Overview
The article "Understanding Autism and Asperger's: A Caring Comparison of Symptoms and Support Needs" offers a compassionate exploration of the distinctions and similarities between autism and Asperger's syndrome. It particularly emphasizes the symptoms and the support required for individuals affected by these conditions. While both are part of the autism spectrum, it is important to recognize that individuals with Asperger's often display milder symptoms and possess better communication skills. This highlights the necessity for tailored support strategies that effectively address their unique challenges. By understanding these nuances, we can foster a more supportive environment for those navigating these conditions.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of neurodevelopmental disorders, autism and Asperger's syndrome present unique challenges and characteristics that many families navigate daily. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a wide range of symptoms, from social communication difficulties to repetitive behaviors. In contrast, Asperger's syndrome, now classified under the ASD umbrella, is characterized by milder symptoms and intact language skills. As awareness grows, so does the need to understand the disparities in diagnosis rates, support needs, and the financial implications for families seeking help.
Recent studies reveal significant variations in prevalence among different demographics, highlighting the importance of addressing potential biases and enhancing access to services. This exploration delves into the complexities of autism and Asperger's syndrome, emphasizing the critical need for tailored support strategies. As society strives for a more inclusive approach to care, it becomes essential to foster understanding and compassion, ensuring that every individual receives the support they deserve.
Name: Defining Autism and Asperger's Syndrome
Autism Asperger's, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Once considered a separate diagnosis, Asperger's condition is now recognized as part of the broader autism Asperger's classification. Individuals with high-functioning conditions typically display milder symptoms and do not experience significant delays in language development, distinguishing them from those with other developmental disorders.
Understanding these definitions is essential, as they lay the groundwork for exploring the nuanced similarities and differences in symptoms and support needs between autism Asperger's and other conditions. Recent studies reveal that the prevalence of ASD varies across different demographics, highlighting notable disparities in diagnosis rates among racial and ethnic groups. For example, data indicates that non-Hispanic White children are diagnosed with the condition at lower rates compared to their non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander peers.
This situation underscores the importance of addressing potential biases in diagnosis and access to services. A case study titled "Racial and Ethnic Differences in ASD Identification" sheds light on these disparities, emphasizing that understanding these differences is crucial for developing targeted strategies to enhance identification and support for children from diverse backgrounds.
Current statistics show that the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is approximately $175.44, which can be a significant financial burden for families seeking help. Additionally, the male-to-female ratio in ASD diagnoses is estimated at 4:1, according to CDC data, although some research suggests a more balanced ratio of 3:1. This discrepancy indicates a need for ongoing investigation into gender differences in ASD identification. Much of this data is derived from Medicaid claims, which play a vital role in estimating ASD prevalence across various populations.
Real-world examples illustrate the diverse manifestations of the condition and related disorders, highlighting the necessity for tailored support approaches. As our understanding of these conditions continues to evolve, expert opinions are shaping the conversation, advocating for a more inclusive approach to diagnosis and treatment that considers the unique experiences of individuals across the spectrum. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences, as every voice contributes to a deeper understanding and better support for all families navigating this journey.
Understanding Diagnostic Criteria for Autism and Asperger's
The diagnostic criteria for autism, Asperger's, and related syndromes have undergone significant changes with the introduction of the DSM-5, reflecting a more nuanced understanding of these conditions. Autism is now diagnosed based on persistent deficits in social communication and the presence of restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. Previously, individuals diagnosed with autism Asperger's are now categorized under Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
This category is characterized by less severe symptoms and the absence of significant language delays, highlighting the spectrum nature of these disorders. In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that approximately 1 in 36 children aged 8 years in the United States was diagnosed with ASD, with a notable disparity in diagnosis rates between genders—about 4% of boys and 1% of girls. This statistic underscores the importance of accurate and timely diagnosis, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Furthermore, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, which is an important consideration for families seeking support.
The DSM-5 emphasizes the necessity of behavioral assessments for diagnosing ASD, as there are currently no laboratory tests available. Routine consultations with experts are essential for handling ASD and related conditions, guaranteeing that people obtain the assistance they require during their growth.
Recent revisions to the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for autism Asperger's spectrum disorder in 2025 have enhanced the comprehension of these conditions. Experts in the field advocate for a collaborative approach to care, as demonstrated by the medical home model for ASD care, which integrates services for individuals and their families. This model has shown a tendency to result in fewer unmet needs and enhanced access to comprehensive healthcare services, ultimately leading to better support for those impacted by developmental disorders.
