Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in the workplace presents both challenges and remarkable opportunities. As organizations increasingly recognize the unique strengths that individuals with autism bring—such as exceptional attention to detail and innovative problem-solving—there is a growing urgency to create inclusive environments that celebrate neurodiversity.
With around 75% of autistic adults facing underemployment or unemployment, the potential for transformative change is clear. By implementing effective accommodations and fostering open dialogue, employers can not only enhance productivity but also cultivate a culture of acceptance and understanding.
This article explores the multifaceted benefits of employing individuals with autism, practical strategies for creating supportive workplaces, and the legal frameworks that ensure compliance and equity for all employees.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Workplace
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) represents a diverse range of neurological conditions that can influence social skills, communication, and behavior. In the workplace, people with ASD often possess remarkable strengths, including heightened attention to detail, a strong capacity for focused work, and unique problem-solving skills. These attributes can significantly enhance workplace dynamics and productivity when recognized and nurtured.
For example, Bryan presently earns $16.71 per hour, the highest he has ever received, demonstrating a successful result in the workplace for those on the spectrum. Employers who understand the varied manifestations of ASD can create an inclusive culture by implementing autism accommodations at work, allowing all employees to flourish. Currently, approximately 75% of adults diagnosed with a developmental disorder in the United States face underemployment or unemployment, which underscores the urgent need for workplaces to provide autism accommodations at work and embrace these skilled individuals.
According to professors at Drexel University, the likelihood of young autistic adults securing employment increases with time post-high school, highlighting the potential for growth when supportive environments are established. Furthermore, this complex neurological condition lacks a cure; however, early therapy and intervention can help manage behaviors and enhance quality of life. Acknowledging the varied abilities and challenges associated with ASD is essential for enhancing job performance and promoting positive interactions among colleagues, which highlights the importance of autism accommodations at work to support awareness, acceptance, and assistance for autistic people.
The Advantages of Employing Individuals with Autism
Individuals on the spectrum bring a remarkable array of unique skills to the workplace, including exceptional analytical abilities, meticulous attention to detail, and innovative problem-solving skills. Recent studies underscore that diverse teams, particularly those inclusive of neurodiversity, often outperform their less diverse counterparts. This performance enhancement arises from the diverse viewpoints and methods that people on the spectrum bring to cooperative activities.
However, the journey toward inclusivity is not without challenges; during the initial COVID-19 lockdown, only 12 of 377 participants (3.2%) completed a survey, highlighting the difficulties faced by both employers and candidates. Employers are increasingly acknowledging that recruiting people on the autism spectrum, along with implementing autism accommodations at work, not only strengthens their workforce but also reinforces a commitment to diversity and inclusion, enhancing both company reputation and staff morale. As one participant noted, opportunities to disclose should be done in a way that reassures the candidate that if they disclose a diagnosis, this absolutely would not impact whether they were offered the role or not.
Moreover, case studies reveal that participants expressed frustration with the focus on social skills in recruitment, emphasizing the need for more flexible and practical hiring methods, such as work trials. As we move into 2024, the evidence continues to mount: organizations that embrace neurodiversity are better positioned to thrive in competitive markets while fostering a more inclusive work environment. This shift is not merely beneficial—it's essential for fostering a culture that values each person's contributions.
Effective Accommodations for Employees with Autism
Accommodations for staff with autism at work are crucial in promoting an inclusive work environment, and they can differ significantly to meet specific needs. An effective starting point is Flexible Work Hours, which allows individuals to start and end their work at times that suit their personal rhythms. This adjustment is particularly beneficial for managing sensory overload, as it enables individuals to avoid peak hours that can be overwhelming.
According to recent statistics, while 74% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a diploma, the transition into the workforce can still present significant challenges, highlighting the importance of autism accommodations at work. In addition to flexible hours, Quiet Spaces can play a crucial role in reducing anxiety and enhancing focus. By providing access to designated quiet rooms or areas, employers can help staff recharge during busy workdays. Furthermore, Clear Communication is vital; using straightforward and concise language in instructions can significantly reduce misunderstandings, promoting a smoother workflow. Employers may also benefit from incorporating Visual Supports like charts and checklists, which assist in task organization and management.
