Introduction
The spectrum of needs in children with Autism and ADHD is diverse and complex, encompassing challenges in social interaction, sensory sensitivities, and attention maintenance. Understanding this broad spectrum is crucial in developing effective strategies for Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. Customizing ABA therapy strategies to meet the individual needs of each child is akin to a writer revising their manuscript, continually adapting and refining strategies to address the evolving needs of the child. By discarding ineffective strategies and incorporating new ones, ABA therapy can be tailored to what matters most to the child and their parents. This article explores the importance of customization in ABA therapy, the strategies used to address specific needs, and the ultimate goal of improving the overall functioning and quality of life for children with Autism and ADHD.
1. The Spectrum of Needs in Children with Autism and ADHD
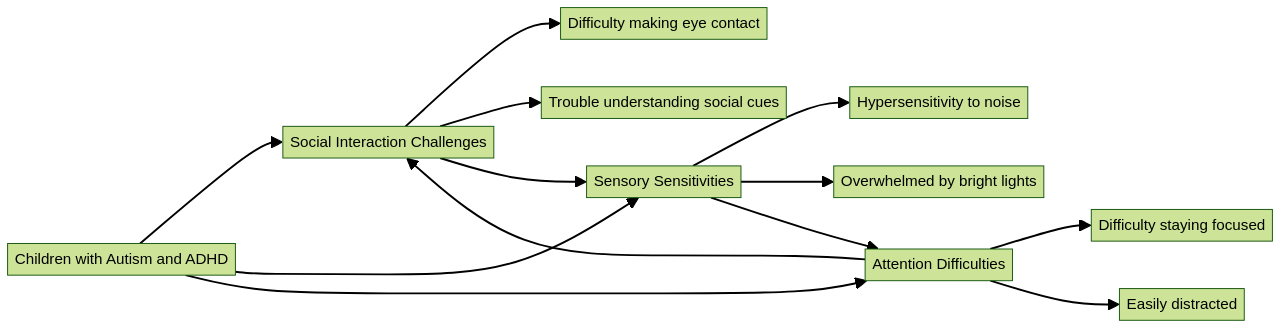
Children with Autism or ADHD come with their unique set of complex needs. These needs can range across a wide spectrum, including but not limited to social interaction challenges, sensory sensitivities, and maintaining attention. Grasping the nuances of this spectrum is an absolutely crucial part of creating effective strategies for Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. These strategies, in turn, need to be customized to meet the individual needs of each child.
Understanding the broad spectrum of needs in children with Autism and ADHD is akin to a writer revising their manuscript.
Just as a writer would seek help from philosophers and mechanics to fine-tune their story, parents and professionals need to continually revise and adapt the ABA therapy strategies to address the evolving needs of the child.
In the realm of ABA therapy, this could mean discarding strategies that are not effective and incorporating new ones that better address the child's unique needs. Just as a writer considers what their readers care about - parks, schools, and monuments in a small-town setting - ABA therapy should consider what matters most to the child and their parents.
Tracking the progress and effectiveness of different ABA strategies is akin to using index cards to map out the structure of a book and identify areas of improvement.
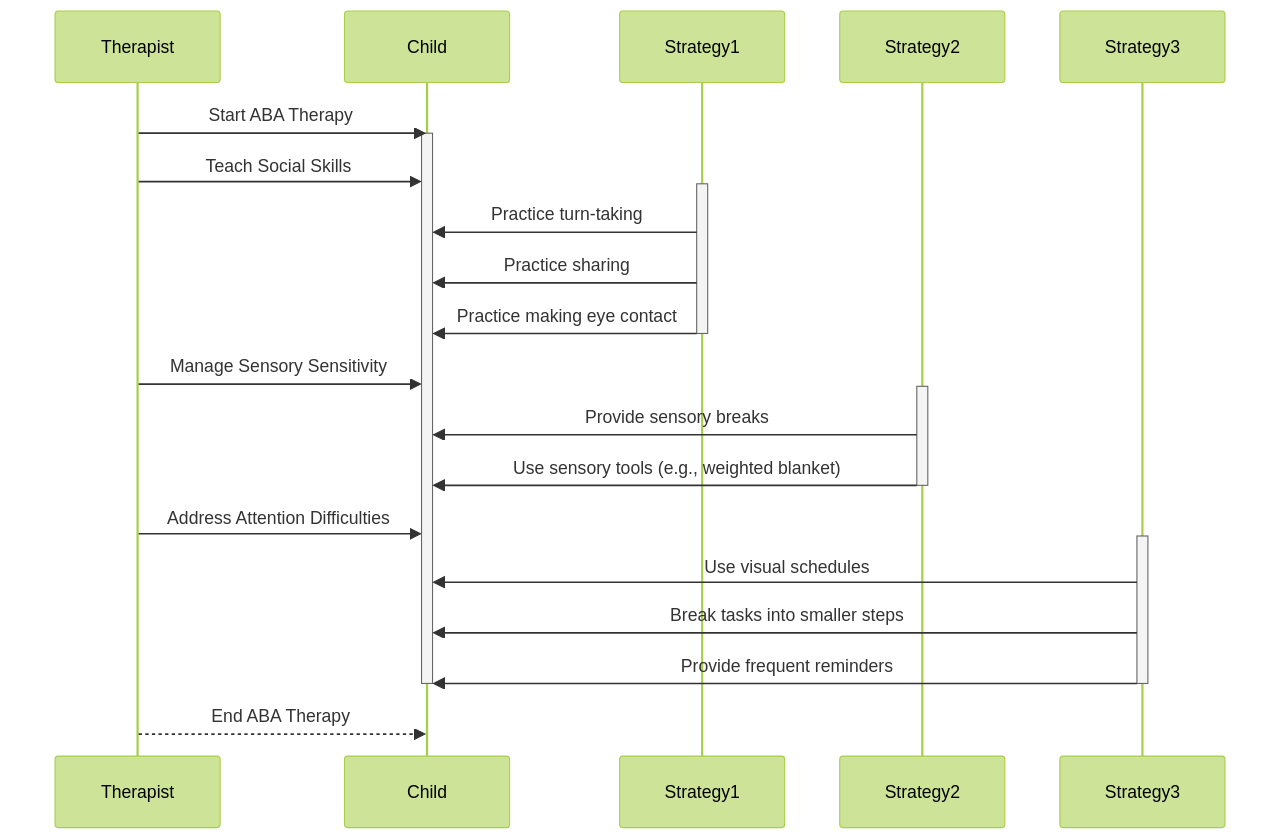
For instance, ABA therapy for children with autism and ADHD often includes teaching social skills through structured activities, using visual supports to enhance communication, implementing social stories or social scripts, and providing opportunities for peer interaction and practice.
These strategies aim to improve social communication, social engagement, and social reciprocity.
Similarly, to manage sensory sensitivity, interventions can include creating a sensory-friendly environment, providing sensory breaks, using sensory tools and techniques, and gradually desensitizing the child to sensory stimuli. The goal is to help children with autism and ADHD develop coping mechanisms and reduce sensitivity to sensory input, thereby improving their overall behavior and functioning.
