Overview
Understanding the DSM criteria for diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for ensuring effective support and intervention. Recognizing the specific symptoms outlined in the DSM-5 can lead to early diagnosis, opening the door to essential resources that significantly improve outcomes for individuals with ASD. This is not just about meeting a checklist; it's about the hope and opportunities that early recognition can provide.
Many parents face the daunting challenge of navigating the complexities of ASD. It can feel overwhelming, but knowing the signs can empower you to seek help sooner. Imagine the difference early intervention can make in your child's life, as evidenced by the success of various intervention strategies.
By understanding and applying the DSM criteria, you can take proactive steps toward securing the support your child needs. Don't hesitate to reach out to professionals who can guide you through this process. Together, we can create a brighter future for those on the spectrum.
Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential in today's world, where about 1 in 36 children receive this diagnosis. This complex condition can feel overwhelming for many families. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) offers a framework for recognizing the signs of autism, which is crucial for accessing vital resources and support. Yet, for parents and professionals, navigating the DSM criteria can be a daunting task.
What challenges do families face in ensuring accurate diagnoses? How can a deeper understanding of these criteria lead to better outcomes for children on the spectrum? By exploring these questions together, we can foster a supportive community that empowers parents and caregivers. Let's embark on this journey to understand autism better, ensuring that every child receives the care and support they deserve.
Clarify Autism Spectrum Disorder and DSM Criteria Importance
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition that can bring about ongoing challenges in social interaction, limited interests, and repetitive behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) outlines the autism DSM criteria for diagnosing ASD, which is essential for ensuring that individuals receive the necessary support and interventions. By understanding the autism DSM criteria, parents and professionals can recognize the signs of autism early on, which paves the way for timely access to resources and interventions that can significantly enhance outcomes for children.
