Overview
The article titled "Understanding Adult Autism Treatment: A Complete Tutorial on Effective Therapies" offers a compassionate exploration of the various effective therapies available for treating adults with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
It draws attention to a diverse range of therapeutic approaches, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Interoception Therapy
By emphasizing the significance of personalized treatment plans, the article seeks to address the unique challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum. This tailored approach not only aims to enhance social skills and emotional regulation but also strives to improve overall quality of life.
It invites readers to reflect on their experiences and consider how these therapies might provide support for their loved ones.
Introduction
In a world where understanding and support for adults with autism is increasingly vital, the complexities of this condition deserve our compassionate attention. Adults on the autism spectrum face unique challenges in social interactions, communication, and sensory sensitivities, navigating a landscape filled with both obstacles and opportunities. Recent studies illuminate the prevalence of co-occurring conditions, highlighting the urgent need for tailored interventions and therapies that address their distinct experiences.
From Cognitive Behavioral Therapy to innovative approaches like Interoception Therapy and Expressive Art Therapy, a variety of strategies are emerging to empower adults with autism. As awareness grows, so too does our commitment to fostering inclusive environments that promote well-being and enhance the quality of life for this diverse community. Together, we can create a supportive network that embraces their experiences and nurtures their potential.
Overview of Autism in Adults: Key Characteristics and Challenges
Autism presents a complex array of characteristics, prominently featuring difficulties in social interactions, communication challenges, and heightened sensory sensitivities. Many individuals on the spectrum struggle to understand social signals, leading to feelings of isolation and anxiety in social situations. Recent studies indicate that the prevalence of co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety and depression, is significant among this population, further complicating their daily experiences.
Notably, the prevalence of ASD among women ranges from 0.72% in Arkansas to 0.97% in Virginia, underscoring the need for increased awareness and tailored support services. Furthermore, findings from a recent study on ASD prevalence can assist states in recognizing the necessity for diagnosing and delivering services to individuals with ASD who remain undiscovered. For instance, a sensitivity analysis of ASD prevalence estimates revealed that individuals aged 6–17 years displayed a higher estimated prevalence of 2.38% compared to 2.21% in the 3–17 years age group, emphasizing the importance of age selection in understanding the characteristics of the condition.
Recognizing these complex challenges is essential for creating customized approaches to adult autism treatment that effectively meet the specific needs of individuals on the spectrum. Additionally, expert opinions highlight that difficulties with social interaction are pervasive, with real-world examples illustrating the profound impact these challenges have on personal and professional relationships. As Eric Jackson notes, "The content provided in this blog has been reviewed by University of Maryland Medical System providers or affiliates who are subject matter experts."
By acknowledging and addressing these traits, caregivers and experts can cultivate a more nurturing atmosphere that encourages improved outcomes for individuals navigating life with developmental disorders.
Exploring Effective Therapies for Adult Autism: An Overview
Effective adult autism treatment for individuals with developmental disorders encompasses a variety of methods, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Interoception Therapy
- Expressive Art Therapy
Each of these treatments addresses specific challenges associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, such as managing anxiety, improving communication, enhancing emotional control, and fostering self-awareness.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy has demonstrated sustained effectiveness over time. Studies indicate that a significant proportion of patients maintain recovery even years after treatment. This approach focuses on altering negative thought patterns and behaviors, making it especially beneficial for individuals navigating the complexities of daily life.
Applied Behavior Analysis continues to be a cornerstone in autism treatment, with recent statistics underscoring its application among adult populations. A systematic review identified:
- 11 prospective studies
- 10 community referral studies
- 8 universal screening studies
These studies reported on 1,658 toddlers with ASD. This highlights the treatment's crucial role in early intervention and its adaptability for older adults.
Interoception Therapy, which helps individuals develop awareness of their internal bodily signals, is gaining traction as a means to enhance emotional regulation and self-management. This treatment is particularly relevant for adults who may find it challenging to identify and respond to their emotional states.
Expressive Art Therapy provides a creative outlet for self-expression, enabling individuals to communicate feelings and experiences that may be difficult to articulate verbally. This approach can facilitate emotional healing and improve social skills through collaborative art-making experiences.
A notable case study titled "Consistency, Certainty, and Change" illustrates the autistic preference for routine and predictability. It emphasizes the importance of organized treatment sessions with clear goals, which can significantly enhance engagement and effectiveness. The findings suggest that establishing a consistent environment and addressing the challenges of change can help autistic clients participate more effectively in treatment, even when they initially resist cognitive adjustments.
Incorporating insights from experts, such as Ralph Moller's assertion that "the significance of personalization in interventions for individuals on the spectrum cannot be overstated," underscores the need for tailored approaches that meet individual needs. Involving a family member as an 'executive secretary' can further support planning and adaptable thinking during counseling sessions, ensuring that the therapeutic process remains effective and responsive to the client's evolving requirements.