For attention difficulties, ABA therapists work closely with children to develop individualized treatment plans that target these issues and teach strategies to improve attention and focus. These strategies may include visual supports, structured routines, prompting and fading techniques, and reinforcement strategies.
By understanding the individual strengths and challenges of each child, therapists can develop interventions that address their specific needs.
For children with autism, strategies may focus on developing social skills, communication abilities, and reducing repetitive behaviors. For children with ADHD, strategies may target improving attention and impulse control, as well as developing organizational and time management skills.
The ultimate goal of ABA therapy is to improve the overall functioning and quality of life for children with autism and ADHD. This process of tailoring strategies is similar to how a writer cuts unnecessary elements from their manuscript and adds new ones to improve their story.
In the end, just as a writer expresses gratitude for the role of editors in the writing process and the importance of their feedback, it is important to acknowledge the crucial role of parents, professionals, and the child themselves in the process of customizing ABA approaches to meet individual needs. The feedback and insights they provide are invaluable in ensuring the best possible outcomes in managing Autism and ADHD.
2. Understanding the Unique Challenges in ABA Therapy for Autism and ADHD
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has been a game-changer for children with Autism and ADHD. Its effectiveness, however, can be influenced by factors such as the child's resistance to change, the ability to transfer skills learned during therapy to everyday life, and managing coexisting conditions. Recognizing these challenges is essential in tailoring ABA strategies that cater to the child's needs.
A case study in progress hints at the potential of a goal-oriented approach to reshape autism treatment. This strategy aims to streamline, coordinate, and monitor the methods, resources, and tools necessary for transformation. The expected outcome could lead to significant changes in the health and therapy industries.
This goal-guided approach is poised to revolutionize how treatment plans for autism are developed, potentially causing industry-wide change. The collaborative and goal-oriented approach looks to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in treatment. It also aims to address the delay in diagnosis and accessing services for autism.
The case study emphasizes the challenges parents face in managing autism diagnosis and treatment. The goal-oriented framework places parents at the center of the process, highlighting the importance of long-term support for the entire family. Subgoals like insurance authorization, early diagnosis, and quick access to services form the core of this approach.
The goal-oriented approach aims to optimize the experience for patients and their families. Benefits include happier families, unlocking the child's potential, and quicker results. It also eases treatment for younger children and reduces paperwork and bureaucratic hurdles. The goal-based system allows for continuous iteration and better results, keeping all parties updated on progress.
