Overview
This article delves into the nuances of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, shedding light on the intricate nature of their symptoms. It compassionately highlights that these disorders frequently co-occur, which can complicate both diagnosis and management. Understanding this complexity is crucial for parents and caregivers seeking clarity in their loved ones' experiences.
The importance of tailored treatment strategies cannot be overstated. Comprehensive approaches that encompass therapy, medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive networks are essential in enhancing overall well-being. By addressing these aspects, we can foster a nurturing environment that promotes healing and growth.
As you navigate this journey, remember that you are not alone. Sharing experiences and seeking guidance can make a significant difference. We encourage you to explore available resources and connect with others who understand the challenges you face. Together, we can cultivate a supportive community that empowers individuals and families alike.
Introduction
In a world where mental health challenges are increasingly acknowledged, grasping the complexities of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety is crucial for effective management and support. These conditions often intertwine, weaving a web of symptoms that can complicate both diagnosis and treatment.
With ADHD characterized by inattention and impulsivity, OCD defined by obsessive thoughts and compulsive actions, and anxiety manifesting as overwhelming fear or worry, individuals may find themselves navigating a tumultuous landscape filled with emotional and behavioral hurdles.
As research sheds light on the prevalence and co-occurrence of these disorders, it becomes evident that awareness and education are essential for families and professionals alike. This article explores the nuances of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, delving into their symptoms, the challenges of co-occurrence, and the strategies needed to foster resilience and well-being.
Together, let’s embark on this journey towards understanding and support.
Defining ADHD, OCD, and Anxiety: Key Concepts and Symptoms
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is marked by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Many individuals face challenges such as difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and an inability to remain still. It’s important to note that ADHD affects three times as many males (13.0%) as females (4.2%), highlighting the need for awareness in understanding how this disorder manifests differently across genders.
On the other hand, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that individuals feel compelled to perform to alleviate anxiety. Common behaviors might include excessive hand-washing or compulsive checking. Anxiety disorders often accompany ADHD and OCD, provoking intense fear or worry, which can lead to physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and restlessness.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for seeking appropriate support and treatment. Current statistics reveal that approximately 6.0% of adults in the United States are affected by ADHD, equating to an estimated 15.5 million diagnosed adults, as noted by Brooke S. Staley. Among children aged 5–17 years, the highest occurrence of ADHD is found in those with public insurance coverage at 14.4%, while uninsured children show the lowest occurrence at 6.3%.
From 2003 to 2011, there was a significant increase in ADHD diagnoses among children, with a staggering 42% rise in reported cases. This underscores the importance of awareness and early intervention. Understanding the interplay between ADHD, OCD, and anxiety is essential for effective management, as these conditions often co-exist, complicating diagnosis and treatment strategies.
If you or someone you know is navigating these challenges, seeking support and resources is a vital step. Sharing experiences can foster a sense of community and understanding, so consider reaching out to others who may be facing similar situations.
The Intersection of ADHD and OCD: Understanding Co-Occurrence
Navigating the co-occurrence of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety can be incredibly challenging for individuals and their families. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder often leads to impulsive behaviors that can interfere with the compulsive actions typical of obsessive-compulsive disorder. This interplay underscores the complex relationship between ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. Such impulsiveness may hinder the ability to follow rituals or routines, exacerbating the distress associated with these conditions.
On the other hand, anxiety stemming from OCD can amplify the distractibility and inattention commonly linked to ADHD, creating a frustrating cycle that complicates daily life. It's essential to recognize how these disorders can intertwine, affecting overall well-being.
Recent research emphasizes the importance of understanding this intricate relationship. For example, a study involving 93 adult Japanese patients with OCD revealed a significant prevalence of symptoms related to ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, indicating that these conditions often overlap. The Executive Overload Model proposed by Abramovitch and colleagues sheds light on this complexity, suggesting that obsessive thoughts in OCD can overwhelm executive functioning, leading to symptoms that may resemble ADHD.
This insight implies that what may seem like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in patients with ADHD, OCD, and anxiety could actually reflect cognitive deficits associated with OCD. This highlights the critical need for thorough evaluations and tailored treatment approaches.
