Overview
The article focuses on the unique challenges and changes that children with autism face during puberty, emphasizing the need for tailored support from parents. It highlights the importance of open communication, structured routines, and specialized strategies to help autistic youth navigate physical and emotional transformations, thereby fostering a nurturing environment for their development.
Introduction
As children transition into puberty, a significant journey unfolds, particularly for those on the autism spectrum. This period is marked by profound physical and emotional changes that can create unique challenges for autistic youth and their families. Understanding the nuances of this transformation is crucial for parents striving to provide the best support. From navigating sensory sensitivities to developing essential life skills, the challenges are multifaceted, yet the right strategies can empower both parents and children.
This article delves into the complexities of puberty in autism, offering insights, practical approaches, and valuable resources to help families foster resilience and independence during this pivotal stage of development.
Understanding the Physical and Emotional Changes of Puberty in Autism
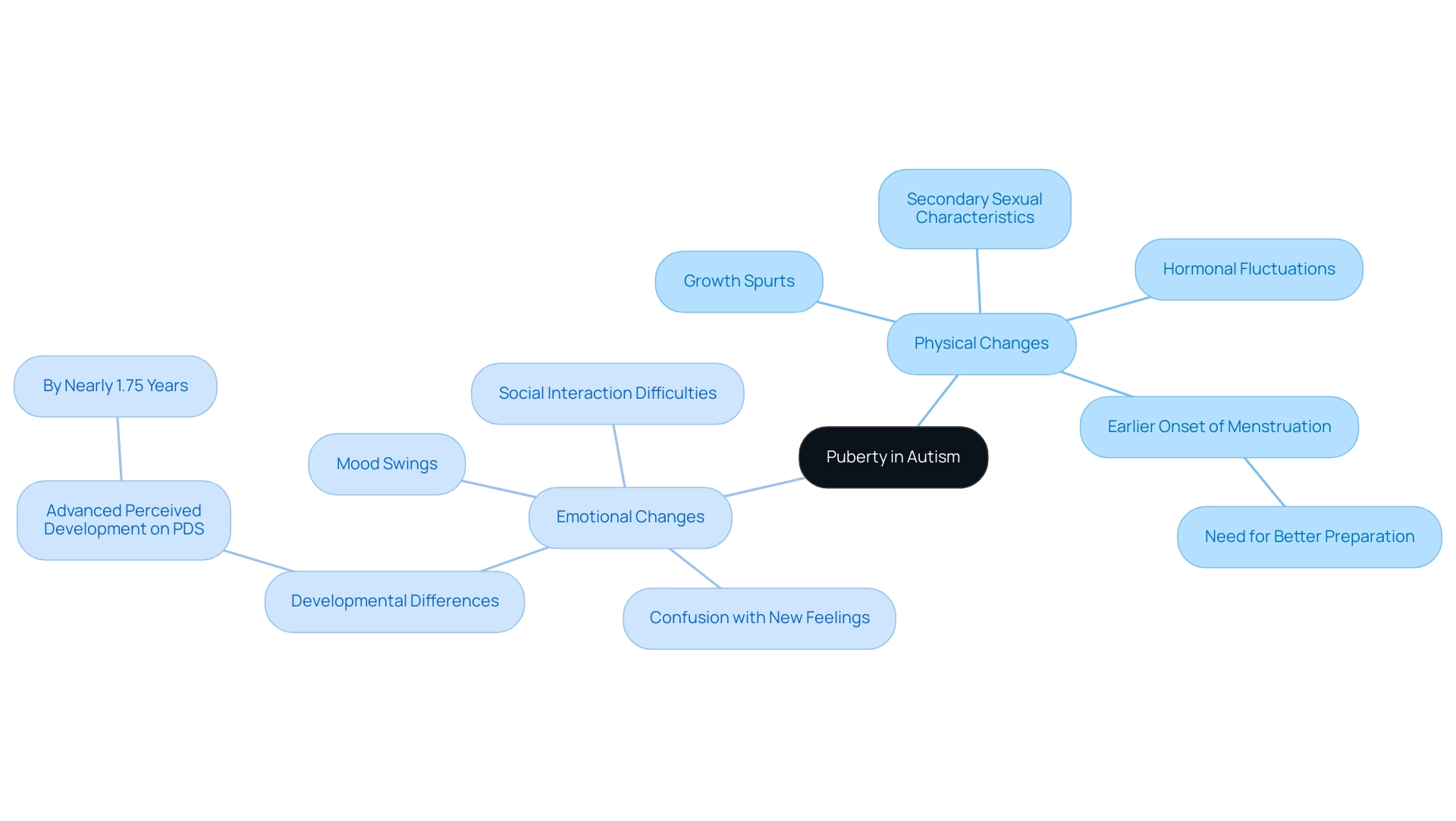
Puberty represents a critical period of transformation for all individuals, yet for those experiencing autism and puberty, this transition can present distinct challenges. During this phase, children undergo physical changes such as:
- Growth spurts
- The emergence of secondary sexual characteristics
- Significant hormonal fluctuations
Emotionally, they may grapple with:
- Intensified mood swings
- Confusion regarding new feelings
- Heightened difficulties in navigating social interactions
Notably, recent findings indicate that girls with autism and puberty experience an earlier onset of menstruation compared to their neurotypical peers, emphasizing the urgent need for tailored education and preparation during this transformative time. Furthermore, research shows that female sex is associated with more advanced perceived development on the PDS by nearly 1.75 years, highlighting developmental differences that can impact emotional well-being. As Teicher M. H. aptly notes,
The effects of childhood maltreatment on brain structure, function, and connectivity
underscores the importance of understanding the emotional shifts that accompany puberty.
This knowledge enables caregivers to anticipate and respond effectively to their offspring's needs, fostering a nurturing environment that embraces their unique developmental trajectory during the pivotal stage of autism and puberty. Additionally, a recent study titled 'Future Directions in Pubertal Research' identified gaps in understanding the relationship between pubertal timing and internalizing symptoms, suggesting that ongoing research is essential to explore these associations more thoroughly. By acknowledging these challenges and adapting their approach, parents can play a vital role in supporting their offspring through this complex journey.