A study on the impact of a data-driven, client-centric approach to ABA therapy for children with ASD was noteworthy. The study examined the correlation between the number of ABA therapy hours and functional outcomes for children with ASD. It also evaluated the shift to telehealth and virtual supervision's impact on ABA therapy outcomes.
The results suggest that children who received ABA therapy based on a data-driven, client-centric approach showed improved outcomes, regardless of the number of therapy hours. The modality of supervision (in-person vs. telehealth) did not significantly impact ABA therapy outcomes.
These findings challenge the traditional linear dose-response relationship between therapy hours and outcomes in ABA therapy. The study underscores the importance of individualized care plans and the customization of treatment dosage based on each child's needs. The results suggest a data-driven, client-centric approach to ABA therapy can improve functional outcomes for children with ASD while maximizing resource efficiency.
Therefore, the approach to ABA therapy should be individualized, keeping the child's unique needs in mind. A goal-led framework and a data-driven, client-centric approach can be instrumental in improving ABA therapy outcomes. Recognizing the challenges and customizing the therapy to meet the child's needs ensures that ABA therapy is as effective as possible.
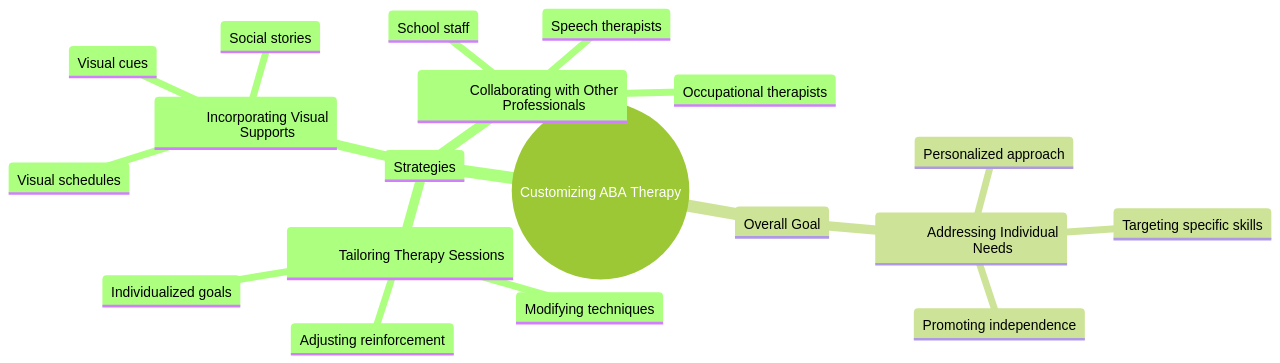
For customizing ABA therapy, strategies may include tailoring therapy sessions to meet the child's specific needs and challenges, incorporating visual supports and cues for better understanding and engagement, and addressing both social and behavioral aspects of their development. Collaborating with other professionals, such as speech therapists or occupational therapists, can provide a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment.
When addressing resistance to change in ABA therapy, consider effective approaches like using visual supports, implementing gradual transitions, providing clear expectations and explanations, offering choices, and incorporating motivational strategies.
To generalize skills beyond the therapy setting, use various settings, involve different people, vary materials and resources, fade prompts gradually, and reinforce generalization.
Co-occurring conditions, like ADHD, can present additional challenges in ABA therapy. It's important for therapists to have strategies to address these conditions and tailor the therapy to meet the individual needs of each child.
To overcome challenges in ABA therapy, it's important to have unlimited digital access to industry insights and resources.
This empowers parents to navigate autism support services more effectively and enhances the overall therapy experience for children with autism and ADHD.
To customize ABA therapy for children with autism and ADHD, consider individual needs and strengths.
Customize ABA therapy to meet your child's individual needs and strengths.
ABA therapy should be tailored to address the specific challenges and goals of each child. Regular assessments and data collection can help inform and guide the customization of ABA therapy for each child.
In conclusion, the approach to ABA therapy should be individualized, always keeping the child's unique needs in mind. A goal-led framework and a data-driven, client-centric approach can be instrumental in improving the outcomes of ABA therapy. By recognizing the challenges and customizing the therapy to meet the child's needs, we can ensure that ABA therapy is as effective as possible.
3. Customizing ABA Approaches: Addressing Individual Needs
Personalizing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) interventions is a nuanced process, akin to tailoring a unique suit to fit the specific needs and preferences of each child. This customization might involve altering the environment to minimize distractions, implementing visual aids to enhance communication, or integrating the child's interests into the therapy to stimulate learning.
Customized ABA therapy strategies for children with autism can include a variety of techniques and interventions tailored to meet the unique needs of each child. These strategies may include visual supports, social stories, token systems, structured schedules, and reinforcement strategies based on the individual's preferences and interests. Collaboration between therapists and caregivers is crucial in creating a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific goals and challenges of the child with autism.
