Overview
Understanding autism burnout is crucial for supporting neurodivergent individuals. This article delves into the symptoms of autism burnout, highlighting how they manifest and why recognizing these signs is essential for effective support. Autism burnout often presents as extreme fatigue, a loss of skills, and heightened sensory sensitivity. These symptoms can profoundly affect daily functioning and mental health.
For parents and caregivers, being informed is the first step toward addressing these challenges. It’s important to recognize that the signs of autism burnout can sometimes be subtle yet impactful. By understanding these symptoms, you can take proactive measures to support your loved ones. Consider sharing your experiences or seeking advice from others who have navigated similar situations.
The journey of understanding autism burnout is not just about recognizing symptoms; it’s about fostering an environment where neurodivergent individuals feel supported. Together, we can create a community that prioritizes awareness and compassion. Let’s work towards ensuring that those affected receive the support they deserve.
Introduction
In a world where understanding autism is more crucial than ever, the phenomenon of autistic burnout emerges as a pressing concern for families navigating the complexities of this condition. This profound state of exhaustion can manifest physically, mentally, and emotionally, often following periods of overwhelming stress or sensory overload. Research indicates that a significant number of autistic children experience burnout, making it essential for parents to recognize its signs and symptoms.
By delving into the characteristics, causes, and impacts of autistic burnout, this article aims to equip caregivers with the knowledge and strategies necessary to support their children effectively. Together, we can foster resilience and promote overall well-being.
Defining Autistic Burnout: What Parents Need to Know
Neurodivergent fatigue represents a profound state of physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion that can affect individuals on the spectrum, particularly manifesting as autism burnout symptoms after extended periods of stress or sensory overload. This condition is characterized by a significant decline in functioning, which may encompass difficulties with daily tasks, communication, and social interactions. Unlike ordinary fatigue, neurodivergent exhaustion often entails a regression of previously acquired skills and an increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli.