The autism DSM criteria serve as a helpful guideline for clinicians, promoting a consistent approach to diagnosis across various settings and practitioners. This consistency is vital for effective treatment planning and support. If you or someone you know is navigating the complexities of autism, remember that you are not alone. Seeking guidance and support can make a world of difference for both you and your child.
Explore DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder
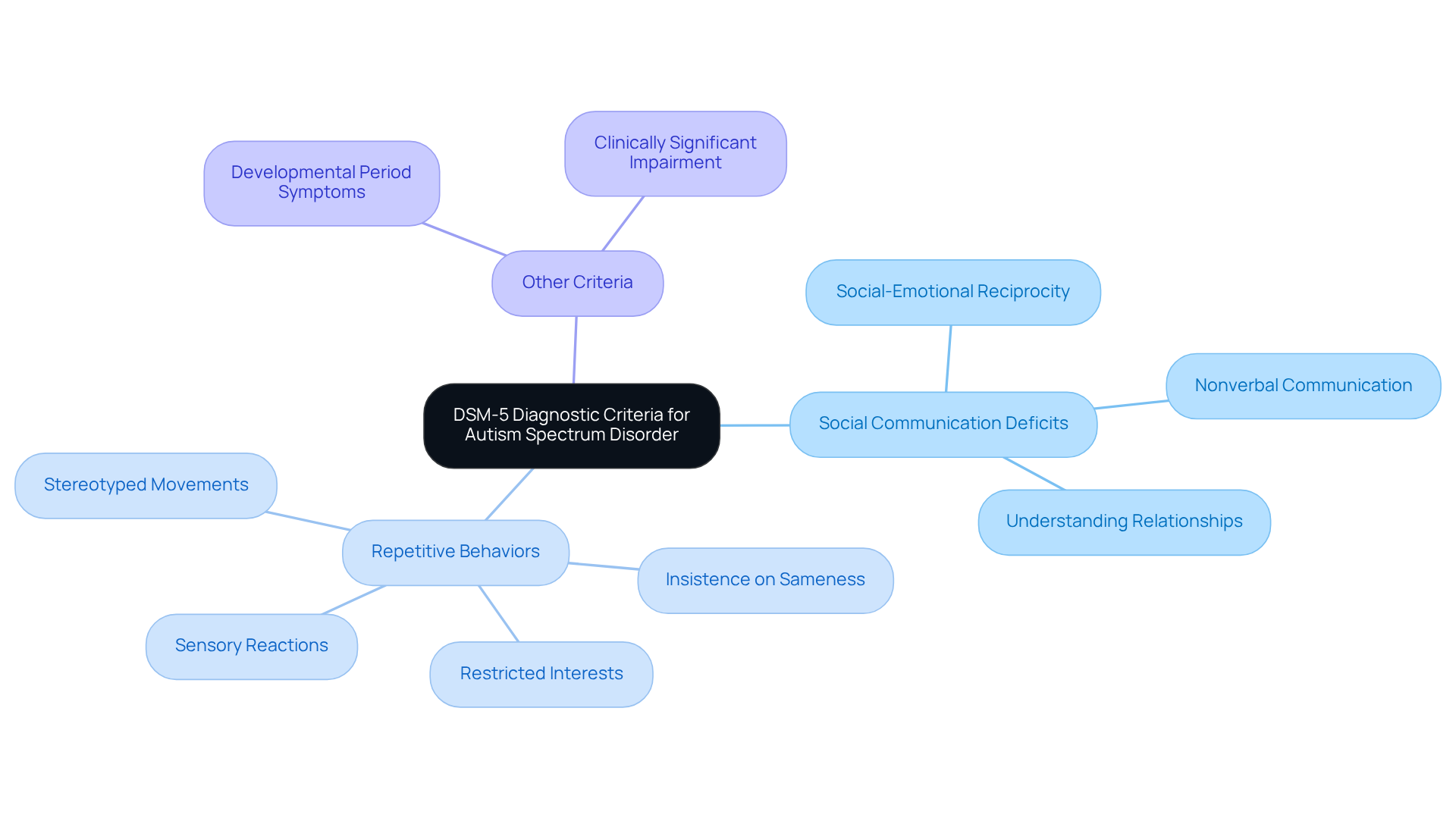
The autism DSM criteria specified in the DSM-5 are essential for parents and professionals to understand when diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). These criteria include:
-
Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across various contexts, which may manifest as:
- Difficulties in social-emotional reciprocity
- Challenges in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction
- Struggles in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships
-
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, evidenced by at least two of the following:
- Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech
- Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of behavior
- Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus
- Hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input or unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment
-
Symptoms must be present during the initial developmental period, even if they do not fully manifest until communal demands exceed limited capacities.
-
Symptoms must cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning.
-
These disturbances are not better explained by intellectual disability or global developmental delay.
Understanding the autism DSM criteria is crucial for identifying signs of autism and pursuing appropriate evaluations. Significantly, about 1 in 36 youngsters are diagnosed with ASD, highlighting the importance of awareness and prompt intervention. Healthcare professionals emphasize that early diagnosis can greatly improve a young person's functioning by providing timely access to supportive resources. As Dr. Amalia Londoño Tobón states, "An early diagnosis can greatly improve a child's functioning by providing the family early access to supportive resources in the community."
Furthermore, advancements in diagnostic tools, such as the Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Modified Checklist for Developmental Disorders in Toddlers (M-CHAT), have improved the precision of autism evaluations. It's also important to note that ASD is reported to be 3.8 times more prevalent among boys (4.3%) compared to girls (1.1%), according to the CDC's Community Report on the condition.
If you suspect your child may be showing signs of ASD, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. Together, we can navigate this journey and ensure the best outcomes for our children.