This approach has shown to be beneficial in assisting individuals with autism navigate their responsibilities with increased confidence.
Mentoring Programs are another significant support, pairing individuals with autism with encouraging mentors. This not only facilitates integration into the workplace but also provides guidance in navigating social dynamics, which can often be challenging. As highlighted by experts, employers are encouraged to utilize best-practice resources to create a more inclusive and supportive work environment.
This fosters excitement about the potential for meaningful employment across various sectors, exemplified by initiatives like ThinkWork!, which focus on improving employment outcomes for individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. The commitment to identifying new opportunities for autistic individuals in the workforce is further underscored by the case study titled 'Enabling Excitement,' which aims to educate and encourage both employers and individuals. By incorporating autism accommodations at work, organizations can foster a more inclusive atmosphere that not only supports autistic individuals but also improves overall workplace culture.
Best Practices for Implementing Autism Accommodations
To effectively apply support measures for individuals with developmental differences in the workplace, employers should adopt several best practices that not only encourage inclusivity but also improve worker well-being:
- Engage in Open Dialogue: Creating a culture of openness is vital. Encourage staff to share their needs and preferences regarding autism accommodations at work, along with their experiences and any difficulties faced, without fear of stigma. This fosters trust and ensures that adjustments are genuinely beneficial.
- Train Staff: Comprehensive training on autism accommodations at work for all personnel can significantly reduce misunderstandings and biases. This initiative is essential for building a supportive environment that incorporates autism accommodations at work, enabling neurodiverse individuals to thrive.
- Regular Check-Ins: Create a routine of scheduled meetings with staff to assess the effectiveness of adjustments. This practice allows for timely adjustments and demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement.
- Document Adjustments: Maintaining thorough records of agreed-upon adjustments ensures consistency and accountability. This documentation serves as a reference point for both management and staff, reinforcing the company's dedication to inclusivity.
- Encourage Feedback: Actively seek input from employees about the autism accommodations at work that are currently in place. This input is essential in assessing whether these measures effectively address their needs and can result in further improvements.
Statistics indicate that those diagnosed with a developmental disorder at a younger age tend to experience greater self-esteem and lower levels of perceived discrimination. This highlights the significance of establishing a welcoming environment that encourages early disclosure and assists people in feeling valued. Moreover, a 2017 study indicated that applicants disclosing a disability, like a developmental disorder, faced a 26% decrease in employer interest, highlighting the ongoing challenges in the hiring process.
As highlighted by Ameri et al., this research underscores the necessity for organizations to tackle possible workplace bias against persons with disabilities.
Moreover, identifying the optimal job fit is crucial for fulfilling employment, which frequently necessitates negotiated modifications and support to tailor the role to the person. This approach is illustrated in the case study titled 'Workplace Accommodation Tips,' which highlights how tailored job roles can lead to success in employment. Therefore, fostering a well-informed workplace not only benefits individuals on the spectrum but enriches the entire organizational culture.
For further insights, the upcoming book 'The Neurodiversity Edge' is poised to provide valuable guidance on embracing neurodiversity in the workplace throughout 2024.