As the landscape of diagnosis continues to evolve, it is essential for parents and professionals to stay informed about these changes. Understanding the diagnostic criteria and their implications can empower families to navigate the complexities of autism and advocate effectively for their children's needs.
Exploring Similarities and Differences in Symptoms
Autism and Asperger's disorder share several common symptoms, such as difficulties in interactions with others and restricted interests. Yet, a key distinction lies in the verbal skills of those with Asperger's, who often exhibit better communication abilities and may possess average or above-average intelligence. In contrast, individuals on the autism spectrum frequently face more significant challenges in both communication and interpersonal engagement.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for creating effective assistance strategies that cater to the specific needs of each individual. Recent studies emphasize that while both conditions are part of the spectrum, the subtleties in symptoms can greatly influence educational and community outcomes. For instance, data from the U.S. Department of Education indicates that 74% of autistic students graduate with a diploma, compared to an 86% graduation rate for all students. This highlights the necessity for customized interventions that address the specific challenges faced by individuals with autism and Asperger's disorder.
Moreover, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, which adds a financial consideration for families seeking support. Support strategies must be differentiated based on these distinctions. For example, while individuals with Asperger's syndrome may benefit from enhanced interpersonal skills training, those with developmental disorders might require more extensive communication assistance. Real-world examples of effective strategies include peer mentoring programs that foster interpersonal skills development and individualized education plans that accommodate varying levels of verbal communication.
Furthermore, mothers frequently emphasize professional attributes, support networks, and education, whereas fathers focus on interpersonal growth and self-care. This underscores the varied needs of families navigating these challenges.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of autism and Asperger's syndrome, it is crucial to stay updated on the latest research findings and expert perspectives. The CDC estimates a male-to-female ratio of 4:1 in the condition, although other studies suggest a ratio closer to 3:1, which is important for understanding demographic considerations. Additionally, community workers need to be educated to assist parents in planning for their child's future, breaking down the planning process into manageable steps.