Navigating the Challenges of Puberty for Children with Autism
Children with autism and puberty often face a particularly challenging time, as they frequently experience heightened sensory sensitivities. In fact, frequencies of endorsed impacts related to sound hypersensitivity can significantly interfere with tasks or opportunities, with a notable statistic of 6.13 (p = 0.013) highlighting this issue. These sensitivities during autism and puberty can significantly affect their comfort levels regarding bodily changes, clothing textures, and different interpersonal situations.
As they navigate this complex stage, social skills also evolve, presenting new dynamics and expectations in peer interactions. A caregiver expressed a common concern, stating, 'I mean that’s part of that major concern… ‘cause as far as I know, there are not very many or any programs that are dealing with sensory things like kids who are low functioning sensory kids.' This underscores the necessity for advocacy and resources for families.
To assist their offspring with autism and puberty, parents can play an essential role by offering clear explanations about the changes they might encounter. Establishing open lines of communication is crucial, as it allows young individuals to voice their feelings and concerns in a safe environment. Engaging in role-playing scenarios stands out as an effective strategy, offering young individuals a chance to practice social interactions in a supportive setting.
This method not only builds confidence but also equips them with the skills to handle real-life situations. Furthermore, dividing personal care tasks into manageable steps, as shown in the case study on teaching personal care skills, is essential for individuals with autism and puberty during adolescence. Research indicates that sensory processing issues can interfere with academic performance, underscoring the importance of understanding and addressing these sensitivities.
By promoting personalized strategies and nurturing a supportive environment, guardians can enable their offspring to manage the challenges of adolescence with enhanced ease and strength.
Empowering Parents: Strategies for Supporting Autistic Children During Puberty
Supporting individuals with autism and puberty through the challenges they face requires a multifaceted approach. Here are key strategies that parents can implement to foster a nurturing environment:
- Open Communication: Establish an atmosphere where discussions about physical and emotional changes are welcomed. This ensures that young individuals feel secure in expressing their thoughts and feelings, paving the way for healthy dialogue. As noted by Howlin (2007), effective communication strategies, such as the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS), were associated with a decrease in severity scores, highlighting the importance of fostering communication.
