Overview
This article delves into the important connection between autism and picky eating, a challenge many families with autistic children face. Selective eating often stems from sensory sensitivities and emotional factors, making it a relatable concern for parents. Understanding this connection is crucial, as it can pave the way for effective management strategies.
To support families, the article emphasizes tailored approaches, such as gradually introducing new foods and creating a nurturing mealtime environment. These strategies not only aim to improve dietary variety but also enhance the overall well-being of children. By fostering a supportive atmosphere, parents can help their children navigate their eating challenges more successfully.
We invite parents to share their experiences and insights in the comments or through our newsletters. Together, we can build a community that understands and addresses the unique needs of children with autism. Let’s work towards creating positive mealtime experiences that nurture both health and happiness.
Introduction
Navigating the world of picky eating can be particularly challenging for families with autistic children, where food selectivity often intersects with sensory sensitivities and emotional dynamics. It's not uncommon for parents to feel overwhelmed, as research shows that a staggering percentage of these children exhibit strong preferences for certain textures and tastes. This can turn mealtime into a battleground of anxiety and frustration.
However, understanding the underlying reasons for picky eating can empower parents to approach this issue with empathy and informed strategies. By exploring effective techniques and fostering a supportive mealtime environment, families can enhance their children's nutritional intake while creating a more positive dining experience.
This article delves into the complexities of picky eating in autistic children, offering insights and practical solutions that can help transform mealtime from a source of stress into an opportunity for connection and growth.
The Connection Between Autism and Picky Eating
Discriminating consumption is a significant concern for many families with children who experience autism and picky eating. Studies indicate that between 46% and 89% of these children exhibit some form of dietary selectivity. This behavior often manifests as a strong preference for specific textures, colors, or varieties of food, leading to a limited diet. Understanding this connection is essential for caregivers, as it reframes picky eating not as a behavioral flaw but as an intrinsic aspect of autism that requires tailored management approaches.
Recent studies have revealed a link between autism and picky eating with sensory sensitivities. Additionally, both parents and professionals frequently face challenges during visits, such as limited time and difficulties in providing nutrition education while the child is present. As one mother of an 11-year-old boy expressed, "And there’s just no good options," highlighting the frustrations many caregivers experience when trying to offer nutritious meals.
By acknowledging that numerous families encounter similar challenges, caregivers can cultivate a sense of community and support, sharing experiences and strategies to collectively address these concerns. Furthermore, case studies, such as the one involving role-playing exercises in ABA therapy, showcase effective strategies that can be employed to address selective food preferences and enhance social skills. This shared understanding empowers parents to approach selective eating with compassion and informed methods, ultimately improving their child's nutritional intake and overall well-being.
Factors Influencing Picky Eating in Autistic Children
Many factors influence selective food preferences in children, especially those with autism and picky eating habits, with sensory sensitivities playing a crucial role. Many autistic individuals experience heightened sensitivity to specific textures, tastes, or scents, leading to aversions that are often linked to autism and picky eating. A recent study highlighted that during the pandemic, parents observed significant changes in their children's dietary patterns, notably an increase in junk food consumption and a decrease in structured meals.
This shift underscores the importance of understanding how external factors can exacerbate selective eating habits, particularly in the context of autism and picky eating, and the broader implications for the health and nutrition of autistic individuals.
Oral-motor delays also have a profound impact on a child's eating habits. These delays can impede a child's ability to chew or swallow certain foods, often resulting in a preference for softer or easier-to-eat options. For example, a case study on feeding issues in youth with autism and picky eating revealed that addressing oral-motor challenges is essential for developing effective management strategies.
By recognizing these challenges, caregivers can better support their children in overcoming feeding difficulties.
To enhance their children's dietary variety, parents can implement tailored approaches, such as gradually introducing new textures or flavors in a gentle manner, particularly for kids facing autism and picky eating. This strategy not only respects the child's sensory preferences but also encourages the exploration of diverse cuisines over time. Engaging with feeding specialists can provide valuable insights into effective methods for managing selective food preferences associated with autism and picky eating, ensuring that caregivers have the necessary knowledge to meet their child's nutritional needs.