This knowledge not only aids in recognizing the similarities and differences between these conditions but also empowers parents and professionals to implement the most effective support strategies for each child. Together, we can foster a more inclusive environment that meets the unique needs of every individual.
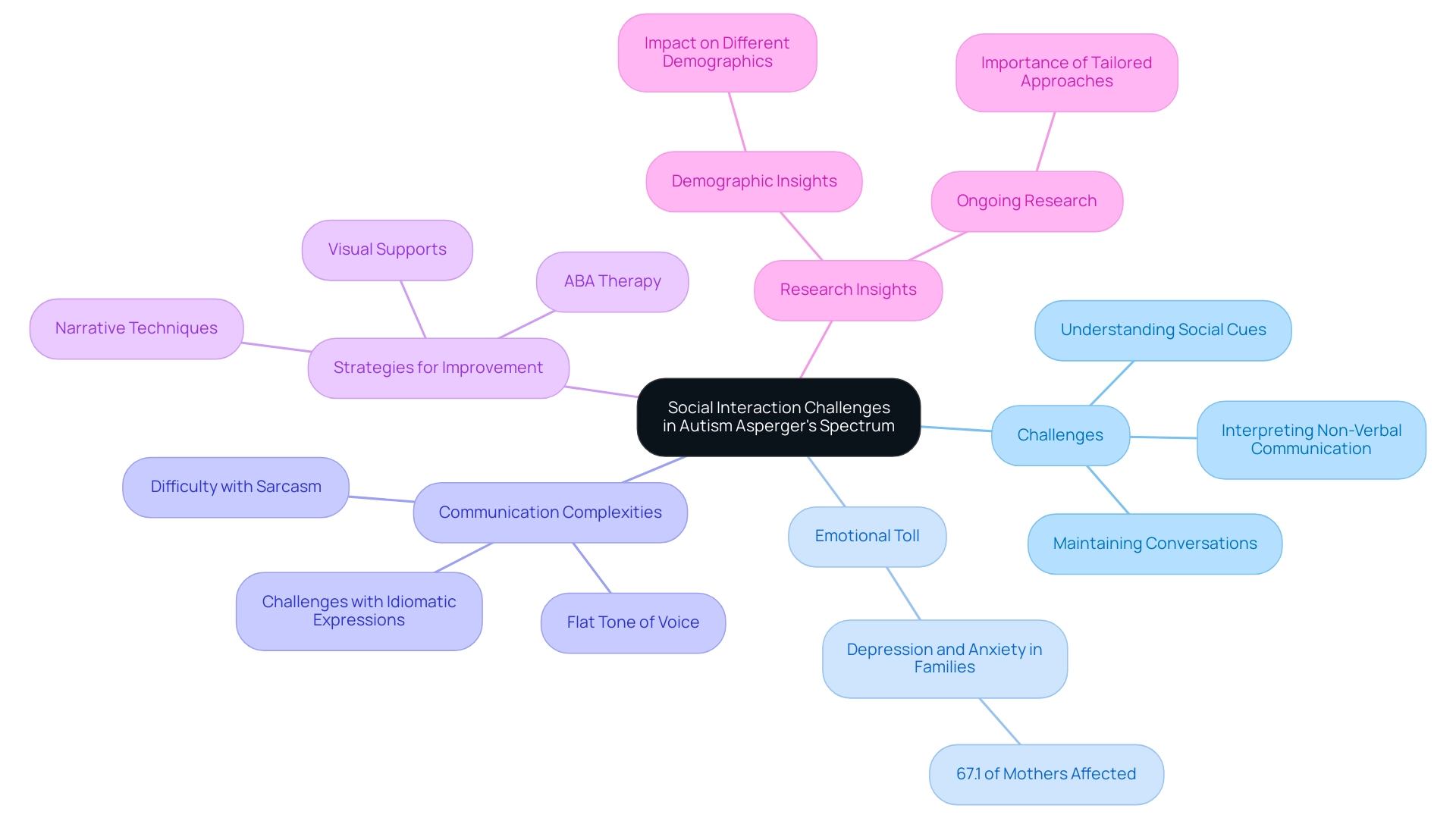
Social Interaction and Communication Challenges
Individuals on the autism Asperger's spectrum often face significant challenges in social interactions. They may struggle to understand social cues, maintain conversations, and interpret non-verbal communication. A striking statistic from Wiley Online Library indicates that 67.1% of mothers of children with autism report experiencing both depression and anxiety symptoms. This statistic highlights the emotional toll that these communication barriers can impose on families. Despite these challenges, many individuals on the autism Asperger's spectrum possess a strong desire to connect socially.
Communication can be particularly complex for these individuals. They might express themselves in a flat tone and find it difficult to grasp nuances like sarcasm or idiomatic expressions, which can complicate their interactions further.
Addressing these communication barriers is crucial for fostering meaningful interactions and relationships. For instance, implementing structured communication strategies—such as visual supports and narrative techniques—can significantly enhance understanding and engagement. Experts emphasize that tailored approaches are vital in bridging the communication gap for individuals on the autism Asperger's spectrum.
Recent case studies, including insights from "Demographic Insights: Who is Affected by Autism?", reveal that when these strategies are effectively employed, individuals demonstrate improved expressive and receptive language skills. This leads to more successful social interactions, which is heartening news for families.
Moreover, ongoing research underscores the importance of recognizing the unique communication difficulties associated with this condition, distinct from autism Asperger's. ABA therapy is widely acknowledged as an effective intervention for developmental disorders, endorsed by major health organizations, and plays a crucial role in addressing these communication challenges. As we look ahead to 2025, understanding these nuances will be essential in developing effective support programs that cater to the unique needs of each person.
By fostering a welcoming atmosphere that actively addresses these challenges, we can empower individuals on the spectrum to navigate their social environments more effectively. Let's work together to create a supportive community that embraces and uplifts everyone.
