Introduction
Children with autism often experience heightened levels of anxiety compared to their neurotypical peers. This anxiety can manifest in various ways, including obsessive behaviors, social withdrawal, and physical symptoms like restlessness and disrupted sleep patterns. Understanding and effectively managing this anxiety is crucial for supporting children with autism.
In this article, we will explore the topic of anxiety in children with autism and discuss strategies for managing it. We will delve into calming techniques that can help children cope with anxiety, such as deep touch pressure and yoga poses. Additionally, we will highlight the importance of modeling these techniques as parents or caregivers and provide tips on creating a supportive environment for children with autism. By implementing these strategies, we can empower children with autism to navigate their anxiety and thrive.
1. Understanding Anxiety in Children with Autism
Children with autism frequently grapple with anxiety more than their neurotypical counterparts. This heightened anxiety can express itself in a multitude of ways, spanning from obsessive actions, social reclusiveness, or even physical signs like restlessness and disturbed sleep patterns. Grasping the essence of this anxiety serves as the foundational step towards its effective management.
A variety of calming techniques can be employed to help children manage their anxiety. These include deep touch pressure, a therapeutic method involving hugs to soothe anxiety. Yoga poses like the downward-facing dog, tree pose, and mountain pose can also prove beneficial in calming the senses and alleviating anxiety in children. Breathing exercises, such as taking a large inhale and exhale, can assist children in calming down.
Additionally, a simple walk can enhance energy levels, fortify muscles, and help relieve anxiety in children. Noise-canceling headphones can serve as a valuable resource for children with anxiety, as they can block background noises and reduce sounds. Listening to music, particularly classical music, can help calm children with anxiety. Learning to step away from anxiety-inducing situations can also be a beneficial technique for children.
As parents or caregivers, it's important to model these calming techniques and teach them to children. This involves introducing them to various environments and social norms.
However, it's important to remember that while we can't eliminate anxiety, we can help children manage it. This involves not avoiding things that make the child anxious but encouraging them to face their fears. Expressing positive and realistic expectations, respecting their feelings without empowering them, and not asking leading questions are all part of this process.
Moreover, it's crucial to avoid reinforcing the child's fears and instead convey confidence in anxiety-provoking situations. Keeping the anticipatory period short and thinking things through with the child helps reduce uncertainty and teaches problem-solving skills. Lastly, modeling healthy ways of handling anxiety can let kids see you managing anxiety calmly and effectively.
Remember, "The best way to help kids overcome anxiety is to help them learn to tolerate it. Over time, the anxiety will diminish," as Grace Berman, LCSW, aptly puts it.
By implementing these strategies, we can create a nurturing environment that encourages desired behaviors and helps children with autism thrive, thereby making the journey of managing anxiety less daunting.
Learn more about strategies for managing anxiety in children with autism.
2. The Link Between Autism and Anxiety: An Overview
The complex interplay between autism and anxiety has been the subject of extensive research. It is well established that the unique ways individuals with autism process and interpret their environment can lead to a predisposition to anxiety disorders. For instance, interpreting social cues, a common challenge for those with autism, can result in social anxiety. Furthermore, any deviation from their preferred routines and predictability, which forms a significant part of their comfort zone, can induce additional anxiety.
However, it's crucial to note that there are effective strategies for managing anxiety in individuals with autism, which can significantly reduce its impact on their everyday lives. These strategies range from creating a structured and predictable environment, utilizing visual aids and social stories to demystify anxiety-inducing situations, to teaching relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation. Sensory strategies can also be employed to assist in regulating sensory input. It's essential that these approaches are customized to suit the individual's specific needs and preferences. Collaboration with a professional who specializes in autism and anxiety can be beneficial in crafting a personalized plan.