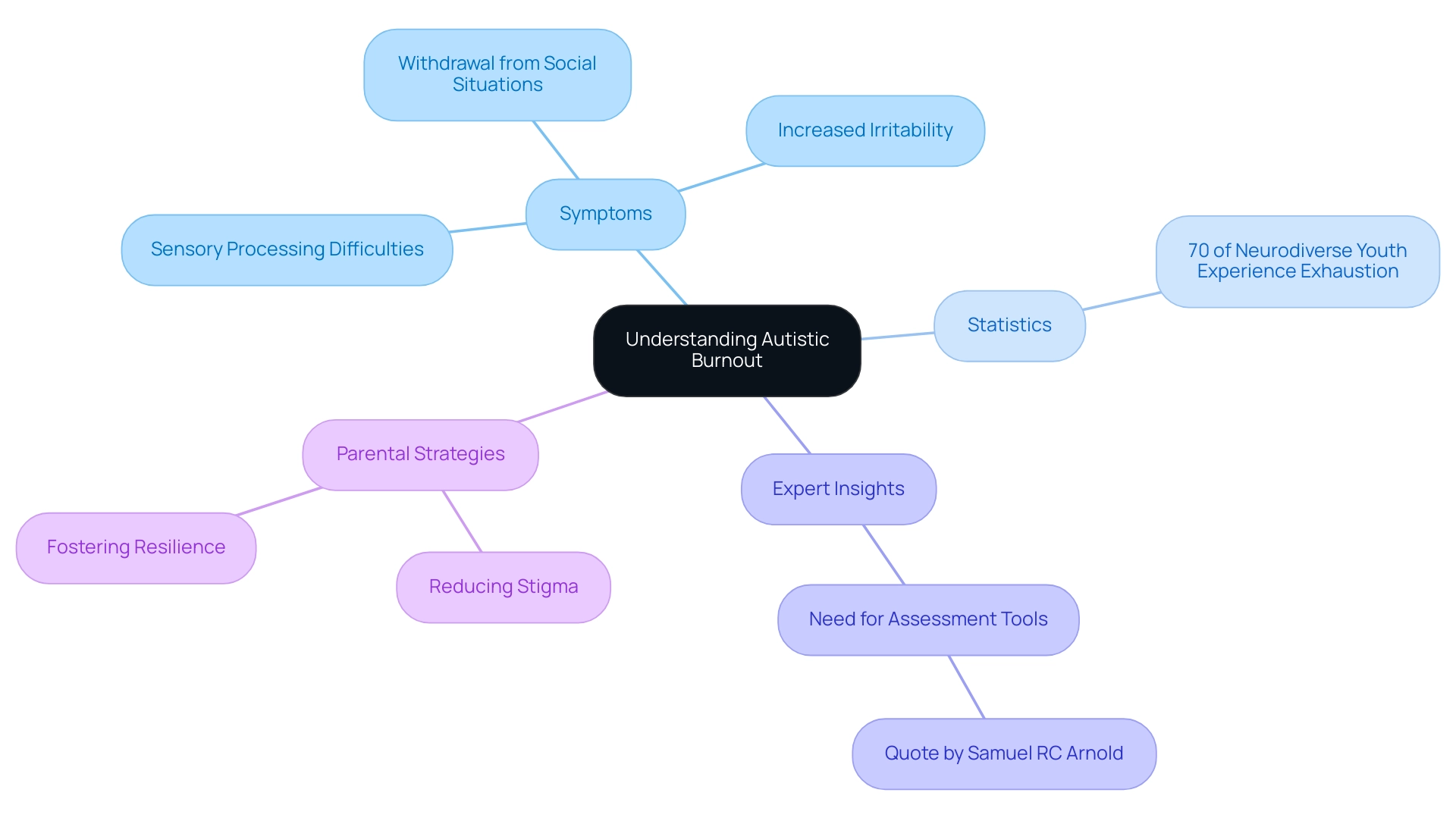
Research indicates that sensory exhaustion can profoundly impact the quality of life for those affected, with studies showing that approximately 70% of neurodiverse youth experience some form of exhaustion during their development. This highlights the critical need for parents to be aware of the signs and symptoms of autism burnout associated with this condition.
Common traits of sensory overload in youth may include:
- Withdrawal from social situations
- Increased irritability
- Difficulties in processing [sensory information
Understanding autism burnout symptoms is essential for parents, as it empowers them to provide the necessary support and interventions tailored to their child's unique needs.
Recent discussions among autism experts underscore the importance of developing effective evaluation tools to identify autism burnout symptoms and related exhaustion. Samuel RC Arnold, a joint first author, remarked, "We need to develop assessment tools that can help identify this exhaustion," stressing that awareness and understanding are vital for fostering improved mental health outcomes.
Moreover, the case study titled 'The Role of Stigma and Masking in Neurodiverse Exhaustion' explores how stigma from family and societal pressures can compel neurodiverse individuals to hide their traits, recognized as a significant risk factor for autism burnout symptoms. Insights from this study may guide strategies to reduce stigma and support individuals on the spectrum in disclosing their diagnosis, ultimately leading to better mental health outcomes.
Additionally, the Q-set highlights traits of neurodivergent exhaustion, emphasizing both internal and external factors influencing fatigue. By recognizing the complexities of neurological fatigue and autism burnout symptoms, parents can more effectively navigate the challenges their children face, fostering a supportive environment that nurtures resilience and well-being. For further resources and assistance, parents are encouraged to explore the information available on signs, symptoms, and treatment options related to developmental exhaustion.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Autistic Burnout
Signs of emotional exhaustion can manifest in various ways, significantly impacting daily life. Recognizing these key indicators is essential for parents seeking to provide the necessary support for their children.
