Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for parents and caregivers striving to support their children effectively. This multifaceted condition presents unique challenges in social communication and behavior, making it crucial for families to recognize the diverse manifestations of autism.
With recent statistics highlighting an increase in diagnoses, particularly among non-White children and girls, the need for informed advocacy and tailored support has never been more pressing. By delving into the genetic factors, environmental influences, and innovative treatment strategies linked to autism, parents can empower themselves with knowledge that not only aids in navigating the complexities of ASD but also fosters an environment where their children can thrive.
This article explores the foundational concepts of autism, the implications of genetic research, and practical steps parents can take to advocate for their child's needs and well-being.
Foundations of Autism: Understanding the Condition
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) represents a complex developmental condition marked by unique challenges in social communication and a tendency toward repetitive behaviors. For parents and caregivers, understanding the intricacies of autism is essential, as it enables them to identify signs and symptoms that may manifest in their offspring. ASD is a spectrum, meaning its manifestations can vary dramatically from one individual to another, encompassing a wide range of abilities and challenges.
Common characteristics often include:
- Difficulties in social interactions
- Hurdles in communication
- The presence of focused interests or behaviors
Recent statistics indicate that among individuals of two or more races diagnosed with ASD, a significant 73.9% had IQ information available, underscoring the importance of comprehensive assessments. Moreover, as the report highlights, there is a notable increase in the identification of ASD, especially among non-White youth and girls, which emphasizes the pressing need for enhanced diagnostic and support services.
As one father noted, addressing unmet support needs is crucial, emphasizing the importance of including time for relaxation and self-care in family routines. Furthermore, specialists suggest instructing autistic individuals in essential life skills to assist them in managing and possibly living autonomously in the future; caregivers are encouraged to emphasize abilities such as:
- Communication
- Shopping
- Personal care
Furthermore, education data sources covering 100% of the population in several states can provide valuable insights into understanding and addressing ASD, thus enhancing advocacy efforts.
By familiarizing themselves with these foundational concepts, parents can become effective advocates for their child's needs, ensuring they receive the necessary support for their development and independence.
The Genetic Landscape of Autism: Key Factors and Variants
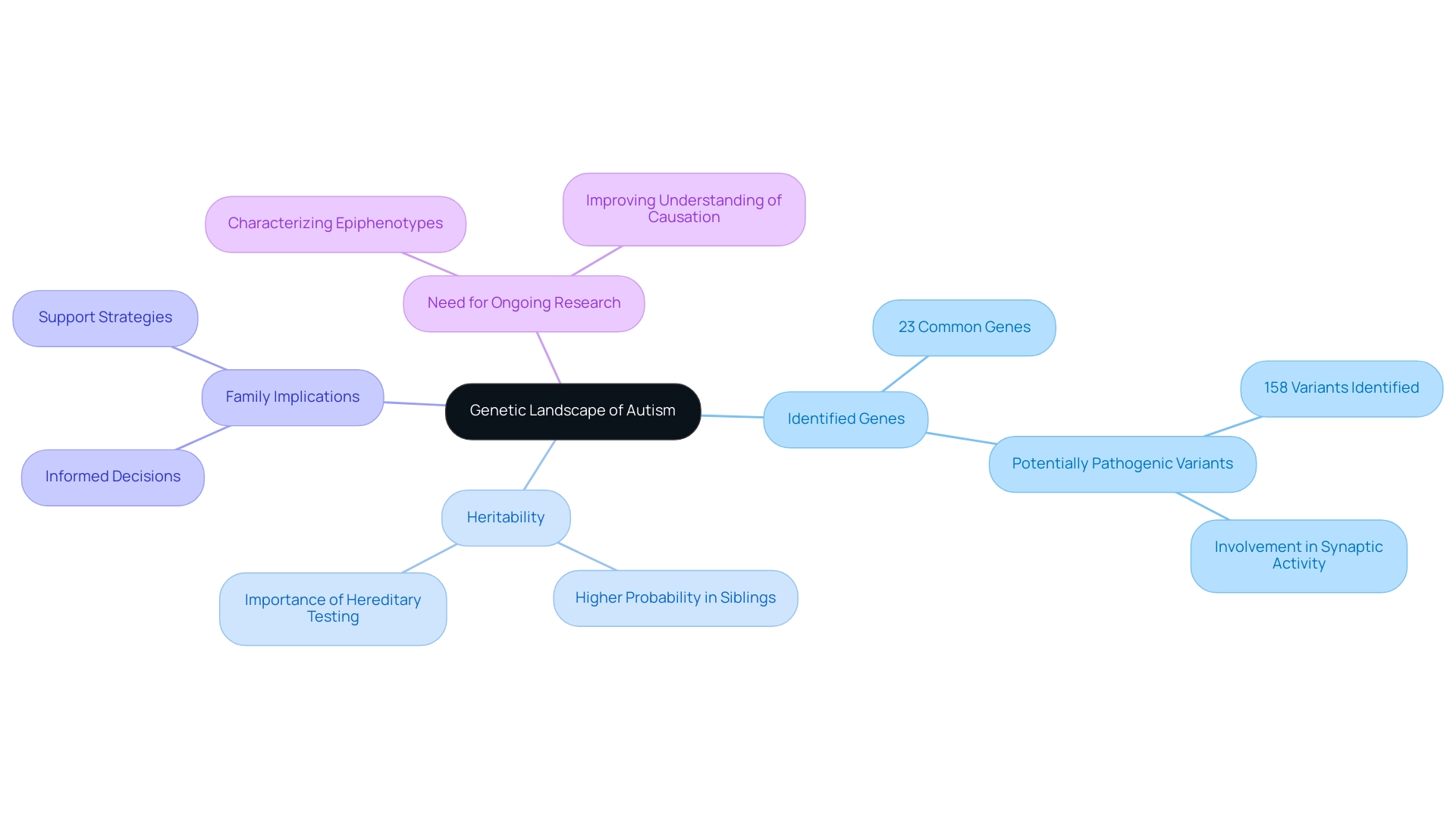
Research underscores the substantial influence of autism and genetics in the development of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Notably, recent findings have identified 23 genes that show commonality among autism and genetics, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, pointing to a complex interplay of genetic factors. Variants in genes related to synaptic functions have been connected to an increased risk of ASD, which emphasizes the importance of understanding autism and genetics, as research shows that the heritability of this condition is notably high.