In addition to these strategies, several interventions have proven effective in mitigating anxiety in individuals with autism. These interventions encompass cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), social skills training, and mindfulness-based approaches. CBT assists individuals with autism in identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, thereby developing coping strategies for anxiety. Social skills training equips them with the tools to navigate social situations, ultimately reducing anxiety during social interactions. Mindfulness-based interventions like yoga and meditation can help individuals with autism manage their anxiety by fostering a focus on the present moment. It's important to engage with a qualified professional to determine the most suitable intervention for each individual with autism.
3. Recognizing Signs of Anxiety in Your Child
Identifying anxiety in children who have autism can be a complex task due to the overlap of symptoms with those of autism itself. Yet, it's important to note that approximately 40% of young people and nearly half of adults with autism meet the clinical criteria for an anxiety disorder. Thus, it's crucial to understand the potential signs of anxiety in these individuals.
One of the most prevalent signs is excessive worry, which may manifest itself in various forms. Children might display heightened fear about everyday situations or may show avoidance behavior, particularly in social situations.
In addition, repetitive behaviors, often a hallmark of autism, can also be an indicator of anxiety. Physical symptoms can be another telltale sign. These may range from restlessness to sleep disturbances, and even include tremors, sweating, and body aches.
Diagnosing anxiety in children with autism can be challenging due to communication difficulties and the child's ability to identify and describe emotions. Therefore, it is crucial to gather information not just from observing the child, but also from parents and teachers who interact with the child daily. This comprehensive view can provide a more accurate understanding of how anxiety might be affecting the child's life.
If you notice persistent signs of anxiety in your child, it is essential to seek professional help. Treatment options often involve adapting cognitive-behavioral therapy to address the unique characteristics of autism, such as using concrete language and incorporating special interests. In some cases, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants may be recommended to help manage anxiety symptoms, but these require careful monitoring for potential side effects.
Mindfulness-based therapies and cognitive-behavioral therapy have shown promise in reducing anxiety symptoms in individuals with autism. However, more research is needed in this area, particularly for adults and those with intellectual disabilities.
Remember, it's essential to approach this issue with understanding and patience. As a parent or caregiver, your support can make a significant difference in helping your child navigate their feelings of anxiety.
4. The Impact of Anxiety on the Behavior and Development of Children with Autism
The impact of anxiety on children diagnosed with autism cannot be overstated.
It plays a pivotal role in shaping their behavior, development, and overall life quality. Anxiety often amplifies challenging behaviors, slows down the development of social skills, and can even impede their capacity to engage in daily activities and learning experiences.
Worth noting is the high prevalence of anxiety among children with autism. A meta-analysis reveals that nearly 40% of children with autism also struggle with at least one form of anxiety disorder. The manifestation of anxiety can be both physical, such as heart palpitations, and emotional, including feelings of worry and unease.
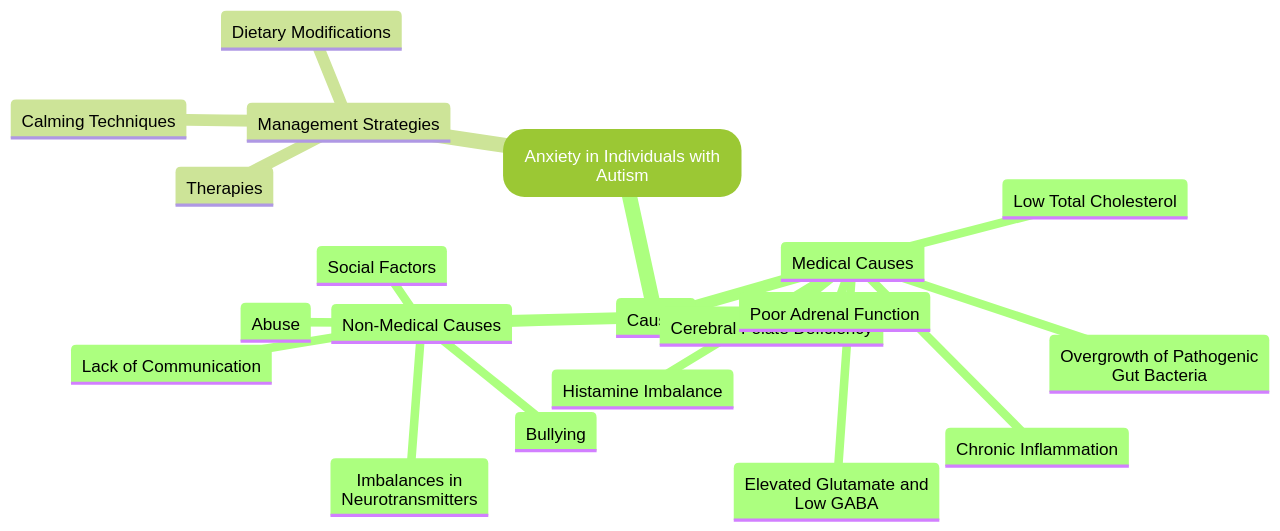
The root causes of anxiety in autism can be both medical and non-medical. Non-medical triggers often revolve around social factors such as lack of communication, bullying, and abuse. On the other hand, medical causes can stem from chronic inflammation, low total cholesterol, cerebral folate deficiency, and imbalances in neurotransmitters like glutamate and GABA.
