Overview
Understanding autism in young adults begins with recognizing the unique challenges they encounter. These challenges often include:
- Social communication difficulties
- Sensory sensitivities
- Mental health issues
All of which can significantly affect their quality of life and prospects for independence. It’s essential to acknowledge these hurdles to foster a deeper understanding of their experiences.
The importance of tailored support and individualized planning cannot be overstated. Effective strategies, such as:
- Job coaching
- Social skills training
- Advocacy
Can truly empower these individuals. By implementing these approaches, we can help them navigate adulthood successfully and enhance their overall well-being.
As we reflect on these insights, consider how you might support someone in your life facing similar challenges. What resources or strategies have worked for you? Share your stories and thoughts, as they can inspire others on this journey. Together, we can create a more supportive environment for young adults with autism, ensuring they have the tools they need to thrive.
Introduction
In a world that often overlooks the nuances of neurodevelopmental disorders, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) emerges as a multifaceted condition that truly deserves our attention and understanding.
With its increasing prevalence among children and young adults, the challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum can profoundly affect their quality of life—impacting everything from social interactions to educational and employment opportunities.
This article seeks to explore the complexities of ASD, shedding light on its key characteristics, the critical importance of early intervention, and the essential role of tailored support systems.
By delving into the unique hurdles that young adults with autism encounter, alongside effective strategies for fostering independence, this comprehensive overview aims to empower parents, caregivers, and advocates in their efforts to cultivate a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with ASD.
Defining Autism Spectrum Disorder: Key Concepts and Characteristics
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges in interpersonal interaction, communication, and behavior. Grasping its key traits is vital for parents and caregivers to effectively assist individuals with ASD.
- Interaction Communication Difficulties: Individuals with ASD often encounter significant challenges in interpreting interpersonal cues, engaging in discussions, and expressing their emotions. Recent research indicates that approximately 2.9% of children exhibit these social communication difficulties, with a confidence interval of 95% (2.7%–3.1%). This highlights the prevalence of this challenge across diverse demographics. The 2020 ADDM Network findings revealed that while early identification of ASD has improved, many children still receive their diagnoses only when they reach school age. It is important to note that the data collected represent averages from specific states and cannot be generalized to the overall U.S. prevalence rate, underscoring the need for timely intervention.
- Repetitive Behaviors: A common trait among individuals with ASD is the tendency to engage in repetitive movements or insist on specific routines. These behaviors can serve as coping mechanisms, providing comfort and predictability in an often overwhelming world. Real-world examples include hand-flapping, rocking, or the need to follow a strict daily schedule, which can be crucial for emotional regulation.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Many individuals with ASD experience sensory processing issues, resulting in either heightened or diminished responses to sensory stimuli. This can manifest as extreme sensitivity to sounds, lights, or textures, making everyday environments challenging. Comprehending these sensory sensitivities is essential for developing nurturing environments that cater to personal needs.
Identifying these traits not only promotes empathy but also provides parents and caregivers with the information required to apply effective strategies and interventions customized to the distinct experiences of individuals with ASD. As noted by Williams AR in the MMWR Surveillance Summary, understanding the prevalence and characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder is crucial for developing effective support systems for affected individuals.
Prevalence and Demographics of Autism in Young Adults
Recent studies reveal that approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. is diagnosed with a developmental disorder, and this rate continues to rise. Notably, the increase among young individuals, particularly females, suggests a broader trend in diagnoses related to these conditions. Current data indicates that by 2025, the prevalence of autism in young adults has emerged as a significant public health concern; 8% of affected students are not completing high school, compared to 5% of their peers.
This disparity highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions and robust support systems. Understanding these trends requires us to consider demographic factors. The CDC reports a male-to-female diagnosis ratio of 4:1, with variations in prevalence rates across different racial and socioeconomic groups. For instance, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic children exhibit higher rates of the condition than their non-Hispanic White counterparts.
