Introduction
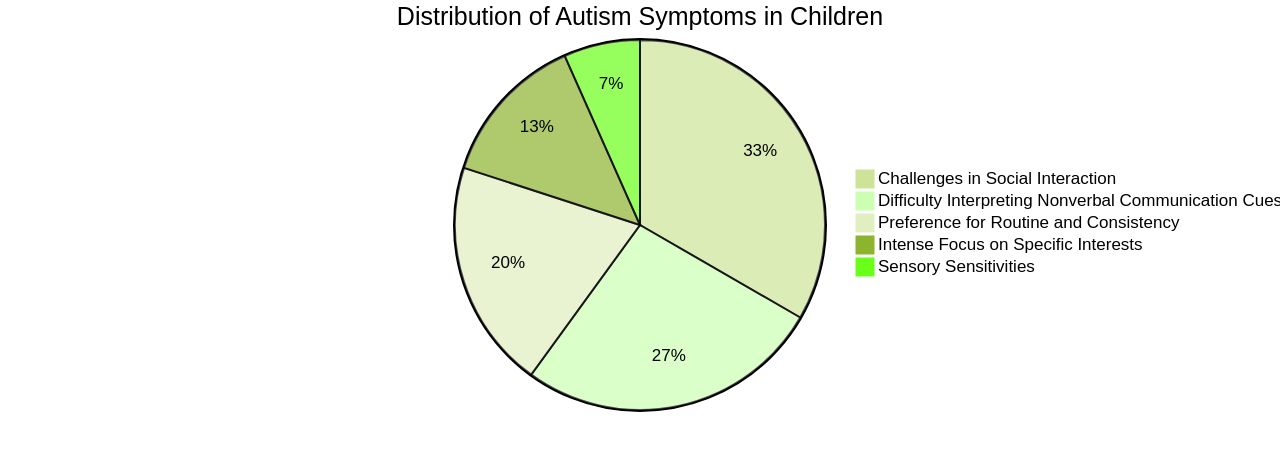
Acquiring a thorough understanding of the manifestations of Asperger's Syndrome is a significant stride for those advocating for children under their care. These manifestations often include challenges in social interaction, difficulty interpreting nonverbal communication cues, a preference for routine and consistency, intense focus on specific interests, and sensory sensitivities.
Recognizing these signs and implementing strategies to address them can facilitate a supportive environment for children to flourish. In this article, we will explore the history and diagnosis of Asperger's Syndrome, as well as provide strategies for parent advocates to help their children thrive.
History of Asperger's Syndrome
Asperger's Syndrome, which was first identified by Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger in the 1940s, gained official recognition as a distinct diagnosis in the 1990s, with its inclusion in prominent diagnostic manuals like the DSM-IV and the ICD-10. The understanding of this condition, however, has evolved over the years, leading to significant changes in classification.
In 2013, Asperger's syndrome was incorporated into the broader category of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) by the DSM-5, indicating that autism is a spectrum of different levels of symptom severity rather than separate disorders. This shift sparked a debate among experts.
While some celebrated it as a way to simplify diagnoses and acknowledge the spectrum nature of autism, others raised concerns about the possible reduction of specialized assistance for individuals who were previously diagnosed with Asperger's. Today, even though it has been officially reclassified, some individuals still use the term 'Asperger's Syndrome' because they find it more familiar or clearer. The evolution of this condition's understanding, from its initial identification to its current classification, offers valuable insights into the development of diagnostic criteria and support services.

Symptoms of Asperger's Syndrome
Acquiring a thorough understanding of the manifestations of Asperger's Syndrome is a significant stride for those advocating for children under their care. These manifestations often include challenges in social interaction, difficulty interpreting nonverbal communication cues, a preference for routine and consistency, intense focus on specific interests, and sensory sensitivities.
Recognizing these signs and implementing strategies to address them can facilitate a supportive environment for children to flourish. For instance, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have developed detailed lists of behaviors and signs associated with Autism, including communication, social behavior, and other behavior, which can be a valuable resource for understanding and addressing these symptoms.
Furthermore, it's crucial to remember that Autism's symptoms may vary, as not all individuals with Autism exhibit the same symptoms. For instance, girls are four times less likely to be diagnosed with Autism than boys.
Likewise, while 31% of children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) fall within the range of intellectual disability, 44% are classified in the average to above-average range. Through consistent monitoring, assessment, and service implementation, advocates can create a personalized plan that caters to the child and family's needs. Open communication and partnership between therapists and families are vital to ensure everyone is working towards the same goals. Ultimately, these strategies can empower advocates to provide comprehensive support to their children, helping them navigate the challenges of Asperger's Syndrome and thrive in their daily lives.
Diagnosis of Asperger's Syndrome
A child's diagnosis of autism, a condition affecting 2% of the population, is a critical juncture that opens doors to tailored resources and support. This stage involves a comprehensive evaluation of the child's social communication abilities, behavioral patterns and developmental history.
