Overview
Understanding Autism Bipolar is about recognizing the unique challenges caregivers face in managing the overlapping symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Bipolar Disorder. These challenges often include mood instability and social withdrawal, which can be particularly difficult to navigate.
Caregivers can effectively support individuals by:
- Establishing routines
- Employing clear communication techniques
- Utilizing emotional regulation strategies
By focusing on these supportive methods, caregivers can create a nurturing environment that fosters understanding and growth.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of mental health, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Bipolar Disorder present unique challenges that can profoundly impact individuals and their caregivers. As awareness of these conditions continues to grow, it becomes increasingly vital to understand their distinct characteristics and the potential overlap between them. Autism affects social communication and behavior, while bipolar disorder introduces unpredictable mood fluctuations. Caregivers must navigate a complex web of symptoms, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
This article delves into the key concepts surrounding both conditions, exploring their interconnectedness. It offers practical strategies for caregivers, ensuring that no child is left behind in their journey toward stability and understanding. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that nurtures growth and resilience.
Define Autism and Bipolar Disorder: Key Concepts for Caregivers
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges, particularly in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. These symptoms often emerge in early childhood and can vary widely in severity.
On the other hand, Bipolar Disorder is characterized by significant emotional fluctuations, including periods of heightened mood (mania or hypomania) and deep lows (depression). Understanding these definitions is vital for caregivers, enabling them to identify symptoms of autism bipolar effectively and tailor their support strategies.
Approximately 2.9% of teenagers aged 13-18 have been diagnosed with mood instability, with 2.6% experiencing severe impairment, according to a case study titled 'Lifetime Prevalence of Mood Instability Among U.S. Adolescents.' Recognizing the characteristics of impulsivity and sleep disturbances in individuals with autism bipolar is essential for caregivers, as it empowers them to navigate the complexities of both autism and bipolar disorder and implement effective support strategies.
