Introduction
Navigating the challenges of insomnia in individuals with autism can feel overwhelming, yet understanding the complexities of this issue is the first step toward fostering better sleep and overall well-being. Research indicates that a staggering 40% to 80% of individuals with autism experience sleep disturbances, which not only disrupt their nightly rest but also contribute to behavioral challenges during the day. This cycle of distress impacts not only the individuals but also their families, highlighting the urgent need for effective strategies and interventions.
From establishing calming bedtime routines to exploring innovative therapies, there are numerous avenues for parent advocates to pursue in their quest to improve sleep quality. By delving into the causes, consequences, and solutions for insomnia, parents can empower themselves with the knowledge needed to support their children in achieving more restful nights and brighter days.
Prevalence of Insomnia in Individuals with Autism
Recent research highlights a striking reality: between 40% to 80% of individuals with autism and insomnia are impacted. Sleep disturbances in this population often manifest as:
- Difficulties falling asleep
- Frequent awakenings throughout the night
- Early morning risings
Families frequently report that these rest challenges not only disrupt nightly slumber but also exacerbate behavioral issues during the day, creating a cycle of distress.
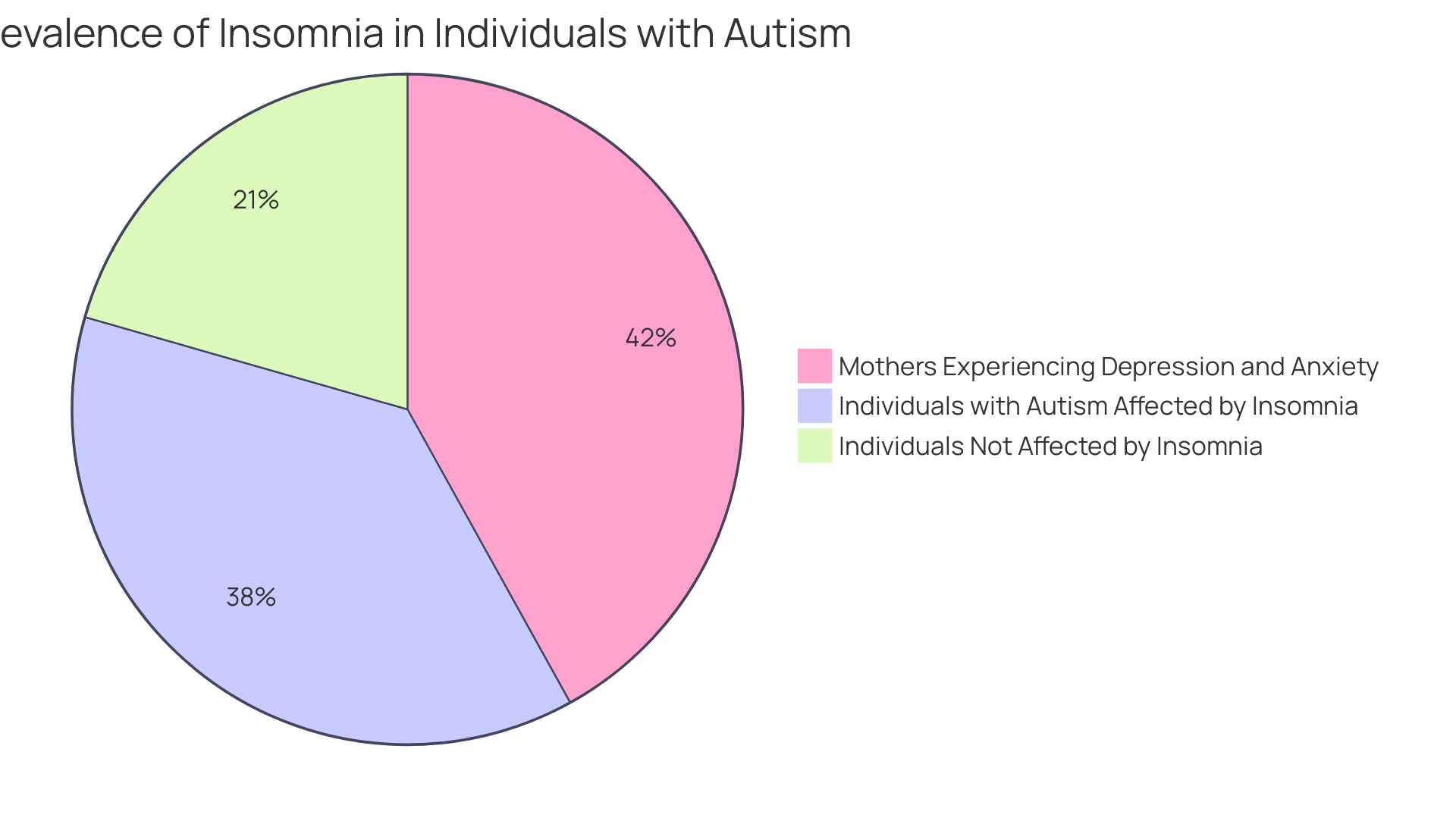
In fact, a concerning 67.1% of mothers reported experiencing both depression and anxiety symptoms, which may be linked to their offspring's sleep issues. This connection underscores the critical need to address insomnia as part of a comprehensive care strategy for individuals dealing with autism and insomnia. Additionally, more than one-third of parents and caregivers of autistic children utilize ABA therapy to help their child overcome the challenges of ASD, indicating the importance of targeted interventions.
