Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be a daunting journey for caregivers, filled with both challenges and opportunities for growth. Understanding the multifaceted nature of autism is essential, as it manifests differently in each individual, shaping their unique strengths and difficulties.
From recognizing early signs in boys to addressing the critical need for timely diagnosis and intervention, caregivers play a pivotal role in advocating for their children. With research highlighting significant disparities in diagnosis and the importance of tailored support, this article delves into effective strategies and resources that empower caregivers to foster an enriching environment.
By equipping themselves with knowledge and tools, advocates can ensure their children thrive, paving the way for a brighter future.
What is Autism? An Overview for Caregivers
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents a range of challenges, particularly in social interaction, communication, and the presence of repetitive behaviors. The spectrum nature of this condition means that its impact varies significantly from one individual to another, leading to different degrees of severity and unique profiles of strengths and challenges. For example, many young boys with autism may struggle to interpret social cues, convey their emotions, or engage in typical play activities.
However, it is crucial for caregivers to recognize that each individual possesses a distinct combination of abilities and challenges that can shape their behavior and learning approaches. By understanding these foundational characteristics, parents and advocates can more effectively support their offspring and pursue the appropriate resources and support systems. Recent data illustrates the complexity of autism prevalence globally:
- While Egypt reports an autism prevalence of 89.40 per 10,000 individuals,
- Qatar has the highest rates at 151.20 per 10,000, reflecting significant disparities in diagnosis and reporting practices.
- In contrast, France has the lowest diagnosed rates at roughly 1 in 144 young individuals.
Furthermore, the National Survey of Children’s Health indicates that children from lower-income households are diagnosed at an average age of 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those in higher-income households. This highlights the essential requirement for timely intervention and assistance, particularly for families navigating these challenges.
Moreover, it's significant that 50% of youth with autism in boys in the U.S. who receive vocational rehabilitation (VR) start those services in high school, emphasizing the importance of early assistance systems. The impact of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy extends beyond the individual, reshaping family communication and coping strategies, which is vital for parent advocates to understand as they seek comprehensive support for their children.
Recognizing Signs of Autism in Boys
Boys with developmental disorders often exhibit a variety of signs that can be critical for early recognition. Key indicators include:
- Difficulty making eye contact
- A limited interest in social interactions
- A strong preference for solitary play
These behaviors can manifest alongside repetitive movements such as hand-flapping or rocking, as well as an intense focus on specific subjects, sometimes to the detriment of engaging in diverse activities.
Additionally, caregivers should remain attentive to communication challenges, which may involve:
- Delayed speech development
- Difficulty grasping social cues
Recent studies have highlighted these behaviors, confirming that the prevalence of autism in boys is notably higher, with disparities evident among different ethnic groups. Specifically, ASD prevalence is:
- 1.8 times higher among Hispanic youth
- 1.6 times higher among non-Hispanic Black youth compared to non-Hispanic White youth
A recent study confirmed these disparities, stating that, 'compared with non-Hispanic White youths, ASD prevalence was 1.8 times as high among Hispanic individuals, 1.6 times as high among non-Hispanic Black youths.' By staying vigilant and documenting these signs, caregivers can take empowered steps to consult with professionals for timely assessments and interventions, paving the way for effective support tailored to their child's unique needs. Furthermore, it is recommended that social workers be educated to assist parents in planning and to break the process into manageable steps.