Utilize Assessment Tools and Methods for Autism Diagnosis
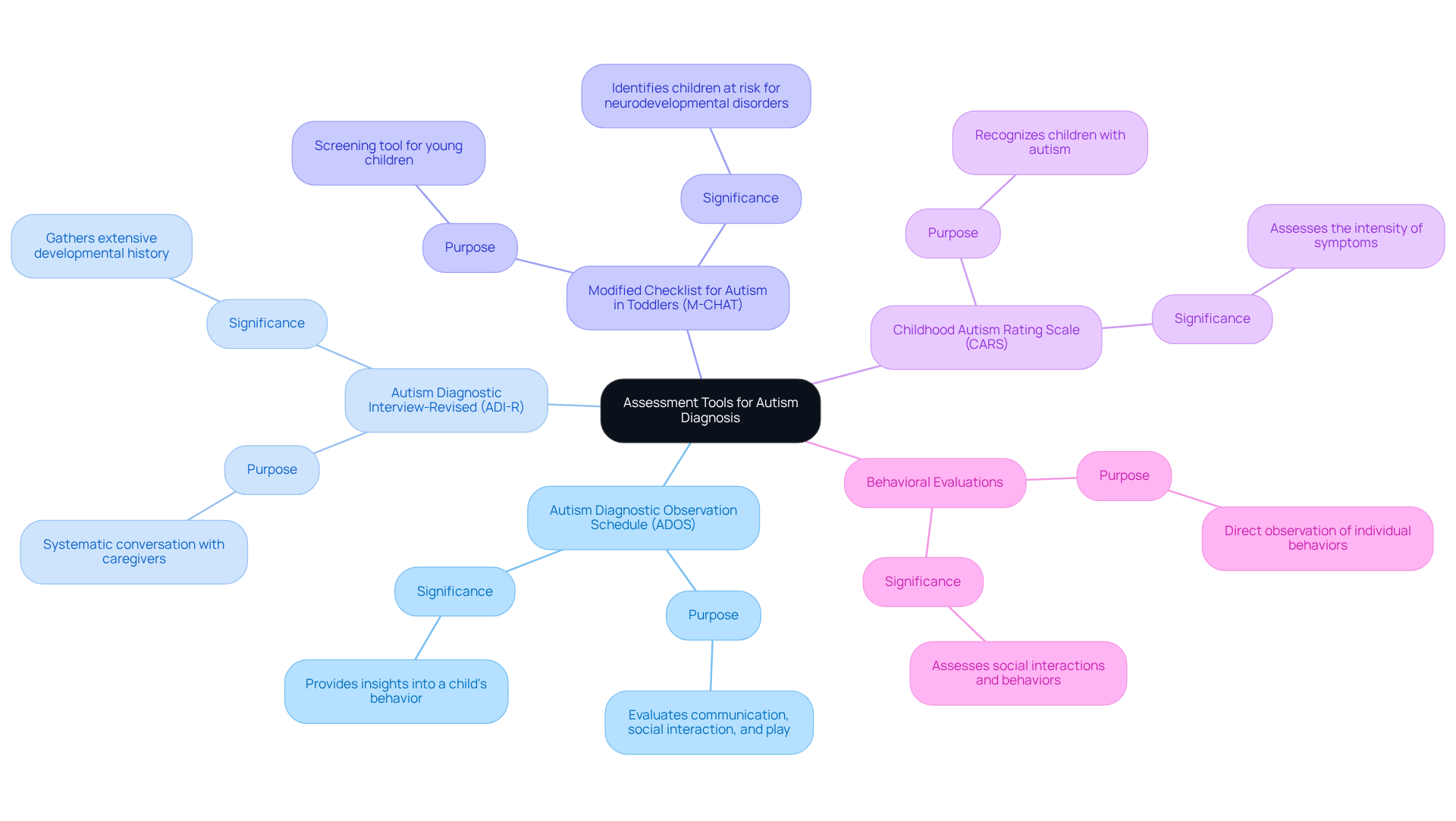
For many parents, navigating the diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder based on the autism dsm criteria can be a daunting journey. Understanding the various assessment tools available can provide clarity and support during this challenging time. Here are some key resources that can help:
-
Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS): This standardized assessment evaluates communication, social interaction, and play in individuals suspected of having a developmental disorder. It offers valuable insights into a child's behavior.
-
Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R): This systematic conversation with caregivers gathers extensive developmental history and behavioral details, helping to paint a fuller picture of the child’s experiences.
-
Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT): Designed for parents, this screening tool helps identify young children at risk for neurodevelopmental disorders early on, allowing for timely intervention.
-
Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS): This resource is used to recognize children with autism and assess the intensity of their symptoms, providing essential information for tailored support.
-
Behavioral evaluations: These evaluations may involve direct observation of the individual in various environments, assessing social interactions and behaviors to gain a deeper understanding of their needs.