This indicates that siblings of individuals identified with the condition have a considerably higher probability of also receiving a diagnosis. A thorough assessment that incorporates hereditary testing and environmental background is essential for grasping the factors of developmental disorders, as emphasized in the case study titled 'Hereditary Factors and Assessment in Developmental Disorders.' Understanding these genetic factors related to autism and genetics is vital for guardians, as it equips them to make informed decisions regarding early interventions and tailored support strategies.
Additionally, it offers crucial insights into family planning, empowering parents as they navigate the challenges related to developmental disorders. As Judy Singer aptly notes,
A rainbow infinity sign is another widely used symbol, representing the diverse spectrum of experiences and the importance of knowledge in fostering understanding and support.
Furthermore, ongoing research is needed to characterize epiphenotypes within the spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders, which underscores the challenges and importance of continued investigation in this field.
Implications of Genetic Research: Treatment and Support Strategies
Recent advances in biological research related to autism and genetics are revolutionizing the approach to treatment and support, providing new opportunities for personalized interventions. By understanding specific hereditary profiles in autism and genetics, therapists can implement tailored strategies that significantly enhance the effectiveness of behavioral therapy and educational approaches. For example, insights into a young person's genetic makeup related to autism and genetics enable professionals to customize interventions that align with individual needs, thus maximizing positive outcomes.
As Dr. Brian Boyd, a distinguished professor at the University of North Carolina, emphasizes, "Whether it’s things like concentrated poverty or racism, understanding how these factors are impacting the ability of autistic people to thrive and have good quality of life is very important." This underscores the socio-economic challenges faced by autistic individuals. Additionally, it's noteworthy that 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, highlighting its prevalence in treatment.
However, it is essential to recognize that ABA is not one-size-fits-all, as illustrated in the case study on Types of ABA Therapy, which demonstrates that different approaches can significantly benefit individuals with autism. Therefore, guardians must stay informed about ongoing research in autism and genetics and actively consider its implications for their offspring's support plans. This proactive involvement not only empowers caregivers but also ensures their children receive the most effective and personalized care possible.
Navigating Genetic Testing: What Parents Should Know
Genetic testing functions as an essential tool for guardians navigating the intricacies of a developmental disorder diagnosis. This process usually entails examining a blood or saliva specimen to identify hereditary variants associated with developmental disorders. Comprehending the possible consequences of DNA testing is essential for caregivers; although it can assist in recognizing risks and directing treatment approaches, it is crucial to acknowledge that it does not offer definitive explanations regarding the fundamental reasons for autism and genetics.