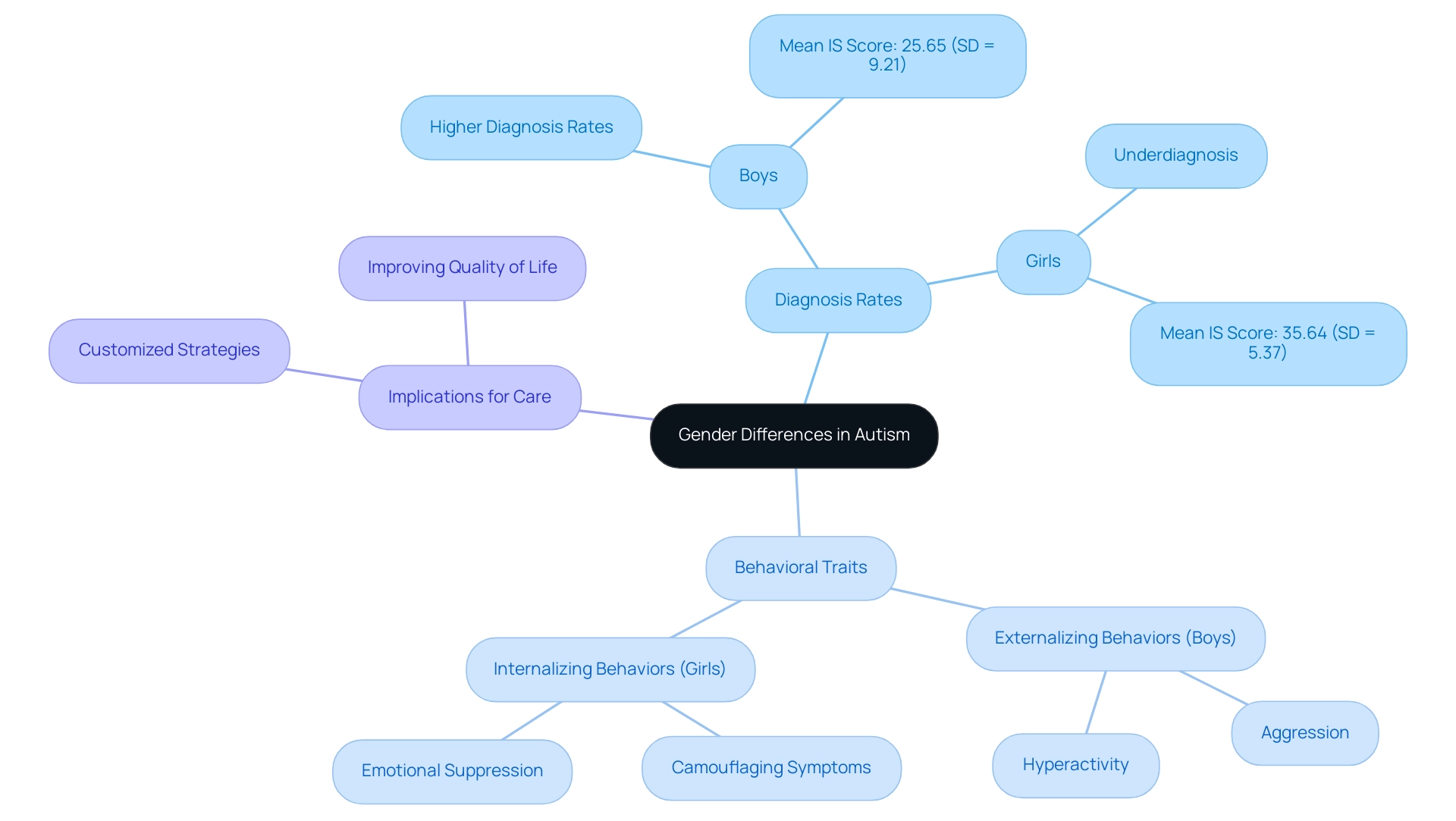
Gender Differences in Autism: Boys vs. Girls
Research consistently shows that the diagnosis of autism in boys occurs at significantly higher rates than in girls, often due to the more pronounced externalizing behaviors they exhibit, such as aggression or hyperactivity. In contrast, girls frequently demonstrate internalizing behaviors, which can lead to their symptoms being overlooked or misinterpreted, resulting in a concerning trend of underdiagnosis. For instance, the mean impulse strength (IS) score on the BEQ was 25.65 (SD = 9.21) for males, compared to 35.64 (SD = 5.37) for females, highlighting the behavioral differences between genders.
This diagnostic gender bias is further compounded by studies indicating that females with developmental disorders may camouflage their symptoms more effectively than their male counterparts. As noted in the case study titled 'Emotional Expressivity and Camouflaging,' emotional expressivity may be suppressed in those attempting to camouflage their symptoms, which could impact their quality of life. This is supported by the findings of Lai et al. (2017), who stated,
- 'Despite the noted limitations, the current study provides an important contribution to the literature on camouflaging in ASD by replicating the finding that females camouflage their ASD symptoms more than males.'
Comprehending these behavioral differences is essential for caregivers; it enables the creation of customized strategies that acknowledge the distinct needs of children with autism in boys and girls. By applying focused measures, advocates can improve the quality of assistance offered, resulting in more tailored care and better results for boys with autism in boys.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
The importance of early diagnosis and support in autism in boys cannot be overstated. Studies consistently show that young individuals who receive early support services often experience improved developmental results, especially in aspects like communication, social interaction, and emotional abilities. As Dr. Akilah Reynolds highlights, early support programs can assist young individuals in acquiring fundamental skills that may be delayed, such as:
- Communication
- Social interaction
- Physical strength and movement
- Thinking
- Emotional skills
This underscores the profound impact that timely support can have on a child's development. It is crucial to note that most diagnoses of ASD are currently performed after the age of four, highlighting the urgency of early intervention. Caregivers are encouraged to be vigilant and proactive in seeking assessments if they observe any signs of autism in boys.
