Overview
Understanding the environmental factors contributing to autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial for enhancing support for individuals and families affected by this condition. By shedding light on key environmental risk factors—such as prenatal exposure to pollutants, maternal health conditions, and socioeconomic circumstances—we can better appreciate how these elements interact with genetic predispositions. This understanding underscores the importance of creating safer environments to mitigate these risks.
As parents, you may find it concerning to navigate these complexities. It's essential to recognize that you are not alone in this journey. Many families face similar challenges, and sharing experiences can foster a supportive community. Imagine how much more empowered we can feel when we come together to address these issues.
Let’s take action by advocating for safer environments and supporting each other in this endeavor. Together, we can create a positive impact on the lives of those affected by ASD, ensuring they receive the support they need and deserve.
Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial in our ever-evolving world, where its prevalence is on the rise, impacting 1 in 36 children in the U.S. This reality can be overwhelming for many families. The intricate relationship between genetic predispositions and environmental factors—such as exposure to pollutants, maternal health, and socioeconomic conditions—plays a significant role in the development of autism. As families navigate these complexities, they often seek effective support strategies to create healthier environments for their loved ones.
What steps can we take together to mitigate these risks and enhance the well-being of individuals on the spectrum? Your voice matters in this journey.
Define Autism and Environmental Factors
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects many families. It is characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors, and it manifests uniquely in each individual, creating a spectrum of symptoms and abilities. Understanding these differences is crucial for parents navigating this journey.
Autism environmental factors play a significant role in an individual's development, especially during critical periods such as prenatal and early childhood stages. These factors can include:
- Exposure to pollutants
- Maternal health issues
- Socio-economic circumstances
Each of these elements, as autism environmental factors, can interact with genetic predispositions, influencing the likelihood of developing ASD.
Recent statistics reveal that 1 in 36 children in the U.S. were identified with ASD in 2023. This number reflects not only a growing awareness but also improved diagnostic practices. It’s important to recognize that many individuals with ASD face additional challenges; for instance, research indicates that 40% of them experience anxiety, highlighting the mental health hurdles that can accompany the condition.
