Overview
The average age for autism diagnosis is around four years, although early signs can manifest as early as 18 months, making timely diagnosis crucial for effective interventions. The article emphasizes that early detection significantly improves outcomes for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and highlights the role of parents and caregivers in advocating for early evaluation and support, which can lead to better developmental trajectories.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of autism diagnosis can be a daunting journey for parents, but understanding the landscape of early detection and intervention is vital for fostering their child's development. With the average age of diagnosis hovering around four years, many children exhibit early signs as young as 18 months, making awareness and proactive engagement essential.
Timely identification not only enhances the potential for effective interventions but also significantly improves long-term outcomes for children on the autism spectrum. This article delves into the critical aspects of autism diagnosis, emphasizing:
- The importance of early screening
- The role of parents and caregivers
- The demographic factors that influence diagnosis age
By equipping themselves with knowledge and resources, parents can become powerful advocates for their children, ensuring that they receive the support necessary to thrive.
What is the Average Age for Autism Diagnosis?
The typical autism diagnosis age is around 4 years, although many youngsters begin to exhibit early signs as young as 18 months. Understanding the importance of early screening and assessment cannot be overstated, as timely diagnoses are critical for implementing effective interventions. With a prevalence of 6.7 per 1,000 youth, it is essential for guardians to become acquainted with developmental milestones and sustain open communication with their pediatricians regarding any concerns.
Notably, early signs such as:
- Delayed speech
- Diminished social engagement
- Repetitive behaviors
can serve as vital indicators. Identifying these early indicators enables caregivers to act decisively, fostering a supportive atmosphere for their offspring's development. As highlighted in recent studies, the earlier the identification, the better the outcomes, affirming that doing well is possible even when an individual meets the criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
Furthermore, the emotional challenges faced by parents are significant, as evidenced by a case study showing that 72.5% of mothers of autistic individuals report experiencing depressive symptoms. This emphasizes the significance of the autism diagnosis age, not only for young individuals but also for the well-being of their families.
The Importance of Early Detection in Autism
The early detection of autism diagnosis age is pivotal, as it opens the door to interventions that can profoundly enhance an individual's communication abilities, social interactions, and overall developmental trajectory. Research indicates that individuals who receive support prior to the autism diagnosis age of three experience significantly better outcomes across multiple facets of life, including academic achievements and social skills. For instance, longitudinal studies reveal that individuals who receive therapy by their autism diagnosis age of two are three times more likely to thrive in inclusive educational environments compared to those who start later (source needed).
Furthermore, it is important to note that individuals with ASD have a 21% rate of epilepsy with co-occurring intellectual disability, compared to just 0.8% in those without ASD, highlighting the broader challenges faced by this population. Effective early intervention strategies, particularly Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, empower youth to acquire essential skills while also mitigating challenging behaviors. The case study titled 'Effective ABA Therapy Intervention Techniques' illustrates various strategies that have successfully supported individuals with developmental disorders in their growth and learning.
This period is critical for parents to proactively engage with professionals, ensuring their offspring receives the necessary support for an appropriate autism diagnosis age.
Understanding Delays in Autism Diagnosis
Delays in diagnosing developmental disorders can arise from a multitude of factors, including the autism diagnosis age, significantly impacting the assistance that youngsters receive. One critical element is the lack of awareness surrounding the symptoms of the condition, which can lead to missed opportunities for early intervention. Research has shown that children who receive early intervention have better outcomes in terms of communication skills, social interaction, and adaptive behaviors.
Cultural differences also play a vital role in how behaviors are recognized and understood; varying beliefs may influence the perception of what constitutes a developmental disorder, such as the autism diagnosis age, leading to disparities in assessment. For example, while studies show no notable differences in prevalence among various racial and ethnic groups, variations exist in the autism diagnosis age and access to resources, emphasizing the urgent need for fair support systems. A case study on racial and ethnic disparities in autism assessment illustrates how these factors can affect the autism diagnosis age and timely interventions.
Furthermore, some young individuals may not display clear symptoms until they are older, complicating prompt assessment and intervention. The emotional burden on families is considerable, with 18.6% of caregivers of autistic individuals fulfilling the requirements for a provisional diagnosis of PTSD. It's crucial for guardians to remain informed about these barriers and to advocate for their children's needs actively.
If there are doubts regarding developmental disorders, seeking evaluations promptly is essential. Moreover, connecting with a support network of fellow caregivers can provide valuable insights and encouragement, fostering a community that empowers families navigating these challenges. As Laura NG, Clinical Operations Manager, emphasizes,
It is important to dispel these misconceptions and promote accurate information and understanding about this condition.