Experts stress the necessity for ongoing research to delineate the unique characteristics of ADHD and OCD symptoms. As Amitai Abramovitch, PhD, notes, "Future studies into the distinct traits of shared ADHD and OCD symptoms may assist in unraveling this intricate matter." Such investigations could significantly help in clarifying the complex dynamics between these disorders, ultimately leading to more effective treatment strategies.
Understanding the interaction between ADHD, OCD, and anxiety is vital for developing comprehensive strategies that address the unique challenges faced by individuals coping with these disorders. The ongoing calls for more research into this relationship further underscore the importance of clarifying these complexities, especially in adult populations. Together, we can work towards better support and resources for those affected.
Diagnosis and Treatment Challenges: Navigating ADHD and OCD
Diagnosing ADHD, OCD, and anxiety can be quite challenging, especially because their symptoms often overlap, leading to potential misdiagnoses. It's crucial for clinicians to conduct thorough evaluations that include behavioral assessments and detailed interviews with caregivers. This approach helps capture the full spectrum of symptoms and ensures that no aspect is overlooked. Recent findings highlight the importance of considering ADHD, OCD, and anxiety symptoms during the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neglecting these can result in treatment approaches that may not be suitable for the individual.
When it comes to treatment options, a combination of medication and therapy is typically recommended. However, finding the right balance can be particularly difficult. For example, stimulant medications often prescribed for ADHD, such as extended-release methylphenidate (ER MPH), might unintentionally exacerbate OCD symptoms in certain individuals. This situation underscores the need for a tailored approach that considers the unique presentation of each disorder.
Statistics reveal that misdiagnosis rates for ADHD, OCD, and anxiety are alarmingly high, with studies suggesting that up to 30% of individuals with ADHD may also meet the criteria for OCD. Such misdiagnoses can impede effective treatment. A systematic review by researchers from Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, including Amitai Abramovitch, emphasizes the necessity for clinicians to be vigilant in recognizing the nuances of these comorbid conditions. As Andrew Mittelman notes, the critical nature of this issue is highlighted in "Comorbidity Between Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Across the Lifespan: A Systematic and Critical Review."
Moreover, case studies examining familial patterns of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety suggest that genetic factors may influence the co-occurrence of these disorders, further complicating the diagnostic process. These insights reinforce the importance of clinicians staying informed about the latest research and adopting a comprehensive, individualized approach to treatment.