These findings suggest that the prevalence of autism in young adults is shaped by a combination of gender, race, and socioeconomic factors, underscoring the necessity for tailored approaches in autism awareness and intervention strategies. It’s also crucial to recognize the emotional challenges families face. A study found that 67.1% of mothers of autistic children reported experiencing both depression and anxiety symptoms, emphasizing the need for comprehensive support for parents. As they navigate these challenges, it is vital to remember that success is attainable even for children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
The American Psychological Association acknowledges Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) as a fact-based treatment with proven effectiveness, reinforcing the importance of evidence-based strategies. By staying informed about these trends and statistics, parents can better advocate for their children and seek resources and support that align with their unique needs. Together, we can foster a supportive community that uplifts families and champions the potential of every child.
Challenges Faced by Young Adults on the Autism Spectrum
Young individuals with autism face unique difficulties that significantly impact their quality of life and future prospects. These challenges are not just statistics; they are real experiences that affect many young adults and their families.
- Social Isolation: Many autistic individuals struggle to form and maintain friendships, leading to profound feelings of loneliness. Research shows that understanding and acceptance of autism are crucial in alleviating this isolation. A study revealed that 16 investigations indicated relationships as a factor negatively linked with loneliness in autistic individuals, emphasizing the importance of connections. As one participant in Ee et al.'s (2019) study poignantly stated, "people have been so cruel to me, I don’t interact ever anymore," highlighting the emotional toll of isolation.
- Employment Barriers: Gaining and keeping a job can be a daunting task for numerous young individuals on the spectrum. Social communication difficulties and workplace dynamics often hinder their ability to navigate job environments effectively. A recent analysis comparing social participation odds ratios found that young individuals with ASD are significantly less likely to engage in social activities than their non-ASD peers. This underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions to enhance social integration and employment readiness. These findings are particularly relevant for young adults with autism who received special education services under the autism eligibility category, reflecting the unique challenges faced by this group.
- Mental Health Issues: Autistic individuals experience higher rates of anxiety and depression, necessitating comprehensive mental health assistance. The challenges of social isolation and employment barriers can exacerbate these mental health issues, creating a cycle that is difficult to break.
Recognizing these challenges is essential for parents and caregivers. It empowers them to advocate effectively for their children. By seeking suitable resources and assistance, they can help their young individuals navigate these obstacles and work towards a more fulfilling life. Together, we can foster understanding and support, ensuring that every young adult with autism has the opportunity to thrive.
Navigating Employment and Independence: Opportunities and Strategies
To empower young adults with autism on their journey toward employment and independence, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Job Coaching: Collaborate with job coaches who specialize in autism to provide personalized support throughout the job search process. These professionals can help identify strengths and areas for improvement, ensuring that the coaching is tailored to the individual's unique needs. Given that autistic individuals often change jobs more frequently than their neurotypical peers, stable job coaching and support are essential for fostering long-term employment success.
- Internships and Volunteer Opportunities: Actively encourage participation in internships or volunteer roles, which are crucial for building practical skills and boosting confidence. Research indicates that individuals with autism who engage in internships are more likely to secure employment after transition, highlighting the importance of these experiences. As Zachary Warren, PhD, emphasizes, "Research to quantify the degree to which these interventions are effective, under what specific circumstances, and for which individuals with ASD is critical for the growing number of adolescents and young individuals with ASD who are approaching the transition to maturity."
- Life Skills Training: Prioritize teaching essential life skills, such as budgeting, cooking, and time management. These competencies are vital for fostering independence and preparing young adults for the responsibilities of adult life.
The significance of job coaching cannot be overstated; it has been shown to enhance vocational outcomes for young adults with autism. A recent follow-up survey indicated that participants in job coaching programs reported improved job retention and satisfaction compared to those who did not receive such assistance. Furthermore, case studies emphasize the need for ongoing research into employment experiences, suggesting that qualitative data could provide deeper insights into the factors influencing job success for autistic individuals.
The limitations of current studies, such as the susceptibility of decision tree analysis to data changes, highlight the need for larger sample sizes to improve the stability of findings.
By integrating these strategies, parents can facilitate a smoother transition for their children, particularly those with autism, into adulthood, equipping them with the tools necessary for success in the workforce. ASD Media is committed to fostering collaboration and growth in the ABA therapy industry, providing valuable resources and support for parents and professionals alike.