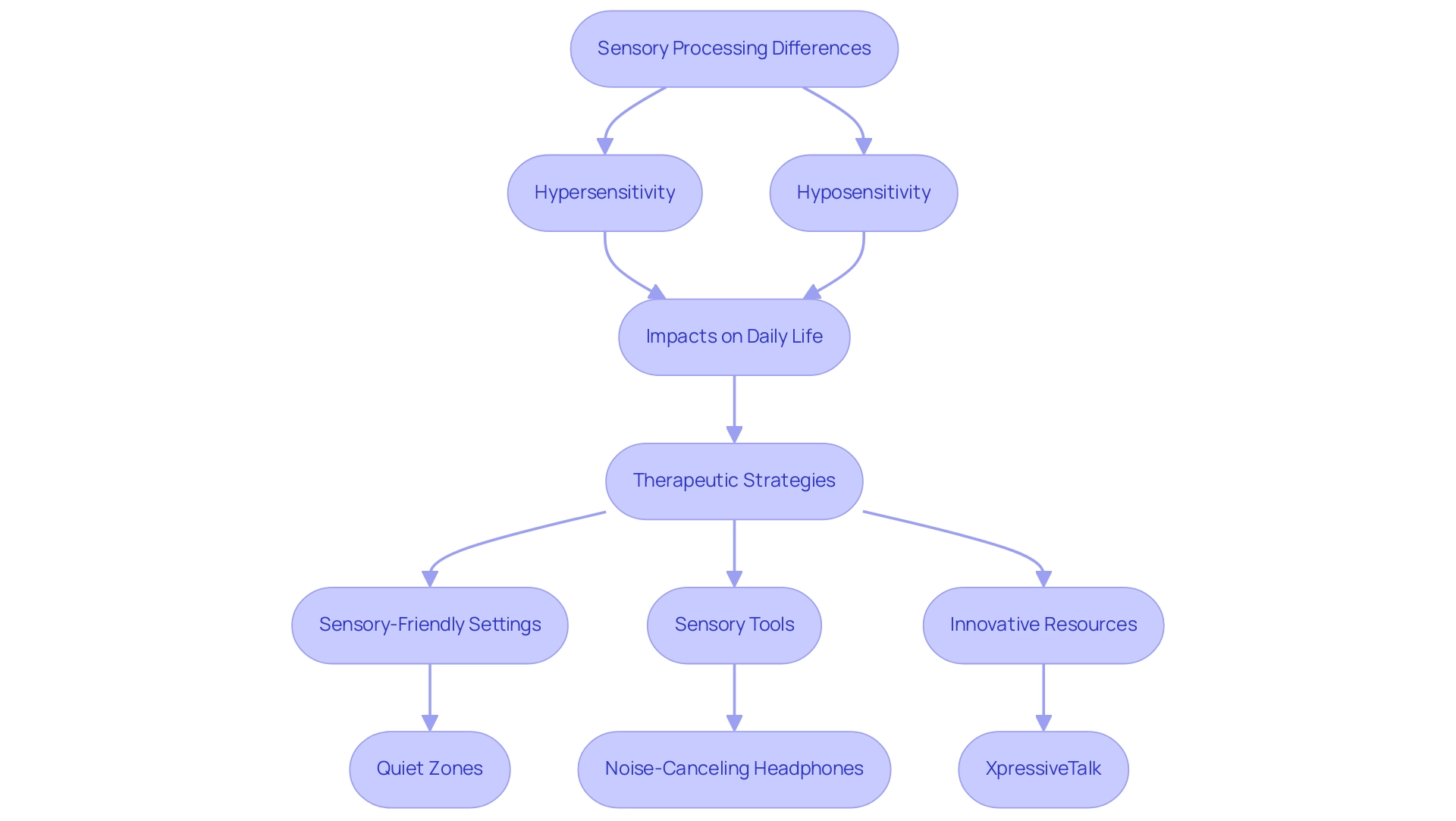
Sensory Processing Differences and Their Impact
Sensory processing differences are notably prevalent among individuals with autism and Asperger's syndrome. Recent findings indicate that a significant portion of this population experiences either hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to various sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, and textures. In 2025, statistics reveal that approximately 4.2% of participants in studies related to attention deficits also reported sensory processing issues, as highlighted in the case study "Profiles of Sensory Processing and Attention in SPD and ASD." This study found that children with sensory processing disorder (SPD) exhibited more pronounced sensory processing issues compared to their peers with developmental spectrum disorder, who tend to show greater attention deficits.
This differentiation is crucial for clinicians, allowing them to tailor therapeutic strategies based on personal profiles. Sensory challenges can lead to heightened anxiety and difficulties in navigating everyday situations, significantly impacting the quality of life for those affected. To support this discussion, the Short Sensory Profile is a parent-reported measure that assesses sensory-related behaviors, demonstrating high reliability and validity. This tool can be instrumental in understanding the sensory challenges faced by those with developmental disorders.
To address these sensory challenges, implementing sensory-friendly strategies is essential. Establishing tranquil settings, using sensory tools, and leveraging resources like XpressiveTalk—an innovative avatar designed to assist people in interpreting emotions through visual cues—can significantly improve overall well-being. Real-world examples of sensory-friendly strategies include the use of noise-canceling headphones in crowded spaces and the establishment of quiet zones in schools and public areas.