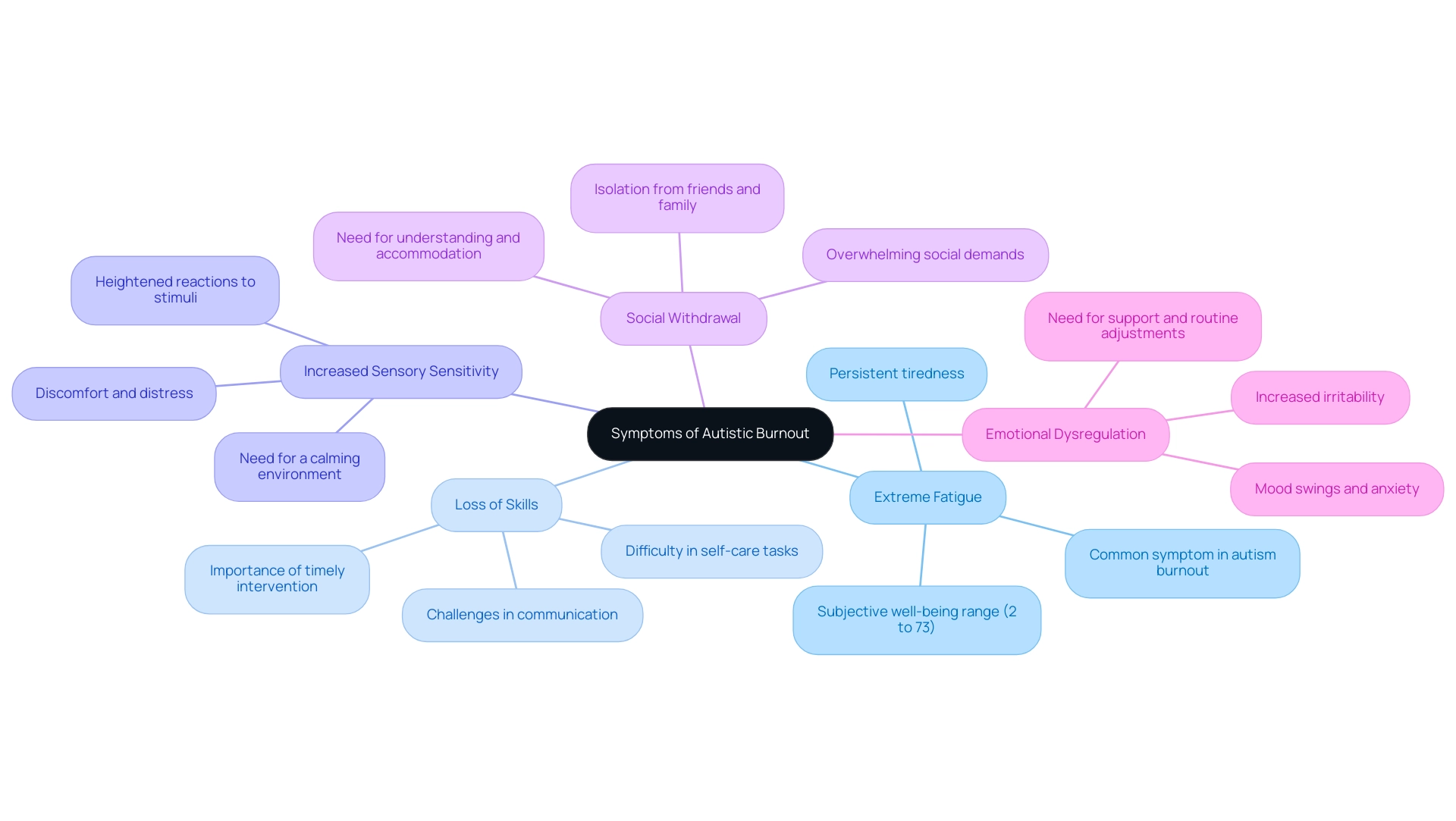
- Extreme Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn't improve with rest can leave individuals feeling drained and overwhelmed. Recent studies highlight that extreme fatigue is a common symptom of autism burnout, with many autistic individuals reporting it as a debilitating aspect of their lives. In a study involving 418 participants, subjective well-being measures ranged from 2 to 73, showcasing the diverse impact burnout can have.
- Loss of Skills: Children may find it challenging to perform tasks they once managed with ease, such as communication or self-care. This regression can be distressing for parents, underscoring the importance of timely intervention and support.
- Increased Sensory Sensitivity: Many autistic individuals experience heightened reactions to sensory stimuli, which can lead to discomfort or distress. This sensitivity can exacerbate feelings of exhaustion, making it vital for parents to cultivate a calming environment.