Developing Social Skills and Building Relationships
Cultivating interpersonal skills is crucial for young individuals with developmental disorders, as it significantly impacts their ability to form meaningful connections and navigate social interactions. Understanding this need is the first step toward fostering these essential skills. Here are several effective approaches to support their development:
- Social Skills Training Programs: Enrolling in structured programs that emphasize social interaction through role-playing and real-life scenarios can be incredibly beneficial. A recent study involving 57 young individuals with autism showed that those who completed a 16-week interpersonal skills course experienced marked improvements in engagement and a reduction in autism-related symptoms. Follow-up evaluations indicated that these gains were not only maintained but further enhanced over time, highlighting the effectiveness of such training. As Elizabeth Laugeson, founder and director of the PEERS Clinic at UCLA, states, "The next step is to wait for a brief pause in the conversation and move closer. The final step is to join the conversation by saying something on topic," emphasizing the importance of active participation in interactions.
- Peer Mentoring: Establishing peer mentoring relationships can provide young adults with valuable role models who exemplify appropriate interpersonal behaviors. Mentors offer guidance and support, facilitating a more personalized approach to interpersonal skills development. Experts note that peer mentoring plays a crucial role in fostering interpersonal competence among individuals with autism, allowing them to learn in a relatable context.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging involvement in community activities allows young individuals to practice their interpersonal skills in a supportive environment. Engaging with peers in various settings reinforces learned behaviors and builds confidence. Real-world examples of successful community involvement initiatives demonstrate how these experiences can lead to lasting improvements in interactions. For instance, a case study titled 'Lasting Gains and Further Improvement' assessed participants with autism who completed a 16-week course designed to enhance interpersonal skills. It revealed notable advancements in interaction abilities, engagement, and a reduction in symptoms associated with social responsiveness. Follow-up evaluations four months later indicated that these gains were maintained, with additional improvements in communication, assertion, responsibility, and empathy, likely due to ongoing caregiver support.
By applying these strategies, young individuals with developmental differences can enhance their social skills, leading to more fulfilling relationships and improved overall well-being. Together, we can support their journey toward meaningful connections.