To reduce distractions and create a conducive environment for ABA therapy, a quiet and organized space is vital. This can be achieved by removing unnecessary items from the therapy area, using visual schedules or timers to provide structure, and using noise-cancelling headphones or white noise machines to block out external sounds. Establishing clear boundaries and rules for behavior in the therapy environment can further reduce distractions and promote a calm and focused atmosphere.
Visual aids in ABA therapy can effectively enhance communication skills. They can provide visual support and reinforcement, helping individuals with autism better understand and process information. Including visual schedules, social stories, and visual prompts in ABA therapy sessions can create a more structured and visually-oriented learning environment, improving outcomes for individuals with autism.
Incorporating a child's interests in ABA therapy can improve engagement. Creating a treatment plan that includes activities and tasks related to the child's specific interests can increase motivation and participation during therapy sessions. Activities and tasks that are enjoyable and meaningful to the child can enhance their engagement and overall progress in ABA therapy.
Tailoring ABA therapy to address individual needs can lead to improved outcomes. A personalized approach allows for more effective intervention and can help individuals generalize skills learned in therapy to real-life situations, promoting greater independence and success in daily life.
To motivate learning in ABA therapy using the child's interests, therapists can use the child's preferred toys, activities, or themes as part of the learning materials or as rewards for completing tasks. This approach helps to maintain their engagement and motivation throughout the therapy sessions, leading to more effective outcomes.
Customizing ABA approaches involves a thorough assessment of specific behaviors that need to be addressed, setting clear goals, individualizing the intervention, incorporating reinforcement, adapting the environment, collaborating with caregivers and professionals, and regularly monitoring progress and making adjustments based on the individual's progress and feedback.
Addressing individual needs in ABA therapy involves conducting thorough assessments and evaluations of each individual's strengths, weaknesses, and specific goals. This allows for the development of personalized treatment plans that target the unique needs of each person. Regular communication and collaboration with the individual, their family, and other professionals involved in their care ensure that the therapy is tailored to their specific needs and goals.
To meet individual needs in ABA therapy, there are various resources and tools available, including personalized behavior plans, visual schedules, social stories, and token boards. Additionally, software programs and mobile applications can assist in creating customized therapy programs and tracking progress.
In essence, customizing ABA approaches is a dynamic and evolving process. It requires a deep understanding of each child's unique needs and the flexibility to adapt and modify strategies. By doing so, we can ensure ABA therapy is more effective in promoting positive behavior changes and skill development, ultimately leading to better outcomes for children with autism.
4. Effective Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors
Addressing challenging behaviors is a cornerstone of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, a method proven effective in improving behavior and quality of life in individuals with autism. The success of these strategies lies in their customization to the unique needs of each child, mirroring the principle of individual tailoring seen in successful corporate overhauls, such as Cigna's comprehensive revamp of its performance management system.
Strategies in ABA therapy vary widely, encompassing techniques from positive reinforcement of desired behaviors to teaching replacement behaviors that serve the same function as challenging ones. Positive reinforcement strategies are a crucial part of ABA therapy, providing rewards or incentives to encourage desirable behaviors. This method motivates individuals to engage in positive behaviors, increasing the likelihood of their repetition in the future. These reinforcements can be tailored to each individual's preferences and may include verbal praise, tokens, stickers, or other rewards, contributing to a positive and supportive environment that encourages learning and growth.
ABA therapy also involves teaching replacement behaviors, where more appropriate and desirable behaviors are identified and taught to replace problematic ones. This approach aids individuals with autism in learning new skills and improving their overall functioning.
Another approach involves altering the environment to reduce the chance of challenging behaviors manifesting. Creating a structured and supportive setting, for instance, can be achieved by implementing visual supports like visual schedules and cues. This helps individuals with autism understand expectations and transitions. Reducing sensory distractions, providing clear and consistent instructions, and using positive reinforcement strategies also contribute to a calm and predictable environment that inhibits challenging behaviors.
Through these personalized strategies, significant enhancements in behavior can be seen, paving the way for an improved quality of life. Just as Cigna's overhaul was tailored to the company's specific needs, so too should strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with autism and ADHD be personalized to each child's unique needs for optimal outcomes. Future-focused results and strengths, constructive communication, and feedback are principles that can also be applied in the context of ABA therapy.
Through such customization, we can foster an environment that not only manages challenging behaviors but also promotes the development of desired behaviors and skills. By implementing industry insights and strategies, professionals can overcome challenges and address these behaviors more effectively. The ultimate goal of ABA therapy is to improve overall functioning and promote a better quality of life for individuals with autism.
5. Navigating Support Services: A Resource Guide for Parents and Professionals
Navigating the maze of support services can indeed be a daunting task for both parents and professionals. However, a well-structured resource guide can serve as a guiding light, helping to demystify the myriad of services available. This guide can provide invaluable insights into eligibility criteria, the process of accessing these services, and the wealth of resources available on various platforms, including official government websites.