- Social Withdrawal: A noticeable tendency to isolate from friends and family can signify exhaustion. This withdrawal often arises from overwhelming social demands, highlighting the need for understanding and accommodating individual needs.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Increased irritability, anxiety, or mood swings frequently accompany autism burnout. As Ella Tabb notes, "Mental health difficulties can feel isolating, but sharing experiences can help." Parents should remain vigilant in recognizing these emotional shifts, as they may indicate a need for support and adjustments in routines.
Identifying these symptoms is crucial for parents to offer the required assistance and adapt their children's surroundings. Engaging with online communities, such as those using the hashtag #ActuallyAutistic, can foster connection and understanding, providing valuable resources and shared experiences that help combat feelings of isolation. A case study titled "Community Support and Knowledge Sharing" emphasized the importance of these online platforms, demonstrating that shared experiences can build empathy and support networks.
By staying informed and proactive, parents can more effectively navigate the challenges of developmental exhaustion, ensuring their children receive the care and understanding they need.
Exploring the Causes of Autistic Burnout
Neurodivergent exhaustion can stem from various factors, including the symptoms of autism burnout, which significantly affect the overall health of neurodiverse individuals. Key contributors to this exhaustion include:
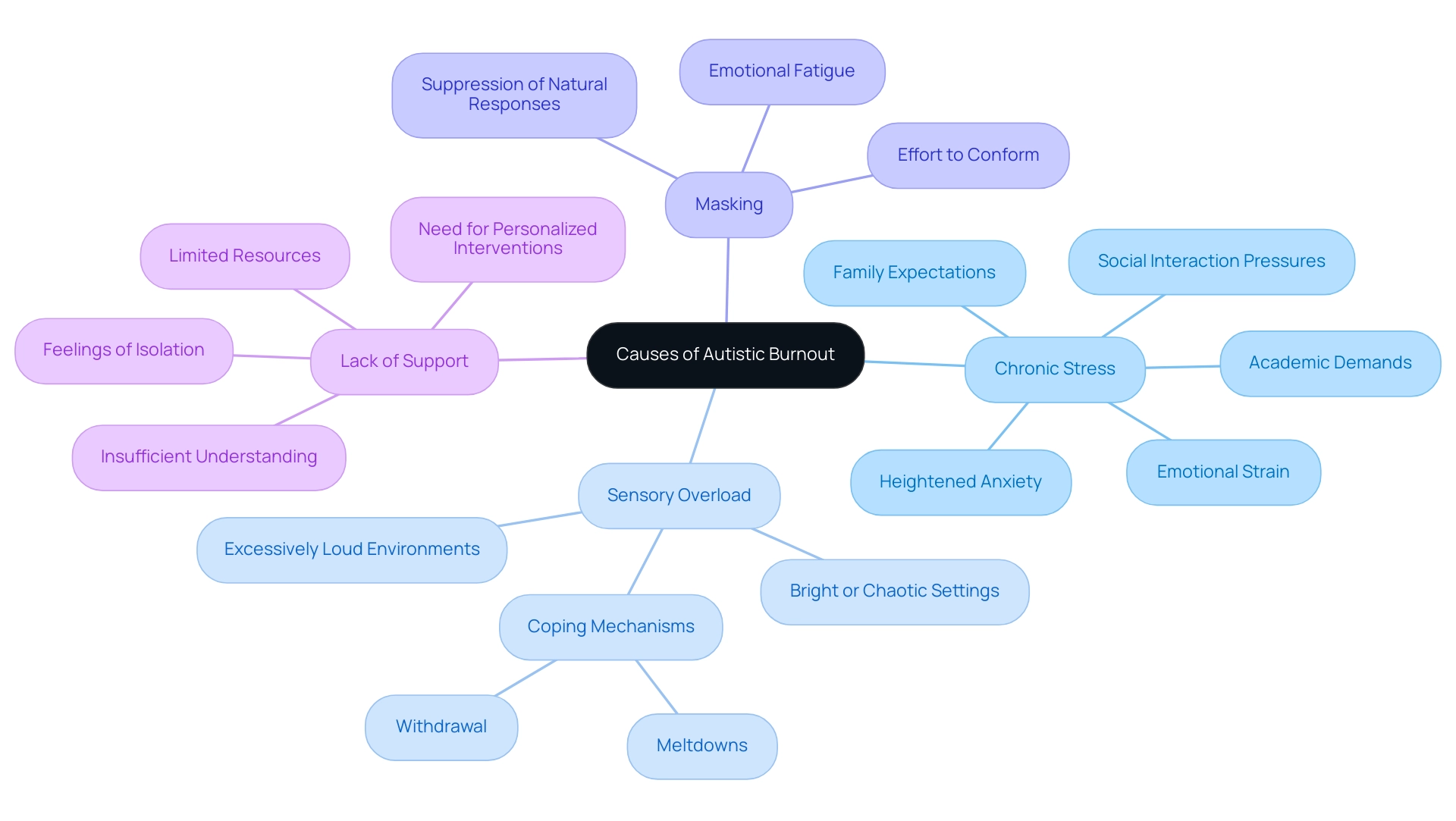
- Chronic Stress: The continuous pressures from social interactions, academic demands, or family expectations can create considerable emotional and physical strain. Research shows that chronic stress is common among individuals on the autism spectrum, with many experiencing symptoms of autism burnout and heightened anxiety compared to their neurotypical peers. A recent case study, "Comparative Analysis of Stress Levels in Adults with ASD and Healthy Volunteers," highlights notable differences in stress responses, enhancing our understanding of how stress impacts social functioning in adults with ASD.