As one caregiver, Anna, shared, "I maybe haven’t cooked as much … like I think I've got into a real rut with food I cook for them," reflecting the challenges many families encounter. Additionally, various organizations offer resources and support for autistic individuals and their families regarding food-related disorders, which can be vital for parents navigating these challenges. Understanding the pandemic's effects on dietary behaviors is crucial for guiding future clinical practices, ensuring families receive the support they truly need.
Understanding the Emotional Impact of Picky Eating
Selective eating profoundly affects the emotional health of both autistic individuals and their families, especially concerning autism and picky eating. For many young individuals on the autism spectrum, mealtime often transforms into a source of significant anxiety and distress, particularly when they are pressured to consume foods they find intolerable. This pressure can lead to power struggles between parents and their children, complicating the already challenging feeding dynamic.
Statistics reveal that 60.6% of individuals with autism and picky eating exhibit high food selectivity, compared to 37.9% of their typically developing peers. This highlights just how prevalent this issue is.
The emotional repercussions of selective food choices can manifest in various ways, particularly for those facing autism and picky eating, including increased anxiety during mealtimes. Research suggests that these struggles can create a tense atmosphere, impacting family dynamics and leading to frustration for both parents and children. For instance, a case study on sociocultural influences on feeding practices illustrates how caregiver educational approaches and limited exposure to diverse foods can reinforce dysfunctional dietary habits. This underscores the necessity for tailored interventions.
As Stephen Shore poignantly observes, "Carrots in a green salad and celery in tuna fish salad are still intolerable to me because of the contrast in texture... However, I take pleasure in consuming celery and baby carrots on their own," which beautifully exemplifies the nuanced preferences that can complicate mealtimes.
To ease these challenges, guardians should aim to cultivate a nurturing mealtime environment that respects their child's emotions and choices. Open communication and patience are vital in this journey. By recognizing their child's unique needs and fostering a collaborative approach, families can navigate the complexities of autism and picky eating together.
This not only alleviates anxiety but also fosters a more positive and enjoyable mealtime experience for all involved. Additionally, establishing a support network through local or online autism support groups can provide caregivers with effective strategies for managing mealtime challenges. It is crucial to acknowledge that further research is needed to understand the factors influencing dietary selectivity and its impact on nutrition, emphasizing the ongoing nature of this issue.
Effective Strategies for Encouraging Dietary Variety
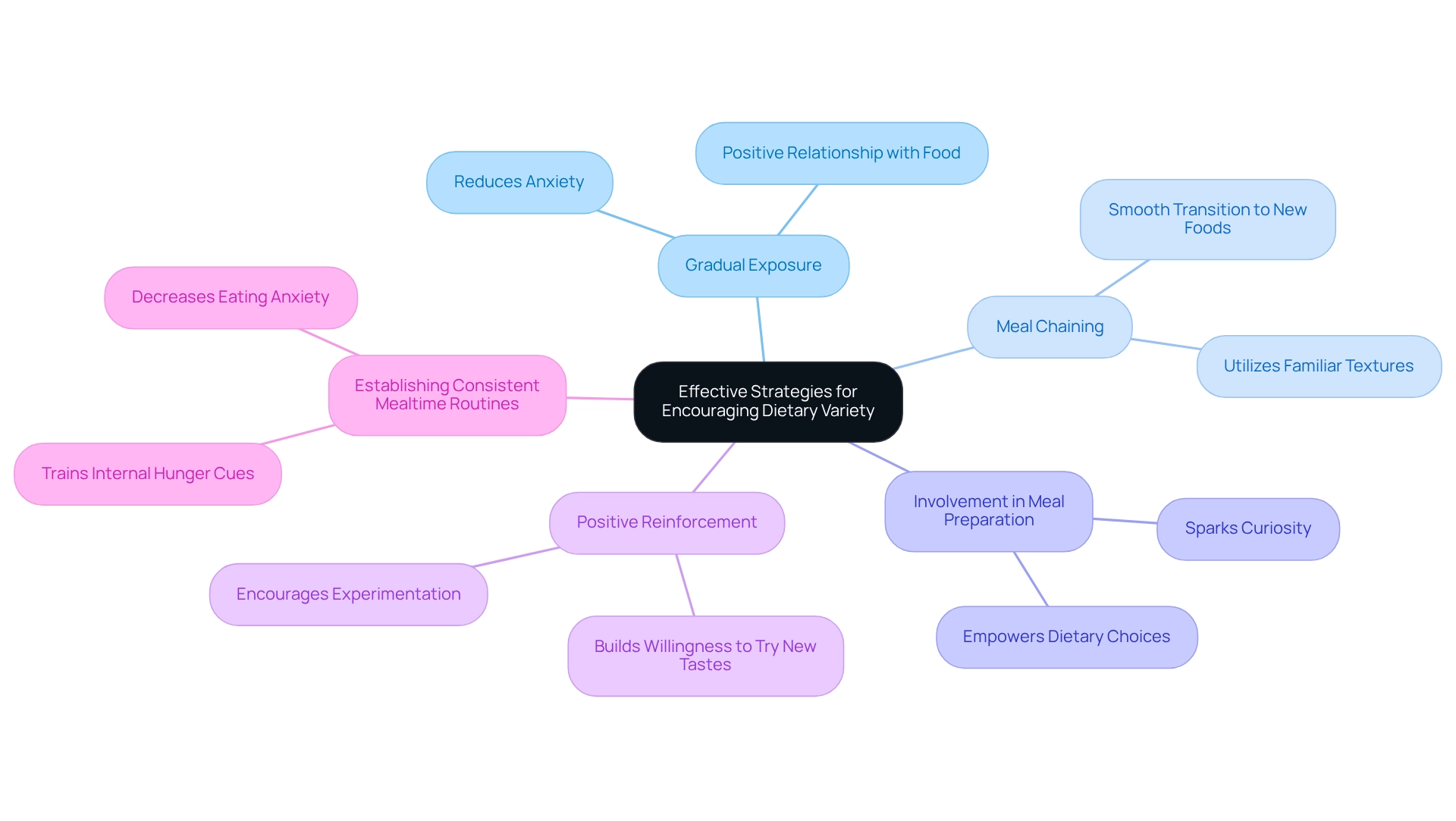
