Introduction
ABA Therapy: Understanding the Principles and Techniques for Effective Behavior Change
ABA therapy, based on the principles of Applied Behavior Analysis, offers a scientific approach to understanding and changing behavior. By identifying the relationship between behavior and the environment, parents and professionals can develop effective intervention strategies. This article explores the principles of ABA therapy, including reinforcement, prompting, shaping, and fading, and how they promote positive behavior change.
Additionally, it delves into the importance of task analysis, the power of positive reinforcement, and the customization of ABA therapy programs for each individual. We will also discuss the role of data collection and analysis in ABA therapy, the transformative impact of case studies and success stories, and address concerns and controversies surrounding its use. Join us as we explore the world of ABA therapy and empower parents to navigate challenges and ensure the well-being of their children.
Understanding the Principles of ABA Therapy
ABA therapy is based on the principles of Applied Behavior Analysis, which is a scientific approach to understanding and changing behavior. It focuses on identifying the relationship between behavior and the environment, and using this knowledge to develop effective intervention strategies. Understanding the principles of ABA therapy is essential for parents and professionals to create meaningful and lasting changes in behavior.
ABA Techniques for Effective Intervention
In ABA therapy, various techniques are employed to promote positive behavior change. These techniques include reinforcement, prompting, shaping, and fading.