Addressing anxiety in individuals with autism requires a multi-faceted approach. Therapies including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), and neurofeedback can provide significant relief. Additionally, mindfulness practices, deep pressure activities, and regular exercise also play a key role in managing anxiety.
Dietary modifications can also contribute significantly to managing anxiety. Steering clear of inflammatory foods such as sugar, dairy, gluten, and soy can help reduce inflammation and anxiety. Supplements like inositol, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), GABA, L-theanine, and valerian root, as well as prescription medications like propranolol, memantine, and hydroxyzine, can be beneficial.
Moreover, teaching children with autism calming techniques can be extremely beneficial. These can range from giving hugs, practicing yoga poses, deep breathing, taking walks, using noise-canceling headphones, listening to relaxing music, to learning to distance themselves from anxiety-inducing situations.
Parents and caregivers play an essential role in teaching and modeling these techniques. Alicia Trautwein, an experienced autism parenting writer, shares invaluable insights on parenting neurodiverse families and offers guidance on calming techniques for children with anxiety. Her free e-book, "Embracing Neurodiversity," is a valuable resource.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the root cause of anxiety in individuals with autism is crucial. Seeking out a functional medicine doctor and specialists can be a significant step in effectively managing anxiety symptoms. The journey may be challenging, but with the right interventions and support, children with autism can navigate their world with less anxiety and more confidence.
5. Strategies for Managing Anxiety in Children with Autism
Addressing anxiety in children with autism necessitates a multifaceted approach. This includes cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to guide them in comprehending and navigating their emotional landscape, mindfulness practices for stress relief, and structured routines to offer a sense of predictability and safety. Furthermore, equipping them with coping mechanisms and fostering a supportive ambiance play a crucial role in managing their anxiety levels.
Incorporating calming techniques such as deep touch pressure, often provided through comforting hugs, can significantly alleviate anxiety. Yoga exercises, particularly poses like the downward-facing dog and mountain pose, have been shown to soothe the senses and mitigate anxiety in children. Breathing exercises, mainly deep inhales and exhales, can serve as a potent tool in anxiety management.
Outdoor walks are known mood enhancers and can help diffuse anxiety. For children who may be overwhelmed by excessive noise, noise-cancelling headphones can shield them from anxiety-inducing sounds. Classical music, known for its calming effect, can also be a valuable resource in these situations.
Teaching children to identify and step away from situations that trigger their anxiety is an empowering strategy that can help them manage their anxiety independently over time. It's essential for parents and caregivers to model these calming techniques, demonstrating their effectiveness and encouraging children to adopt them.
The power of a supportive environment cannot be overstated. Expressing positivity and setting realistic expectations can provide children with a sense of security and confidence. It's important to acknowledge their feelings without empowering their fears, and to avoid reinforcing their anxieties.