- Sensory Overload: Environments that are excessively loud, bright, or chaotic can overwhelm individuals on the spectrum, leading to autism burnout symptoms like distress and exhaustion. Data indicates that sensory overload frequently triggers children on the spectrum, often resulting in autism burnout symptoms such as meltdowns or withdrawal as coping mechanisms.
The effort to conform to neurotypical behaviors—often referred to as masking—can be exhausting and may lead to autism burnout symptoms. This constant self-regulation to fit in socially can result in emotional fatigue, as individuals suppress their natural responses to navigate social situations. Blythe A. Corbett emphasizes that "context matters when seeking to understand physiological reactivity to social stressors in youth with ASD," underscoring the importance of recognizing individual experiences of stress.
- Lack of Support: Insufficient understanding or resources from family, schools, or the community can intensify feelings of isolation and stress. Many individuals on the spectrum report that a lack of suitable support frameworks plays a significant role in their experiences of autism burnout symptoms. With a global occurrence of ASD around 1 percent, as highlighted by the recent Lancet Commission, there is a growing demand for personalized intervention methods, emphasizing the necessity for tailored support for individuals on the spectrum.
Understanding these causes is crucial for parents and caregivers. By identifying the signs of emotional exhaustion and autism burnout symptoms along with their triggers, they can create a more accommodating environment that supports their children's unique needs, ultimately fostering resilience and well-being. This aligns with ASD Media's mission to empower parents and professionals to unlock the potential of children with autism and ADHD.
The Impact of Autistic Burnout on Daily Life and Mental Health
The effects of autistic burnout can be profound, significantly impacting various aspects of life, including:
- Daily Functioning: Many individuals face considerable difficulty in completing routine tasks, leading to increased dependence on caregivers. This struggle often manifests as autism burnout symptoms, which can result in a lack of motivation and energy, making even simple activities feel overwhelming.
- Mental Health: Concerns such as anxiety and depression frequently accompany autism burnout symptoms, indicating a state of autistic exhaustion. Recent studies reveal that individuals experiencing this exhaustion often report feelings of frustration and a lack of focus, which can exacerbate existing mental health challenges. Users have shared feelings of frustration, lack of focus, and diminished interest in food, underscoring the behavioral and functional impacts of autism burnout symptoms.
- Social Relationships: Interactions with peers and family members can become strained due to withdrawal or irritability. The inability to engage socially may lead to feelings of isolation, further exacerbating autism burnout symptoms and impacting mental well-being, thus reinforcing the cycle of exhaustion.
- Academic Performance: Many individuals struggle to maintain focus and engagement in school settings. This can result in declining grades and reduced participation in classroom activities, which may affect long-term educational outcomes.
Understanding these effects is essential for parents advocating for suitable accommodations and support systems. By recognizing the indicators of emotional exhaustion, caregivers can enhance their assistance to loved ones in managing autism burnout symptoms, fostering an environment that prioritizes mental wellness and health. Recent documents emphasize the importance of validating the experiences of individuals affected by autism burnout symptoms and increasing awareness of sensory exhaustion, which can lead to improved access to necessary modifications and support.