Moreover, the economic burden of ASD is significant, with 28.4% of costs attributed to loss in parental productivity. Grasping autism environmental factors is essential for creating effective support plans for individuals with developmental disorders and their families.
As we learn more about ASD, let’s continue to foster understanding and compassion. Sharing experiences and resources can help build a supportive community for all affected by this condition. If you have stories or insights to share, we encourage you to connect with us through comments or newsletters. Together, we can make a difference.
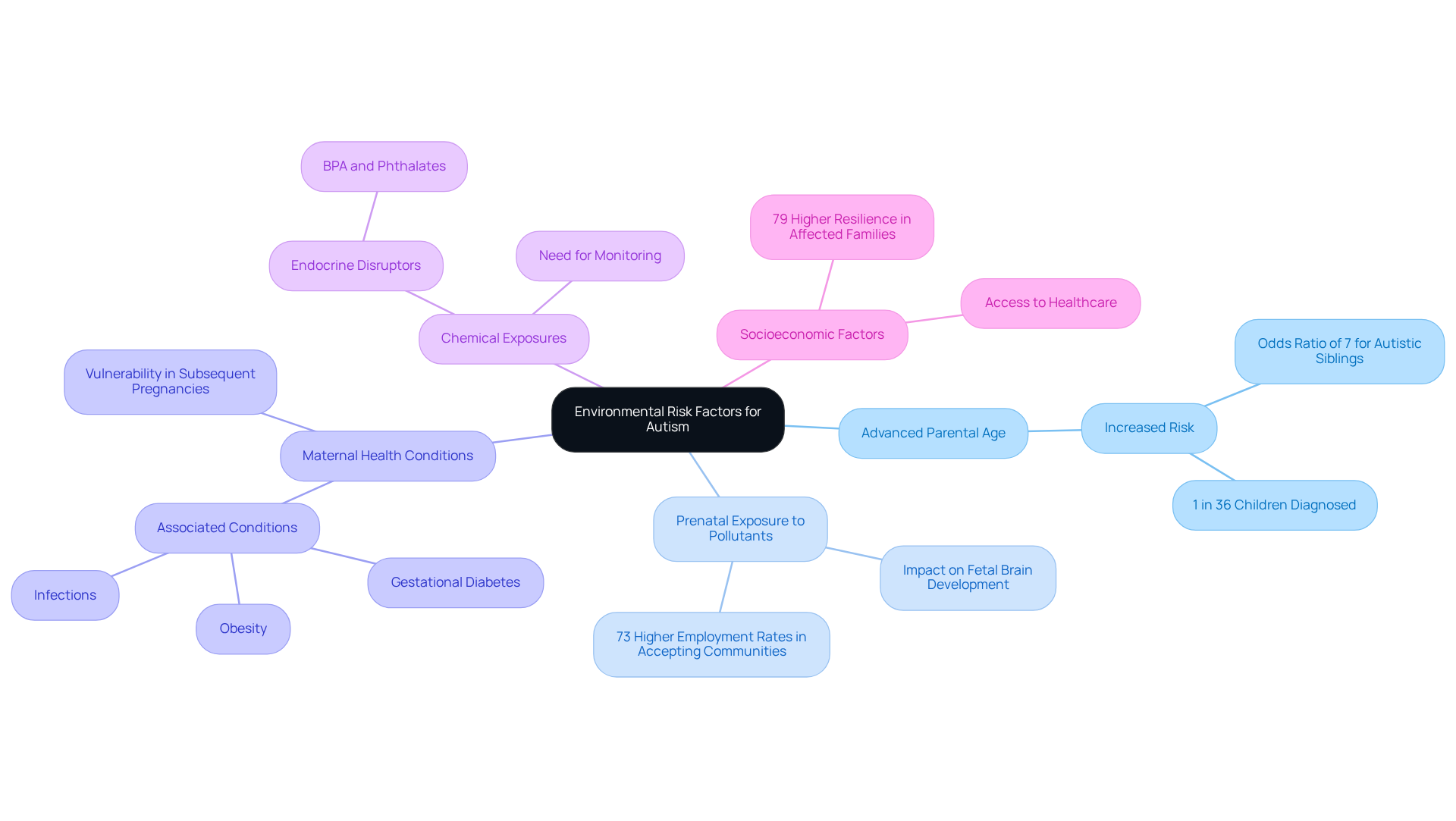
Identify Key Environmental Risk Factors for Autism
Several key environmental risk factors have been identified in relation to autism, and understanding these can empower parents and caregivers to create safer environments for their children.
- Advanced Parental Age: Research shows that older parental age at conception significantly increases the risk of autism in offspring. The odds ratio for having an autistic sibling is roughly 7, highlighting the complex interplay of genetics and context. With 1 in 36 children diagnosed with spectrum disorder, it’s vital to grasp these risk factors and their implications.
- Prenatal Exposure to Pollutants: Exposure to air pollution, pesticides, and other toxins during pregnancy can adversely affect fetal brain development. Communities that embrace initiatives for accepting individuals on the spectrum report 73% higher employment rates for autistic adults, illustrating that addressing external factors can lead to improved outcomes.
- Maternal Health Conditions: Conditions such as gestational diabetes, obesity, and infections during pregnancy are associated with a heightened likelihood of autism. Mothers who have children with autism may be more vulnerable to environmental insults in subsequent pregnancies, underscoring the critical importance of maternal health.
- Chemical Exposures: Chemicals like Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, found in many plastics and personal care products, can disrupt endocrine functions and negatively impact neurodevelopment. Prenatal guidelines emphasize the need for monitoring exposure to these chemicals to mitigate potential risks.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Lower socioeconomic status can restrict access to healthcare and support services, potentially worsening developmental challenges. Families affected by developmental disorders report 79% higher levels of resilience compared to typical families, indicating that supportive environments can significantly aid in navigating these challenges.
Understanding these factors is essential for parents and professionals dedicated to fostering safer environments and advocating for better health practices. As one proponent poignantly stated, "Just because I can’t speak doesn’t mean I have nothing to say," reminding us of the importance of comprehending and supporting individuals on the spectrum.