It's crucial to note that autism diagnosis isn't reliant on medical tests but instead uses the DSM-5 criteria. These criteria necessitate that autism's core features be present early in a child's life, although, for some, symptoms may only become apparent when social demands surpass their coping abilities.
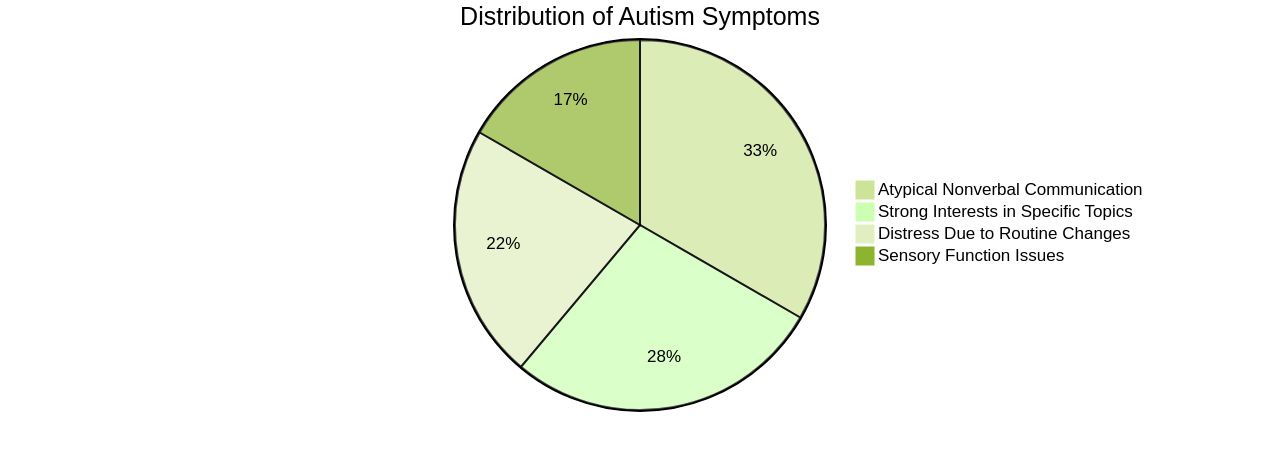
Furthermore, challenges may be concealed by learned coping strategies and support systems. Common characteristics observed in children with autism include atypical nonverbal communication, such as avoiding eye contact, displaying few facial expressions, or speaking in a monotone voice.
Other signs may include a strong interest in a specific topic or item and experiencing extreme distress due to changes in routine or diet. It's essential to acknowledge that these characteristics vary widely and their presence doesn't necessarily indicate autism.
However, if your child exhibits these behaviours, a screening is highly recommended. Autism is often associated with sensory function, leading children to become selective about food, potentially causing nutritional deficiencies. Therefore, during the diagnostic process, it's critical to assess co-occurring conditions like anxiety or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The collaboration with healthcare professionals to secure an accurate diagnosis is crucial. They can provide a deeper understanding of the child's condition and the best strategies to manage it, ensuring the child's overall well-being. It's important to remember that each child is unique, and their experience with autism will be too.
Strategies for Parent Advocates
A proactive and informed approach is necessary to help children with Asperger's Syndrome thrive. Carolann Jackson, a tireless advocate for her daughter, Nita, who has been diagnosed with Asperger's Syndrome, exemplifies the importance of establishing a strong support network.
The establishment of Supporting Asperger Families in Essex (SAFE), which is a beacon of support for numerous families, was led by Carolann's unwavering commitment. Early detection of autism, including Asperger's Syndrome, is crucial.
Routine screening during well-baby checkups, as recommended by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), can help identify Asperger's. Connecting children and families to support and services as early as possible can have a significant impact, especially for those with Asperger's syndrome.
As part of the process, a comprehensive assessment is conducted to create a personalized plan and consistent monitoring is implemented to ensure the child with Asperger's continues to benefit. Open communication, asperger's, is paramount in building an effective partnership between therapists and families. It's also important to remember that every child's journey is unique, and progress often comes with challenges in individuals with Asperger's. Listening to families who have overcome these challenges can be remarkably encouraging and foster hope for individuals with Asperger's. By implementing these strategies, parents can create a nurturing and supportive environment for their children with Asperger's Syndrome.

Conclusion
Understanding the history and diagnosis of Asperger's Syndrome is crucial for parent advocates. Recognizing the manifestations, such as social interaction challenges and sensory sensitivities, helps create a supportive environment for children to flourish.
Resources like those developed by the NICHD and CDC are invaluable in addressing these symptoms. Diagnosing autism requires collaboration with healthcare professionals.
Parent advocates should build a support network and seek early detection through routine screening. Partnerships with therapists and open communication are vital in creating personalized plans. By implementing these strategies, parent advocates can create a nurturing environment where their children with Asperger's Syndrome thrive. Every child's journey is unique, but with proactive support and unwavering commitment, they can navigate challenges and flourish in their daily lives.