In summary, the complexities surrounding the diagnosis and treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder require a nuanced understanding and a commitment to ongoing education in the field. By confronting these challenges directly, clinicians can enhance outcomes for individuals managing these interconnected conditions. If you or someone you know is navigating these challenges, seeking support from professionals who understand the intricacies of these disorders can make a significant difference.
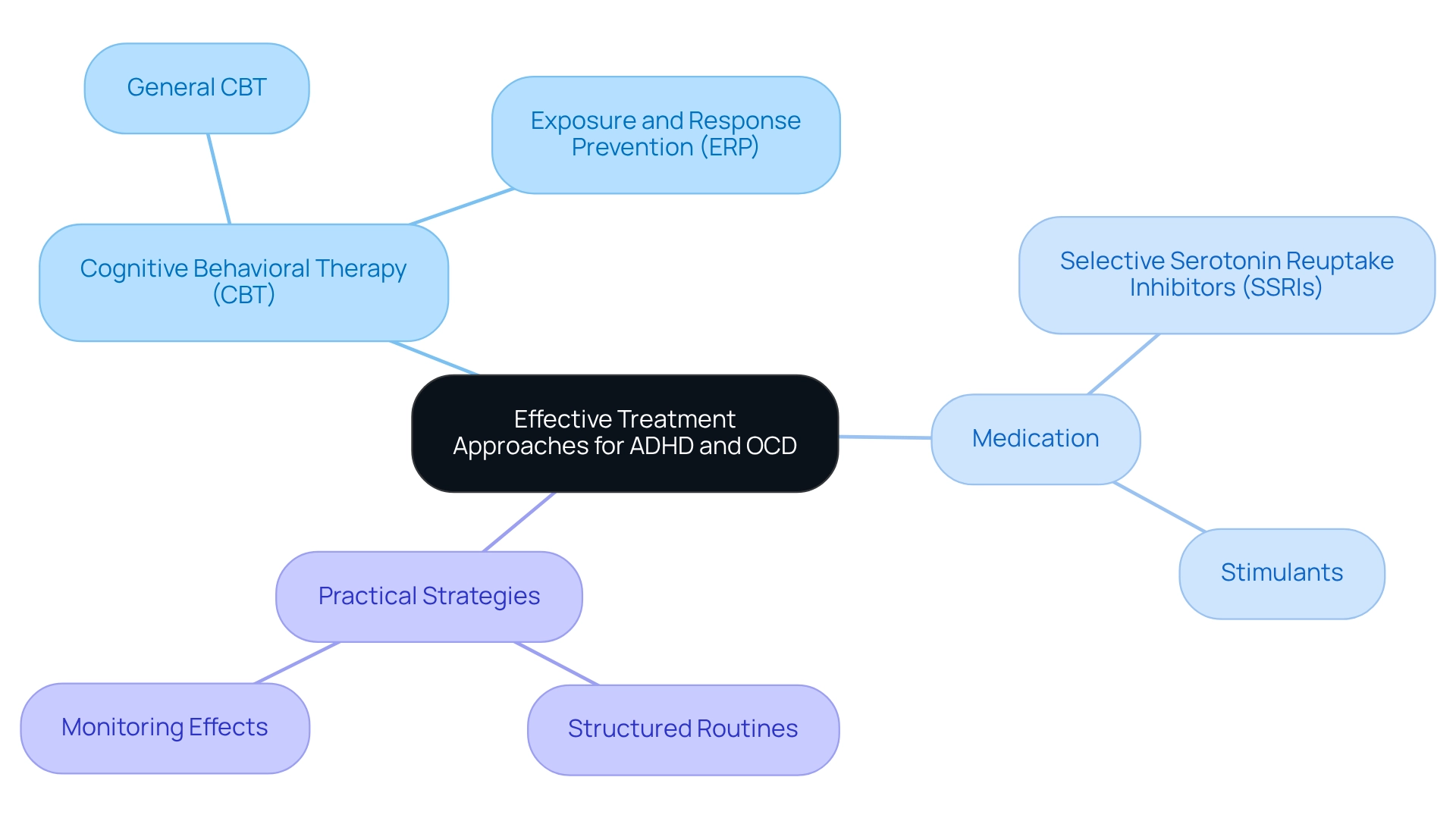
Effective Treatment Approaches: Strategies for Managing ADHD and OCD Together
Effectively managing ADHD, OCD, and anxiety together requires a thoughtful and multifaceted strategy. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as a highly effective treatment for these disorders, primarily by reshaping negative thought patterns and behaviors. Notably, Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is a specialized CBT method that offers particular benefits for individuals with OCD, enabling them to confront their fears without resorting to compulsive behaviors.
Incorporating structured routines can significantly assist individuals facing attention difficulties, promoting organization and alleviating anxiety levels. Research shows that establishing consistent daily schedules can enhance focus and reduce feelings of overwhelm, especially for those grappling with ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. Moreover, caregivers are encouraged to explore medication options, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for OCD and stimulant treatments for ADHD, to help manage these conditions effectively.
It is essential to monitor the effects of these medications closely to ensure they yield optimal outcomes.
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of CBT in treating ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, suggesting that a strong therapeutic alliance and clear patient expectations are crucial predictors of successful treatment outcomes. For instance, a randomized controlled trial demonstrated that metacognitive therapy led to greater reductions in inattentive symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder compared to supportive therapy, underscoring the importance of tailored therapeutic approaches. This research was jointly funded by the Economic and Social Research Council and Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust, with no conflicts of interest reported by the authors.
In practical applications, integrating ERP within CBT frameworks has shown promising results, with significant improvements reported in managing OCD symptoms. The attrition rate for these therapies is around 15.2%, reflecting a solid commitment from participants to engage in their treatment journey. As J D Feusner noted, "Mechanisms of cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder involve robust and extensive increases in brain network connectivity."
By utilizing these effective strategies, caregivers can empower individuals to navigate the challenges of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, fostering resilience and enhancing mental well-being. Sharing experiences and seeking support can make a meaningful difference in this journey.