Early identification of autism in boys not only facilitates access to critical resources and therapies but also helps them thrive in their learning environments. Recent discoveries further endorse the notion that younger individuals gain considerable advantages from assistance because of their heightened brain plasticity and behavioral adaptability. For instance, a case study titled 'Comparison of Matched Subgroups' found that even when matched for initial severity, younger individuals showed significantly larger improvements in total ADOS-2 CSS and SA CSS compared to older peers.
Connecting with experts early on enables parents to manage the challenges of support strategies effectively, ultimately promoting a brighter future for their children. Additionally, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends early screening, reinforcing the importance of proactive assessments by caregivers.
Effective Strategies and Resources for Caregivers
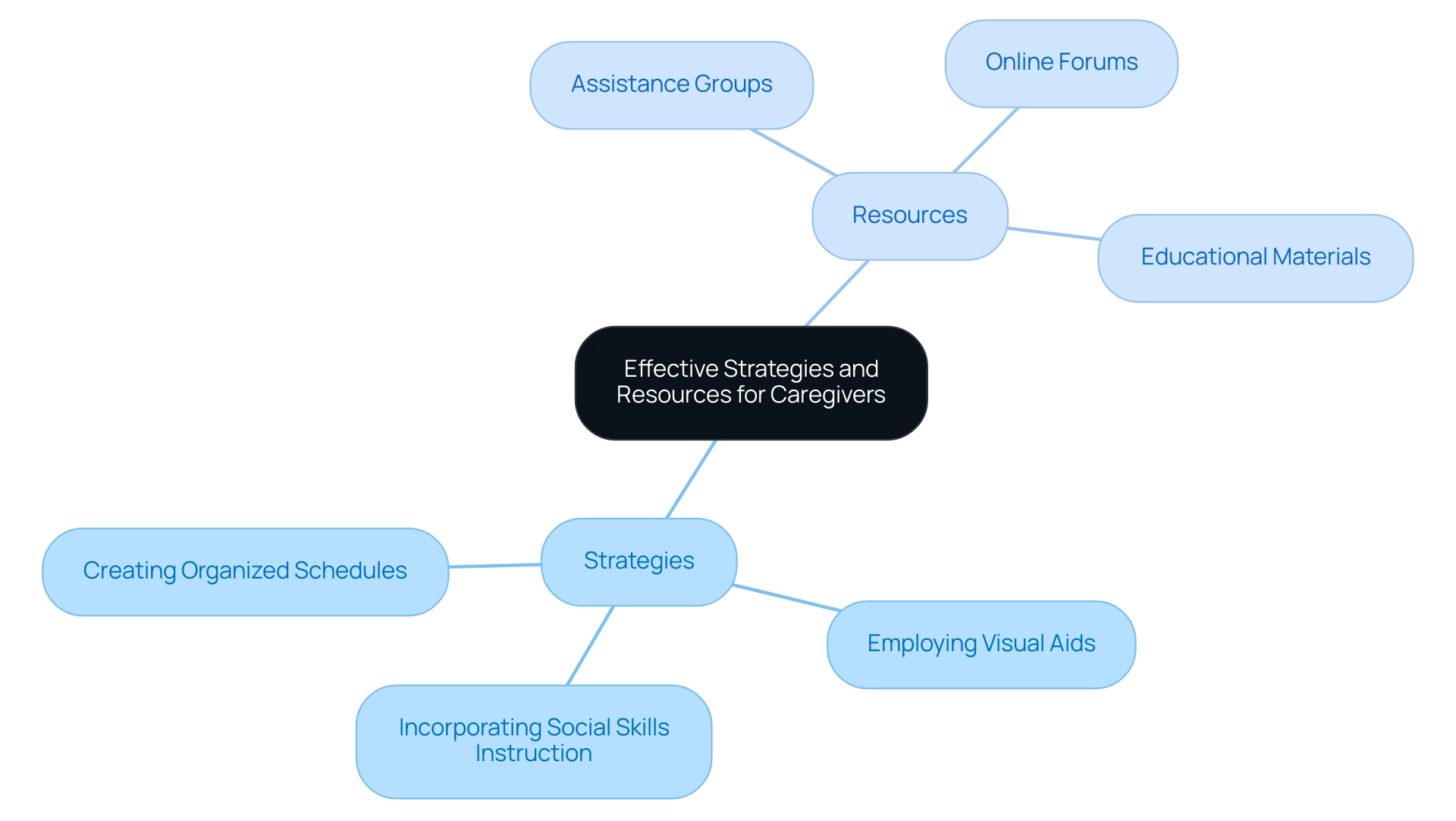
Assisting boys with developmental disorders, such as autism in boys, necessitates a considerate method that emphasizes efficient techniques like:
- Creating organized schedules
- Employing visual aids
- Incorporating social skills instruction into daily tasks
Creating a predictable environment plays a crucial role in reducing anxiety and enhancing learning opportunities. Research indicates that the average age for a reliable autism diagnosis hovers around two years, yet intervention often begins later, at approximately 4.7 years.