Legal Framework and Compliance for Autism Accommodations
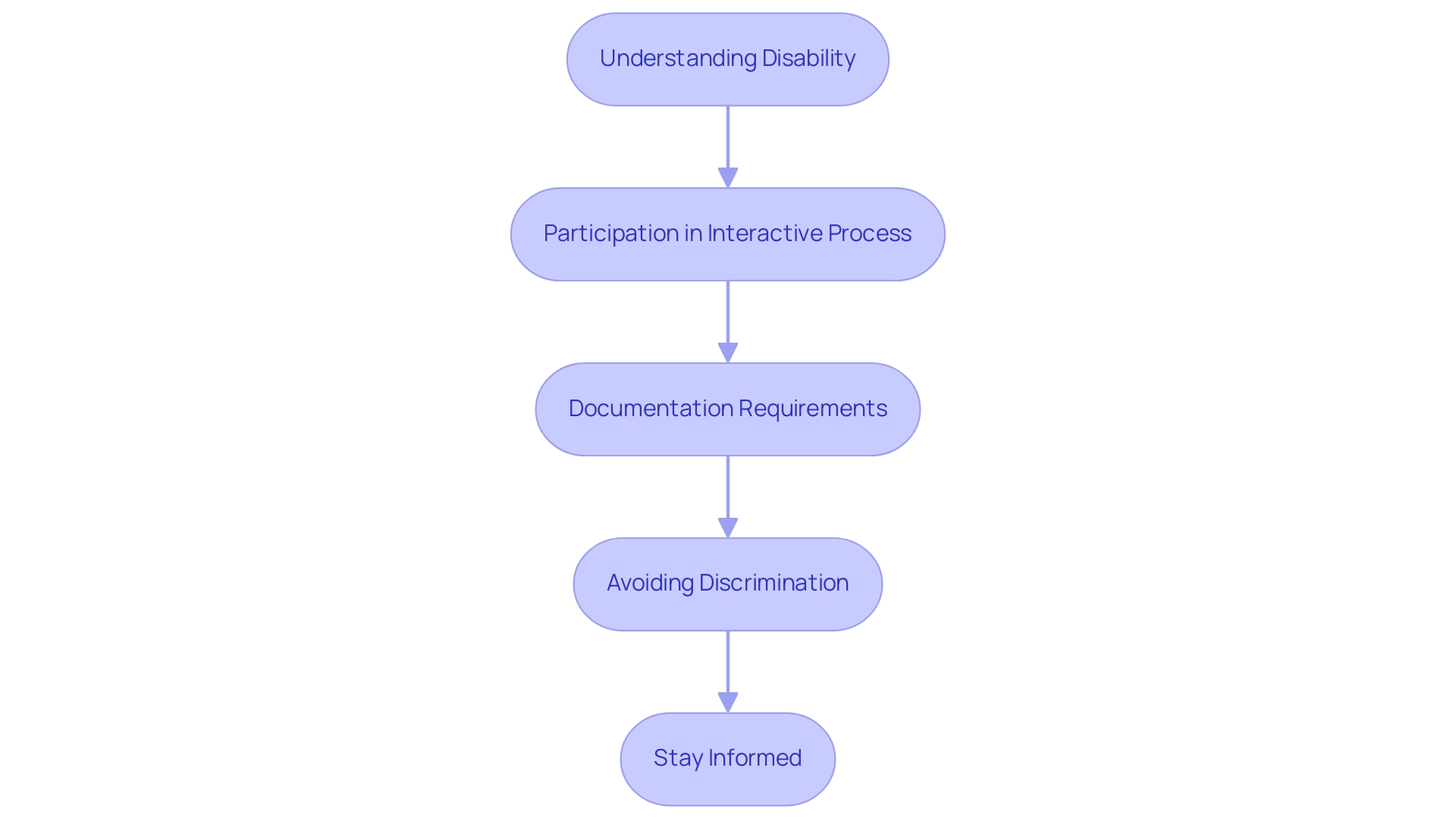
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), employers are required to provide autism accommodations at work for workers with disabilities, including those on the spectrum. Here's how to ensure your workplace is compliant and supportive:
-
Understanding Disability: It's crucial to recognize that this condition qualifies as a disability under the ADA.
This acknowledgment is the first step in providing the necessary autism accommodations at work that enable individuals with autism to thrive in the workplace.
-
Participation in Interactive Process: Employers must actively participate in dialogue with staff to identify and agree upon appropriate adjustments. This interactive process is not only a legal requirement but also fosters an inclusive environment where employees feel valued and heard, particularly regarding autism accommodations at work.