Helping children strategize their responses to anxiety-provoking situations, keeping the anticipatory period short, and modeling healthy ways of handling anxiety can help them better manage their emotional responses. Remember, it's not about eliminating anxiety but helping children navigate through it. Reinforcing their efforts and hard work in facing their fears is a crucial part of this journey.
By adopting these strategies, we can help children with autism manage their anxiety, equipping them with the tools they need to thrive.
6. Role of ABA Therapy in Addressing Anxiety Issues
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is an instrumental tool in alleviating anxiety symptoms in children diagnosed with autism. The methodology behind ABA therapy is the use of positive reinforcement to incentivize desired behaviors, subsequently reducing those linked to anxiety. This approach not only aids in behavior modification but also equips children with effective coping mechanisms. It further enhances their social skills, which can contribute significantly to diminishing their anxiety levels.
In the course of the therapy, calming techniques are employed, such as embracing, practicing yoga, deep breathing, and taking serene walks, to help children manage their anxiety. These techniques are taught to children, and caregivers or parents are encouraged to model these approaches, thereby cultivating an environment conducive to their mental well-being.
The therapy is further enriched by incorporating resources like books, audios, and courses focusing on peaceful parenting. These resources cover a broad spectrum of topics ranging from managing anger and aggression, dealing with body image and eating issues, to addressing concerns such as bullying, depression, and divorce. The guidance provided through these resources helps parents in raising children who are emotionally and socially intelligent, resilient, and considerate.
ABA therapy also provides support for special needs, offering tips and resources for handling social anxiety, phobias, and selective mutism. The therapy is designed to create a more peaceful home environment and raise children who are not just happy but also responsible.
The effectiveness of ABA therapy is further evidenced by the testimonials of parents, expressing their gratitude for the guidance and support provided. The therapy is seen as a practical tool that brings about positive changes in the behavior of children with autism, ultimately leading to a significant reduction in their anxiety levels.
In conclusion, ABA therapy is not just a treatment but a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety in children with autism, fostering their development and enhancing their quality of life.
Discover how ABA therapy can help children with autism manage anxiety.
7. Parent Advocacy: Empowering Parents to Support Their Children’s Mental Health Needs
The task of supporting a child's mental health needs can be a daunting one, especially when your child is navigating the challenges of autism and anxiety.
However, as parents, we are uniquely positioned to advocate for our children's rights and to ensure that they have access to the necessary support and services they need.