The document titled 'Recommendations for Addressing Autistic Exhaustion' highlights the necessity for therapists to acknowledge fatigue, particularly the autism burnout symptoms, and suggests that suicide prevention programs consider its significance. Additionally, creating comfortable environments for expressing neurodiverse traits can help alleviate the draining effects associated with autism burnout symptoms. As Ella Tabb observes, understanding the concept of double empathy has important implications for practice, underscoring the need for a supportive approach for individuals facing exhaustion.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Preventing Autistic Burnout
To effectively manage and prevent autistic burnout, parents can adopt several key strategies that foster a nurturing environment:
- Create a Structured Routine: Establishing predictable schedules is crucial for reducing anxiety and providing a sense of security. Research indicates that structured routines can significantly enhance the emotional well-being of autistic individuals, leading to a decrease in anxiety levels and an increase in overall functioning. Given that humans have an average attention span of just 8.25 seconds, which has decreased by nearly 25% over the past two decades, the importance of structured routines becomes even more apparent in helping young individuals focus and feel secure.
- Limit Sensory Overload: Identifying and minimizing sensory triggers in the environment is essential. Many individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) experience heightened sensitivity to sensory inputs, which can lead to overwhelming situations. As noted by Wendy L. Stone, individuals with ASD often struggle with participating in everyday home routines, such as bedtime or bath time. By creating a sensory-friendly environment, parents can help mitigate these challenges and foster a sense of calm.
- Encourage Breaks: Regular downtime is vital for recharging, especially after stressful activities. Permitting young ones to take breaks can assist them in regulating their energy levels and avoiding exhaustion. This practice aligns with expert recommendations that emphasize the importance of self-care in daily routines, reminding parents to prioritize these moments of rest.
- Promote Self-Advocacy: Teaching children to express their needs and preferences fosters independence and empowers them to navigate their environments more effectively. This skill is crucial in helping them articulate when they feel overwhelmed or need a break, which can significantly reduce the risk of burnout and enhance their overall well-being.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Engaging with therapists or groups that specialize in autism can provide additional insights and resources. Professionals can offer tailored strategies and support, helping families navigate the complexities of autism and its associated challenges. As Dr. Carly Lapin states, by incorporating the principles of ABA, therapists empower youngsters to cultivate flexibility, resilience, and adaptive coping mechanisms.
In a case study titled "Sensory Differences and Daily Occupations," parents reported significant challenges related to auditory and tactile sensitivities, which often triggered meltdowns during daily routines. By understanding their offspring's unique sensory experiences, they were able to implement more effective strategies for managing these situations, ultimately leading to improved family dynamics and reduced anxiety.
By incorporating these strategies into everyday routines, parents can establish a nurturing atmosphere that aids in handling emotional exhaustion and autism burnout symptoms while enhancing overall wellness for their offspring. Additionally, it is crucial to acknowledge that ABA therapy is customized to address each child's distinct requirements, emphasizing the importance of these strategies in managing autism burnout symptoms and associated exhaustion.
The Role of Support Systems in Addressing Autistic Burnout
Support systems play a crucial role in alleviating the effects of autism burnout symptoms, providing parents with essential tools and connections to navigate challenges effectively. Here are some key strategies for building a robust assistance network:
- Building a Network: Connect with other parents, groups, and community resources. Sharing experiences and strategies not only fosters a sense of belonging but also offers practical solutions to common challenges faced by families of children on the spectrum.
- Engaging Professionals: Collaborate with therapists, educators, and healthcare providers who specialize in autism. Their expertise can provide tailored assistance and guidance, ensuring that both guardians and individuals receive the necessary support to thrive.
- Utilizing Online Resources: Take advantage of online forums, webinars, and educational materials focused on managing autistic burnout. These resources can provide valuable insights and strategies, making it easier for parents to access information and support from the comfort of their homes.
- Encouraging Peer Support: Facilitate friendships and social connections for children with autism. Establishing these relationships can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and enhance emotional well-being, which is vital for coping with burnout.
