Introduction
Navigating the world of toddler development can often feel overwhelming, especially when faced with common concerns like drooling. For many parents, the sight of their two-year-old drooling may raise questions and worries about their child's health and development. While drooling is typically a normal part of this stage, understanding its causes and implications is essential for ensuring a child's well-being. Recent research sheds light on the connection between drooling and crucial developmental milestones, such as speech.
By recognizing the significance of drooling and employing effective management strategies, parents can empower themselves to support their child's growth and communication skills. This article delves into the nuances of drooling in toddlers, explores its potential links to speech delays, and offers practical solutions to help parents navigate these challenges with confidence.
Understanding Drooling in Two-Year-Olds: Common Concerns
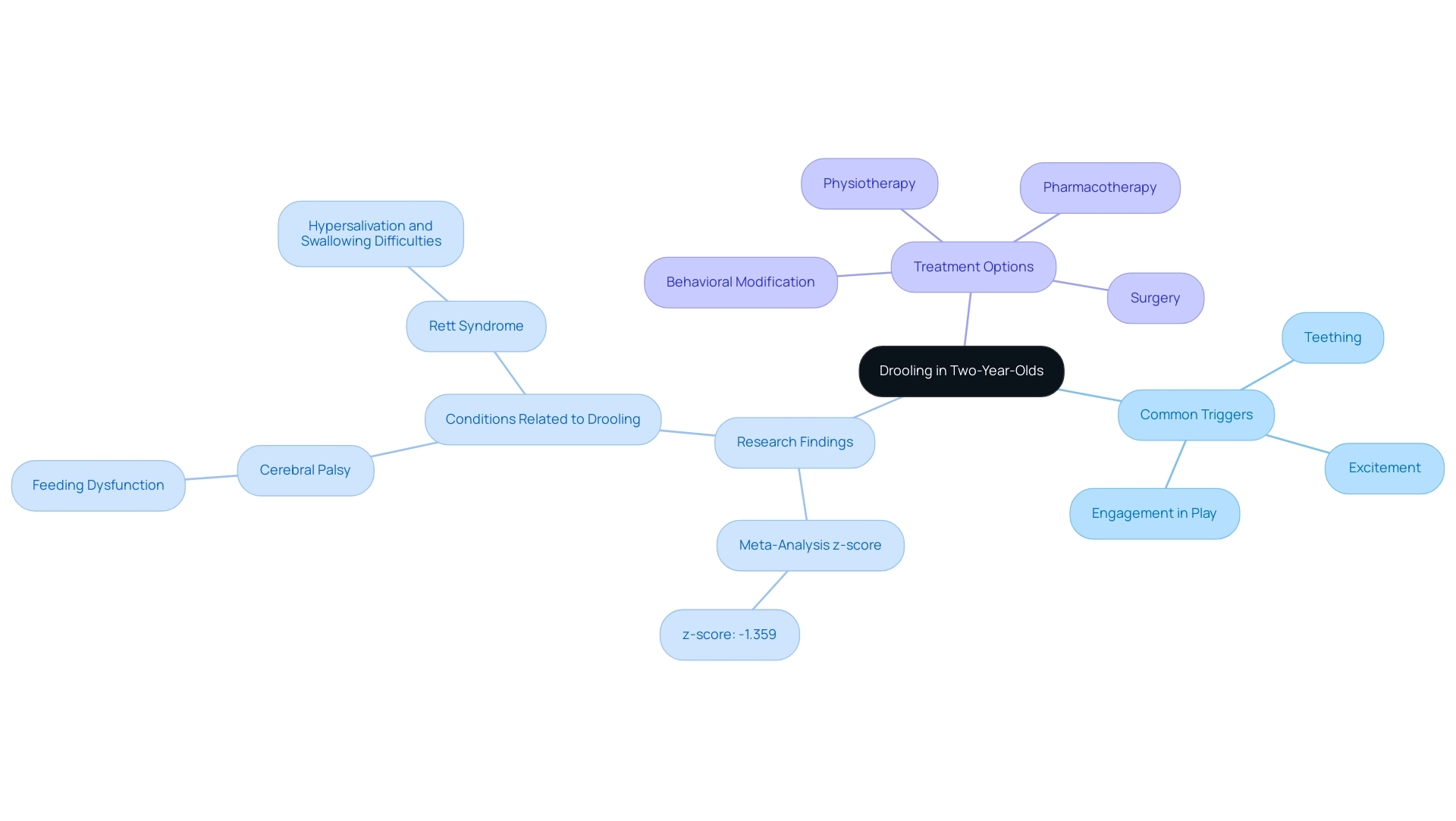
Drooling in toddlers, particularly those around the age of two, is a typical aspect of development that often does not indicate a significant issue, except in cases of 2 year old drooling speech delay. During this stage, children are still honing their oral motor skills, which can lead to heightened saliva production and occasional swallowing difficulties. Common triggers for salivation include:
- Teething
- Moments of excitement
- Simply being deeply engaged in play
Research indicates that saliva leakage prevalence in toddlers is not uncommon, with a recent meta-analysis revealing a z-score of –1.359, indicating various contributing factors to be considered. However, if a young one displays excessive saliva or experiences further symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or feeding issues related to a 2 year old drooling speech delay, it is essential for parents to consult a pediatrician. This proactive approach can help identify any underlying concerns, especially in cases related to conditions such as cerebral palsy, where feeding dysfunction can impact growth and overall health.
As C Pion Kao from Alberta Children’s Hospital notes, "Treatment options for moderate and severe salivation include physiotherapy, behavioral or biofeedback modification, pharmacotherapy and surgery." Furthermore, a case study on Rett syndrome demonstrates that excessive saliva is a common symptom resulting from hypersalivation and swallowing challenges in impacted youths. By acknowledging that excessive saliva production can be a standard part of toddler development, parents can alleviate some of their worries and better support their child's growth.