Explore the Impact of Environmental Factors on Neurodevelopment
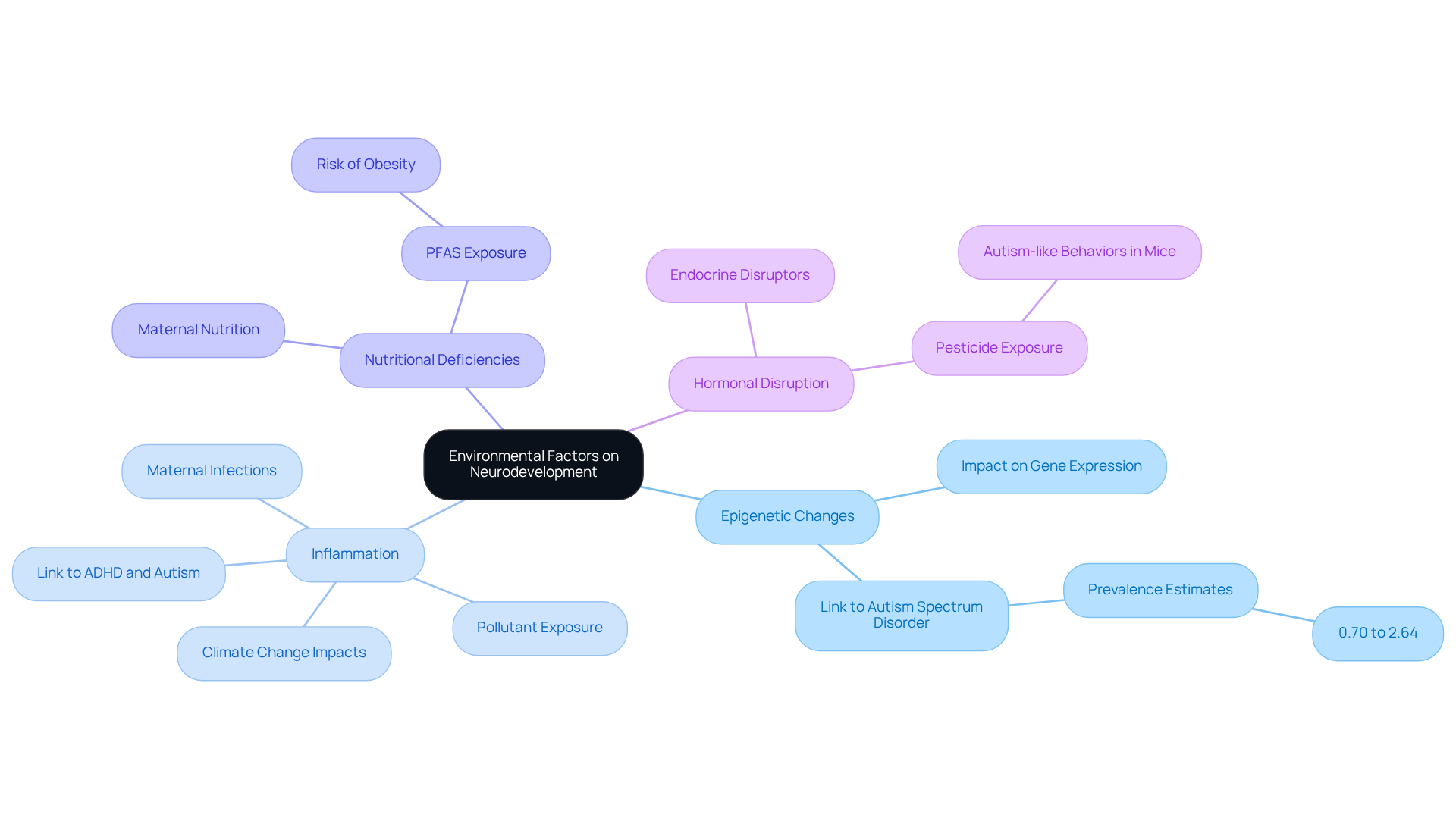
Environmental factors significantly influence neurodevelopment through several mechanisms that are important for parents to understand:
-
Epigenetic Changes: Environmental exposures can induce modifications in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself. Recent research highlights that such epigenetic changes may play a crucial role in brain development and function, potentially increasing the risk associated with autism environmental factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Prevalence estimates for ASD range from 0.70% to 2.64%, underscoring the importance of comprehending these ecological impacts.