Practical solutions, such as establishing bedtime routines and considering melatonin supplements, can significantly enhance the quality of rest. By understanding the high prevalence of rest disturbances and advocating for these interventions, parent advocates can foster better rest and, consequently, enhance overall well-being.
Understanding the Causes of Insomnia in Autism
Individuals with autism and insomnia are influenced by multiple interrelated factors, with sensory sensitivities standing out as a significant contributor. These sensitivities can make the resting environment uncomfortable, making it challenging for children to settle down at night. Combined with anxiety and stress, which often lead to racing thoughts as bedtime approaches, these elements, along with autism and insomnia, create a perfect storm for disturbances in rest.
Furthermore, the presence of co-occurring conditions such as ADHD and epilepsy frequently complicates rest patterns, amplifying the difficulties faced. Significantly, random missing data for diary variables occurred for 11 recorded days across the entire sample, which is only 0.01%, underscoring the reliability of the research. As emphasized in the case study titled 'Conclusion on Rest in Adults with HFASD,' poor rest quality continues into adulthood for those with autism and insomnia, highlighting the need for customized interventions.
Furthermore, while subjects did not vary from controls regarding age, education, intelligence, or body mass index, they showed higher BDI scores, suggesting a significant psychological factor that influences rest in autistic persons. As Emma K. Baker states,
These findings support the notion that issues related to rest, in particular insomnia, continue into adulthood in those with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder.
This underscores the necessity for parents to thoroughly understand the underlying issues associated with autism and insomnia.
By doing so, they can develop more supportive nighttime routines and environments tailored to their offspring's unique needs, ultimately fostering healthier rest patterns.
Effective Solutions for Managing Insomnia in Autism
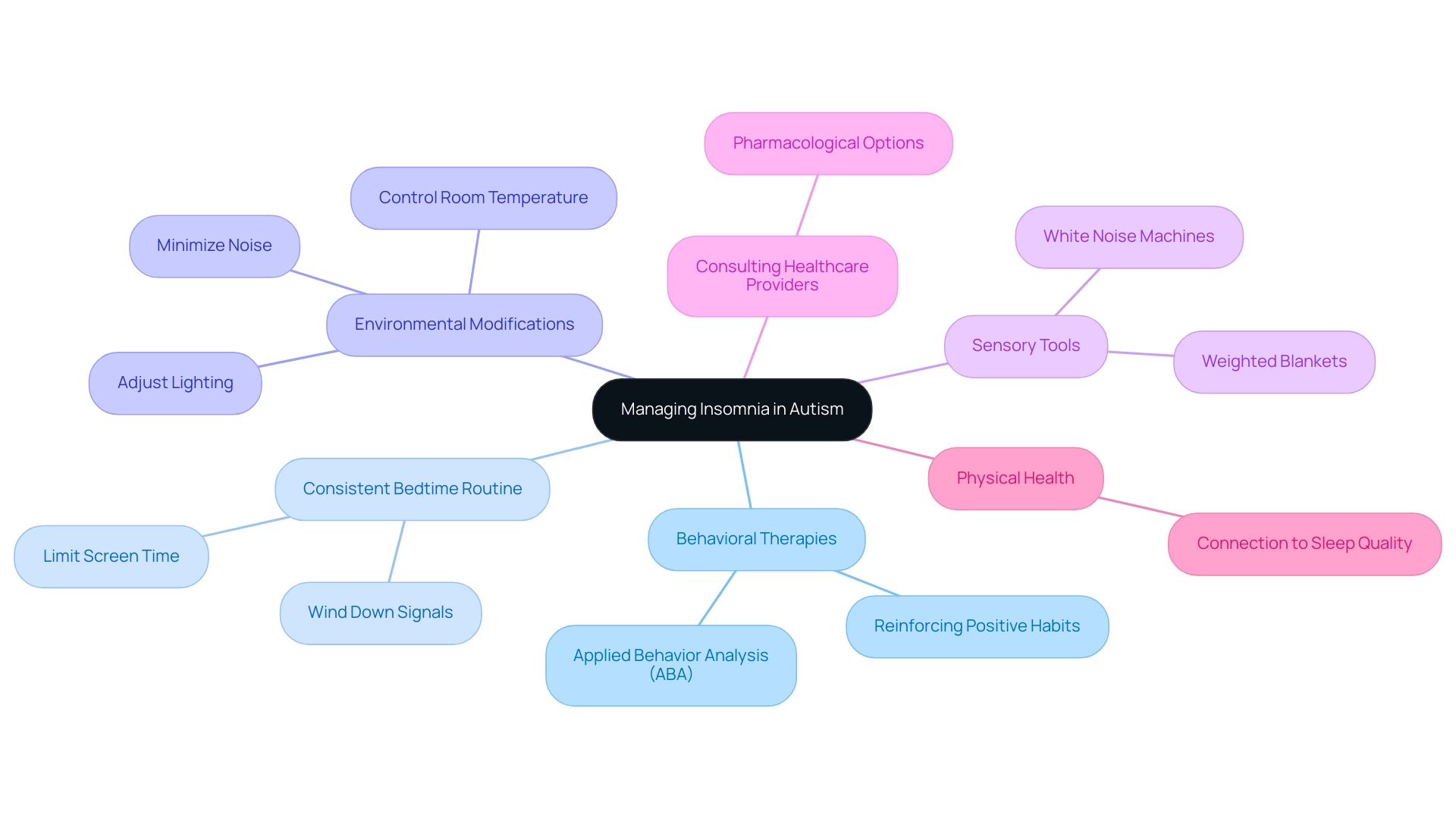
Managing insomnia in individuals with autism and insomnia requires a multifaceted approach that considers each child's unique needs. A 2019 study indicated that nearly 80% of preschoolers with autism and insomnia experience disturbances during rest, highlighting the prevalence of rest issues in this population. One effective method is the implementation of behavioral therapies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), which focuses on reinforcing positive habits related to rest and addressing behaviors associated with autism and insomnia.