Research indicates that effective networks can lead to better outcomes for families. For instance, a state-sponsored initiative in Pennsylvania utilized a comprehensive survey methodology to assess the quality of autism-related services, underscoring the importance of diverse assistance systems in improving care quality. The study's findings highlight the effectiveness of these systems, as illustrated by the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.850 for the R-SPS-A, demonstrating strong reliability in measuring assistance system effectiveness.
Moreover, expert opinions affirm that a strong network not only mitigates the challenges associated with autism burnout symptoms but also empowers parents to advocate more effectively for their children. The CDC estimates a male-to-female ratio of 4:1 in autism, highlighting the prevalence of the condition and the critical need for robust assistance systems. By prioritizing these connections, parents can cultivate a nurturing environment that fosters resilience and growth.
It is essential to recognize that the cross-sectional design of the study limits the ability to establish causal relationships, adding complexity to our understanding of the effectiveness of support systems. Additionally, the research received approval from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, enhancing the credibility of the findings presented.
Autistic Burnout vs. Regular Burnout and Depression: Key Differences
Autistic burnout, while sharing some characteristics with regular burnout and depression, presents distinct differences that are essential for parents and caregivers to recognize.
- Causes: Autistic burnout is primarily triggered by social demands and sensory overload, contrasting with regular burnout, which is often linked to work-related stressors. This distinction highlights the unique challenges faced by individuals on the autism spectrum.
Individuals undergoing developmental fatigue may exhibit symptoms such as skill regression and heightened sensory sensitivity. These symptoms, often categorized as autism burnout symptoms, are less prevalent in instances of regular fatigue, where emotional exhaustion and detachment are more common. Research indicates that the ω for the PHQ-9, a measure of self-reported depressive symptoms, was found to be 0.89, suggesting a significant correlation between depressive symptoms and individuals on the autism spectrum (Kroenke et al., 2001).
- Recovery: The recovery process from autistic burnout typically requires a more extended period and specific strategies tailored to the individual's unique needs. This may include adjustments in the environment, therapeutic interventions, and assistance systems that cater to sensory sensitivities and social demands.
Understanding these key differences is vital for parents to effectively support their children and seek appropriate interventions. Research suggests that grasping the subtleties of sensory fatigue can lead to improved outcomes in managing symptoms and enhancing overall well-being. For instance, the occurrence of developmental fatigue can be considerable, with numerous individuals sharing experiences that sharply contrast with those of their neurotypical counterparts.
The case study titled "Data Analysis Methodology" illustrates how quantitative data can reveal similarities and differences in viewpoints on neurodevelopmental fatigue, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the topic. By fostering awareness and providing targeted support, parents can play a crucial role in their child's journey toward recovery and resilience. Moreover, the reliability coefficients for the CBI scales, although somewhat lower than for the ABM factors, offer insight into the assessment of exhaustion and its implications for comprehending neurodivergent fatigue.
It is also important to acknowledge that the authors of the research received no specific funding for this work and valued the insights and feedback from members of their advisory and pilot groups, emphasizing the collaborative nature of the research.
Self-Care Practices for Parents and Caregivers Supporting Autistic Individuals
Self-care is vital for parents and caregivers seeking to sustain their well-being while addressing the symptoms of autism burnout when supporting autistic individuals. By implementing effective self-care strategies, you can significantly alleviate stress and manage autism burnout symptoms, ultimately enhancing your overall quality of life. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Set Boundaries: Learning to say no to non-essential commitments is crucial for protecting your time and energy. Establishing clear boundaries helps prevent burnout, particularly autism burnout symptoms, and allows you to focus on your own needs. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can significantly reduce stress levels. These practices not only encourage relaxation but also enhance emotional resilience, empowering you to tackle challenges more effectively.
- Seek Social Assistance: Connecting with friends, family, or support groups provides an invaluable outlet for sharing experiences and feelings. Engaging with others who understand the unique challenges of caregiving fosters a sense of community and belonging.
- Prioritize Physical Health: Maintaining regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep is essential for overall health. Research indicates that physical well-being directly impacts emotional resilience, which is important for coping with the demands of caregiving and managing autism burnout symptoms. In fact, the severity of ASD symptoms has been positively associated with parenting stress, with mothers showing a β = .41 and fathers a β = .38, underscoring the need for effective self-care strategies.