-
Inflammation: Maternal infections or exposure to pollutants can trigger inflammatory responses that negatively impact fetal brain development. Studies indicate that inflammation during pregnancy is linked to a higher prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders, including ADHD and autism environmental factors. A report by the American Psychological Association emphasizes the irreversible prenatal impacts of climate change, further highlighting the significance of autism environmental factors in our lives.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate maternal nutrition during pregnancy can limit the availability of essential nutrients necessary for optimal brain development. This deficiency has been linked to a heightened chance of neurodevelopmental disorders, emphasizing the importance of adequate maternal health. Additionally, early life contact with PFAS has been associated with an increased risk of being overweight or obese during childhood and adolescence, complicating neurodevelopmental outcomes further.
-
Hormonal Disruption: Chemicals that disrupt endocrine function can interfere with hormonal signaling pathways critical for brain development. For instance, contact with specific pesticides has been shown to hinder brain activity and trigger autism-like behaviors in animal studies, highlighting the role of autism environmental factors in neurodevelopmental outcomes. Edward Daniel Levin, a professor of pharmacology, points out that chemical pollution ought to be included in the climate change discussion, as it impacts alterations in the ecosystem that affect brain development.
Understanding these effects is crucial for parents and professionals, as it can guide choices concerning surroundings during pregnancy and early childhood, ultimately fostering healthier developmental paths for children. Moreover, research on low-level pesticide contact has associated it with autism environmental factors, providing compelling examples of how these external factors can affect neurodevelopment through autism-like brain alterations in male mice. We encourage you to share your experiences or thoughts on this topic—your voice matters in this important conversation.
Strategies for Mitigating Environmental Risks
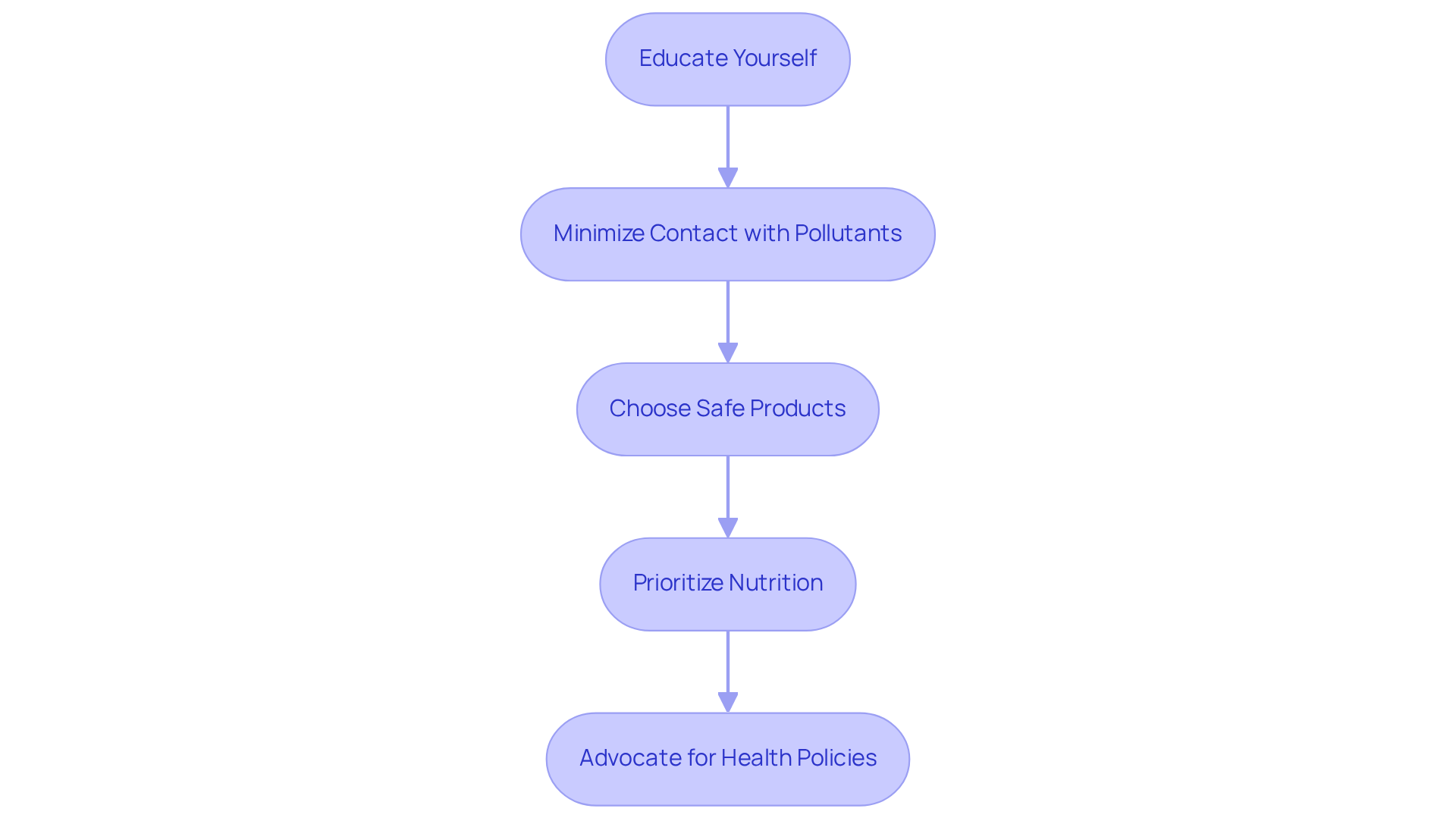
To help address environmental risks associated with autism, consider these thoughtful strategies:
- Educate Yourself: Staying informed about environmental toxins and their potential effects on health is crucial. Resources from reputable organizations can offer valuable insights into how these pollutants may impact development.
- Minimize Contact with Pollutants: You can limit exposure to air pollution by avoiding high-traffic areas, using air purifiers, and ensuring good ventilation in your home. Many households remain unaware of the dangers posed by toxins in nature, making knowledge essential.
- Choose Safe Products: Opt for products that are free from harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates. Seek out eco-friendly and non-toxic alternatives in your household items and personal care products to reduce exposure to hazardous substances.
- Prioritize Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients during pregnancy and early childhood is vital for supporting optimal brain development. Your dietary choices can significantly impact the risks linked to ecological factors.