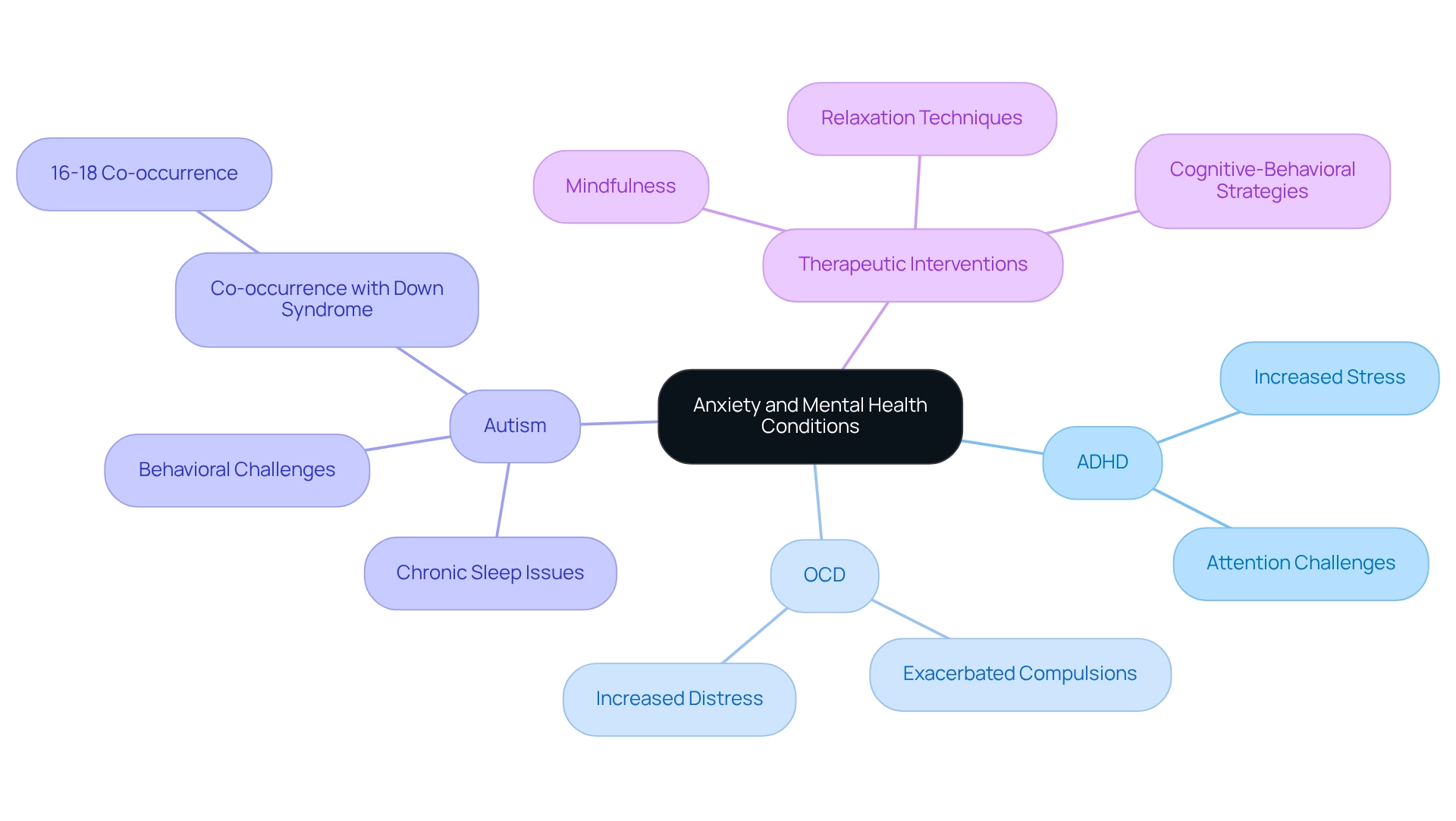
Understanding Anxiety's Role: The Impact on ADHD and OCD
Anxiety profoundly influences conditions like ADHD, OCD, and autism, often intensifying symptoms and complicating treatment approaches. Many parents and caregivers of children with ADHD report that their loved ones experience heightened stress due to challenges with attention and organization. Similarly, those with OCD may find their compulsions exacerbated by underlying anxiety, creating a cycle that leads to increased distress and functional difficulties.