To encourage dietary variety in picky eaters, parents can implement several effective strategies that nurture curiosity and ease anxiety.
- Gradual Exposure: Start by introducing new items gradually, with small portions alongside familiar favorites. This gentle approach can significantly reduce the anxiety often linked to trying new foods, particularly for children facing challenges related to autism and picky eating. By making the experience less intimidating, parents can foster a more positive relationship with food.
- Meal Chaining: Consider utilizing the meal chaining method, which involves introducing foods that share similar textures or flavors with those that the child already enjoys. For example, if a child loves mashed potatoes, parents might try introducing mashed sweet potatoes. This strategy can create a smoother transition to new meals, making the process feel less overwhelming.
- Involvement in Meal Preparation: Engaging children in the cooking process can be a game changer. Allowing them to participate in meal preparation not only sparks their curiosity about new dishes but also empowers them to take responsibility for their dietary choices. This involvement can be particularly beneficial for children dealing with autism and picky eating, as it helps them feel more connected to the food they eat.
- Positive Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement plays a crucial role in encouraging children to experiment with new dishes. By offering rewards and encouragement, parents can foster a willingness to try different tastes. This approach is especially important for those facing challenges with autism and picky eating, as it can lead to a more adventurous palate over time.
- Establishing Consistent Mealtime Routines: Creating a sense of security and predictability through consistent mealtime routines is essential. Regular meal times help train a child's internal hunger cues and promote acceptance of meals at set times, ultimately decreasing anxiety related to eating. As previously noted, "it’s so important to eat on a schedule."
In a case study focusing on family meals, it was suggested that parents concentrate on the meals rather than the child's negative behaviors, such as spitting or whining. By fostering positive discussions about meals, families can create a more enjoyable dining experience. This approach not only helps decrease disruptive behaviors but also promotes a healthier relationship with nutrition. It aligns beautifully with the strategies mentioned, emphasizing the importance of focusing on food during mealtimes.
Creating a Positive Mealtime Environment
Creating a positive mealtime atmosphere is crucial for fostering healthy eating habits in children with autism. Here are several effective strategies to consider:
- Minimize Distractions: A calm dining area, free from distractions like television or loud noises, significantly enhances a child's focus on their meals. Research shows that hyperresponsivity is common in children with autism, making a serene environment essential for their comfort and concentration. This is especially important as many families, like Mrs. Turner’s, may feel overwhelmed by mealtime challenges, particularly when lacking effective feeding strategies.