These methods not only reduce sensory overload but also promote a more inclusive atmosphere for individuals with autism and Asperger's, ultimately aiding their growth and social integration. By embracing these approaches, we can foster understanding and support for those navigating sensory processing differences.
Building a Supportive Environment for Individuals with Autism and Asperger's
Creating a supportive atmosphere for individuals with autism Asperger's requires a deep understanding of their unique needs and challenges. Structured routines are essential in fostering a sense of security and predictability, significantly reducing anxiety and enhancing overall functioning. It's important to note that around 50% of mothers of autistic children experience symptoms of depression. This statistic underscores the necessity for robust family support systems that can alleviate stress and promote well-being.
Incorporating visual supports and clear communication strategies can greatly enhance understanding and engagement for those on the spectrum. For example, visual schedules can assist children in anticipating daily activities, which helps reduce uncertainty and promotes independence. The Safe Kids Worldwide campaign emphasizes that children, including those with developmental differences, should not be left home alone before the age of 12 or 13, depending on their maturity.
This highlights the importance of teaching fundamental life skills to help children with autism Asperger's manage everyday activities and strive for greater autonomy.
Building an inclusive community is crucial for the development of individuals with autism Asperger's. Advocacy groups stress the importance of creating environments where people feel safe, understood, and valued. The American Psychological Association recognizes Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) as a fact-based treatment with proven effectiveness, reinforcing the need for evidence-based approaches to support those on the spectrum.
By working together, parents and professionals can share resources and strategies that lead to positive outcomes. Community initiatives that promote social interaction and skill-building can significantly improve the quality of life for those on the spectrum. NASD Media offers a variety of resources designed to empower parents and professionals in fostering these supportive environments. By providing access to crucial information, strategies, and community connections, families can navigate challenges more effectively, ensuring that both parents and children flourish.
As we look ahead to 2025, it is vital to continue developing strategies that support individuals with autism Asperger's, nurturing a culture of inclusivity and understanding that benefits the entire community.
Conclusion
Understanding autism and Asperger's syndrome is crucial for fostering an inclusive society that truly meets the diverse needs of individuals on the spectrum. The distinctions between these conditions—encompassing their symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and support requirements—highlight the importance of tailored approaches to care. As the prevalence of autism continues to rise and disparities in diagnosis rates become more apparent, it is essential to address biases and enhance access to services for all families.
The complexities of social interaction, communication challenges, and sensory processing differences further underscore the need for individualized support strategies. Families and professionals must come together to create structured, supportive environments that promote understanding and acceptance. Implementing evidence-based practices, such as applied behavior analysis (ABA) and sensory-friendly strategies, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with autism and Asperger's syndrome.
As we move forward as a society, let us keep the emphasis on compassion and inclusivity at the forefront. By recognizing and addressing the unique challenges these individuals face, we can ensure that everyone receives the support they deserve. Together, we can pave the way for a brighter, more inclusive future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Asperger's or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Asperger's, now recognized as part of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Individuals with high-functioning conditions typically exhibit milder symptoms and do not experience significant delays in language development.
How has the classification of Asperger's changed?
Asperger's condition was once considered a separate diagnosis but is now categorized under Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in the DSM-5, reflecting a more nuanced understanding of autism and its spectrum nature.
What are the demographic disparities in ASD diagnosis?
Studies show that the prevalence of ASD varies across demographics, with non-Hispanic White children diagnosed at lower rates compared to non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander children. This highlights potential biases in diagnosis and access to services.
What is the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services for ASD in the U.S.?
The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is approximately $175.44, which can be a significant financial burden for families seeking help.
What is the male-to-female ratio in ASD diagnoses?
The estimated male-to-female ratio for ASD diagnoses is about 4:1 according to CDC data, although some research suggests a more balanced ratio of 3:1, indicating a need for further investigation into gender differences in ASD identification.
What role do behavioral assessments play in diagnosing ASD?
Behavioral assessments are crucial for diagnosing ASD, as there are currently no laboratory tests available. Routine consultations with experts are essential to ensure individuals receive the necessary support during their development.
What is the medical home model for ASD care?
The medical home model for ASD care integrates services for individuals and their families, resulting in fewer unmet needs and better access to comprehensive healthcare services, ultimately improving support for those affected by developmental disorders.
Why is it important for families to stay informed about changes in diagnostic criteria?
Understanding the evolving diagnostic criteria and their implications empowers families to navigate the complexities of autism and advocate effectively for their children's needs.