- Routine and Structure: Maintaining consistent daily routines is essential as it offers the predictability that can assist autistic individuals in managing the uncertainties that come with autism and puberty. A stable environment can significantly reduce anxiety during this transitional period. The ANOVA results, which demonstrated a statistically significant model (F = 2.182, p = 0.008), highlight the importance of structured approaches in supporting these individuals.
- Education: Utilize age-appropriate literature and resources that explain the relationship between autism and puberty in a manner that resonates with autistic individuals. By contextualizing these changes, you can help demystify the process and alleviate fears.
- Interpersonal Skills Development: Consider enrolling your offspring in specialized interpersonal skills development programs designed specifically for autistic youth. These workshops can facilitate the development of essential social competencies, enhancing their interactions with peers. A case study titled 'Communication and Language Skills in Individuals with ASD' found significant delays in communication abilities among individuals with ASD, emphasizing the need for focused training to enhance these skills and their emotional well-being.
- Professional Support: Seeking the expertise of therapists or counselors who specialize in autism can provide tailored strategies to address individual challenges. This expert advice can be essential in assisting both guardians and youngsters manage the challenges of adolescence.
By implementing these strategies, backed by evidence and expert insights, caregivers can significantly improve their offspring's emotional well-being and interpersonal skills, especially concerning autism and puberty, creating a supportive environment during this critical developmental stage.
Essential Resources and Educational Tools for Parents of Autistic Teens
Navigating the transition of adolescence for children with autism can be challenging, but guardians have access to a wealth of supportive resources to guide them through this critical period:
- Books: Consider titles like The Autism Spectrum Guide to Adolescence, which offers tailored insights to help understand and manage the changes associated with adolescence. Additionally, The Social Survival Guide for Teens on the Autism Spectrum is available for $8.24, providing valuable strategies for social interactions during this time, especially regarding autism and puberty.
- Webinars and Workshops: Numerous organizations regularly host events focused on autism and puberty. These sessions offer expert guidance and opportunities for Community Connection, allowing caregivers to learn from professionals and each other.
- Online Forums: Platforms such as the Autism Support Network enable caregivers to connect, share experiences, and seek advice in a supportive online environment. This peer interaction can be incredibly validating and informative.
- Local Support Groups: Joining local caregiver support groups fosters a sense of community, offering practical tips and shared experiences from those facing similar challenges. These local connections can be invaluable during this transition.
- Professional Consultations: Engaging with ABA therapists or counselors provides personalized strategies tailored to individual needs, ensuring that guardians receive targeted support for their offspring's unique circumstances.
Incorporating insights from Ido Kedar, who challenges misconceptions in autism theories while documenting his personal growth, can further empower guardians during this transition. By exploring these resources, caregivers can empower themselves with knowledge and assistance, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of adolescence, especially the challenges related to autism and puberty for their autistic teenagers. Notably, a practicing adolescent psychiatrist has reviewed 'Parenting ASD Teens' and recommends it as a valuable resource for effective parenting strategies.
Encouraging Independence and Self-Care in Autistic Youth During Puberty
To empower youth with autism during puberty in developing independence and self-care, parents can adopt several effective strategies:
- Teach Personal Hygiene: Introduce personal hygiene routines gradually, utilizing visual schedules to break down steps such as bathing, dental care, and grooming. This structured approach aids in reinforcing these essential habits, making them more manageable for autistic teens. According to the Community-Based Skills Assessment (CSA), skill levels are typically assessed starting at age 12, making this an important time to focus on these skills.
- Life Skills Training: Actively involve teens in everyday tasks such as cooking, laundry, and budgeting. This hands-on experience not only builds confidence but also equips them with crucial life skills necessary for adulthood. As Drew Melson from the Sarah Dooley Center for Autism emphasizes, > life skills are a vital part of autism education <. Additionally, implementing ABA therapy can enhance family dynamics, as families learn to collaborate in supporting the individual's development.