Reinforcement involves providing rewards or positive consequences for desired behaviors, while prompting involves providing cues or guidance to help individuals perform a specific behavior. Shaping involves breaking down complex behaviors into smaller, manageable steps, and fading involves gradually reducing the use of prompts or supports as individuals become more independent.
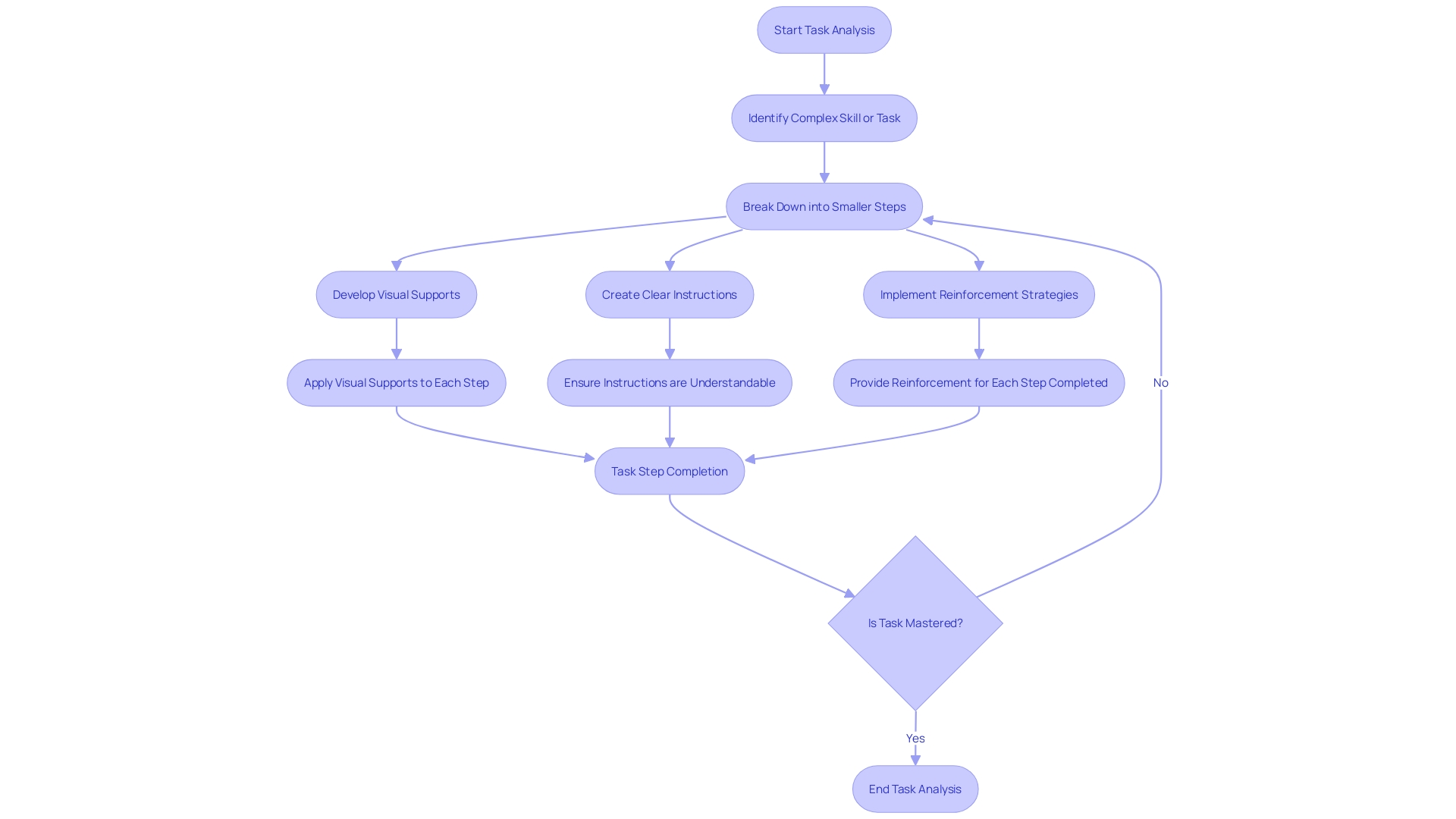
Task Analysis in ABA Therapy: Examples and Strategies
Task analysis is a crucial component of ABA therapy, as it involves breaking down complex skills or tasks into smaller, achievable steps. This allows individuals to learn and master skills more effectively.
Examples of task analysis in ABA therapy include teaching a child to brush their teeth, tie their shoes, or complete a puzzle. Strategies for task analysis include using visual supports, providing clear instructions, and offering reinforcement for each step completed.
Positive Reinforcement in ABA Therapy
Positive reinforcement is a core principle of ABA therapy and involves providing rewards or positive consequences to increase the likelihood of desired behaviors. Reinforcement can take various forms, such as praise, tokens, or access to preferred activities or items. It is important for parents and professionals to understand the power of positive reinforcement in shaping behavior and promoting skill acquisition.
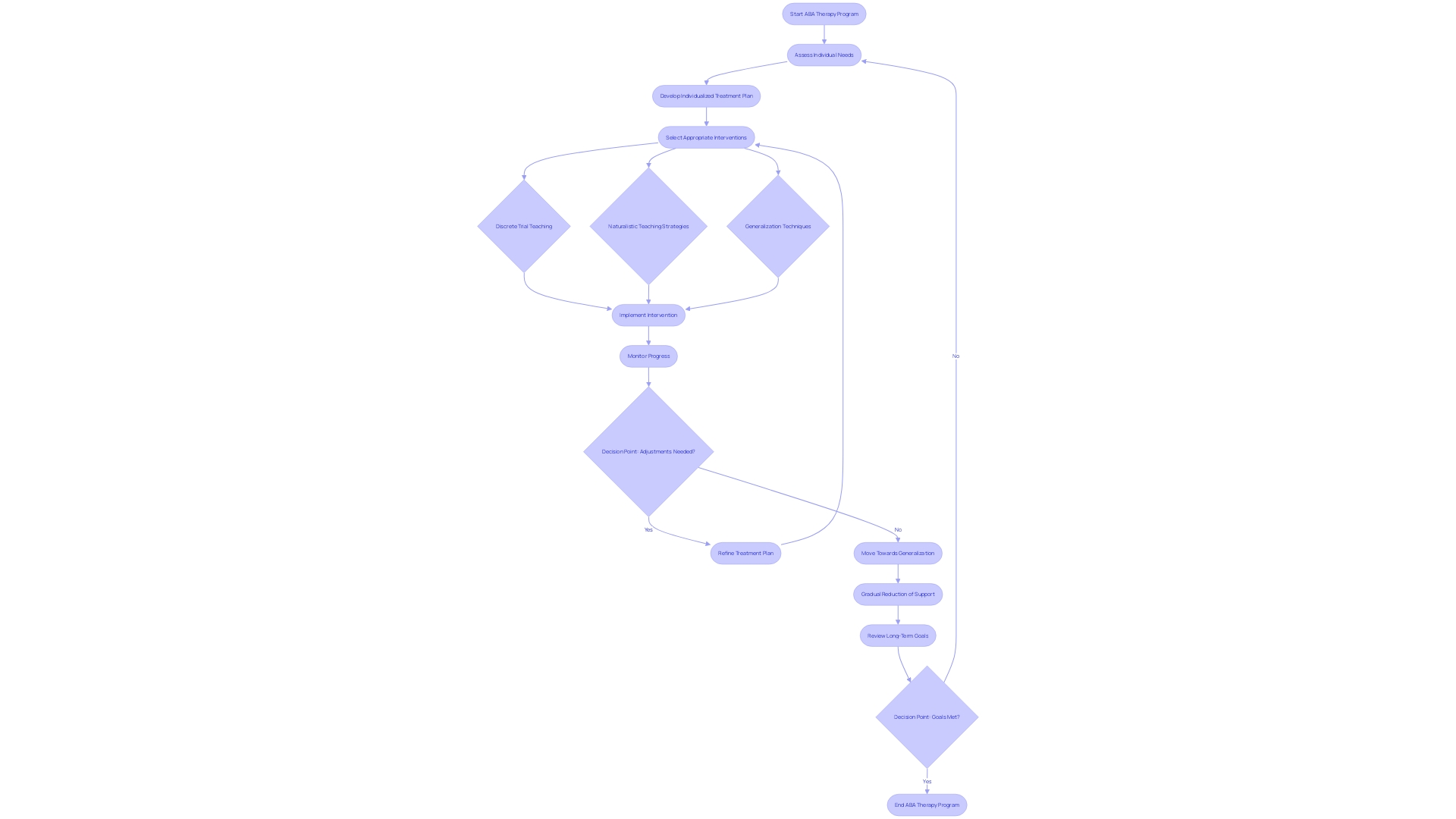
ABA Therapy Programs: Customized for Each Individual
ABA therapy programs are highly individualized and tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual. This customization ensures that interventions are relevant and effective in promoting behavior change.