One such resource is the official United States government's website, which is a rich source of information. It offers a plethora of resources, including assistance in finding help, support, and healthcare services. It provides comprehensive information on various types of treatment providers, insurance coverage, and payment options, as well as practical tools for managing mental health issues.
In addition, the website caters to specific demographic groups, including veterans, active service members, American Indians, Alaska Natives, and LGBTQ+ individuals. It also offers resources for parents, caregivers, educators, and community leaders. This makes the website an invaluable asset for those seeking information on prevention methods, harm reduction strategies, and recovery support resources.
For those navigating the complex world of substance abuse disorders, the government website offers resources on various substances, including alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, opioids, and other drugs. It also provides information on grants and funding opportunities, training programs for healthcare professionals, and resources for addressing disparities in behavioral health.
Within the realm of mental health, the website provides information on suicide prevention and crisis hotlines. It extends resources for schools and campus health, as well as information on laws and regulations related to substance abuse and mental health. The website is a valuable tool for prevention, treatment, and recovery services and offers resources for data collection and program evaluation.
The website also hosts information on programs and initiatives led by SAMHSA, including contact information and resources for specific SAMHSA offices and centers. It's a comprehensive platform that provides resources for specific populations, such as older adults and LGBTQ+ individuals.
However, another essential resource can be found at www.asd.media. This website contains a comprehensive guide to aid parents and professionals in navigating the support services available for children with autism. It provides information and strategies for promoting social skills in children with autism, alongside troubleshooting tips. This guide aims to empower parents and help unlock their children's potential by providing the necessary support and guidance. It can be found under the "news" section of the website.
In the end, the power to make informed decisions lies in the hands of parents and professionals. With the aid of such resource guides, they can ensure that the child receives the necessary support. This, in turn, will empower them to navigate the maze of services with confidence, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their children.
6. Enhancing Social Skills Development through ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a potent tool for fostering social skill development in children diagnosed with Autism and ADHD. It encompasses teaching societal norms and expectations, creating opportunities for social engagement, and employing role-play techniques to simulate real-life social situations. The enhancement of social skills through ABA therapy significantly bolsters a child's capacity to interact with others and take part in social events.
Among specialized therapy services, institutions such as the Star Institute stand out for their comprehensive offerings. They provide a broad spectrum of services, including occupational therapy, speech language therapy, and mental health services tailored to children and adults' unique needs. The institute also offers autism-specific programs, such as school readiness and superhero training programs, designed to prepare children for the social demands of school life.
The Star Therapy Approach, adopted by the Star Institute, underscores the importance of sensory processing and sensory integration in therapy. This approach aligns with the ABA therapy's aim of enhancing social skills. Sensory integration therapy helps children better understand and react to the world around them, improving their social interactions.
The Star Institute also offers social skills groups for children, providing a platform for them to engage in activities and build social cognition, communication, and problem-solving skills. These groups create a supportive environment where children can learn and grow while interacting with their peers.
Children with ADHD often face challenges with social skills due to weakened executive functions in their brain. These children may require additional support in rebuilding their social skills, especially after prolonged periods of social distancing. ABA therapy can address these needs by identifying the root cause of social ineptness and providing targeted strategies for improvement.
For example, direct instruction and real-world practice can help children with executive function weaknesses learn to self-regulate and engage in appropriate social behaviors. Techniques such as assigning a mission or focused behavior for the child to practice during play dates can help them work on specific skills. Pre-planning play dates and controlling the activities and environment can create a conducive setting for practicing social skills.
The enhancement of social skills through ABA therapy is a multi-faceted process that involves teaching societal norms, creating opportunities for social interaction, and providing real-world practice. Institutions like the Star Institute offer a range of services that support this process, emphasizing the importance of personalized, comprehensive therapy in improving the social abilities of children with Autism and ADHD.
Effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism and ADHD can include various forms of therapy, such as ABA therapy. ABA therapy focuses on teaching specific skills and behaviors through positive reinforcement and repetition. It can help children with autism and ADHD develop social skills by targeting specific areas of difficulty, such as eye contact, turn-taking, and conversational skills.
Additionally, social skills groups and social stories can also be beneficial in teaching and practicing social skills in a structured and supportive environment. It is important to work closely with professionals and specialists to determine the most appropriate strategies for each child's unique needs. ABA therapists use different techniques to effectively teach social skills to children with autism. These techniques may include breaking down social rules into smaller, more manageable steps, using visual supports such as social stories or visual schedules, incorporating social skills training into everyday activities and routines, and providing frequent opportunities for practice and reinforcement.