Establishing a consistent bedtime routine is vital for children experiencing autism and insomnia, as it signals that it’s time to wind down. Cutting down on screen time prior to bedtime can be beneficial for individuals dealing with autism and insomnia by lessening overstimulation and facilitating a smoother shift to rest. Additionally, environmental modifications play a crucial role; adjusting lighting, controlling room temperature, and minimizing noise can significantly enhance rest quality for individuals dealing with autism and insomnia.
Incorporating calming sensory tools, such as weighted blankets or white noise machines, can provide comfort and promote relaxation for those dealing with autism and insomnia. As noted, 'Tailored treatments for enhancing rest may ease all forms of autism,' underscoring the importance of individualized strategies. While behavioral strategies are essential, consulting a healthcare provider about pharmacological options may also be beneficial in certain cases, particularly those related to autism and insomnia.
Moreover, the case study titled 'Physical Health and Sleep' reinforces the connection between maintaining physical health and managing insomnia, particularly in relation to issues such as autism and insomnia, thereby adding depth to the discussion on achieving restorative rest. As a parent advocate, exploring these diverse solutions not only empowers you but can lead to meaningful improvements in your child's rest quality.
Impact of Insomnia on Daily Life for Autistic Individuals
Autism and insomnia profoundly affect the daily functioning of autistic people, leading to a range of challenges that can hinder their development. Research shows that up to 83% of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face daily disturbances during rest, often presenting as symptoms of autism and insomnia, including:
- Bedtime resistance
- Daytime drowsiness
Data from the BNSQ indicates that on average, these individuals experience durations of rest that fall below recommended levels, with low rest efficiency reported in many cases.
The consequences of rest deprivation are significant; it frequently results in:
- Increased irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Heightened anxiety
These issues can exacerbate behavioral challenges, making it even more difficult for children to navigate social interactions and succeed academically. Extended latency to rest, awakening after falling asleep, and low rest efficiency are frequent observations in individuals experiencing autism and insomnia, further emphasizing the essential requirement for focused interventions.