Mental Health and Well-Being: Understanding the Needs of Young Adults
Mental health is a fundamental component of overall well-being for young adults with autism. Many of these individuals confront significant challenges related to anxiety and depression. Studies reveal that:
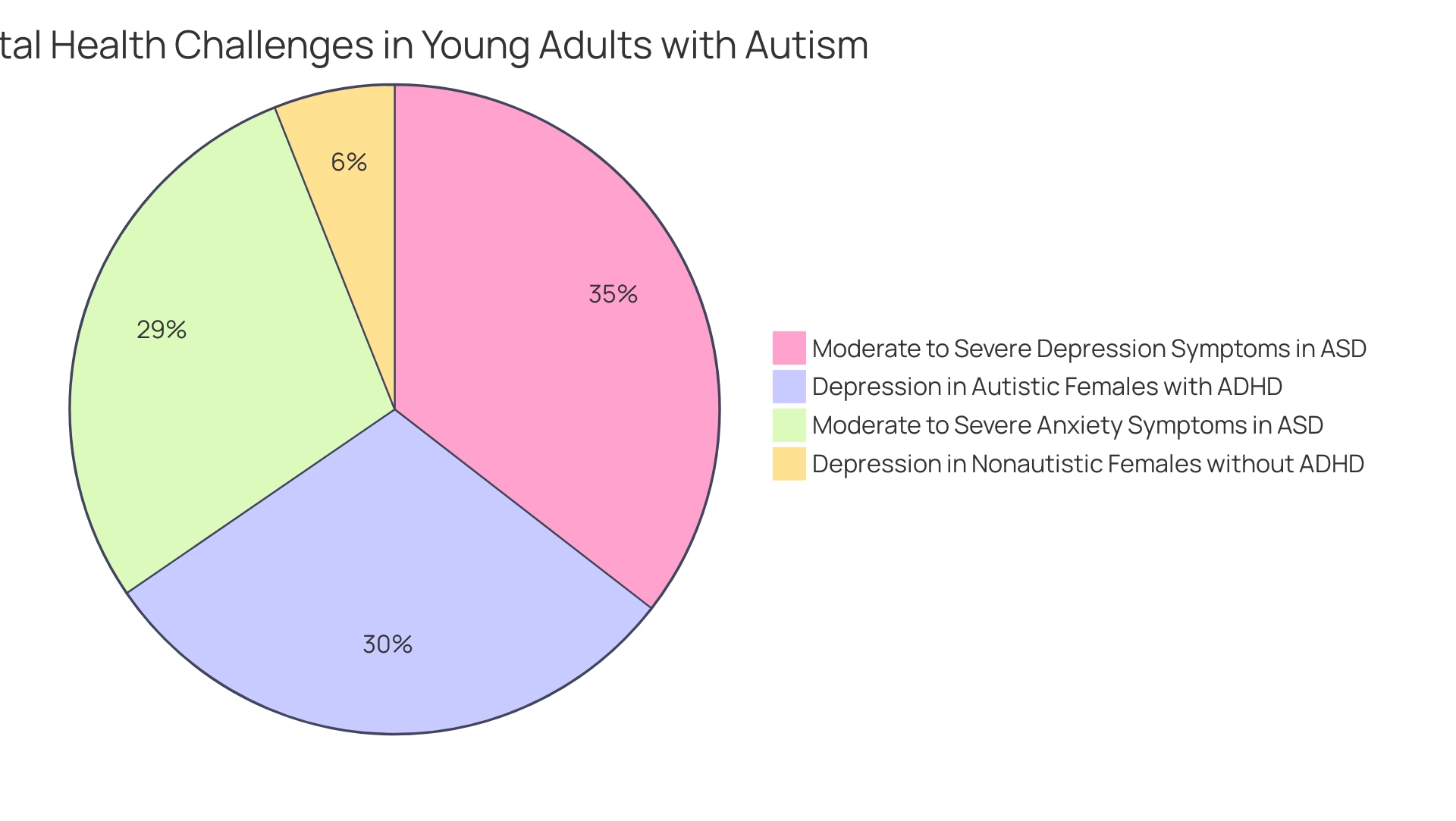
- 37% of individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) report moderate to severe anxiety symptoms.
- 46% experience similar levels of depression.
- Notably, 38.8% of autistic females with ADHD face depression compared to just 7.8% of nonautistic females without ADHD, highlighting the gender differences in mental health challenges.
These issues are often intensified by social difficulties, making it crucial for parents and caregivers to take proactive steps in addressing mental health needs. Access to tailored mental health services is vital for young individuals with autism. Effective resources should be designed to meet their unique requirements, ensuring they receive the appropriate support. Unfortunately, many still encounter barriers to accessing these essential services, underscoring the need for advocacy and improved service availability.
Encouraging the development of coping strategies is another key aspect of supporting mental health. Techniques such as mindfulness, stress management, and emotional regulation can significantly enhance resilience. By fostering these skills, parents can empower their children to navigate the complexities of adulthood more effectively.
As van Steensel and colleagues noted, autistic youth have higher rates of anxiety compared to those with ADHD, emphasizing the prevalence of anxiety and depression among autistic individuals. The findings from the case study titled "Anxiety and Depression in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder" revealed that:
- 37% of individuals diagnosed with ASD reported moderate to severe anxiety symptoms.
- 46% reported moderate to severe depression symptoms.
Factors such as younger age, female gender, and heightened severity of the condition were recognized as contributors to anxiety symptoms.
The mental health environment for young individuals with developmental disorders, particularly concerning autism, requires ongoing focus and resources. This is especially important given the constraints of current research, including reliance on cross-sectional data and the possible overrepresentation of studies from developed nations. By prioritizing mental health, parents can play a crucial role in helping their children thrive in adulthood, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
Supporting the Transition to Adulthood: Key Considerations
Supporting the transition to adulthood for young adults with autism is a journey that requires thoughtful consideration of several critical factors.