ABA therapy programs may include a combination of discrete trial teaching, naturalistic teaching strategies, and generalization techniques. The goal is to provide a comprehensive and well-rounded approach to address the unique challenges and goals of each individual.
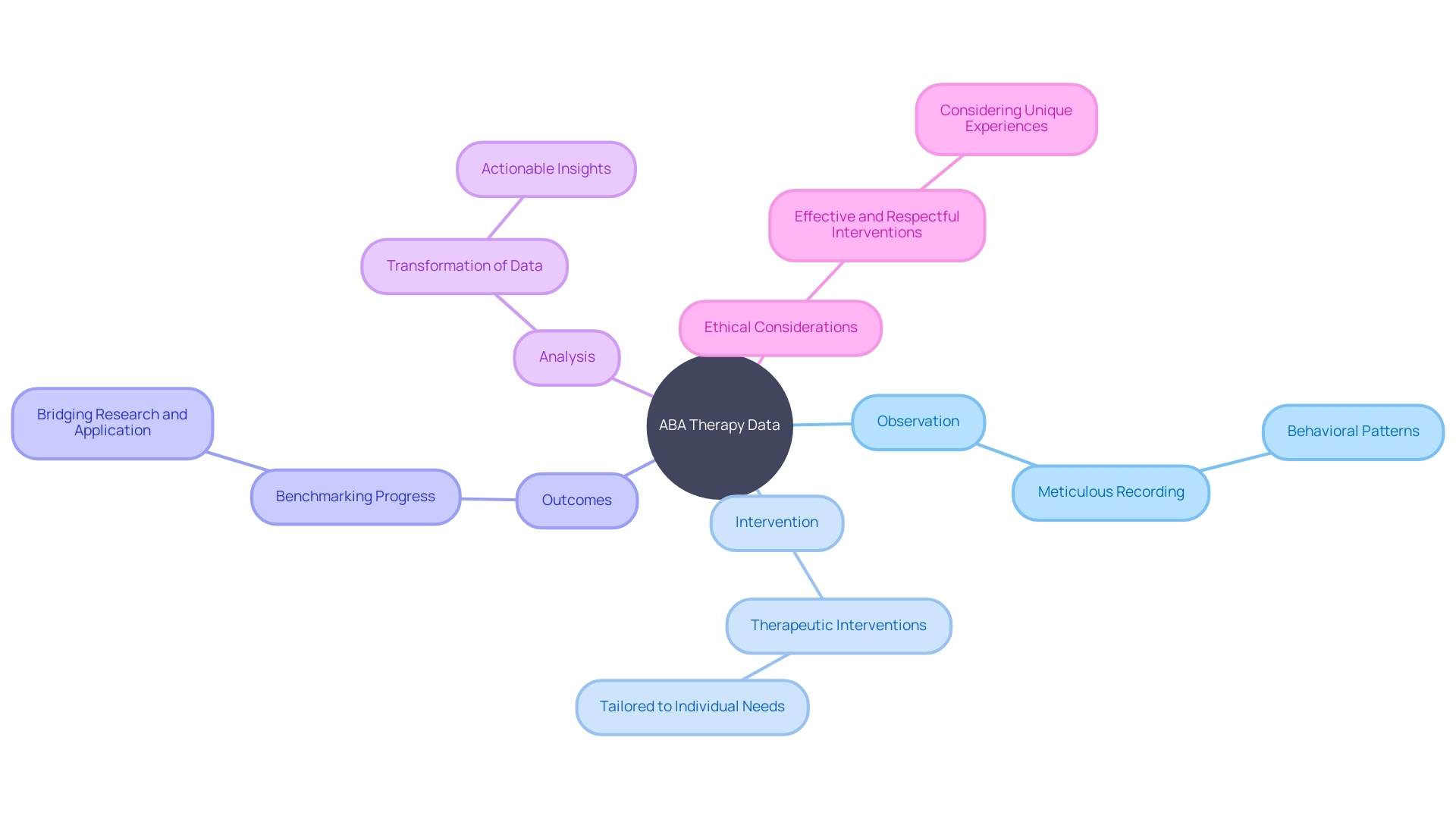
The Role of Data Collection and Analysis in ABA Therapy
In the realm of ABA therapy, meticulous data gathering and scrutiny are indispensable. This methodical approach entails the careful observation and recording of behavioral patterns, therapeutic interventions, and their outcomes.
Through this lens, both parents and professionals can discern trends, gauge the efficacy of treatments, and tailor interventions to meet the evolving needs of individuals with autism. For example, direct observation and specialized behavior rating scales furnish a granular view of a child's behavior, while standardized assessments benchmark progress against established norms.
The transformation of raw data into actionable insights is a cornerstone of ABA, as it underpins the evidence-based modification of therapeutic strategies. Recent research underscores the necessity of high-caliber studies in the field, revealing that many past interventions were marred by design flaws, clouding our understanding of their true impact. This insight is echoed at conferences, where the focus is not only on the latest advances in cognitive behavioral therapy but also on bridging the gap between research and real-world application, particularly in diverse and underserved communities. As we harness data to catalyze change, it's crucial to ensure that interventions are not only effective but also respectful and responsive to the unique experiences of those with autism.