Furthermore, current statistics from the ADDM Network reveal a rising prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder, underscoring the importance of awareness and understanding within the caregiving community. Together, we can foster an environment of support and compassion for those affected.
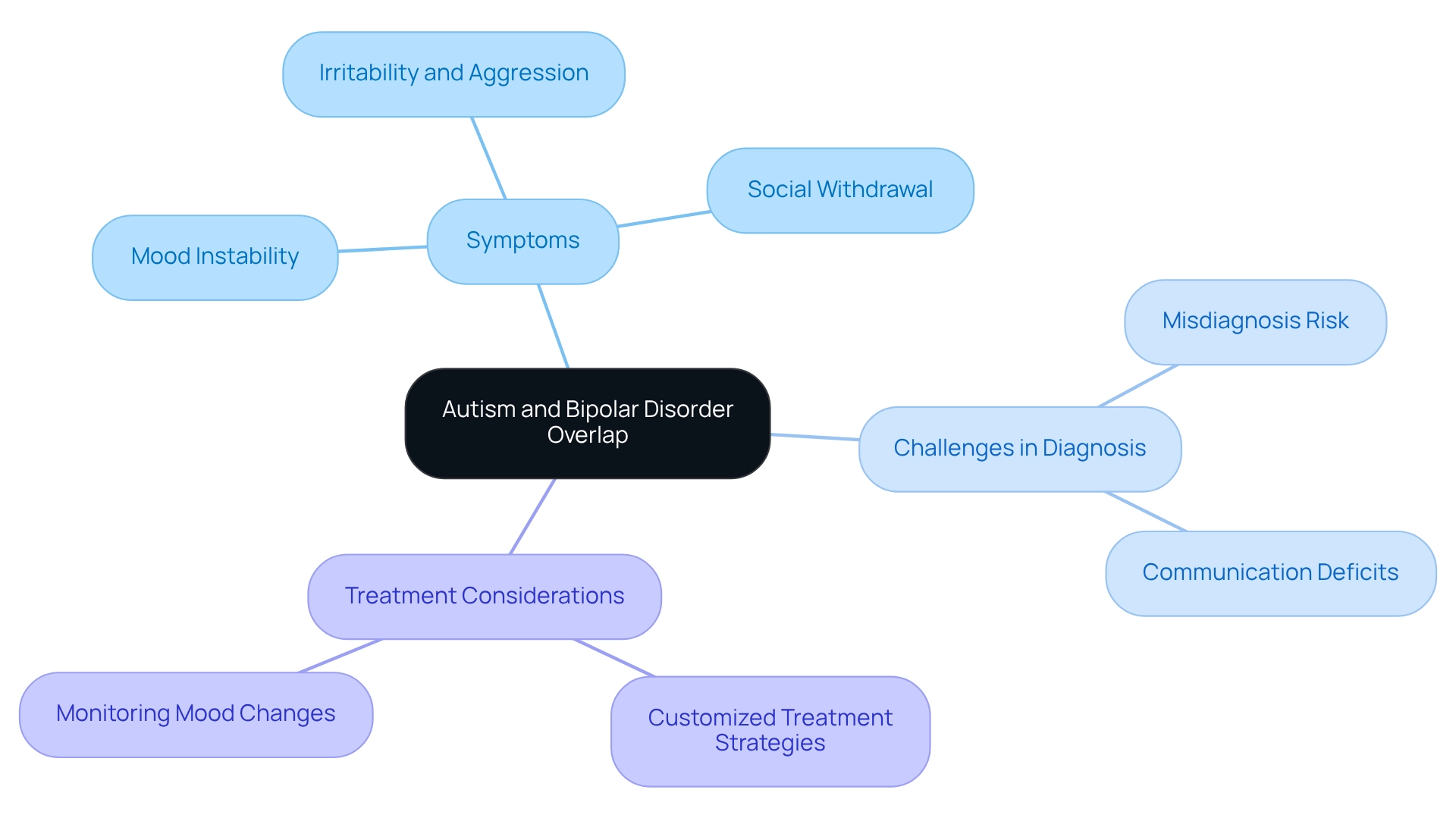
Explore the Connection: Autism and Bipolar Disorder Overlap
Studies show that individuals on the autism spectrum have a notably increased likelihood of developing mood swings compared to the overall population. Approximately 27% of individuals with autism bipolar may exhibit symptoms consistent with bipolar disorder. This connection is especially troubling, considering the overlapping symptoms of autism bipolar—irritability, emotional fluctuations, and social withdrawal—that complicate both diagnosis and treatment.
- Mood Instability: Both conditions can manifest as fluctuations in mood, although the triggers and expressions may vary.
- Irritability and Aggression: These behaviors are common in both conditions, involving neurodevelopmental differences and mood instability, presenting challenges for caregivers in management.
- Social Withdrawal: Individuals may retreat socially due to overwhelming emotions or difficulties in social interactions.
Recognizing these overlaps is essential for caregivers to prevent misdiagnosis and ensure effective interventions. Vigilance in monitoring mood changes and behavioral patterns is crucial, as these observations can significantly inform treatment decisions. Recent studies emphasize the need for meticulous diagnostic practices to correctly recognize mood conditions in young individuals with developmental differences, highlighting the significance of customized treatment strategies.
Moreover, communication deficits in young individuals with the condition may interfere with reporting suicidal behaviors, adding another layer of complexity to diagnosis and treatment. A case study titled 'Challenges in Diagnosing Autism Bipolar' emphasizes the difficulties in diagnosis due to overlapping symptoms and the potential for misdiagnosis in youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder. As noted by Boris Birmaher, MD, "Future work is needed to explore the impact of specific pharmacologic and psychosocial treatments on the clinical course of BD in youth with ASD." Furthermore, studies show that the dangers for manic-depressive illness are considerably greater among individuals with autism bipolar compared to their siblings without autism, further emphasizing the prevalence of this condition within the autism community.
Implement Support Strategies: Managing Autism and Bipolar Disorder
Caregivers face unique challenges when managing neurodevelopmental conditions and mood disorders, but several strategies can help navigate this journey with compassion and understanding.
