Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for providing the right support to affected children and their families. ASD is a multifaceted condition that goes beyond communication and behavior challenges. It's a lifetime journey that requires a holistic approach and personalized interventions.
With the prevalence of ASD rising, early diagnosis and intervention are more important than ever. This article delves into the early signs of ASD, the importance of early detection and intervention, screening methods, and strategies for parent advocates to support children with ASD. Join us as we explore this topic and empower parents to navigate the challenges and ensure the well-being of their children on the autism spectrum.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Understanding the multifaceted nature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for providing the right support to affected children and their families. ASD is not just a condition impacting communication and behavior; it's a lifetime journey that requires a holistic approach to each unique case.
The individual struggles of children with ASD, such as sensory sensitivities and social challenges, are amplified by systemic barriers like healthcare inaccessibility and socioeconomic hurdles. With the prevalence of ASD rising to 1 in 36 children, the urgency for early diagnosis and intervention is greater than ever.
These early steps can lead to significantly improved outcomes, with studies indicating that only 10-20 percent of children diagnosed before 5 years of age are able to live independently as adults. Disrupted dopaminergic signaling has been identified as a potential factor in ASD, pointing to new therapeutic targets that could reshape treatment approaches.
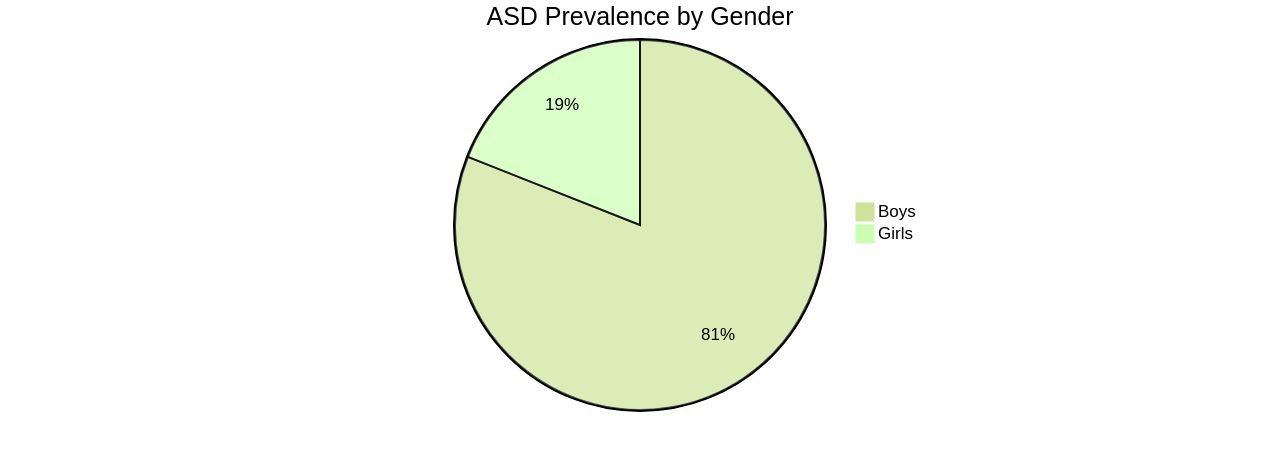
Moreover, treatments for ASD must be tailored to each individual, focusing on minimizing symptoms that affect daily life. With the knowledge that ASD prevalence is similar across all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups, and that boys are four times more likely to be diagnosed than girls, it is essential for support systems to be inclusive and person-centered. In Australia, for instance, the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) provides tailored support plans for children with ASD, emphasizing the importance of early intervention. The challenge remains to ensure that all children, regardless of background, receive the necessary support and services to thrive.
Early Signs and Symptoms of ASD in Young Children
Early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is pivotal for initiating timely support and intervention. Notable early signs in toddlers to watch for include delays in speech or language, limited social interaction, such as reduced eye contact, and repetitive movements like hand-flapping. Changes in routine or sensory sensitivities are also telltale markers.
Recent research highlights that despite the identification of behavioral indicators within the first year, the average age of ASD diagnosis is around 3 years, delaying crucial early intervention. Studies emphasize the need for continuous monitoring of infants and toddlers to spot subtle behavioral shifts that could signal ASD, urging for more community-based early detection before 18 months. Experts now understand that ASD is not a uniform condition but a spectrum, with a range of symptoms and severity levels.
It is critical to remember that autism is a neurological disorder, not a mental health condition, and it affects individuals uniquely. Early diagnosis is the gateway to early intervention, which can greatly impact the trajectory of a child's development. With only a small percentage of children diagnosed before age 5 able to live independently in adulthood, the importance of early recognition and action cannot be overstated.