The current pandemic has seen a significant rise in mental health challenges among children. For instance, the prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms in youth has doubled compared to pre-pandemic numbers. It's crucial to remember that children may express their struggles differently and these signs can change as they grow, so it's important to keep an open line of communication with them.
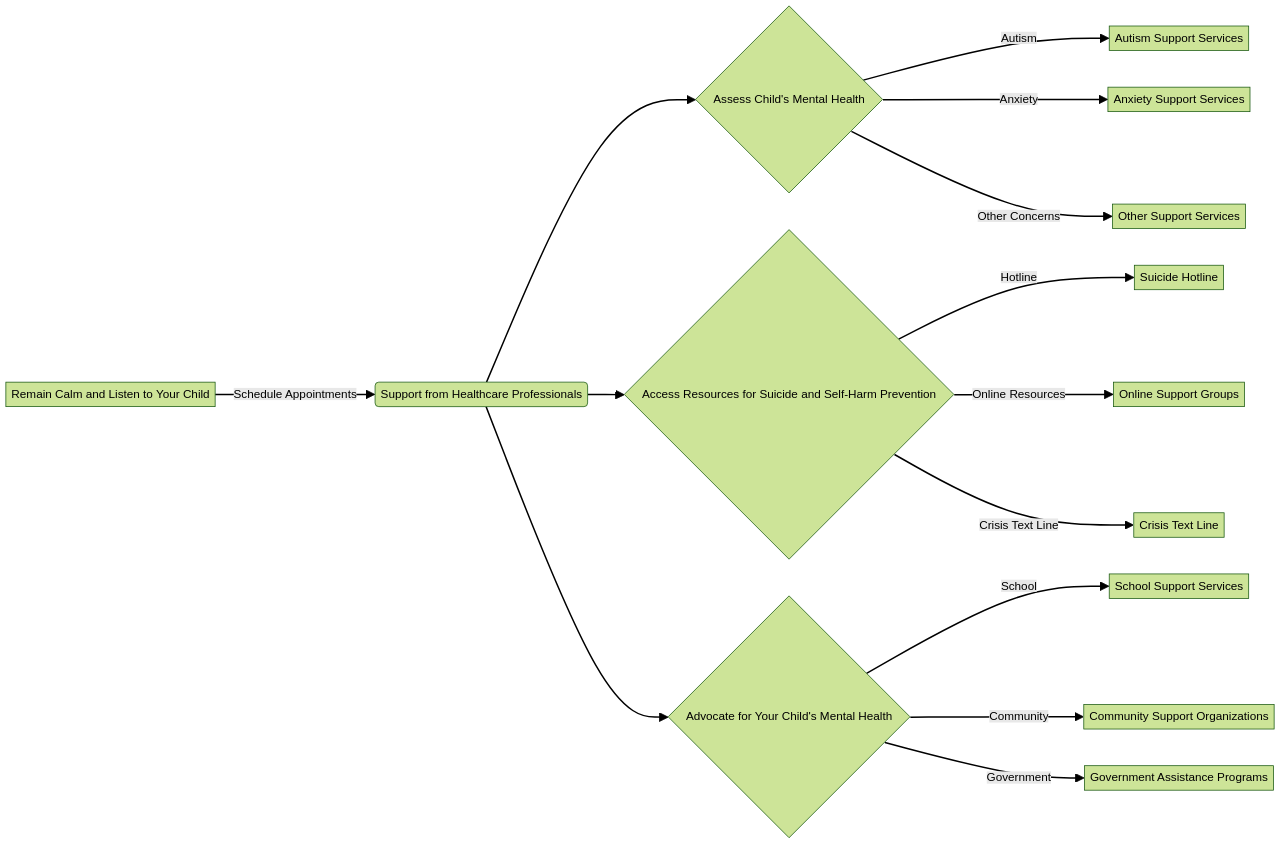
In the face of such challenges, there are a few steps you can take to support your child. When your child opens up about their struggles, it's critical to remain calm and avoid reacting negatively. Trust your child and listen to their feelings without judgment. This will assure your child that they are not alone, and it's a sign of strength to seek help.
Next, schedule an appointment with your family doctor to discuss your child's symptoms and feelings. While waitlists for mental health services can be long, parents have found success in checking in with the agency they are on waitlists with for appointment cancellations. It's also important to keep your child informed about the process and reassure them that help is on the way.
Part of supporting your child's mental health also involves taking care of your own mental health. Reach out to family support partners for nonjudgmental support and assistance. Remember, it's okay to ask for help, and it's crucial to prioritize your own mental health as well.
In addition to these steps, it's also crucial to develop a safety plan and access resources for suicide and self-harm prevention, if needed. Joining a network of parents can also provide much-needed support and advice, helping you understand the mental health and educational systems better and learn about your child's rights and treatment options.
In the end, it's about empowering parents with the right knowledge and resources to improve the mental health outcomes for children with autism and anxiety. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and help is always available.
8. Building a Positive Behavior Support System to Manage Anxiety
Establishing a robust positive behavior support system is a proven technique for mitigating anxiety in children diagnosed with autism. This process entails the formation of a nurturing environment that not only endorses positive behaviors but also diminishes the stimuli that trigger anxiety. This strategy could encompass the establishment of structured routines, setting clear expectations, and the utilization of positive reinforcement to stimulate desired behaviors.
A child's environment plays a significant role in shaping their behavior, and this is particularly true for children with autism. By creating an atmosphere that encourages positive behavior, parents and caregivers can help their children manage the symptoms of anxiety. This supportive environment can be achieved by providing a structured routine that offers predictability and security. It's important to remember that children with autism often thrive on routine, and a disruption in their schedule can lead to an increase in anxiety.