Chronic sleep issues are frequently reported among parents of autistic children, with many adults on the autism spectrum also facing sleep difficulties. These challenges can further escalate stress and behavioral concerns, making it crucial to address them effectively.
To combat stress, a variety of therapeutic interventions have shown promise. Mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, and cognitive-behavioral strategies are among the most effective methods for alleviating stress's impact on ADHD, OCD, and anxiety symptoms. Real-life examples highlight how these interventions can lead to improved outcomes and overall well-being.
For instance, consider a case study involving individuals with Down syndrome and autism, which reveals that 16-18% of those with Down syndrome also have autism. Understanding the co-occurrence of these conditions is essential, as effective management of anxiety and related issues can significantly enhance mental health and support.
Statistics indicate that anxiety can worsen symptoms of ADHD, OCD, and autism, underscoring the need for parents and professionals to implement effective strategies. By focusing on comprehensive treatment approaches that include stress management, individuals can look forward to a more positive outlook. As Cleveland Clinic’s mental health experts emphasize, addressing anxiety is vital not only for symptom reduction but also for improving the quality of life for those affected by ADHD, OCD, and anxiety.
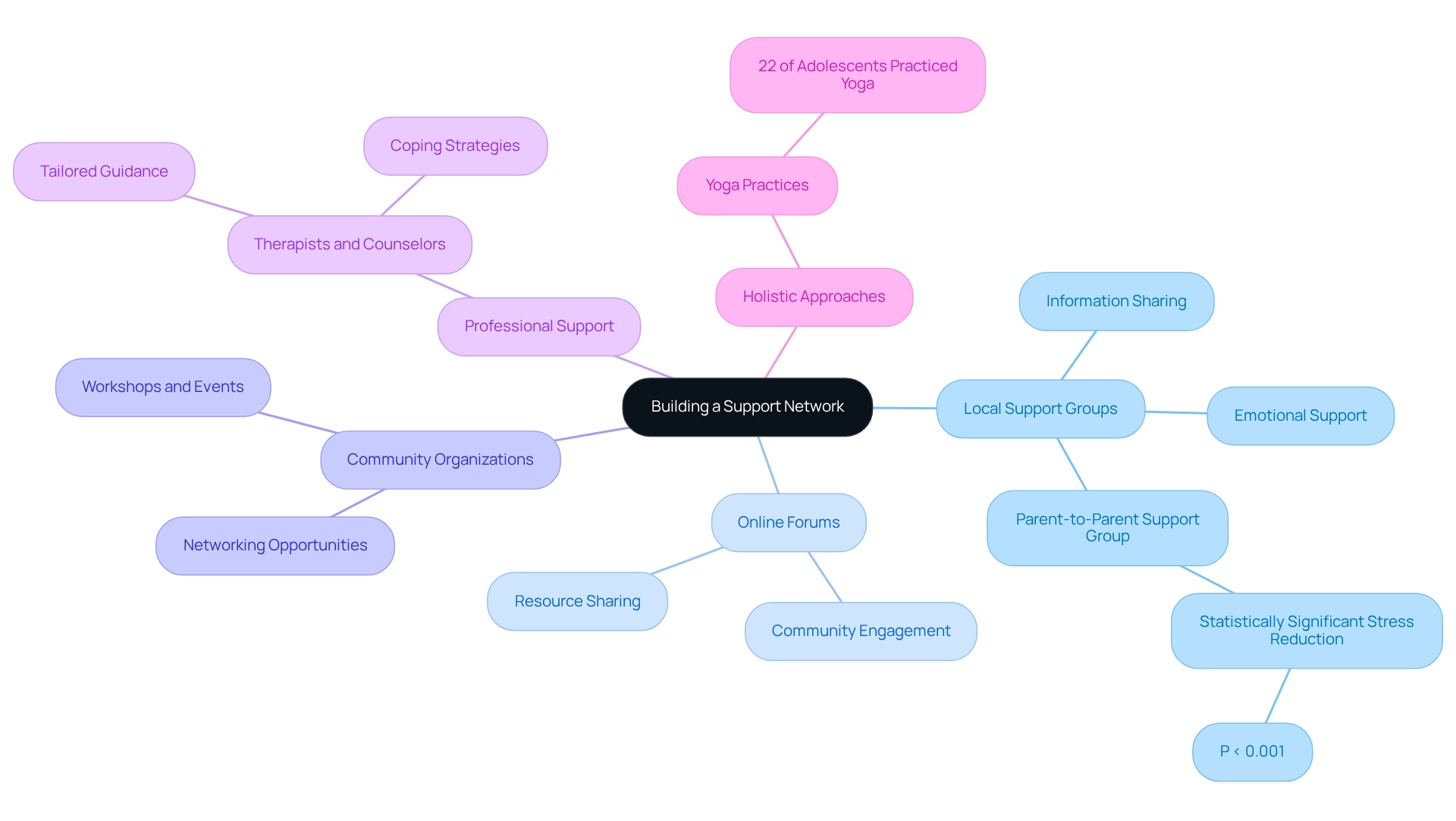
Building a Support Network: Resources for Families and Individuals
Creating a strong support system is essential for families navigating the challenges of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, especially given the significant comorbidity of these issues. Local support groups, online forums, and community organizations offer invaluable resources, providing both information and emotional backing. Engaging with other families who share similar experiences fosters a sense of belonging and significantly alleviates feelings of isolation.