As we move through 2025, the landscape of therapies for individuals on the spectrum continues to evolve. Ongoing research and practical implementations are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment options for adults with the condition.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addressing Anxiety and Behavioral Challenges
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a highly effective intervention for adult autism treatment, particularly in addressing anxiety and behavioral challenges. This therapeutic method empowers individuals to identify and change negative thought patterns, nurturing a more positive mindset. Techniques such as exposure treatment play a crucial role in gradually easing anxiety linked to social interactions or specific triggers, enabling individuals to navigate their environments with increased confidence.
Research highlights that financial stability significantly impacts psychological well-being, accounting for 75.8% of the variance in overall Psychological Stress Index (PSI) scores (p < 0.001). This underscores the vital need for accessible mental health resources, including tailored CBT programs that can enhance coping mechanisms for anxiety. However, fail-safe N calculations reveal that numerous new studies are necessary for non-significance, pointing to ongoing research challenges in this area.
Despite the proven efficacy of CBT for children and adolescents, there remains a considerable gap in research focused on individuals with high-functioning conditions. Only seven studies have specifically explored cognitive-behavioral treatment trials for university students with developmental disorders, highlighting an urgent need for targeted interventions in this demographic. A review of current literature on CBT for anxiety disorders indicates that while the therapy is beneficial for younger groups, there is a pressing need for adult autism treatment programs tailored specifically for adults, particularly those in educational settings.
Practical applications of CBT illustrate its advantages in enhancing the quality of life for adults with developmental disorders. For instance, case studies reveal that individuals who engage in CBT report notable reductions in anxiety levels and improved coping strategies. One significant case study involved a customized CBT program that included problem-solving skills training, demonstrating enhanced psychological well-being among mothers of children with developmental disorders.
As the field continues to evolve, expert insights stress the necessity of developing CBT techniques that address the unique challenges faced by adults with developmental disorders, ensuring they receive the support needed to thrive.
In summary, CBT stands out as a vital resource for adults with developmental conditions, offering practical strategies to manage anxiety and enhance overall well-being. As research progresses, focusing on adult autism treatment will be essential in bridging existing gaps and fostering a more inclusive approach to autism care.
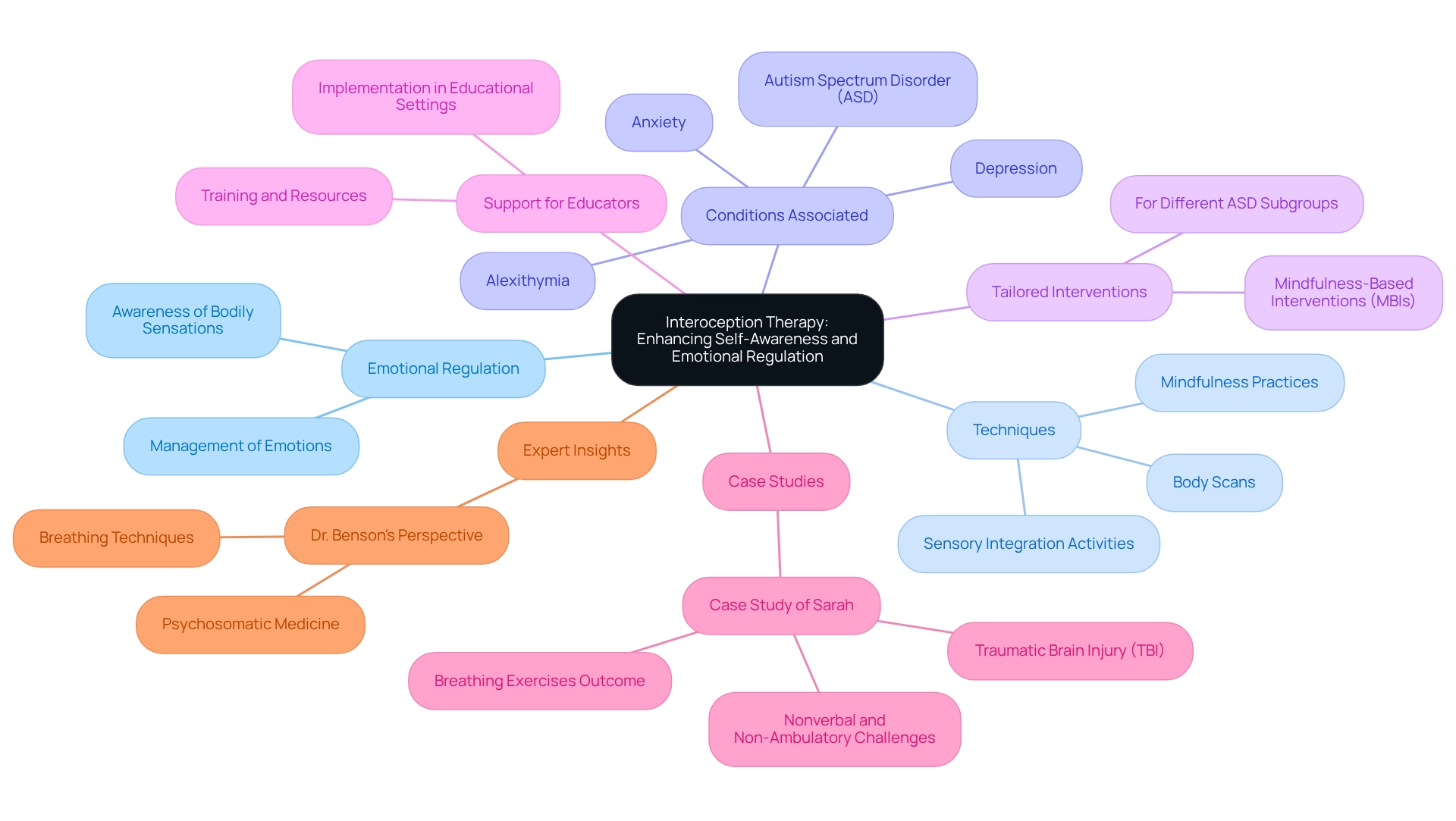
Interoception Therapy: Enhancing Self-Awareness and Emotional Regulation
Interoception treatment plays a crucial role in enhancing a person's awareness of internal bodily sensations, which is vital for effective emotional regulation. By equipping individuals with the skills to notice and understand these signals, interoception treatment empowers them to manage their emotions more effectively. Techniques employed in this therapy often include mindfulness practices, body scans, and sensory integration activities, all designed to foster a deeper understanding of how emotions manifest physically.