Setting clear expectations is another crucial component of a positive behavior support system. Children with autism may struggle with understanding social norms and expectations, which can lead to feelings of anxiety. By providing clear and consistent expectations, parents and caregivers can help alleviate some of this anxiety.
Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool in encouraging desired behaviors. By rewarding positive behavior with praise or rewards, children are more likely to repeat these behaviors in the future. This can significantly reduce instances of anxiety and help children with autism feel more confident and secure.
It's also crucial to remember that every child is unique, and what works for one child may not work for another. Therefore, it's essential to tailor the positive behavior support system to the individual needs of the child. This might involve a combination of different strategies, such as visual schedules, social stories, and sensory activities.
Ultimately, the goal of a positive behavior support system is to provide children with autism the tools they need to manage their anxiety effectively. This not only improves their quality of life but also empowers them to reach their full potential.
9. Navigating Support Services for Children with Autism and Anxiety
Navigating the labyrinth of support services for youngsters struggling with autism and anxiety can seem like a daunting task for parents.
Yet, with the right direction and access to appropriate resources, this journey can transform into a more manageable experience. The first step lies in comprehending the spectrum of available services and understanding the rights of your child. It's also essential to champion their needs proactively.
Support services come in various forms including therapeutic interventions, educational assistance, and community resources. Therapy can range from behavioral therapy to speech and language therapy, each catering to different needs of your child. Educational support can be in the form of Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or 504 plans, aimed at ensuring your child's unique educational needs are met. Community resources can include local support groups and recreational activities designed for children with autism and anxiety.
It's important to remember that children with autism often interpret anxiety as anger. This distinction is important for parents to comprehend to better understand their child's emotional landscape. Moreover, these children may have frequent meltdowns, stemming from constant stress and heightened sensory sensitivities. Even minor changes in routine or sensory environment can act as trigger points for these meltdowns.
Children with autism often grapple with recognizing and labeling their own emotions, a condition known as alexithymia. This makes it critical for parents to model sensory supports and validate their child's emotions to help reduce stress and prevent meltdowns.
While learning about neurotypical social skills can be beneficial for children with autism, it's important to not enforce this as a mask they need to wear. Open and honest conversations about emotions can help these children understand and navigate social situations better.
Remember, each child is unique and what works for one may not work for another. Therefore, navigating this journey requires patience, understanding, and continuous learning. The goal should always be to create an environment where your child feels supported and understood.
Conclusion
Children with autism often experience heightened levels of anxiety compared to their neurotypical peers. This anxiety can manifest in various ways, including obsessive behaviors, social withdrawal, and physical symptoms like restlessness and disrupted sleep patterns. Understanding and effectively managing this anxiety is crucial for supporting children with autism.
In this article, we explored the topic of anxiety in children with autism and discussed strategies for managing it. We delved into calming techniques that can help children cope with anxiety, such as deep touch pressure and yoga poses. Additionally, we highlighted the importance of modeling these techniques as parents or caregivers and provided tips on creating a supportive environment for children with autism. By implementing these strategies, we can empower children with autism to navigate their anxiety and thrive.
The broader significance of the ideas discussed in this article lies in the positive impact they can have on the lives of children with autism. By understanding the unique challenges they face and providing them with effective tools to manage their anxiety, we can greatly improve their overall well-being. These strategies not only help alleviate immediate symptoms but also equip children with lifelong coping mechanisms that will serve them well into adulthood. It is our responsibility as parents, caregivers, and society as a whole to create an inclusive and supportive environment where children with autism can thrive.
To support your child in managing their anxiety, start implementing these strategies today. Model calming techniques such as deep touch pressure and yoga poses, create a structured and predictable environment, and provide a nurturing space where your child feels understood and supported. By taking these steps, you can make a significant difference in helping your child navigate their anxiety and lead a fulfilling life.