By remaining proactive and informed, caregivers can significantly enhance their offspring's pathway to support and success.
The Role of Parents and Caregivers in Autism Diagnosis
Parents and caregivers are often the first to notice developmental differences in their offspring, making their observations invaluable for the autism diagnosis age process. Research highlights that documented concerns can significantly influence outcomes, as evidenced by the mean ADI-R social impairment score of 21.9 for youngsters of individuals with technical occupations, compared to 17.4 for those in non-technical fields. This disparity illustrates how informed advocacy plays a critical role in securing appropriate evaluations.
Open communication with healthcare professionals is essential; by clearly expressing their insights and concerns, guardians can effectively advocate for their dependent's needs, particularly when discussing autism diagnosis age. Aisha S. Dickerson, PhD, a specialist in biostatistics and epidemiology at the Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences, emphasizes the importance of parental involvement, stating, "The publisher's version of this article is available at Res Autism Spectr Disord." Participating in this process not only strengthens guardians but also establishes the foundation for their offspring's access to critical interventions.
Furthermore, the report titled 'Future Research Directions for ASD' underscores the significance of studying the life course development of youth with ASD to understand their long-term outcomes and needs, reinforcing the necessity for ongoing parental advocacy. Through these collaborative efforts, parents can foster a supportive network that aids in the developmental journey, ensuring that evaluations are not only conducted but are also reflective of their unique needs.
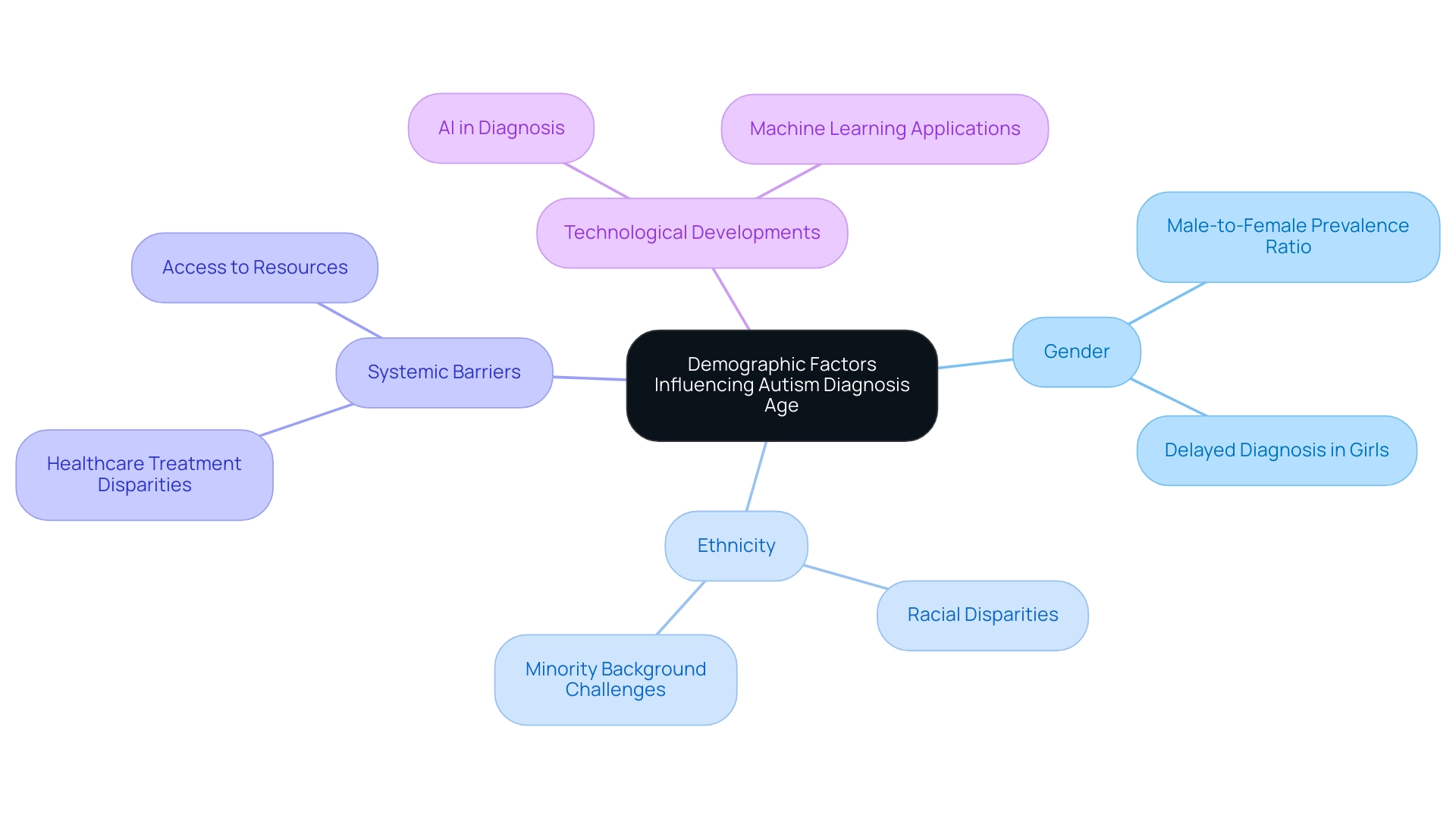
Demographic Factors Influencing Autism Diagnosis Age
Research consistently highlights that demographic factors, including gender and ethnicity, significantly impact the autism diagnosis age. For instance, girls are frequently diagnosed later than boys due to the subtle presentation of their symptoms, with a male-to-female prevalence ratio of 11.4 indicating a consistent trend of higher ASD prevalence in males. This delay can hinder early intervention and support, particularly concerning autism diagnosis age.