- Use Visual Supports: Implementing visual schedules or charts can help outline mealtime routines, offering children a clear understanding of what to expect. This approach alleviates anxiety and promotes a sense of security during meals.
- Make Meals Enjoyable: Infusing fun into mealtime can transform the experience. Consider themed dinners or creatively showcasing dishes to engage children and stimulate their interest in trying new foods.
- Encourage Family Meals: Sharing meals as a family reinforces social skills and models positive eating behaviors. This communal aspect can inspire children to explore various cuisines in a nurturing atmosphere.
- Be Patient and Flexible: Allowing children to engage with their food at their own pace is vital. Avoiding pressure to eat fosters a relaxed environment, encouraging exploration and reducing stress around mealtime.
These strategies are supported by case studies highlighting the prevalence of feeding issues in children with autism, which are significantly more common than in their typically developing peers. The study titled "Eating and Mealtime Behaviors in ASD" underscores the need for further research to understand these challenges and the importance of tailored approaches. By establishing a supportive mealtime atmosphere, families can greatly influence their children's dietary habits and overall health.
As David noted, "it's very stressful. It's one of the most difficult aspects of all of his diagnosis," highlighting the emotional toll these challenges can take on families. Understanding that there is no one-size-fits-all method to nourish children with autism allows parents to manage these challenges more effectively.
The Importance of Patience and Consistency in Feeding
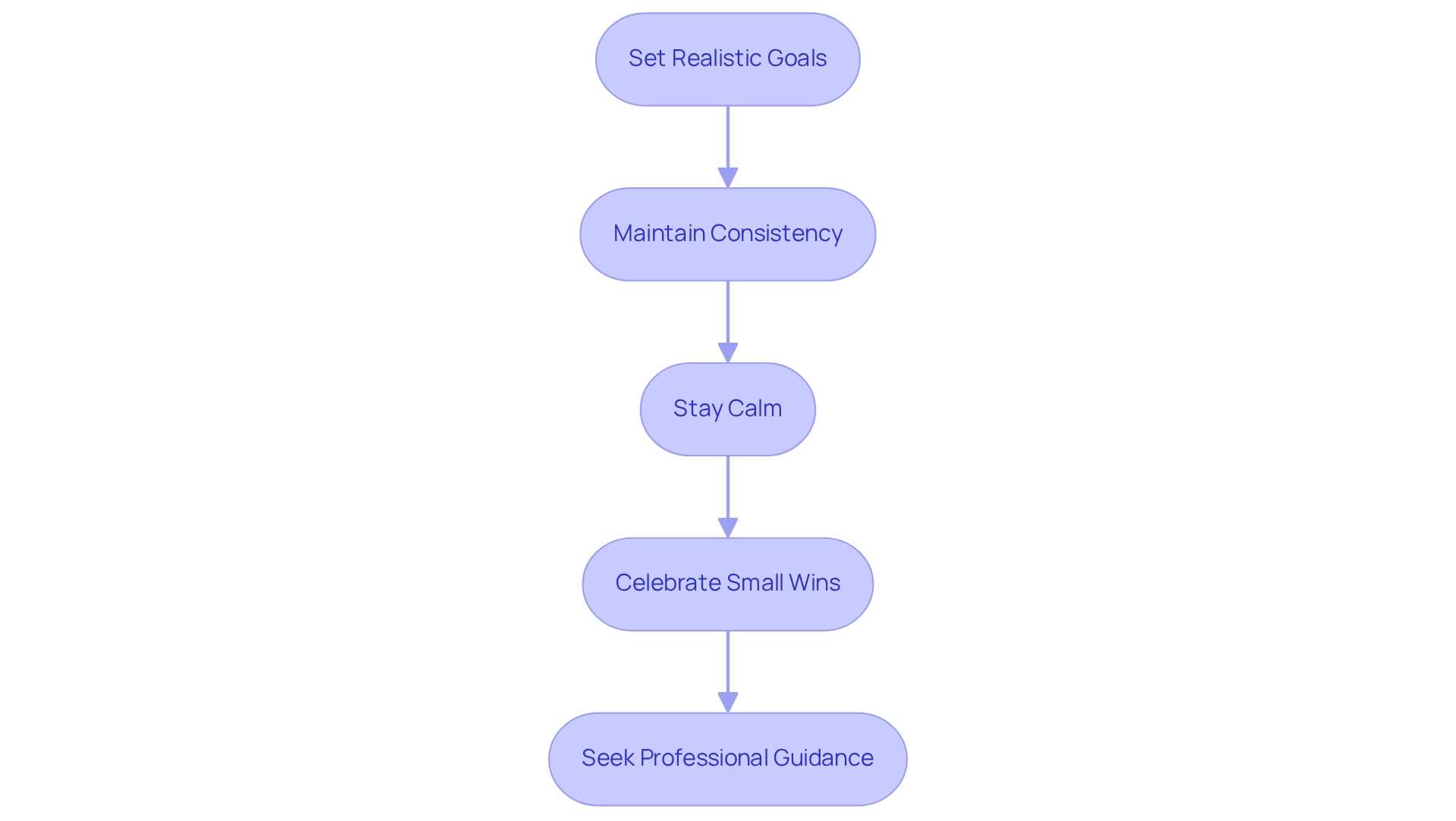
Addressing selective food preferences in children with autism and picky eating requires a long-term commitment characterized by patience and consistency. As you embark on this journey, it’s important to remember that you are not alone, and there are effective strategies to support you.
- Set Realistic Goals: Understand that changing eating habits is a gradual process. Establish small, attainable goals for introducing new items, rather than expecting immediate acceptance. This approach aligns with expert recommendations that emphasize the importance of setting realistic expectations for dietary changes. Insights from a case study on collaborative goal-setting in malnutrition interventions highlight the necessity for education in shared decision-making, which can enhance your child’s participation in dietary modifications.
- Maintain Consistency: Regularly present new options multiple times, even if they are initially rejected. Research indicates that repeated exposure can significantly enhance acceptance over time, making it crucial to persist in introducing new options. Additionally, using smaller plates can trick the mind into feeling satisfied with smaller portions, which may help in managing portion sizes when introducing new foods.