For instance, a recent study on a Parent-to-Parent Support Group for caregivers of children with ASD and attention difficulties revealed a statistically significant decrease in stress and worry levels among participants (P < 0.001). This finding underscores the effectiveness of such networks. As Edna Grunblatt observed, "Silvia Brem and Edna Greenblatt have contributed equally to the work," emphasizing the collaborative nature of support in these communities. Additionally, professionals like therapists and counselors can offer tailored guidance, equipping families with effective coping strategies.
Statistics show that 22% of adolescents have practiced yoga in the past year, highlighting the growing interest in holistic approaches that can complement traditional therapies. By engaging in these support networks, families can not only share their challenges but also gain insights from expert viewpoints, ultimately enhancing their ability to manage issues related to ADHD, OCD, and anxiety together.
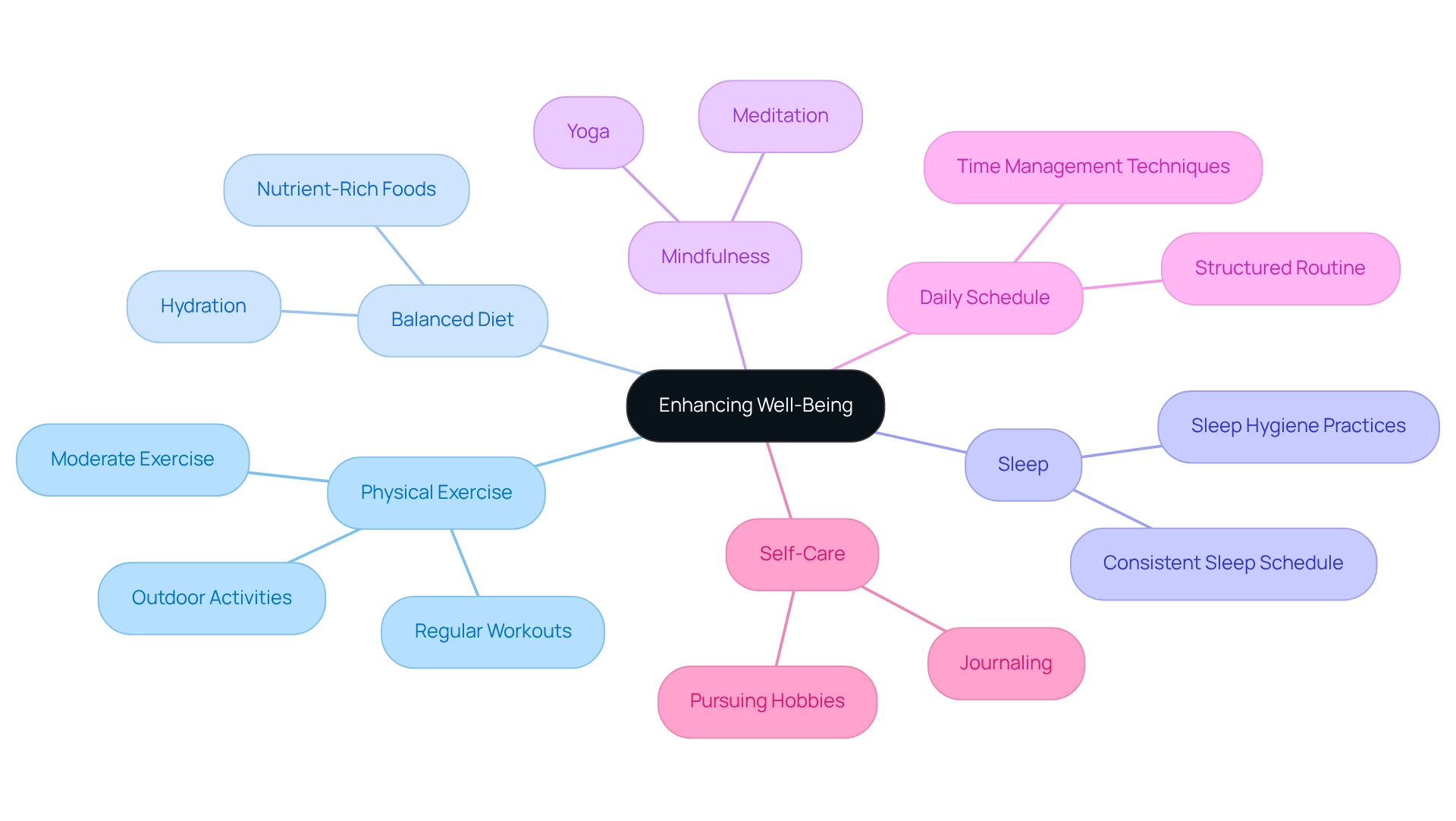
Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care: Enhancing Well-Being
Lifestyle changes are essential for effectively managing conditions such as ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. Engaging in regular physical exercise can significantly enhance mental health outcomes for individuals facing these challenges. Research shows that exercise boosts mood and cognitive function, making it a critical part of a holistic management strategy.
A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, supports brain health, while getting enough sleep is vital for emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Incorporating mindfulness practices, like meditation and yoga, can further ease anxiety and improve focus. These techniques promote relaxation and help individuals develop better coping strategies. Establishing a consistent daily schedule provides the structure that many people with attention difficulties find beneficial, reducing feelings of chaos and enhancing time management skills.
Self-care practices, such as journaling and pursuing hobbies, play a significant role in building emotional resilience. These activities allow individuals to express their thoughts and feelings, contributing to better mental health. For example, a case study on lifestyle changes for managing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and OCD revealed that participants who engaged in regular journaling experienced reduced anxiety levels and improved emotional clarity.