- Take Breaks: Scheduling regular time away from caregiving responsibilities is crucial for recharging. Short breaks can help you regain perspective and energy, ultimately benefiting both you and your children.
Prioritizing self-care not only enhances your well-being but also helps mitigate autism burnout symptoms, allowing you to better assist your children. A study on the Mindful Self-Care for Caregivers (MSCC) program highlighted that mindfulness practices can effectively lower levels of depression, anxiety, and stress among caregivers. Participants reported positive experiences, indicating that acknowledging your own needs is essential for managing the stress associated with caregiving.
As noted by Doyle et al., nurturing parents’ competence and confidence through intentional intervention is key in supporting the social-emotional development of children. By embracing these self-care practices, you can foster a healthier relationship with your responsibilities, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for both yourself and the individuals you support.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing autistic burnout is crucial for the well-being of autistic individuals and their families. This phenomenon, characterized by profound exhaustion and a decline in functioning, can significantly impact daily life, mental health, and social relationships. By understanding the signs and symptoms of autistic burnout—such as extreme fatigue, skill regression, and increased sensory sensitivity—caregivers can better support their children and create a nurturing environment that promotes resilience.
The causes of autistic burnout are multifaceted, ranging from chronic stress and sensory overload to the exhaustion of masking behaviors. By identifying these triggers, parents can implement effective strategies to mitigate their effects. Establishing structured routines, promoting self-advocacy, and encouraging regular breaks can make a meaningful difference. Additionally, building strong support systems through community connections and professional guidance empowers families to navigate the complexities of autism more effectively.
It is essential to differentiate between autistic burnout and regular burnout or depression to provide appropriate support and interventions. Understanding these distinctions can lead to better outcomes for individuals experiencing burnout, fostering a path toward recovery and resilience. Moreover, self-care practices for parents and caregivers are equally important, as they play a vital role in sustaining their well-being while supporting their children.
Ultimately, by fostering awareness and understanding of autistic burnout, families can work together to create a supportive environment that prioritizes mental health and encourages the growth and development of autistic individuals. The journey may be challenging, but with the right knowledge and resources, caregivers can make a meaningful difference in their children's lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is neurodivergent fatigue?
Neurodivergent fatigue is a profound state of physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion that can affect individuals on the autism spectrum, particularly manifesting as autism burnout symptoms after prolonged stress or sensory overload.
How does neurodivergent fatigue differ from ordinary fatigue?
Unlike ordinary fatigue, neurodivergent exhaustion often involves a regression of previously acquired skills and increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, alongside a significant decline in functioning, which may affect daily tasks, communication, and social interactions.
What percentage of neurodiverse youth experience exhaustion during their development?
Research indicates that approximately 70% of neurodiverse youth experience some form of exhaustion during their development.
What are common signs of sensory overload in youth?
Common signs of sensory overload may include withdrawal from social situations, increased irritability, and difficulties in processing sensory information.
Why is it important for parents to understand autism burnout symptoms?
Understanding autism burnout symptoms empowers parents to provide necessary support and interventions tailored to their child's unique needs.
What do autism experts say about evaluating autism burnout symptoms?
Autism experts emphasize the need for developing effective evaluation tools to identify autism burnout symptoms and related exhaustion, highlighting that awareness and understanding are crucial for improving mental health outcomes.
How can stigma and masking contribute to neurodiverse exhaustion?
Stigma from family and societal pressures can compel neurodiverse individuals to hide their traits, which is recognized as a significant risk factor for autism burnout symptoms.
What are some traits of neurodivergent exhaustion?
Traits of neurodivergent exhaustion include both internal factors, such as emotional dysregulation, and external factors, like social withdrawal and increased sensory sensitivity.
What are key indicators of emotional exhaustion in children?
Key indicators include extreme fatigue, loss of skills, increased sensory sensitivity, social withdrawal, and emotional dysregulation.
How can parents support their children experiencing developmental exhaustion?
Parents can support their children by recognizing symptoms, providing a calming environment, adapting routines, and engaging with online communities for shared experiences and resources.