- Advocate for Health Policies: Engaging in community initiatives to promote policies that reduce pollutants and enhance public health standards can make a difference. Your advocacy can lead to greater public awareness and action against harmful environmental practices.
By implementing these caring strategies, you can help create a healthier environment for children, potentially reducing the risk of autism and supporting their overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between autism and environmental factors is crucial for creating a nurturing environment for individuals on the spectrum. Recognizing the significant role that various environmental influences play in the development of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) enables caregivers and professionals to navigate the complexities associated with this condition more effectively. Acknowledging these factors not only enhances awareness but also empowers families to make informed decisions that can positively impact their children's lives.
Several critical environmental risk factors have been highlighted, such as:
- Advanced parental age
- Prenatal exposure to pollutants
- Maternal health conditions
- Chemical exposures
- Socioeconomic status
Each of these elements contributes to understanding how external influences can affect neurodevelopment and potentially increase the likelihood of ASD. By focusing on education, minimizing exposure to harmful substances, and advocating for healthier policies, we can create safer environments that promote better outcomes for children.
The significance of addressing autism environmental factors cannot be overstated. By sharing knowledge and experiences, communities can come together to support individuals with ASD and their families. Engaging in discussions, advocating for change, and implementing practical strategies are vital steps toward fostering a healthier future for all affected by autism. Together, our collective effort to understand and mitigate these environmental risks will not only aid in developing effective support systems but also contribute to a more compassionate society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors, which manifest uniquely in each individual.
What are some environmental factors associated with autism?
Environmental factors associated with autism include exposure to pollutants, maternal health issues, and socio-economic circumstances, particularly during critical periods like prenatal and early childhood stages.
How do environmental factors interact with genetic predispositions in autism?
Environmental factors can interact with genetic predispositions to influence the likelihood of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
What are the current statistics on autism prevalence in the U.S.?
As of 2023, 1 in 36 children in the U.S. were identified with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), reflecting both growing awareness and improved diagnostic practices.
What additional challenges do individuals with ASD often face?
Many individuals with ASD face additional challenges, including mental health issues, with research indicating that 40% experience anxiety.
What is the economic impact of ASD on families?
The economic burden of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is significant, with 28.4% of costs attributed to loss in parental productivity.
Why is understanding autism environmental factors important?
Understanding autism environmental factors is essential for creating effective support plans for individuals with developmental disorders and their families.