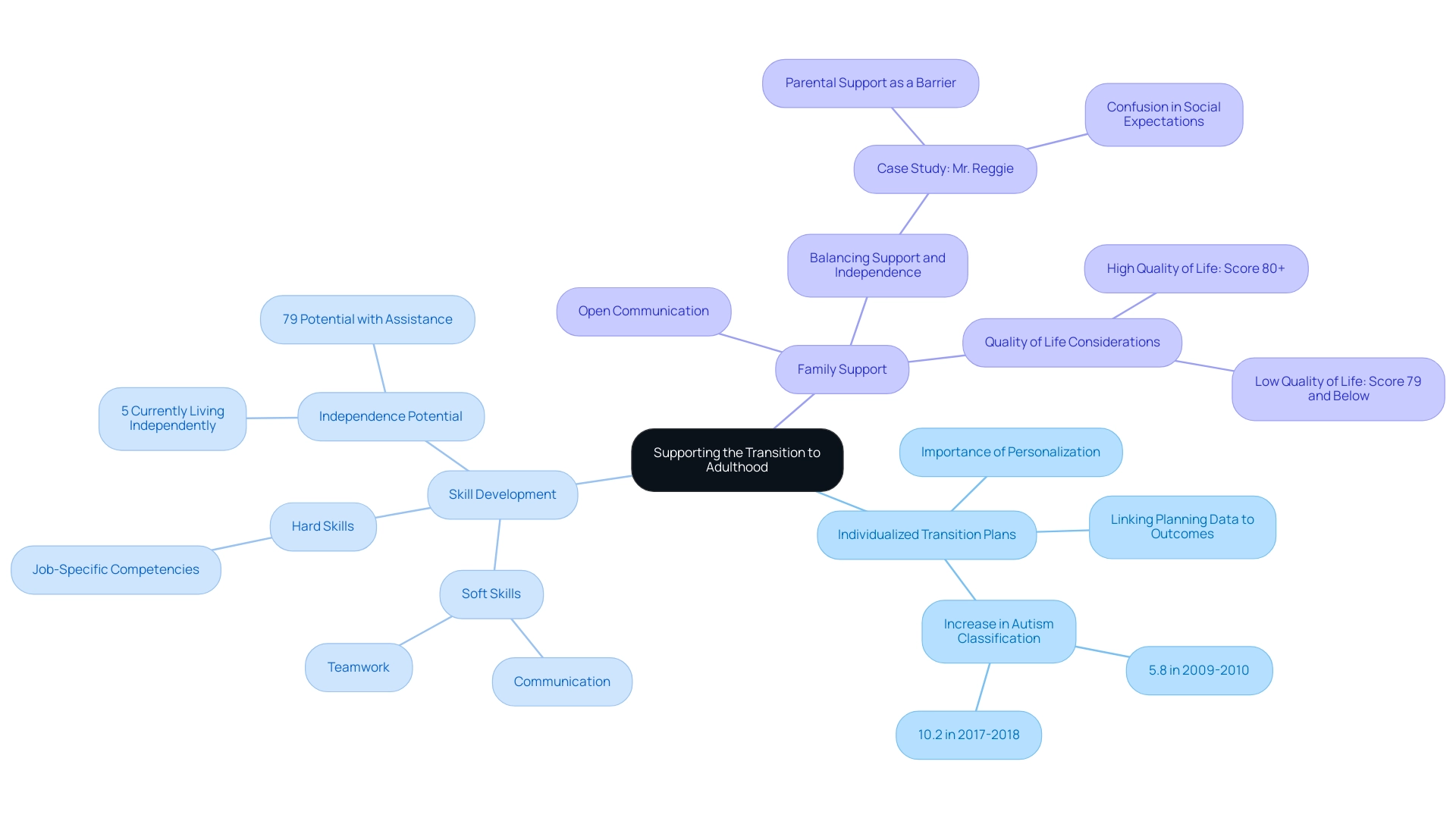
Individualized Transition Plans: Collaborating with educators to create personalized transition plans is essential. These plans should be tailored to meet the unique needs of each young individual, ensuring they are equipped with the necessary tools to navigate adulthood successfully. Future studies emphasize the importance of linking transition planning data to postsecondary outcomes, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of these plans. Notably, the percentage of adolescents served under an autism classification increased from 5.8% in 2009-2010 to 10.2% in 2017-2018, underscoring the growing recognition of autism in young adults and its implications for transition planning.