Role-play activities can be beneficial in improving social skills in children with autism and ADHD. Role-play allows children to practice different social scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. It helps them develop skills such as turn-taking, empathy, and perspective-taking. By engaging in role-play activities, children with autism and ADHD can enhance their social interactions and communication skills.
ABA therapy focuses on using positive reinforcement and behavior modification techniques to teach and reinforce appropriate social behaviors. Through structured interventions and individualized treatment plans, ABA therapists can help children with autism and ADHD learn how to initiate and maintain social interactions, follow social cues, and understand and respond appropriately to social situations. This can greatly enhance their ability to interact and communicate effectively with others.
7. Empowering Parents: Tools and Strategies for Balancing Responsibilities
Parenting, especially for those nurturing children with special needs, can be an intricate labyrinth of responsibilities. The everyday life of such parents is filled with a spectrum of duties and obligations. However, certain strategies can empower parents to manage their roles effectively and assure the overall well-being of their child.
One of the main challenges parents encounter is societal expectations that mothers should bear the primary responsibility for children. This can lead to an imbalance, particularly when the mother takes on more responsibilities. A countermeasure for this is for parents to cultivate a balanced approach where tasks are equally divided. For instance, fathers can contribute by taking on non-feeding care, such as changing diapers and cooking, providing the mother with some respite. This not only distributes the workload but also fosters a deeper understanding of the child's needs in both parents.
Spending solo time with the child is another effective strategy. It offers parents, especially fathers, valuable experience and practice. It also provides an opportunity for the child to bond with each parent individually.
Effective time management techniques are crucial for successfully managing various roles and responsibilities. Keeping track of who does what and when can ensure that the workload is balanced. A helpful exercise can involve considering how one would handle the kids alone for an extended period. This hypothetical scenario can offer insights into parenting equality.
Remember, balanced parenting models are challenging to find due to societal norms, but each family can create a model that works best for them. The ultimate goal is to ensure that every parent feels empowered and capable of caring for their child while also taking care of themselves.
In managing these challenges, remember that small changes can have a significant impact. Just as independent women scholars balance their professional responsibilities with caring for their families, parents can make incremental adjustments to their routines and responsibilities. These changes, evaluated and iterated over time, can help achieve a more balanced life.
Finally, it's essential to let go of idealized notions of balance. Each day brings with it different challenges and responsibilities, and it's okay if things don't go according to plan. Remember, the ultimate goal is to ensure the well-being of your child while also taking care of yourself.
In your parenting journey, seeking support from others can be beneficial. Join parent support groups or communities where you can connect with other parents facing similar challenges. These groups often provide a safe space for sharing experiences, seeking advice, and receiving emotional support. Additionally, reaching out to friends, family members, or trusted individuals in your network can also be beneficial. They may be able to offer practical assistance or simply lend a listening ear when you need to talk. Remember, seeking support is not a sign of weakness, but rather a way to ensure you have the resources and encouragement you need to be the best parent you can be.
Practising self-care is crucial for parents to maintain their physical and mental well-being. Activities such as setting aside time for relaxation, engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy, seeking support from friends or support groups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercise and proper nutrition can be beneficial. Prioritizing one's own well-being can better navigate the challenges of supporting their child and maintain a healthy balance in their lives.
8. Fostering a Collaborative Community in ABA Therapy: Benefits and Strategies
The impact of a collaborative community within the sphere of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy cannot be overstated. It serves as a cornerstone, nurturing parents and professionals alike, fostering a culture of shared experiences, mutual support, and collective learning. This collaborative approach brings forth numerous benefits - from promoting a deeper understanding of effective treatment strategies to ongoing professional growth.
Establishing effective communication platforms is one strategy that underpins the construction of such a community. These platforms, which could include online forums, social media groups, or professional networking platforms, facilitate the flow of ideas and knowledge, enhancing the ABA therapy process. They create a space where parents and professionals can share their journey, learn from each other, and grow together.
Events, although not explicitly mentioned, are another strategy that can foster community spirit. These could range from workshops and seminars to informal gatherings, providing opportunities for interaction, learning, and mutual support. It is also important to provide resources that foster collaboration. Resources could be as varied as informative articles, expert-approved information, or even stories from readers. These tools offer valuable insights into various aspects of ABA therapy, enhancing knowledge and skills, and leading to a more effective and collaborative approach to therapy.
Fostering collaboration in ABA therapy can also be achieved through several best practices. Clear communication channels between therapists, parents, and other professionals involved in the therapy process are crucial. This can be facilitated through regular meetings, sharing of progress reports, and maintaining open lines of communication. Encouraging a team approach in ABA therapy, involving all relevant stakeholders in the treatment planning and decision-making processes, can lead to a comprehensive approach to therapy.