Recent discussions emphasize the need for guardians to engage in meaningful conversations with healthcare providers about the benefits and limitations of genetic testing. This dialogue ensures that they are well-informed and empowered in making decisions regarding their offspring's care. As a parent advocate, fostering this communication can enhance the overall support network for your offspring.
Significantly, almost a fourth of school-age autistic children are flourishing in all developmental domains, highlighting the necessity of personalized interventions and the potential of informed hereditary insights. Furthermore, identifying the genetic causes of autism and genetics can enhance healthcare access and inform prognosis for adults with ASD, as highlighted in a recent study advocating for increased access to genetic testing. Parents are encouraged to approach this journey collaboratively, breaking down the planning process into manageable steps, and seeking guidance from knowledgeable professionals, including social workers who can assist in planning and provide support at every stage.
As one healthcare provider noted, 'Genetic testing can open doors to understanding and support that families need.' This reinforces the importance of a comprehensive approach to developmental disorder care.
Gene-Environment Interactions: A Holistic View of Autism
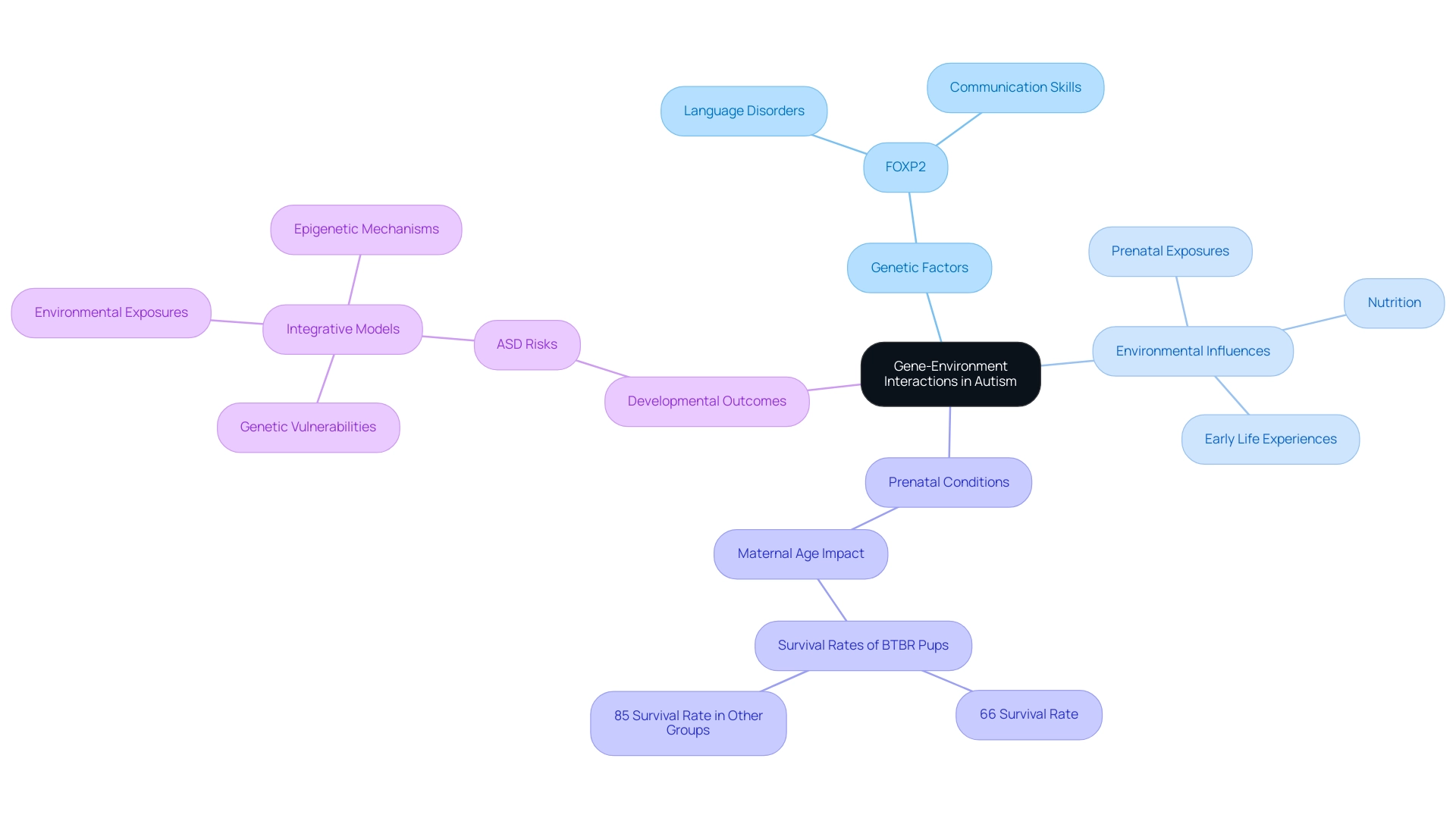
Gene-environment interactions are crucial in comprehending the complexities of developmental disorders. While hereditary predispositions undeniably contribute to the risk of developmental disorders, recent findings emphasize the significant role of environmental factors, including prenatal exposures, nutrition, and early life experiences. As M.M. Ziętek notes,
'Prenatal gene-environment interactions mediate the impact of advanced maternal age on mouse offspring behavior,' highlighting the importance of these interactions in shaping developmental outcomes. For instance, a study revealed that only 66% of BTBR pups born from older females survived to postnatal day 24, in contrast to over 85% survival rates in other groups. This stark difference highlights the potential impacts of prenatal conditions on development.