This understanding is reinforced by statistics showing disparities in speech and language delays among children from different racial and socioeconomic backgrounds. Healthcare providers are now incorporating routine screening into well-baby checkups to identify early signs of autism as soon as 12-14 months. Such proactive measures can connect children and families to supportive services at the earliest stage possible, offering the best chance for positive outcomes.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Recognizing the early signs of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a critical step in providing the necessary support and interventions for children. Research indicates that symptoms of ASD can emerge in the first two years of life, often discernible through retrospective videotape analysis, parental reports, and high-risk sibling studies.
Despite these early behavioral markers, the average age of ASD diagnosis hovers around 3 years, delaying essential early interventions during a crucial developmental period. Only 24% of children are diagnosed before entering school, and 70% of practitioners do not use standardized diagnostic instruments for the initial diagnosis.
Early intervention is pivotal; it can shape a child's social, communicative, and cognitive development, enhancing their overall quality of life. It's imperative that we leverage the advanced understanding of early ASD signs to reduce the age of diagnosis.
This means advocating for repeated monitoring of behavior over time to chart the subtle changes in infants and toddlers at risk for ASD. The reality is stark: only 10-20% of children diagnosed with ASD before the age of 5 have the potential to live independently as adults. This underscores the importance of early and accurate diagnosis, which can open the door to tailored interventions such as speech and occupational therapy, applied behavior analysis (ABA), and other specialized programs. With a strong genetic component, ASD's development is also influenced by environmental factors, necessitating a nuanced approach to treatment that considers the dynamic interplay of these elements. As we push for earlier identification and intervention, we are not only advocating for better outcomes but also empowering children with ASD to reach their fullest potential.
Screening and Early Detection Methods for ASD
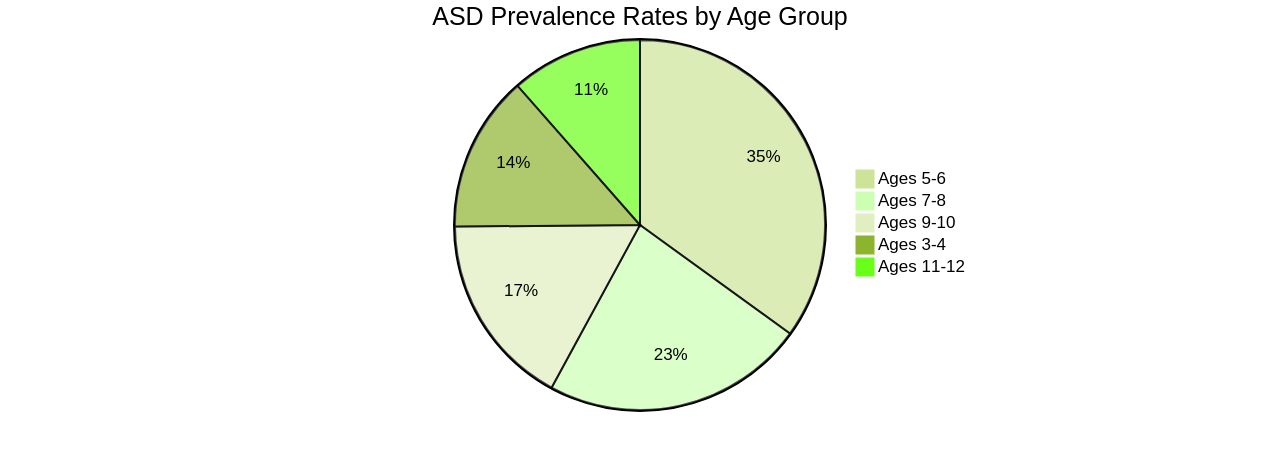
Understanding the importance of early detection in children at risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is pivotal. Developmental screenings by healthcare professionals and further assessments by autism specialists are key steps in identifying children who may benefit from early interventions. This is backed by research, such as a study in Egypt which found ASD prevalence rates of 3.4% among children aged 3 to 12 using the GARS-2.
Another significant finding from the same research showed that preschool children, particularly between ages 5 to 6, had the highest prevalence rate (6.4%). These numbers underscore the critical necessity for early detection, particularly as the most common age for ASD presentation is between 2 to 5 years. Innovations like the SenseToKnow app, developed by researchers at Duke University, are enhancing the accuracy of ASD screening.
This app, which assesses children's responses to visual stimuli, is a promising tool for identifying early signs of ASD and has been used to screen toddlers during routine well-child visits. It is important to note that while screening tools are helpful, they are not definitive for diagnosis. A positive screening result should lead to a comprehensive evaluation by a trained professional to determine the need for treatment and early developmental intervention.
Recent advancements also include the efforts of organizations like The Autism Community in Action (TACA), which supports families and emphasizes the benefits of early behavioral therapy. Furthermore, the acquisition by NeuroQure aims to provide families with diagnostic support within weeks of birth, significantly reducing the traditionally lengthy diagnostic process for ASD. With early and accurate diagnosis, children with ASD can access the necessary support and services, leading to more optimal outcomes.