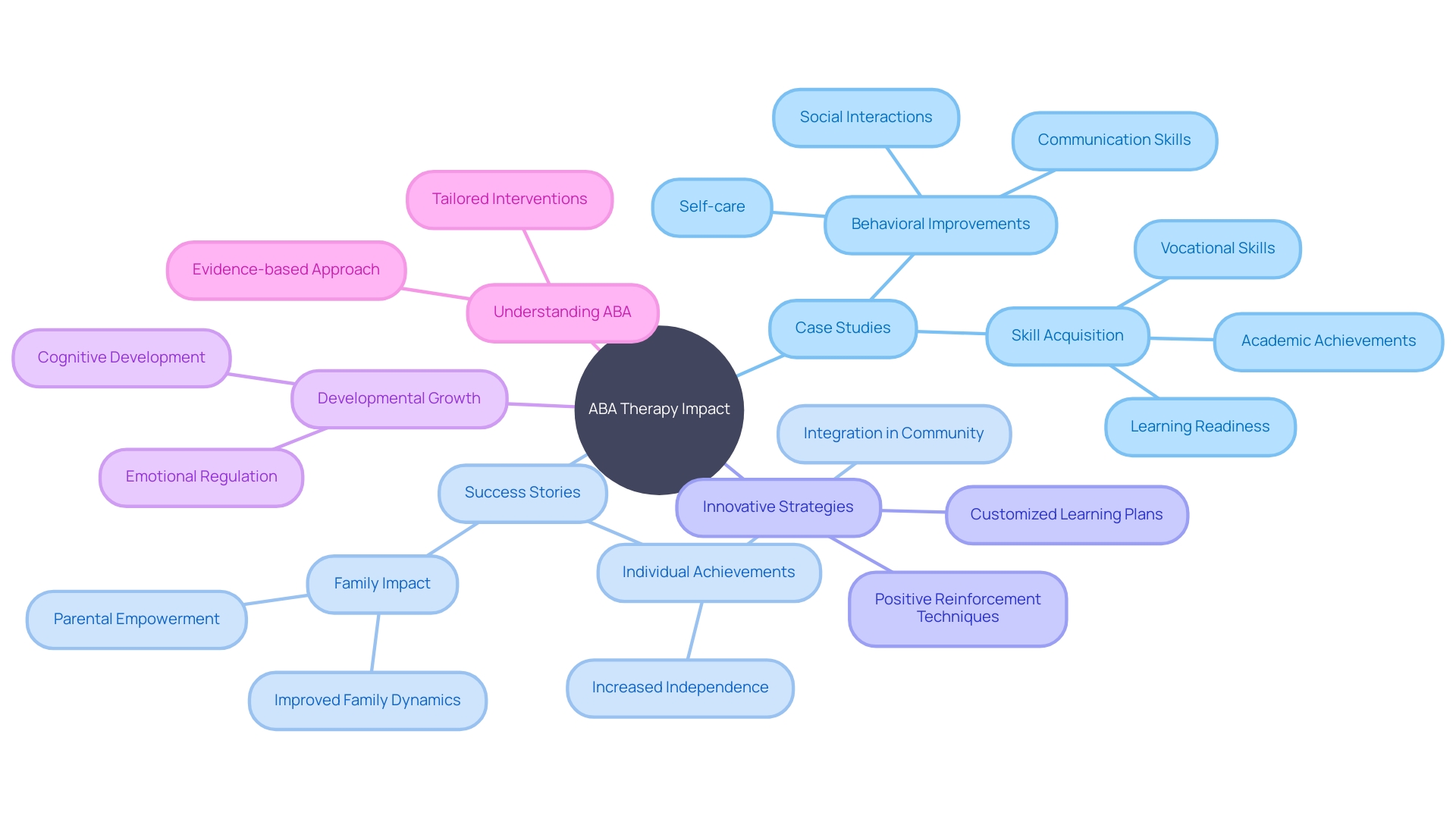
ABA Therapy in Practice: Case Studies and Success Stories
The transformative power of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is vividly illustrated through various case studies and success stories. These narratives not only highlight the profound changes in the behaviors and skills of individuals with autism but also offer a beacon of hope and a roadmap for parents and practitioners. By delving into these real-life scenarios, one can discover innovative strategies and grasp the full spectrum of possibilities that ABA therapy brings to the table, fostering a deeper understanding of its role in supporting developmental growth.
Addressing Concerns and Controversies Surrounding ABA Therapy
While ABA therapy has proven to be highly effective for many individuals, there are also concerns and controversies surrounding its use. It is important for parents and professionals to be aware of these concerns and to have open and honest discussions about them.
Some common concerns include the use of aversive techniques, the potential for over-reliance on prompts, and the need for cultural sensitivity in ABA therapy. By addressing these concerns and controversies, parents and professionals can work towards ensuring the ethical and effective implementation of ABA therapy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ABA therapy, based on the principles of Applied Behavior Analysis, offers a scientific approach to understanding and changing behavior. By identifying the relationship between behavior and the environment, parents and professionals can develop effective intervention strategies.
ABA therapy employs techniques such as reinforcement, prompting, shaping, and fading to promote positive behavior change. Task analysis is a crucial component of ABA therapy, allowing complex skills or tasks to be broken down into smaller, achievable steps.
Positive reinforcement plays a key role in shaping behavior and promoting skill acquisition in ABA therapy programs. These programs are highly individualized and tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual, utilizing a combination of teaching strategies and generalization techniques.
The role of data collection and analysis is indispensable in ABA therapy. Meticulous observation and recording of behavioral patterns and therapeutic interventions help discern trends, gauge efficacy, and tailor interventions to evolving needs.
Case studies and success stories vividly illustrate the transformative power of ABA therapy, offering hope and guidance for parents and practitioners. While concerns and controversies exist surrounding ABA therapy, it is important to address them openly and honestly. Discussions should focus on ethical implementation, avoiding aversive techniques, minimizing reliance on prompts, and promoting cultural sensitivity. In navigating challenges and ensuring the well-being of their children, parents can empower themselves with knowledge about the principles and techniques of ABA therapy. By understanding its transformative impact through case studies and success stories, they can advocate for effective interventions while addressing concerns to ensure ethical implementation.