Creating a positive and supportive environment is another vital aspect of fostering collaboration. Recognizing and celebrating achievements, providing constructive feedback, and implementing strategies that encourage teamwork and cooperation contribute to this positive environment. This supportive atmosphere is instrumental in creating meaningful change in the lives of children undergoing ABA therapy, improving the skills of professionals in the field, and ensuring the best possible outcomes.
In essence, fostering a collaborative community within ABA therapy is about building a space where everyone involved feels supported, heard, and valued. It's about unity, collective learning, and a shared goal of helping children with autism thrive. With the right strategies, resources, and practices in place, ABA therapy can be a collaborative journey that benefits everyone involved - from professionals to parents, and most importantly, the children themselves.
9. Continuous Improvement in ABA Therapy: The Role of Collaboration and Resources
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, an ever-evolving field, thrives on knowledge enhancement, strategy refinement, and the integration of feedback. In this journey, the power of collaboration and resource sharing is instrumental. The shared wisdom of parents, professionals, and the community can significantly enhance the effectiveness of strategies that address the unique needs of children.
Reflecting on a case study that utilizes a goal-led approach for autism treatment serves as a prime example. This approach aims to address the challenges of assembling, coordinating, and tracking the necessary methods, resources, and tools to bring about transformational change. The goal-led approach brings about a new level of efficiency and effectiveness by leveraging collaboration. It focuses on several subgoals, such as insurance authorization, early diagnosis, and quick access to services, thus taking treatment to a new level.
Another study highlights the impact of a data-driven, client-centric approach to ABA therapy for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study aimed to understand the relationship between treatment dose and functional outcomes in children receiving ABA therapy. The results suggest that individualized treatment plans tailored to each child's needs may be more effective than the number of hours of ABA therapy alone.
To continuously improve ABA therapy, it is crucial to implement strategies that enhance therapy outcomes and overcome challenges. Staying updated on the latest knowledge in ABA therapy is an essential part of this process. Attending workshops, conferences, and seminars focusing on the latest research and advancements in the field, reading relevant literature, and participating in online courses or webinars are some ways to do this.
Feedback is another vital aspect of improving ABA therapy outcomes. Proactively seeking feedback can provide valuable insights into the implementation of ABA therapy and help overcome challenges. Reliable resources are also crucial for continuous improvement in ABA therapy. Utilizing these resources can help practitioners stay updated with industry insights and best practices, contributing to the continuous refinement of ABA therapy techniques.
Sharing experiences is an effective approach to improving ABA therapy strategies. By exchanging knowledge and insights with other professionals, therapists can learn from each other's successes and challenges. This collaborative approach can lead to the development of more effective strategies and interventions for individuals with autism. Strategies for better meeting the spectrum needs of children in ABA therapy can include individualized treatment plans, structured and predictable routines, visual supports, social stories, and the use of positive reinforcement.
In conclusion, the continuous improvement in ABA therapy is a collective effort. Parents, professionals, and the community share resources, experiences, and insights to enhance their strategies, ensuring they are best suited to meet the unique needs of each child. This collective wisdom, combined with a data-driven, client-centric approach, can lead to improved outcomes for children with ASD. Learning, refining, and implementing new strategies is the cornerstone of continuous improvement in ABA therapy.
10. Staying Updated on ABA Therapy: The Importance of Access to Current Information
Staying informed about the latest developments in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is essential for both parents and professionals. This is not only about being aware of the latest research findings, but also about understanding the evolving strategies and trends within the field. Recognizing the dynamic nature of the discipline, which is steadily informed by new insights, innovative techniques, and a deeper understanding of the diverse needs of children with Autism and ADHD, is crucial.
The Association for Behavior Analysis International (ABAI) plays a significant role in this context. As a nonprofit organization, its mission is to foster the growth and vitality of behavior analysis science, thereby enhancing societal welfare. It's a hub for research, education, and practice in the field of behavior analysis, offering a wealth of information and opportunities for its members.
ABAI's offerings span events, a higher education learning center, journals, and career opportunities. These resources play a pivotal role in keeping parents and professionals updated on ABA therapy. The organization also manages a press center that disseminates statements, press releases, and relevant information for media contacts, thus extending the reach of essential updates in the field.
For a comprehensive background on ABAI, the organization provides a fact sheet available for download. Contact information for ABAI is readily accessible, and quick links are provided for member login, continuing education, joining ABAI, videos, donating, the learning center, cart/checkout, journals, events calendar, jobs, and subscribing to the newsletter.
In the dynamic landscape of ABA therapy, staying updated is not just beneficial but necessary. The latest research on ABA therapy for autism and ADHD provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of this treatment approach. Research studies may focus on various aspects of ABA therapy, such as its impact on improving social skills, reducing challenging behaviors, and enhancing overall functioning in individuals with these conditions. By staying informed about the latest research, parents and professionals can ensure that they are providing the most evidence-based and effective interventions.