-
Documentation Requirements: Maintaining accurate records of requests for assistance and the measures taken to address them is essential. Documentation acts as a reference for compliance and assists in ensuring that adjustments are effectively implemented.
-
Avoiding Discrimination: It’s imperative to ensure that hiring, promotion, and termination practices are free from discrimination against individuals on the spectrum.
This commitment to fairness is critical for nurturing a diverse workforce and promoting equity in the workplace, which includes providing autism accommodations at work.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly updating your knowledge on the latest laws and regulations related to disability rights is vital. The Department has emphasized that accessible medical care is fundamental for health equity, stating,
Accessible MDE is vital for health equity, person-centered care, and access to medical care for patients with disabilities.
Additionally, in facilities specializing in treating mobility conditions, at least 20% of MDE units must meet the Standards for Accessible MDE, underscoring the importance of compliance in broader disability accommodations. Furthermore, exploring alternative approaches to accessibility standards, such as those discussed in recent case studies, can provide valuable insights into effective compliance strategies for employers, especially in relation to autism accommodations at work. By following these guidelines, employers can create a more inclusive environment that not only complies with the law but also advocates for the rights and needs of employees with autism.
Conclusion
Creating inclusive workplaces for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic advantage. By recognizing and embracing the unique strengths that autistic individuals bring, such as exceptional attention to detail and innovative problem-solving abilities, organizations can enhance productivity and foster a culture of acceptance. The alarming statistic that around 75% of autistic adults face underemployment highlights the urgent need for change, making it essential for employers to implement effective accommodations and engage in open dialogue.
Practical strategies, such as:
- Flexible work hours
- Quiet spaces
- Clear communication
can significantly improve the work experience for individuals with autism. Moreover, training staff and encouraging regular feedback ensures that accommodations meet the evolving needs of employees. The commitment to inclusivity not only benefits autistic individuals but enriches the organizational culture as a whole.
Finally, understanding the legal frameworks that support these initiatives, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act, further solidifies the foundation for equitable practices in the workplace. By prioritizing neurodiversity and fostering an environment where every individual feels valued, organizations can position themselves for success in a competitive market while making a meaningful impact on the lives of their employees. Embracing this journey is not just beneficial; it is essential for cultivating workplaces where everyone can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) represents a diverse range of neurological conditions that can influence social skills, communication, and behavior.
What strengths do individuals with ASD bring to the workplace?
Individuals with ASD often possess remarkable strengths, including heightened attention to detail, a strong capacity for focused work, and unique problem-solving skills, which can significantly enhance workplace dynamics and productivity.
What is the current employment situation for adults with developmental disorders in the U.S.?
Approximately 75% of adults diagnosed with a developmental disorder in the United States face underemployment or unemployment, highlighting the urgent need for workplaces to provide autism accommodations.
How can employers create an inclusive culture for individuals with ASD?
Employers can create an inclusive culture by understanding the varied manifestations of ASD and implementing autism accommodations at work, allowing all employees to flourish.
What is the impact of early therapy and intervention for individuals with ASD?
Early therapy and intervention can help manage behaviors and enhance quality of life for individuals with ASD, although there is currently no cure for the condition.
How does neurodiversity benefit workplace performance?
Diverse teams, particularly those inclusive of neurodiversity, often outperform less diverse counterparts due to the unique viewpoints and methods that individuals on the spectrum bring to cooperative activities.
What challenges do employers face in recruiting individuals with ASD?
Employers face challenges such as a lack of flexible hiring methods and a focus on social skills in recruitment, which can frustrate candidates on the autism spectrum.
What is the importance of disclosing a diagnosis during the hiring process?
Candidates should feel reassured that disclosing a diagnosis will not impact their chances of being offered a role, which is crucial for fostering an inclusive hiring environment.
Why is embracing neurodiversity essential for organizations?
Organizations that embrace neurodiversity are better positioned to thrive in competitive markets and foster a more inclusive work environment, which enhances company reputation and staff morale.