By beginning early with organized assistance, caregivers can significantly influence their offspring's development. Resources such as:
- Assistance groups
- Online forums
- Educational materials
are invaluable for fostering community and offering guidance. Engaging with professionals, including board-certified behavior analysts (BCBAs)—of which there are nearly 60,000 practicing in the U.S.—can provide personalized strategies that effectively address specific behaviors and promote skill development.
A study from the NCBI highlights a concerning statistic: among insured children referred for ABA-based behavioral health treatment, only 15% received 80% or more of the recommended treatment hours. This underscores the importance of advocating for adequate resources and supports. Furthermore, it is essential to recognize the challenges autistic individuals face during their transition to adult life, as emphasized by Autism Speaks.
Understanding dropout rates among autistic students is critical to improving their educational and employment outcomes after high school. By leveraging these strategies and resources, caregivers can create an enriching environment that nurtures growth and learning for boys with autism in boys.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a deep understanding of its multifaceted nature, particularly as it manifests differently in each child. Recognizing early signs, especially in boys, is crucial for timely intervention. Caregivers must remain vigilant and proactive, as early diagnosis can significantly enhance developmental outcomes and provide essential support during formative years.
The disparities in diagnosis, particularly among different socio-economic groups and genders, highlight the importance of tailored approaches. Boys often exhibit more pronounced behaviors that lead to earlier diagnoses, while girls may go unnoticed due to subtler symptoms. Understanding these differences allows caregivers to advocate more effectively for their children, ensuring they receive the support they need.
Implementing effective strategies, such as structured routines and visual supports, can create a nurturing environment that fosters growth and learning. Engaging with professionals and utilizing available resources empowers parents to navigate the challenges of autism more effectively. By prioritizing early intervention and personalized care, caregivers can pave the way for their children to thrive, ultimately leading to a more promising future. Every action taken today is a step toward ensuring that children with autism receive the opportunities they deserve to flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Its impact varies significantly among individuals, leading to different degrees of severity and unique profiles of strengths and challenges.
How do boys with autism typically behave?
Boys with autism may struggle to interpret social cues, convey emotions, and engage in typical play activities. They often exhibit difficulty making eye contact, limited interest in social interactions, a strong preference for solitary play, and may display repetitive movements or intense focus on specific subjects.
What are some common communication challenges faced by individuals with autism?
Communication challenges may include delayed speech development and difficulty grasping social cues.
What are the global prevalence rates of autism?
Autism prevalence varies by country: Egypt reports 89.40 per 10,000 individuals, Qatar has the highest rates at 151.20 per 10,000, while France has the lowest diagnosed rates at roughly 1 in 144 young individuals.
How does socioeconomic status affect the diagnosis of autism?
According to the National Survey of Children’s Health, children from lower-income households are diagnosed at an average age of 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years for those from higher-income households, indicating a need for timely intervention and assistance.
What is the significance of vocational rehabilitation (VR) for youth with autism in the U.S.?
In the U.S., 50% of boys with autism who receive vocational rehabilitation start these services in high school, highlighting the importance of early assistance systems.
How does Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy impact families?
ABA therapy not only benefits the individual with autism but also reshapes family communication and coping strategies, which is crucial for parent advocates seeking comprehensive support.
What disparities exist in autism prevalence among different ethnic groups?
ASD prevalence is notably higher among Hispanic youth (1.8 times higher) and non-Hispanic Black youth (1.6 times higher) compared to non-Hispanic White youth.
What steps can caregivers take for early recognition of autism?
Caregivers should remain vigilant for signs such as difficulty making eye contact, limited social interest, and communication challenges, and document these behaviors to consult with professionals for timely assessments and interventions.