As BTK noted, 'Addressing rest issues is crucial for improving overall health and functioning in autistic individuals.' By proactively addressing issues related to autism and insomnia, families can significantly enhance their offspring's quality of life, fostering better social engagement and academic performance. As advocates for our children, it is vital to recognize the impact that enhanced rest can have on their overall well-being.
Innovative Approaches to Treating Insomnia in Autistic Adults
Recent studies have unveiled innovative strategies for addressing insomnia related to autism and insomnia in autistic adults, prominently featuring mindfulness-based interventions and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) specifically designed for disturbances during rest. These methods not only promote relaxation but also provide people with practical tools to tackle their rest challenges. As one participant noted, 'the way that I can conceptualize general talking therapies such as psychotherapy and counselling would not be particularly relevant to me and the issues that I have with rest... that kind of anxiety isn’t really tied to a specific trigger or... something that I think could be spoken away or helped through talking therapies.'
This emphasizes the limitations of conventional treatments for certain people dealing with autism and insomnia. Additionally, the use of melatonin supplementation has garnered attention as a viable aid for rest, ideally utilized in conjunction with behavioral strategies to enhance quality of rest. Research indicates that this pharmacological intervention may be more effective when paired with these approaches.
Moreover, understanding the intricacies of rest problems, particularly regarding autism and insomnia in autistic individuals, is essential; for example, research has indicated a connection between hypoxaemic load in apnoea and acute alterations in T-wave amplitude, highlighting the multifaceted character of disturbances in rest. As clinical trials explore these innovative treatments, it’s vital for parents to stay involved with healthcare providers, advocating for the best and most up-to-date options available for their offspring. By staying informed, parents can confidently navigate the complexities of sleep issues associated with autism and insomnia, ensuring their child's well-being and restful nights.
Conclusion
Addressing the intricate challenges of insomnia in individuals with autism is essential for promoting their overall well-being. The prevalence of sleep disturbances, affecting between 40% to 80% of this population, highlights the urgent need for effective interventions. By understanding the multifaceted causes of insomnia—ranging from sensory sensitivities to co-occurring conditions—parents can create supportive environments that cater to their children's unique needs.
Implementing targeted strategies, such as:
- Establishing consistent bedtime routines
- Utilizing behavioral therapies
- Considering pharmacological options when necessary
can significantly enhance sleep quality. The evidence suggests that these approaches not only improve sleep but also mitigate the behavioral challenges that arise from sleep deprivation, leading to a more harmonious daily life for both children and their families.
As advocates, parents play a crucial role in exploring and advocating for diverse solutions to insomnia. By remaining informed and actively participating in their children's care, they can foster healthier sleep patterns and, ultimately, a brighter future. The journey to better sleep is not just about restful nights; it is about empowering individuals with autism to thrive during the day, enhancing their quality of life and overall development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What percentage of individuals with autism experience insomnia?
Recent research indicates that between 40% to 80% of individuals with autism and insomnia are affected.
What are common sleep disturbances experienced by individuals with autism?
Common sleep disturbances include difficulties falling asleep, frequent awakenings throughout the night, and early morning risings.
How do sleep challenges impact families of individuals with autism?
Families report that sleep challenges disrupt nightly rest and exacerbate behavioral issues during the day, creating a cycle of distress.
What mental health issues do parents of autistic children face in relation to sleep problems?
A concerning 67.1% of mothers of autistic children reported experiencing depression and anxiety symptoms, which may be linked to their child's sleep issues.
What interventions are commonly used to address challenges associated with autism?
More than one-third of parents and caregivers of autistic children utilize ABA therapy to help their child overcome challenges related to autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
What practical solutions can improve sleep quality for individuals with autism?
Practical solutions include establishing bedtime routines and considering melatonin supplements to enhance the quality of rest.
What role do sensory sensitivities play in sleep disturbances for children with autism?
Sensory sensitivities can make the resting environment uncomfortable, making it difficult for children to settle down at night.
How do co-occurring conditions affect sleep patterns in individuals with autism?
Conditions such as ADHD and epilepsy frequently complicate rest patterns, amplifying the difficulties faced by individuals with autism.
What does research suggest about the continuity of sleep issues into adulthood for individuals with autism?
Research emphasizes that poor rest quality continues into adulthood for those with autism and insomnia, highlighting the need for customized interventions.
Why is it important for parents to understand the underlying issues associated with autism and insomnia?
Understanding these underlying issues allows parents to develop more supportive nighttime routines and environments tailored to their child's unique needs, ultimately fostering healthier rest patterns.