Strategies for Parent Advocates: Supporting Children with ASD
Supporting a child with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires dedication, compassion, and an adaptive approach. Parents can empower their children by gaining knowledge about the condition and the spectrum of interventions available.
This understanding facilitates informed advocacy and decision-making. Establishing a robust support network is equally crucial.
By connecting with other families dealing with similar challenges, parents can share experiences and resources, providing each other with emotional strength and practical advice. Close collaboration with professionals is essential for creating tailored plans that cater to a child's unique needs.
This synergy between healthcare providers, educators, and families can lead to progress in the child's development. Promoting inclusion and acceptance within educational and community settings enriches the child's social experiences, fostering a sense of belonging.
Moreover, parents must prioritize their well-being to maintain resilience. Self-care is not an indulgence but a necessity for those navigating the parenting journey with a child on the autism spectrum.
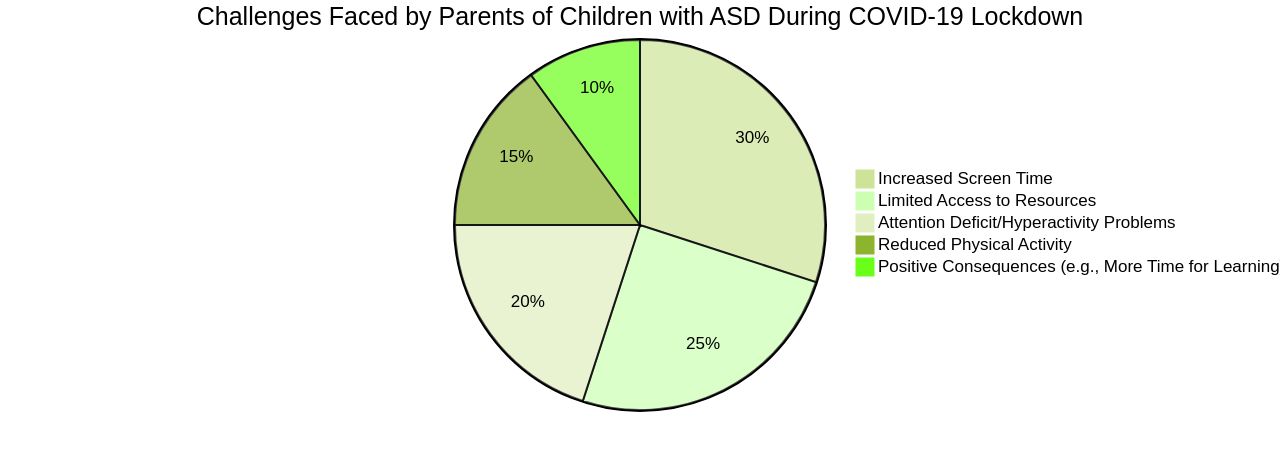
Research underscores the importance of early intervention, with studies indicating that targeted behavioral therapies can enhance cognitive abilities and social skills. Parents themselves can be taught to implement these interventions, contributing to improved child outcomes and more meaningful parent-child interactions. Still, challenges persist, such as limited access to resources, which can hinder a child's development. Recent studies have shown that during the COVID-19 lockdown, some children with ASD experienced positive changes, such as reduced attention deficit/hyperactivity problems, and parents found more time for constructive activities like learning and online therapy. However, the same studies reported concerns over increased screen time and reduced physical activity. As each child with autism is unique, every day presents a new opportunity for growth and learning. It is with hopefulness and a commitment to independence that parents and advocates continue to strive for the best possible outcomes for their children.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for providing the right support to affected children and their families. Early diagnosis and intervention are more important than ever, as they can significantly improve outcomes for children with ASD. Notable signs of ASD in young children include delays in speech or language, limited social interaction, repetitive movements, changes in routine, and sensory sensitivities.
Routine screenings during well-baby checkups can help identify these signs as early as 12-14 months, connecting children and families to supportive services at the earliest stage possible. Early diagnosis paves the way for early intervention, which plays a vital role in a child's development. Tailored interventions such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and specialized programs can make a significant difference in a child's social, communicative, and cognitive abilities.
Screening methods like the SenseToKnow app are enhancing the accuracy of ASD screening. While screening tools are not definitive for diagnoses, a positive result should lead to a comprehensive evaluation by a trained professional. As parent advocates, it's essential to empower ourselves with knowledge about ASD and available interventions.
Establishing a strong support network with other families facing similar challenges is crucial. Collaboration with professionals helps create tailored plans for our children's unique needs. Promoting inclusion and acceptance within educational and community settings enriches our children's social experiences.
Prioritizing our own well-being through self-care is necessary for resilience on this parenting journey. By understanding the early signs of ASD, advocating for early diagnosis and intervention, utilizing screening methods, and implementing strategies as parent advocates - we can navigate the challenges alongside our children on their journey towards well-being and success. Together, we can empower our children with ASD to reach their fullest potential.