The Link Between Drooling and Speech Delay: What Parents Should Know
Research increasingly highlights a significant correlation between excessive drooling and the 2 year old drooling speech delay in toddlers. Children experiencing a 2 year old drooling speech delay often encounter obstacles in developing the oral motor abilities essential for clear communication, which can hinder their capacity to produce sounds and words effectively. This is particularly concerning as language development milestones are critical during early childhood.
Significantly, research indicates a p-value for Gross motor skills of <0.01, suggesting a strong statistical correlation between saliva flow and the 2 year old drooling speech delay. According to a case study titled 'Clinical Evaluation of Drooling,' a thorough history and physical examination are crucial for understanding drooling and its implications for language development, considering factors like age of onset and chronicity. According to specialists in the area, parents should stay alert regarding their offspring's language development, particularly if they notice a 2 year old drooling speech delay, and seek the advice of communication therapists when substantial delays or issues occur.
As noted by Mr. Sulakhan Chopra of the University of Calgary Medical Library, 'The authors are grateful to Mr. Sulakhan Chopra for assistance in the preparation of the manuscript.' Timely support, customized to the individual requirements of every young person, can significantly influence their capacity to conquer communication difficulties and improve their expressive abilities. An anticipatory strategy is crucial in guaranteeing that young individuals achieve their full potential in communication development.
Effective Strategies for Managing Drooling and Enhancing Speech Development
Managing a 2 year old drooling speech delay while encouraging language development involves a multifaceted approach that parents can confidently adopt. Here are several effective strategies:
-
Oral Motor Activities: Involve your child in enjoyable tasks that improve oral motor abilities.
Simple exercises like blowing bubbles or sipping through straws can significantly strengthen the muscles essential for speech. As research highlights, these activities are vital for developing articulation skills. However, as H.M. Clark notes, 'In general, research does not support the use of nonspeech exercises for control of salivation or for improved articulation,' suggesting the need for targeted activities.