- Stay Calm: Approach mealtime with a composed demeanor. Children are sensitive to their parents' feelings; if they sense frustration or anxiety, it may increase their hesitation to try new dishes. Creating a calm atmosphere can foster a more positive dining experience.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge and celebrate any progress, no matter how minor. Positive reinforcement can act as a strong motivator, inspiring your child to keep trying new foods. This aligns with findings from case studies that highlight the effectiveness of celebrating incremental achievements in dietary changes.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If challenges persist, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or a feeding specialist. These experts can provide customized strategies and assistance tailored to your child’s specific needs, ensuring a more effective approach to handling selective food preferences. Expert advice can offer tailored nutritional suggestions, emphasizing the significance of aligning dietary changes with your child’s personal goals, as underscored by Group B's statement regarding consideration of patients' objectives.
Implementing these strategies can create a nurturing environment that encourages children, particularly those with autism and picky eating, to expand their dietary choices over time. This journey, while challenging, can ultimately lead to healthier habits and greater well-being for your child.
Resources and Support for Parents of Picky Eaters
- Support Groups: Engaging with local or online support groups can be invaluable for caregivers of picky eaters. These platforms create opportunities for sharing experiences, strategies, and encouragement, fostering a sense of community and understanding among families facing similar challenges. However, obstacles such as inflexible service delivery models and time constraints can hinder access to these essential resources. Have you found a group that resonates with you?
- Professional Guidance: Seeking advice from pediatricians, registered dietitians, or feeding specialists can provide parents with tailored strategies to address selective food preferences. These experts offer insights into nutritional requirements and effective methods to encourage healthier dietary habits. Dietitians emphasize the importance of a structured approach that includes gradual exposure to new foods and positive reinforcement, which can significantly enhance a child's willingness to try different foods. Have you considered reaching out to a specialist?
- Educational Resources: There is a wealth of educational materials, including websites, books, and articles, focused on autism and picky eating challenges. These resources equip caregivers with practical advice and insights that can help navigate the complexities of their children's dietary habits. What resources have you found helpful?