It's important to remember that using these tools effectively, especially when assessing autism dsm criteria, requires trained professionals who can interpret the results accurately. As a parent, being proactive in discussing these options with your child’s healthcare provider can ensure a thorough assessment. You are not alone in this journey; seeking support and understanding is a vital step forward.
Implement Early Intervention and Support Strategies for Better Outcomes
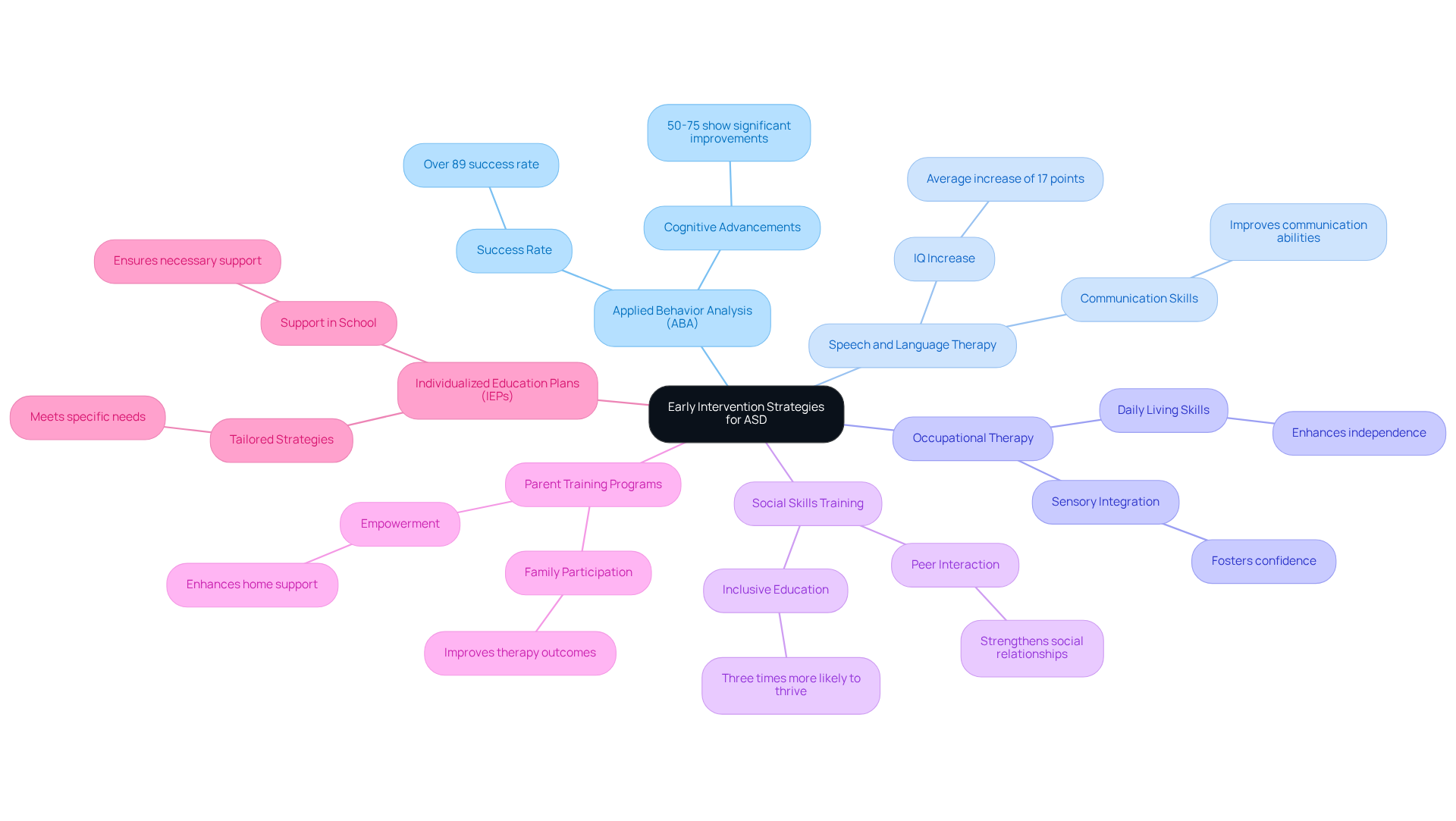
Timely intervention is vital for individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) under the autism DSM criteria, as it can lead to significant developmental advancements. When we consider the journey of our children, we recognize the importance of effective strategies that can truly make a difference.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): This evidence-based approach uses reinforcement techniques to encourage positive behaviors while minimizing challenging ones. Research highlights that ABA therapy has an impressive success rate of over 89% in treating youth with ASD, significantly enhancing communication abilities and adaptive functioning. Moreover, 50-75% of youth undergoing intensive ABA therapy for two or more years show remarkable cognitive advancements in accordance with autism DSM criteria.