-
Teething Relief: If teething is contributing to drooling, consider providing safe teething toys. These can alleviate discomfort and assist your little one in managing excessive saliva production during this transitional phase.
-
Frequent Swallowing Practice: Encourage your young one to practice swallowing regularly.
Drinking from a cup or taking small sips of water throughout the day can promote better swallowing habits and reduce drooling.
-
Communication Therapy: Engaging with a qualified therapist can be invaluable. They can customize particular exercises to enhance your offspring's speech clarity while tackling saliva issues, providing expert strategies that align with your offspring’s needs.
-
Consistent Monitoring: Keep a close watch on your offspring's progress. Document any changes and communicate with healthcare professionals about persistent concerns. This proactive strategy guarantees that your offspring receives the essential assistance to flourish.
Furthermore, take into account environmental elements that may affect salivation. For example, the case study titled 'Tackling Nighttime Salivation' demonstrates how a young person's sleeping position can affect salivation, emphasizing the significance of consulting healthcare professionals if problems continue. As noted in studies such as Mass et al., which examined children with familial dysautonomia, excessive salivation can indicate serious health issues that deserve attention.
By embracing these strategies, you create a nurturing environment that fosters your child's communication skills while effectively managing the challenges associated with 2 year old drooling speech delay. Remember, addressing excessive saliva production is not just about comfort; it can also indicate underlying health issues that deserve attention. If drooling persists, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, don't hesitate to seek medical advice.
Conclusion
Drooling in toddlers, particularly around the age of two, is a common developmental phase that typically does not signify serious health concerns. Understanding the normalcy of drooling, alongside recognizing when it might indicate more significant issues, empowers parents to take proactive steps. Factors such as teething, excitement, and engagement in play can all contribute to drooling, and while it is usually harmless, excessive drooling or accompanying symptoms warrant consultation with a pediatrician.
Moreover, the link between drooling and speech development cannot be overlooked. Research emphasizes the impact that difficulties with saliva control can have on oral motor skills, which are essential for clear speech. By remaining vigilant about their child's speech milestones and seeking help from speech therapists when necessary, parents can facilitate early interventions that significantly enhance their child's communication abilities.
Implementing effective strategies to manage drooling while supporting speech development is crucial. Engaging toddlers in oral motor activities, providing teething relief, encouraging swallowing practices, and maintaining consistent monitoring can all contribute to minimizing drooling and fostering effective communication. Ultimately, addressing drooling is not solely about comfort; it is a vital aspect of ensuring overall health and developmental success. By taking these proactive measures, parents can create a nurturing environment that promotes their child's well-being and communication skills, paving the way for a bright future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is drooling in toddlers a normal part of development?
Yes, drooling in toddlers, especially around the age of two, is a typical aspect of development and usually does not indicate a significant issue.
What are some common triggers for increased saliva production in toddlers?
Common triggers for salivation in toddlers include teething, moments of excitement, and being deeply engaged in play.
When should parents be concerned about their toddler's drooling?
Parents should consult a pediatrician if their toddler displays excessive saliva or experiences symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or feeding issues, particularly related to a speech delay.
What does research say about saliva leakage in toddlers?
Research indicates that saliva leakage prevalence in toddlers is not uncommon, with a recent meta-analysis revealing a z-score of –1.359, suggesting various contributing factors.
What underlying conditions could be associated with excessive drooling?
Excessive drooling can be associated with underlying concerns such as cerebral palsy, which may lead to feeding dysfunction and impact growth and overall health.
What treatment options are available for moderate to severe salivation in toddlers?
Treatment options for moderate and severe salivation include physiotherapy, behavioral or biofeedback modification, pharmacotherapy, and surgery.
Can excessive saliva production be a symptom of specific conditions?
Yes, excessive saliva production can be a common symptom in conditions like Rett syndrome, which involves hypersalivation and swallowing challenges.
How can parents support their child's growth in relation to drooling?
By understanding that excessive saliva production can be a standard part of toddler development, parents can alleviate worries and better support their child's growth.