Furthermore, the significance of genes such as FOXP2, linked to language disorders, demonstrates how particular mutations can affect communication abilities in individuals with developmental conditions. Integrative models that focus on autism and genetics combine genetic, environmental, and epigenetic factors, emphasizing that a holistic approach—recognizing the interplay of these elements—can provide a deeper understanding of spectrum disorder (ASD) risks. As parents, being aware of these interactions empowers you to create supportive environments that nurture your offspring's development.
By promoting healthy lifestyle choices and remaining vigilant about environmental influences, you can play an active role in addressing the challenges associated with autism, ultimately enhancing your child's well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a vital step for parents and caregivers looking to support their children effectively. The complexities of autism, characterized by a spectrum of social communication challenges and behavioral patterns, call for a comprehensive understanding of its signs, symptoms, and the diverse experiences individuals may have. With the increasing prevalence of diagnoses, especially among non-White children and girls, it is imperative for families to recognize the importance of tailored support and advocacy.
Genetic research has unveiled significant insights into the hereditary aspects of autism, highlighting the interplay between genetics and environmental factors. Armed with this knowledge, parents can make informed decisions about early interventions and personalized treatment strategies that align with their child's unique needs. Genetic testing serves as a powerful tool in this journey, providing critical information that can guide care while fostering meaningful dialogue with healthcare providers.
Moreover, recognizing the role of gene-environment interactions enables parents to cultivate nurturing environments that support their child's development. By understanding how various factors influence autism, parents can take proactive steps to advocate for their children's needs, ensuring they receive the comprehensive support required to thrive.
Ultimately, by embracing knowledge and understanding the multi-faceted nature of autism, parents can empower themselves and their children, creating pathways for growth, independence, and a fulfilling life. The journey may be challenging, but with informed advocacy and a supportive framework, every child has the potential to shine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition characterized by unique challenges in social communication and a tendency toward repetitive behaviors. It is a spectrum, meaning its manifestations can vary dramatically from one individual to another.
What are common characteristics of ASD?
Common characteristics of ASD include difficulties in social interactions, hurdles in communication, and the presence of focused interests or behaviors.
What recent statistics highlight the diagnosis of ASD?
Recent statistics indicate that among individuals of two or more races diagnosed with ASD, 73.9% had IQ information available. There is also a notable increase in the identification of ASD, particularly among non-White youth and girls.
Why is it important for parents and caregivers to understand ASD?
Understanding ASD helps parents and caregivers identify signs and symptoms in their children, allowing them to advocate effectively for necessary support and services for their development and independence.
What life skills should caregivers focus on teaching autistic individuals?
Caregivers are encouraged to emphasize essential life skills such as communication, shopping, and personal care to assist autistic individuals in managing their lives and potentially living autonomously in the future.
How does genetics play a role in ASD?
Research has identified 23 genes associated with autism, indicating a complex interplay of genetic factors. The heritability of ASD is notably high, meaning siblings of individuals diagnosed with the condition have a higher probability of also receiving a diagnosis.
What is the significance of hereditary testing in understanding ASD?
A thorough assessment that includes hereditary testing and environmental background is essential for understanding the factors contributing to developmental disorders, which can help guardians make informed decisions regarding early interventions and tailored support strategies.
What ongoing research is needed in the field of ASD?
Ongoing research is necessary to characterize epiphenotypes within the spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders, highlighting the challenges and importance of continued investigation in understanding ASD and related conditions.