- Speech and Language Therapy: This therapy is crucial in improving communication skills, addressing one of the main challenges faced by children with autism as defined by the autism DSM criteria. Studies indicate that those receiving early intervention can experience an average IQ increase of 17 points, opening doors to more opportunities.
- Occupational Therapy: Focused on enhancing daily living skills and sensory integration, occupational therapy helps young individuals adapt to their environment, fostering independence and confidence.
- Social Skills Training: This training equips children with essential tools to interact appropriately with peers and adults, thereby strengthening social relationships. Remarkably, children who begin therapy by age two are three times more likely to thrive in inclusive educational settings, paving the way for a brighter future.
- Parent Training Programs: These programs empower parents with strategies to support their children's development at home, enhancing the overall effectiveness of interventions. Active family participation in therapy sessions has been shown to significantly improve outcomes, creating a nurturing environment for growth.
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Tailored educational strategies cater to the specific needs of students with autism in school settings, ensuring they receive the support necessary to flourish.
By applying these approaches promptly, we can witness enhanced communication, improved social abilities, and an overall better quality of life for individuals diagnosed according to the autism DSM criteria. This not only establishes a solid foundation for their future success but also highlights the significant savings—an estimated $1.3 million per child over their lifetime—by reducing long-term care needs. Together, let's advocate for our children's needs and explore these resources for their brighter tomorrow.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) through the lens of the DSM criteria is essential for effective diagnosis and support. The DSM-5 offers a structured framework that helps clinicians identify ASD, ensuring individuals access the necessary interventions and resources. This understanding empowers parents and professionals to recognize early signs of autism, fostering a proactive approach to securing timely support. Ultimately, this enhances the quality of life for those affected.
Key insights from the article emphasize the importance of the DSM-5 criteria, which include:
- Persistent deficits in social communication
- Restricted behaviors
- The necessity for symptoms to cause significant impairment
Additionally, the article highlights the role of advanced diagnostic tools and early intervention strategies, such as:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Speech therapy
in improving outcomes for children diagnosed with autism. By leveraging these insights, families can navigate the complexities of ASD with greater confidence and clarity.
Given the significant prevalence of autism and the profound impact that early intervention can have, advocating for awareness and understanding of the DSM criteria is imperative. By doing so, communities can better support families on their journey, ensuring that every child has access to the resources and interventions they need to thrive. Engaging with healthcare professionals, utilizing assessment tools, and implementing effective support strategies can pave the way for a brighter future for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition characterized by ongoing challenges in social interaction, limited interests, and repetitive behaviors.
Why is the DSM criteria important for diagnosing ASD?
The DSM criteria are essential for diagnosing ASD as they ensure individuals receive the necessary support and interventions, allowing for early recognition of autism signs and timely access to resources.
How do the autism DSM criteria benefit clinicians?
The autism DSM criteria provide a helpful guideline for clinicians, promoting a consistent approach to diagnosis across various settings and practitioners, which is vital for effective treatment planning and support.
What can parents and professionals gain from understanding the autism DSM criteria?
By understanding the autism DSM criteria, parents and professionals can recognize the signs of autism early, leading to timely access to interventions that can significantly enhance outcomes for children.
What should individuals navigating autism know?
Individuals navigating the complexities of autism should know that they are not alone, and seeking guidance and support can make a significant difference for both them and their child.