To discover new strategies for ABA therapy in autism and ADHD, consulting with experts in the field or referring to reputable research studies and publications is advisable. These sources offer up-to-date information on the latest advancements in ABA therapy techniques specifically tailored for individuals with autism and ADHD.
Emerging trends in ABA therapy for autism and ADHD include the use of digital platforms for unlimited digital access to therapy resources and services. These platforms offer enhanced implementation of ABA therapy, providing industry insights for overcoming challenges and improving outcomes. Furthermore, empowering parents to navigate autism support services is another emerging trend in ABA therapy. By unlocking the potential of parents to actively participate in their child's therapy, it can lead to more effective and comprehensive treatment for autism and ADHD.
To stay updated on ABA therapy, regularly visiting trusted websites and resources that provide information on the latest developments and research in this field is important. Subscribing to newsletters or joining online communities focused on autism and ADHD can also help parents and professionals stay informed about new techniques, strategies, and advancements in ABA therapy.
Through resources like ABAI and the aforementioned strategies, parents and professionals can stay at the forefront of developments in the field. This ensures they are equipped with the most current knowledge and strategies, empowering them to provide the most effective support possible, tailored to meet the unique and diverse needs of children with Autism and ADHD.
Conclusion
The spectrum of needs in children with Autism and ADHD is diverse and complex, encompassing challenges in social interaction, sensory sensitivities, and attention maintenance. Understanding this broad spectrum is crucial in developing effective strategies for Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. Customizing ABA therapy strategies to meet the individual needs of each child is akin to a writer revising their manuscript, continually adapting and refining strategies to address the evolving needs of the child. By discarding ineffective strategies and incorporating new ones, ABA therapy can be tailored to what matters most to the child and their parents.
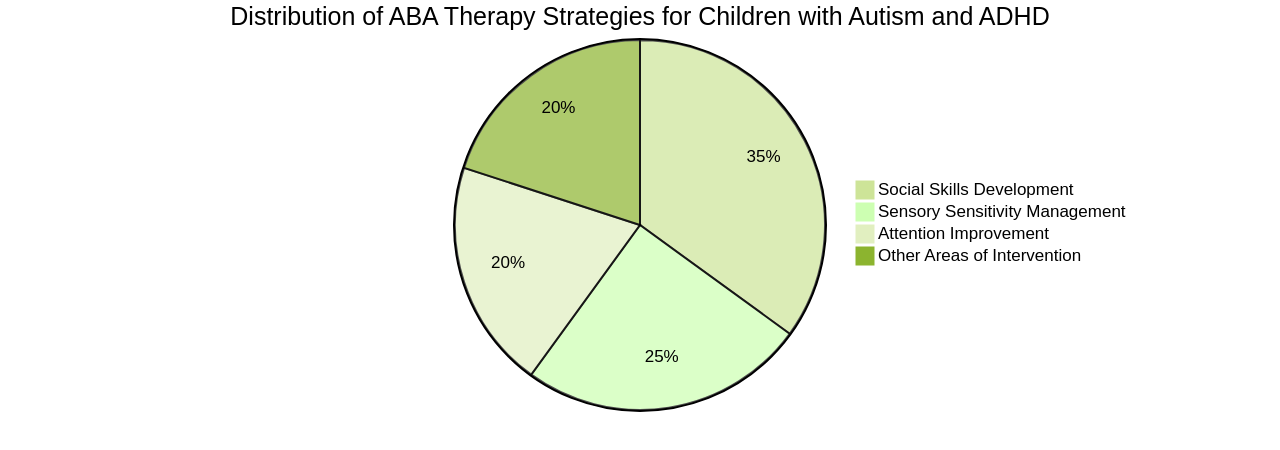
The importance of customization in ABA therapy cannot be overstated. It allows therapists to address specific challenges and goals for each child, creating interventions that are personalized and effective. Strategies such as teaching social skills through structured activities, using visual supports to enhance communication, implementing social stories or scripts, and providing opportunities for peer interaction can improve social communication and engagement. Additionally, interventions that focus on managing sensory sensitivities can create a sensory-friendly environment and gradually desensitize the child to sensory stimuli. For attention difficulties, individualized treatment plans can target attention improvement through visual supports, structured routines, prompting techniques, and reinforcement strategies.
The ultimate goal of ABA therapy is to improve the overall functioning and quality of life for children with Autism and ADHD. By customizing ABA approaches based on the unique needs of each child, therapists can optimize outcomes and promote positive behavior changes. It is crucial for parents, professionals, and the community to collaborate in this process by sharing resources, experiences, and insights. By staying updated on the latest research findings and advancements in ABA therapy through reputable organizations like ABAI, parents and professionals can ensure they are equipped with the most current knowledge to provide effective support. To start customizing ABA therapy for your child or seeking more information on ABAI resources .