Skill Development: A dual focus on both soft skills—such as communication and teamwork—and hard skills, including job-specific competencies, is vital for preparing young individuals for the workforce. Statistics reveal that while only 5% of individuals with autism in young adults currently live independently, up to 79% have the capability to do so with suitable assistance. This highlights the necessity of comprehensive skill development programs that empower individuals to thrive in various environments. As noted by "New Direction for Young Adults," a significant number of individuals with autism can achieve independence with appropriate support.
Family Support: Open communication within the family is crucial during this transition phase. Discussing expectations and concerns can help alleviate anxiety and foster a supportive atmosphere. A case study involving Mr. Reggie illustrates how parental assistance can sometimes inadvertently act as a barrier to independence, leading to confusion in social expectations. This case highlights the complexities of parental involvement and the need for a balanced approach that encourages autonomy while providing necessary guidance. By addressing these considerations, parents can play a pivotal role in facilitating a smoother transition for their children, particularly those with autism in young adults, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and independence as they step into adulthood. Individuals with disabilities living independently and engaged in employment, with a total quality of life score of 80 and above, are identified as having a high quality of life, emphasizing the importance of supporting young people in achieving independence.
Tailored Support and Individualized Planning for Young Adults
Customized assistance plays a vital role for young individuals with developmental differences, profoundly influencing their growth and self-sufficiency. It's essential to explore key approaches that can make a difference:
- Individualized Education Programs (IEPs): Regularly updating IEPs is crucial to align with the evolving goals and needs of young adults. A recent study revealed that only 28 out of every 100 students with developmental disorders had primary goals focused on independent living. This highlights a significant gap in transition planning. As Matthew J Maenner, PhD, from the CDC, noted, "This study identified potential gaps and disparities in educational services and transition planning among adolescents, which are crucial for addressing autism in young adults, aiding in guidance for schools and families."
- Personalized Assistance Plans: Crafting assistance plans that specifically address individual challenges—such as communication difficulties or sensory sensitivities—can lead to more effective outcomes. Real-world examples illustrate that personalized strategies can significantly enhance daily functioning and social interactions.
- Regular Assessments: Conducting frequent evaluations allows for the assessment of progress and necessary adjustments to assistance strategies. This ongoing process ensures that the support provided remains relevant and effective.
The significance of customized assistance cannot be overstated. Research indicates that many IEPs fall short in adequately addressing social skills, with an average of just 1.6 postsecondary goals recognized in a study examining IEPs for transition-age students with developmental disorders. The study titled "Quality of Transition IEPs for Students with Autism in Young Adults" revealed that while all IEPs included an employment postsecondary goal, less than half included an independent living goal.
Moreover, collaboration with education partners, families, and adolescents is crucial to improving the transition planning process. By implementing these tailored support strategies, parents can play a pivotal role in enhancing their child's journey toward independence and success. Additionally, there is an urgent need for more research on transition planning and IEPs specifically addressing the ongoing challenges faced by students with autism in young adults.
Advocacy and Initiatives: Empowering Young Adults with Autism
Advocacy plays a crucial role in empowering young adults with developmental differences, nurturing a more inclusive society. It is vital for parents to engage in initiatives that can make a significant impact:
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Participate in campaigns that foster understanding and acceptance of autism within your community. These efforts not only raise awareness but also promote respect for individuals on the spectrum, contributing to a more supportive environment. Autism Acceptance Month emphasizes understanding and respecting those with this condition, aligning with recent campaigns that highlight the importance of community support. It's worth noting that research indicates over 60% of people know someone with a developmental disorder, underscoring the need for shared awareness. As Nicole J Rinehart from Deakin University observes, "These findings suggest that lower perceived levels of community supportiveness may reduce the involvement of children with ASD in community activities and increase feelings of isolation in their caregivers."