- Workshops and Seminars: Participating in workshops or seminars centered on feeding strategies for children with autism can be beneficial. These events often provide practical learning experiences and promote community support, allowing guardians to connect with specialists and other families. Have you attended any workshops that made a difference?
- Community Programs: Many communities offer programs or classes that focus on nutrition and cooking for children with special needs. These initiatives not only educate guardians but also encourage social interaction among children, creating a nurturing environment for learning and growth. What local programs have you explored?
- Statistics on Selective Consumption: Research indicates that issues related to autism and picky eating are common among children, with many guardians reporting challenges in meal preparation and acceptance of various foods. Understanding these statistics can help caregivers feel less isolated and more empowered to seek support. For instance, a case study on dining preferences reveals that changing habits, such as dining out at least once a week, can educate caregivers about meal choices and preferences. How do you cope with these challenges?
- Expert Opinions: Dietitians highlight the importance of professional guidance in addressing selective eating, particularly in the context of autism and picky eating. They advocate for a structured approach that includes gradual exposure to new foods and positive reinforcement, which can greatly improve a child's willingness to try different foods. As Ellen Gerrits notes, collaboration and support are vital in navigating these challenges, aligning with ASD Media's mission to foster a supportive community. Additionally, for those struggling to find time for grocery shopping, utilizing a grocery delivery service can save time and reduce stress, offering a practical solution for busy parents. What strategies have you implemented to ease your routine?
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of picky eating in autistic children reveals that this issue is not merely a matter of stubbornness or behavior; it is intricately linked to sensory sensitivities, emotional dynamics, and individual health needs. By recognizing that food selectivity is common among autistic children, parents can adopt a more empathetic approach, utilizing strategies that respect their child's unique preferences and challenges.
Key strategies, such as:
- Gradual exposure to new foods
- Involving children in meal preparation
- Creating a positive mealtime environment
can significantly improve eating habits and reduce anxiety. Additionally, fostering open communication and patience transforms mealtimes into opportunities for connection rather than conflict. It is essential for families to establish routines, celebrate small victories, and seek professional guidance when necessary to ensure their children receive adequate nutrition.
Ultimately, navigating picky eating in autistic children requires a commitment to understanding, flexibility, and ongoing support from both professionals and the community. By fostering a nurturing and collaborative atmosphere, families can promote healthier eating habits and enhance the overall well-being of their children. Embracing these strategies not only alleviates mealtime stress but also strengthens the family bond, turning what was once a battleground into a space for growth and connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is discriminating consumption in relation to children with autism?
Discriminating consumption refers to the dietary selectivity observed in many children with autism, where they exhibit strong preferences for specific textures, colors, or varieties of food, often leading to a limited diet.
How prevalent is picky eating among children with autism?
Studies indicate that between 46% and 89% of children with autism display some form of dietary selectivity.
Why is it important for caregivers to understand picky eating in children with autism?
Understanding picky eating as an intrinsic aspect of autism, rather than a behavioral flaw, helps caregivers adopt tailored management approaches that can improve the child's nutritional intake and overall well-being.
What role do sensory sensitivities play in picky eating among autistic children?
Many autistic individuals have heightened sensitivity to specific textures, tastes, or scents, leading to aversions that contribute to their picky eating habits.
How did the pandemic affect children's dietary patterns according to recent studies?
During the pandemic, parents observed an increase in junk food consumption and a decrease in structured meals among their children, highlighting how external factors can exacerbate selective eating habits.
What impact do oral-motor delays have on children's eating habits?
Oral-motor delays can hinder a child's ability to chew or swallow certain foods, often resulting in a preference for softer or easier-to-eat options.
What strategies can parents use to enhance their children's dietary variety?
Parents can gradually introduce new textures or flavors in a gentle manner, respecting the child's sensory preferences while encouraging exploration of diverse cuisines over time.
How can feeding specialists assist parents dealing with picky eating?
Feeding specialists can provide valuable insights and effective methods for managing selective food preferences associated with autism and picky eating, ensuring caregivers can meet their child's nutritional needs.
What resources are available for families dealing with food-related disorders in autistic individuals?
Various organizations offer resources and support for autistic individuals and their families regarding food-related disorders, which can be vital for parents navigating these challenges.