Furthermore, expert insights highlight the importance of integrating physical activity into daily routines. Research indicates that even moderate exercise can lead to substantial improvements in the symptoms of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, reinforcing the connection between physical health and mental well-being. As noted by MB, a consultant for P1Vital, "Incorporating lifestyle changes is vital for individuals dealing with ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, as it complements traditional treatment methods."
Additionally, ADHD is recognized as a disability under the Equality Act in the UK, underscoring the importance of effective management strategies. Findings suggesting potential overlaps in neural dysfunction among ADHD, OCD, and anxiety further emphasize the need for personalized lifestyle changes. By prioritizing these adjustments, individuals can create a supportive environment that enhances their ability to manage OCD and stress effectively.
The extensive research, featuring 125 reviews published from 1991 to 2023, supports the discussion on OCD and stress management, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach.
Advocacy and Education: Empowering Parents and Caregivers
Continuous learning and support are vital for parents and caregivers of individuals navigating ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. Staying informed about the latest research, treatment options, and support resources empowers families to make informed decisions that can profoundly affect their children's lives. For instance, a 2022 survey revealed that nearly 78% of children diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder also have at least one co-occurring condition, with worry being one of the most prevalent.
This underscores the importance of parents understanding the complexities of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, as well as their interconnections. Notably, the Revised Children's Manifest Anxiety Scale score was recorded at 10.8 for the OCD-only group, indicating a significant level of anxiety that deserves attention.