- Encourage Decision Making: Provide opportunities for your young one to make choices regarding their clothing, food, and activities. This fosters a sense of control and responsibility, which is essential for their development and self-esteem.
- Promote Independence: Encourage participation in activities or clubs that resonate with their interests. These settings can foster friendships and improve interpersonal skills, particularly through organized peer interactions, as shown in the case study 'Harnessing Peer Dynamics to Enhance Interpersonal Skills in ABA Therapy,' where youngsters exhibited enhanced interaction abilities through such engagements. It’s also important to recognize the complexities of social interactions, such as eye contact, which can be challenging for autistic youth, as discussed in the article 'Exploring the Relationship Between Autism and Eye Contact.'
- Utilize Technology: Leverage apps designed to support self-management and skill-building. These engaging tools can make learning self-care and independence enjoyable and accessible, reinforcing the skills your child is developing in a fun and interactive way. By implementing these strategies, parents can significantly contribute to fostering independence and self-care in their autistic teens, particularly during the challenging period of autism and puberty, helping them navigate this critical developmental stage with confidence.
Conclusion
Understanding and supporting children with autism during puberty is a multifaceted challenge that requires awareness, empathy, and effective strategies. As highlighted throughout this article, the physical and emotional changes of puberty can be particularly intense for autistic youth, necessitating tailored approaches that address their unique needs. From navigating sensory sensitivities to fostering open communication, parents play a crucial role in guiding their children through this transformative period.
Implementing structured routines, utilizing educational resources, and encouraging life skills training are essential strategies that can empower autistic teens. These methods not only help mitigate anxiety but also foster independence and self-care, equipping them with the tools they need to navigate adolescence with confidence.
Moreover, the wealth of resources available—from books and webinars to professional consultations—provides parents with valuable support and insights. By leveraging these tools and building a strong support network, families can create an environment that nurtures resilience and growth.
Ultimately, the journey through puberty for children on the autism spectrum is complex, but with the right strategies and resources, parents can foster a sense of security and empowerment. This proactive approach not only enhances their child's emotional well-being but also paves the way for a more confident and independent future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What physical changes do children with autism experience during puberty?
During puberty, children with autism experience physical changes such as growth spurts, the emergence of secondary sexual characteristics, and significant hormonal fluctuations.
What emotional challenges do children with autism face during puberty?
Emotionally, children with autism may experience intensified mood swings, confusion regarding new feelings, and heightened difficulties in navigating social interactions.
How does the onset of menstruation differ for girls with autism compared to neurotypical peers?
Recent findings indicate that girls with autism experience an earlier onset of menstruation compared to their neurotypical peers, highlighting the need for tailored education and preparation during this time.
What developmental differences are observed in girls with autism during puberty?
Research shows that female sex is associated with more advanced perceived development on the Pubertal Development Scale (PDS) by nearly 1.75 years, which can impact emotional well-being.
Why is understanding emotional shifts during puberty important for caregivers of children with autism?
Understanding emotional shifts allows caregivers to anticipate and respond effectively to their children's needs, fostering a nurturing environment that supports their unique developmental trajectory.
What challenges do children with autism face regarding sensory sensitivities during puberty?
Children with autism often experience heightened sensory sensitivities during puberty, particularly related to sound, which can interfere with their comfort regarding bodily changes, clothing textures, and interpersonal situations.
How can parents assist their children with autism during puberty?
Parents can assist by offering clear explanations about the changes their children may encounter, establishing open lines of communication, engaging in role-playing scenarios, and dividing personal care tasks into manageable steps.
What role does communication play in supporting children with autism during puberty?
Open communication allows young individuals to voice their feelings and concerns in a safe environment, which is crucial for their emotional support and understanding during this complex stage.
Why is there a need for advocacy and resources for families of children with autism during puberty?
There is a necessity for advocacy and resources due to the lack of programs addressing sensory issues and the unique challenges faced by children with autism, particularly those with low-functioning sensory sensitivities.