Establish a Routine:
- Consistency is Key: A structured daily schedule fosters predictability, significantly reducing anxiety and behavioral issues. Research indicates that children with developmental disorders flourish on routine, which can also assist those with bipolar disorder by offering stability in their daily lives. Individuals on the spectrum often struggle with flexibility and adapting to change, making routines essential for their emotional well-being.
Communication Techniques:
- Use Clear Language: Simplifying communication and incorporating visual aids can enhance understanding, making it easier for children to grasp complex concepts. As noted by Autism Speaks, when this developmental disorder occurs in someone with Down syndrome, the characteristics of the condition may be observed in addition to the symptoms of Down syndrome, highlighting the need for tailored communication strategies.
- Active Listening: Encouraging open dialogue and validating feelings fosters trust and emotional safety, which are essential for children navigating the complexities of both conditions.
Emotional Regulation Strategies:
- Teach Coping Skills: Introducing techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or sensory breaks can empower children to manage their emotional responses effectively.
- Monitor Triggers: Identifying and documenting triggers for emotional fluctuations or behavioral outbursts allows caregivers to develop proactive strategies, enhancing emotional stability.
Professional Support:
- Therapeutic Interventions: Engaging with mental health professionals for therapy options, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be tailored to address the unique needs of children with both developmental disorders and bipolar disorder. Research indicates that OCD is more common in teens and adults with developmental disorders, and distinguishing OCD from typical behaviors can be challenging. Therefore, seeking evaluation from experienced mental health providers is crucial.
- Medication Management: Consulting healthcare providers about appropriate medications can help stabilize mood and manage symptoms effectively, ensuring a holistic approach to care.
Build a Support Network:
- Connect with Other Caregivers: Joining support groups enables caregivers to share experiences and strategies, significantly reducing feelings of isolation and stress. This community support is invaluable in navigating the challenges of caring for children with autism and bipolar disorder.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Bipolar Disorder can be a daunting journey for caregivers. It's crucial to understand the distinct characteristics of each condition, as this knowledge empowers caregivers to identify symptoms and tailor their support strategies effectively. The overlapping symptoms of mood instability, irritability, and social withdrawal add to the challenge, underscoring the need for vigilance and careful diagnostic practices.
Creating a supportive environment for children facing these challenges can be achieved through:
- Structured routines
- Clear communication techniques
- Emotional regulation strategies
Professional interventions, including therapeutic options and medication management, are vital in fostering stability and enhancing emotional well-being. Moreover, building a robust support network by connecting with other caregivers can alleviate feelings of isolation, offering a comforting sense of community in the caregiving experience.
Ultimately, understanding and managing both autism and bipolar disorder transcends merely addressing symptoms; it’s about nurturing resilience and growth in children. By prioritizing awareness and implementing effective strategies, caregivers can significantly enhance the quality of life for those they support, ensuring that no child is left behind on their path to stability and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges, particularly in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms often emerge in early childhood and can vary widely in severity.
What characterizes Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar Disorder is characterized by significant emotional fluctuations, including periods of heightened mood (mania or hypomania) and deep lows (depression).
Why is it important for caregivers to understand the definitions of ASD and Bipolar Disorder?
Understanding these definitions is vital for caregivers as it enables them to identify symptoms of autism and bipolar disorder effectively and tailor their support strategies accordingly.
What percentage of teenagers are diagnosed with mood instability?
Approximately 2.9% of teenagers aged 13-18 have been diagnosed with mood instability, with 2.6% experiencing severe impairment.
What symptoms should caregivers recognize in individuals with autism and bipolar disorder?
Caregivers should recognize characteristics of impulsivity and sleep disturbances in individuals with autism and bipolar disorder, as this knowledge empowers them to navigate the complexities of both conditions and implement effective support strategies.
What do current statistics reveal about the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Current statistics from the ADDM Network reveal a rising prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder, highlighting the importance of awareness and understanding within the caregiving community.




