not a limitation but a different perspective on experiencing the world. As Dr. Deborah Bilder, M.D., from The University of Utah puts it, the needs of autistic individuals have become focal points for health care professionals. With the right support, self-advocacy, community, and acceptance, individuals with autism can thrive, highlighting the importance of understanding and supporting the diverse experiences and needs of individuals on the autism spectrum.
The Levels of Autism
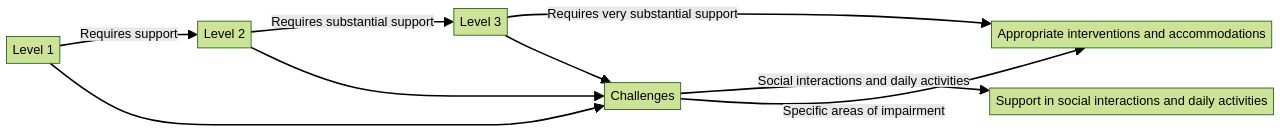
The levels of autism differ in each individual, making Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) a complex and multifaceted condition. The range of severity and impact on daily life led to the establishment of three primary levels of autism:
- Level 1: Requiring Support
Individuals with autism levels classified as Level 1 generally require support to navigate social interactions and daily activities.
Individuals with autism may struggle with initiating and sustaining conversations, adapting to changes in routines, and understanding non-verbal cues. However, individuals with varying levels of autism can function independently with appropriate support and accommodations. 2.
Level 2: Requiring Substantial Support
Individuals with autism levels of Level 2 require more substantial assistance in managing social interactions and daily life. Individuals with autism levels may experience significant difficulties with communication, social skills, and managing daily routines. Individuals with autism levels may exhibit repetitive behaviors or restricted interests that can interfere with their functioning.
Despite these challenges, individuals with varying levels of autism can achieve meaningful progress and independence with the right support and interventions. 3. Level 3: Requiring Very Substantial Support
Individuals with high autism levels require intensive support in all areas of their lives due to severe impairments in social communication and behavior.
Individuals with varying autism levels may encounter significant challenges in verbal and non-verbal communication and may display repetitive or self-injurious behaviors. Individuals with high levels of autism require intensive interventions to navigate daily life and may require lifelong assistance. It's important to remember that every individual is unique and may not fit perfectly into the categories of autism levels.
Moreover, individuals with autism can lead fulfilling lives by having the right support, understanding, and accommodations that cater to their specific autism levels. This includes early intervention, an understanding of their communication needs, and a willingness to learn about their unique perspectives. Our understanding and support of individuals with autism will continue to evolve as research progresses in the field of autism levels.
Understanding the Differences in Autism Levels
Autism, a complex spectrum of neurodiverse conditions, affects individuals to varying extents, mirroring the diverse nature of human brains. Research has unveiled distinctive brain structures, debunking misconceptions about autism's causality, affirming it is not induced by vaccines or parenting styles. Rather, it is believed to be linked to heredity and genetics, with ongoing research exploring potential genetic irregularities in autistic individuals.
Autism's prevalence is considerably higher than previously estimated. A University College London study indicates that the autistic population in England may exceed 1.2 million, nearly double the government's figure. This discrepancy is attributed to changes in diagnostic criteria, which have broadened autism's scope, and to a significant number of undiagnosed autistic adults.
Understanding the autism spectrum's diversity is critical to tailoring interventions and support. This understanding allows for individualized approaches, ensuring autistic individuals receive necessary resources and strategies to thrive. For instance, children diagnosed by age 4 are fifty times more likely to receive services, yet children of color often face diagnosis delays due to systemic barriers and stigma.
Boys are approximately four times more likely to receive an autism diagnosis than girls, but research suggests girls may present different characteristics and could be undiagnosed. Such knowledge empowers parents, educators, and professionals to advocate for appropriate resources and accommodations. It also highlights the need for improved training and services to better support autistic families, focusing on autism's positive aspects and addressing the challenges, responsibilities, and celebrations of parenthood.
Embracing Neurodiversity
The neurodiversity concept is a potent instrument in transforming societal attitudes towards autism. It underscores the unique strengths and potentialities of those with autism, rather than only spotlighting their challenges. This shift in perspective is vital for nurturing acceptance and inclusion.
For example, the autism spectrum includes one in every 36 children in the U.S. and one in every 100 in the UK. Each of these individuals carries a distinctive set of skills, perspectives, and abilities that should be recognized and valued. New studies show that individuals with neurodevelopmental conditions like autism often showcase remarkable creativity, resilience, and problem-solving skills.
Acknowledging these strengths not only diminishes stigma but also paves the way for enhanced educational and employment outcomes. Furthermore, this perspective shift aligns with many within the autistic community who advocate for understanding and acceptance rather than 'fixing.' However, acceptance remains a hurdle.
A recent survey of autistic individuals from eight countries discovered that only 23.5% felt accepted by society. Despite this, the tide is shifting. Increasingly, the neurodiversity concept is being accepted in schools, workplaces, and homes.
This shift isn't just about acceptance but also about recognizing the valuable contributions that individuals with autism make to society. Essentially, understanding autism and neurodiversity isn't about focusing on deficits, but rather about celebrating diversity and cultivating environments that value and support all individuals. It's about recognizing the potential in every child and adult with autism, and acknowledging their unique contributions to society.
To aid in understanding and accepting autism, www.asd. Media offers unlimited digital access with different subscription options, including a yearly subscription and a monthly subscription. This resource can be accessed by clicking the subscribe button on the website.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex and diverse condition that affects individuals in unique ways. Understanding the genetic basis of autism, debunking misconceptions, and embracing neurodiversity are crucial for supporting individuals on the spectrum.
The levels of autism provide a framework for understanding severity and impact on daily life, but it's important to remember that every individual is unique. Tailored interventions and early diagnosis can help individuals thrive.
By recognizing the strengths of autistic individuals and fostering acceptance and inclusion, we can create supportive environments that empower all individuals. With appropriate support and accommodations, individuals with autism can lead fulfilling lives. In summary, by understanding the unique nature of autism, debunking misconceptions, embracing neurodiversity, and providing support and accommodations, we can ensure the well-being and success of individuals on the autism spectrum.