Furthermore, individuals from minority backgrounds often encounter systemic barriers and racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare treatment that exacerbate the delays in the autism diagnosis age. A striking statistic reveals that among individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), 71.6% had an ASD ICD code, indicating a pressing need for awareness surrounding these disparities.
As noted by Constantino et al.,
Sadly, the findings of Constantino et al. mirror previous studies, some of which were published almost 2 decades ago and suggest little progress in equitable care and that health disparities for youth of color with ASD persist.
Recent developments in AI and machine learning technologies are being considered to enhance clinical decision-making in ASD diagnosis, aiming to reduce biases in the diagnostic process. This underscores the essential need for guardians to comprehend these factors and actively pursue the necessary resources and assistance for their offspring, regardless of their demographic background.
By being informed about these disparities, parents can better advocate for timely evaluations and interventions, particularly considering the autism diagnosis age, ensuring their children receive the care they deserve.
Conclusion
Timely and accurate autism diagnosis is crucial for ensuring children receive the interventions they need to thrive. As highlighted, the average diagnosis age is around four years, yet many children display key signs as early as 18 months. Recognizing these early indicators—such as delayed speech and diminished social engagement—empowers parents to seek early screening and intervention. The benefits of addressing autism promptly cannot be overstated; children who receive support before the age of three often experience significantly improved developmental outcomes.
The role of parents and caregivers is paramount in navigating the autism diagnosis journey. Their observations and concerns can drive effective communication with healthcare professionals, ultimately influencing the quality of evaluations and interventions. Additionally, understanding the demographic factors that can affect diagnosis age, such as gender and ethnicity, underscores the importance of equitable access to resources. By remaining informed and proactive, parents can advocate effectively for their children, ensuring they receive timely and appropriate care.
In conclusion, the journey toward an autism diagnosis may be complex, but it is one that can lead to a brighter future for children and their families. By prioritizing early detection, engaging with professionals, and fostering a supportive community, parents can significantly enhance their child's developmental trajectory. Empowered with knowledge and a strong support network, families can navigate the challenges of autism with confidence, paving the way for their children to reach their full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical age for an autism diagnosis?
The typical age for an autism diagnosis is around 4 years, although many children may begin to show early signs as young as 18 months.
Why is early screening and assessment important for autism?
Early screening and assessment are crucial because timely diagnoses allow for effective interventions, which can significantly enhance a child's development and overall outcomes.
What are some early signs of autism that parents should look for?
Early signs of autism include delayed speech, diminished social engagement, and repetitive behaviors.
How does early identification of autism affect outcomes for individuals?
Research shows that the earlier individuals receive support, particularly before the age of three, the better their outcomes across various areas, including communication, social skills, and academic achievements.
What percentage of mothers of autistic individuals report experiencing depressive symptoms?
A case study indicates that 72.5% of mothers of autistic individuals report experiencing depressive symptoms.
What challenges do individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face?
Individuals with ASD have a higher rate of epilepsy (21%) and co-occurring intellectual disability compared to those without ASD (0.8%), highlighting the broader challenges faced by this population.
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, and how does it help?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is an effective early intervention strategy that helps youth acquire essential skills while also mitigating challenging behaviors.
What role do parents play in the early diagnosis of autism?
Parents are encouraged to proactively engage with professionals to ensure their child receives the necessary support for an appropriate autism diagnosis age.