Engaging in advocacy initiatives, such as participating in community awareness campaigns or support groups, is essential for enhancing understanding and reducing stigma surrounding ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. As highlighted by the CDC, the number of U.S. children identified with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder has surged, with an additional 1 million children diagnosed between 2016 and 2022. This increase emphasizes the critical role of parental advocacy in fostering understanding and support for affected families.
Moreover, current trends in education regarding attention disorders and OCD reveal the need for comprehensive resources tailored for parents. Educational initiatives that address the intersection of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety can equip parents with the essential knowledge to navigate their children's challenges effectively. For example, a case study titled "Co-occurring Conditions in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" illustrates that many children diagnosed with this condition also face other simultaneous issues, complicating their treatment and management.
Real-world examples of educational resources include workshops, online courses, and community support groups that encourage collaboration among families.
By becoming informed advocates, parents can better support their children experiencing ADHD, OCD, and anxiety while contributing to a more inclusive community. Advocacy efforts not only raise awareness but also foster the development of effective strategies for managing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and anxiety, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for children and their families. Furthermore, ongoing research into synaptic genes linked to ADHD and the structural differences in OCD patients, such as reduced grey matter in various brain regions, further highlights the complexities of these conditions and the necessity for informed advocacy.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of ADHD, OCD, and anxiety is essential for effective management and support. Each condition presents unique symptoms, yet they often coexist, complicating diagnosis and treatment. This interplay necessitates a comprehensive approach that takes into account their overlapping characteristics. Misdiagnosis is common, highlighting the need for thorough evaluations and tailored treatment strategies that address the specific challenges posed by each disorder.
Effective management relies on a combination of therapeutic interventions, lifestyle modifications, and the establishment of strong support networks. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), particularly through techniques like Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), has proven beneficial for individuals facing these intertwined challenges. Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity, mindfulness practices, and structured routines can significantly enhance overall well-being and resilience.
Advocacy and education are pivotal in empowering families and caregivers. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options fosters better decision-making, while community engagement helps mitigate stigma and raise awareness. As the prevalence of these conditions continues to rise, the collective effort of families, professionals, and researchers will be crucial in improving outcomes for individuals affected by ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. By embracing a holistic approach that combines education, support, and effective treatment strategies, a better quality of life can be achieved for those navigating these complex mental health challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
ADHD is marked by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, leading to challenges such as difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and an inability to remain still.
How does ADHD prevalence differ between genders?
ADHD affects three times as many males (13.0%) as females (4.2%), indicating a need for awareness about how the disorder manifests differently across genders.
What is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)?
OCD is characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that individuals feel compelled to perform to alleviate anxiety, such as excessive hand-washing or compulsive checking.
How are anxiety disorders related to ADHD and OCD?
Anxiety disorders often accompany ADHD and OCD, leading to intense fear or worry, which can manifest as physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and restlessness.
What are the statistics regarding ADHD in the United States?
Approximately 6.0% of adults in the U.S. are affected by ADHD, equating to an estimated 15.5 million diagnosed adults. Among children aged 5–17 years, the highest occurrence of ADHD is in those with public insurance coverage at 14.4%.
What trend has been observed in ADHD diagnoses from 2003 to 2011?
There was a significant 42% increase in reported ADHD cases among children during this period, highlighting the importance of awareness and early intervention.
How do ADHD, OCD, and anxiety interact with one another?
ADHD can lead to impulsive behaviors that interfere with the compulsive actions typical of OCD, while anxiety from OCD can amplify distractibility and inattention associated with ADHD, creating a frustrating cycle.
What recent research has been conducted regarding ADHD, OCD, and anxiety?
A study involving 93 adult Japanese patients with OCD revealed a significant prevalence of symptoms related to ADHD, OCD, and anxiety, indicating that these conditions often overlap.
What is the Executive Overload Model?
This model suggests that obsessive thoughts in OCD can overwhelm executive functioning, leading to symptoms that may resemble ADHD, highlighting the need for thorough evaluations and tailored treatment approaches.
Why is ongoing research important for understanding ADHD and OCD?
Experts stress the necessity for ongoing research to delineate the unique characteristics of ADHD and OCD symptoms, which could assist in developing more effective treatment strategies for individuals coping with these disorders.