- Policy Advocacy: Collaborate with local and national organizations to advocate for policies that benefit individuals on the spectrum. Effective policy advocacy can lead to meaningful changes in funding and resources, ensuring that young adults receive the assistance they need. Recent discussions in the field have highlighted the impact of community supportiveness on the involvement of individuals with autism in community activities, emphasizing the necessity for robust advocacy efforts. Organizations like the Moose Foundation often back these initiatives, aiding research in neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Assistance Networks: Consider creating or joining assistance networks that allow families to exchange resources and strategies for effective advocacy. These networks can serve as a vital lifeline, offering emotional support and practical advice. By connecting with others, families can amplify their voices and influence policy changes that directly affect their loved ones. Furthermore, recognizing the contributions of diverse perspectives, such as those highlighted in the case study honoring Black scientists, is essential in addressing systemic issues and enhancing visibility within the community.
By actively engaging in these advocacy efforts, parents can significantly contribute to creating a more inclusive society for their children, ensuring that they empower young adults with autism to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is vital for fostering a supportive environment for individuals on the spectrum. This article has explored the key characteristics of ASD, including social communication difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Recognizing these traits is essential for parents and caregivers to provide effective support. The rising prevalence of autism among young adults highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions and awareness, as many face significant challenges related to social isolation, employment barriers, and mental health issues.
The journey toward independence for young adults with autism can be significantly enhanced through tailored support strategies such as:
- Job coaching
- Life skills training
- Social skills development
These approaches empower individuals to navigate adult life more effectively, promoting their ability to form meaningful relationships and secure employment. Furthermore, addressing mental health needs through appropriate services and coping strategies is crucial to improving overall well-being.
Ultimately, advocacy plays a pivotal role in creating a more inclusive society. By actively engaging in community awareness campaigns, policy advocacy, and support networks, families can help elevate the voices of individuals with autism, ensuring they receive the resources and respect they deserve. As society continues to evolve, fostering understanding and acceptance of autism will not only benefit individuals on the spectrum but also enrich our communities as a whole. Prioritizing these efforts will pave the way for a brighter future for young adults with autism, empowering them to thrive in all aspects of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges in interpersonal interaction, communication, and behavior.
What are the common interaction communication difficulties faced by individuals with ASD?
Individuals with ASD often struggle with interpreting interpersonal cues, engaging in discussions, and expressing emotions. Approximately 2.9% of children experience these social communication difficulties.
What are repetitive behaviors in individuals with ASD?
Repetitive behaviors are common traits in individuals with ASD, including movements like hand-flapping or rocking, and insistence on specific routines. These behaviors can provide comfort and predictability in overwhelming situations.
How do sensory sensitivities affect individuals with ASD?
Many individuals with ASD experience sensory processing issues, leading to heightened or diminished responses to sensory stimuli, such as extreme sensitivity to sounds, lights, or textures, which can make everyday environments challenging.
What is the prevalence of autism in children and young adults?
Recent studies indicate that approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. is diagnosed with a developmental disorder, with rising rates particularly among young individuals and females.
What are the emotional challenges faced by families of autistic children?
A study found that 67.1% of mothers of autistic children reported experiencing symptoms of both depression and anxiety, highlighting the need for comprehensive support for parents.
What is the male-to-female diagnosis ratio for autism?
The CDC reports a male-to-female diagnosis ratio of 4:1, with variations in prevalence rates across different racial and socioeconomic groups.
What barriers do young individuals with autism face in employment?
Young individuals with ASD often encounter challenges in gaining and maintaining employment due to social communication difficulties and workplace dynamics, making it harder to navigate job environments.
How does social isolation affect young individuals with autism?
Many autistic individuals struggle to form and maintain friendships, leading to feelings of loneliness. Understanding and acceptance of autism are crucial in alleviating this isolation.
What mental health issues are prevalent among individuals with autism?
Autistic individuals experience higher rates of anxiety and depression, which can be exacerbated by challenges related to social isolation and employment barriers.