Research indicates that atypical interoception is frequently associated with conditions such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), anxiety, and depression. This underscores the importance of tailored interventions that address the unique needs of different ASD subgroups. Mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have shown promise in helping individuals enhance their emotional awareness and regulation skills; however, there remains a significant lack of resources specifically tailored for young patients. This gap highlights the urgent need for interventions that cater to the diverse needs of individuals with ASD.
Furthermore, the need for expanded support for educators in implementing these therapeutic approaches is increasingly clear. By providing educators with essential materials and training, we can improve the efficacy of interoception practices in educational environments, ultimately benefiting students with autism.
A compelling case study illustrates the success of interoception techniques in real-life situations. Sarah, a ten-year-old girl who became nonverbal and non-ambulatory following a traumatic brain injury, faced significant challenges in emotional and cognitive regulation. Through the use of nonverbal methods and visual aids, she learned to identify and label her bodily states, linking them to her emotions. The introduction of breathing exercises not only helped her relax during hygiene tasks but also resulted in a smoother and less distressing experience overall. This situation highlights the broader significance of interoception treatment for emotional management in individuals on the autism spectrum, particularly regarding adult autism treatment, as comparable methods can be adapted to support their distinct challenges.
Expert views further emphasize the importance of adult autism treatment, especially concerning interoception. Dr. Benson, a professor at Duquesne University, notes that breathing techniques derived from psychosomatic medicine are instrumental in helping children notice, label, and manage their bodily sensations and emotions. This method is especially beneficial for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and is a key component of adult autism treatment, as it promotes a deeper understanding of their emotional environment and improves their ability to navigate everyday challenges.
As ongoing studies continue to explore the connection between mindfulness techniques and interoception therapy, the necessity for enhanced support for teachers and caregivers becomes increasingly evident. By prioritizing these therapeutic methods, we can significantly enhance emotional regulation and overall well-being for individuals on the spectrum.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Building Skills and Confidence in Adults
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a structured and evidence-based approach that emphasizes the reinforcement of positive behaviors while teaching new skills. For individuals with autism, ABA is not just a method; it is a lifeline that has proven crucial in improving communication, social skills, and daily living abilities. Research reveals that less than half (46%) of children continue treatment for 24 months, highlighting the urgent need for effective and sustained interventions, including adult autism treatment, which can also provide significant benefits to adults.
ABA employs techniques such as task analysis and reinforcement strategies, tailored to meet the unique strengths and goals of each individual. This customization is essential, as it allows for the development of personalized treatment plans that foster independence and build confidence. As Ralph Moller aptly noted, "The significance of personalization in therapy for individuals on the spectrum cannot be overstated."
The results of ABA are especially significant in enhancing communication abilities among individuals with autism. Real-world examples illustrate how individuals have successfully utilized ABA techniques to express themselves and engage in social interactions. For instance, case studies reveal that adults who participated in ABA programs showed remarkable improvements in both verbal and non-verbal communication, leading to stronger relationships and increased participation in community activities.
Moreover, the focus on collaboration and development within the ABA field is vital. ASD Media is dedicated to fostering a supportive community that encourages sharing experiences and learning from one another. This support is essential for the ongoing development of effective therapies.
Expert opinions consistently highlight the role of ABA in adult autism treatment, underscoring its effectiveness in skill-building. Continued research and policy advancements are crucial to ensure that all individuals on the spectrum receive the comprehensive support they need to thrive in society. As our understanding of the spectrum condition expands, the demand for effective therapies like ABA becomes increasingly vital, paving the way for success stories that inspire hope and progress in the community.
Alternative Augmentative Communication (AAC): Facilitating Communication for Adults
Alternative Augmentative Communication (AAC) encompasses a diverse range of methods and tools designed to assist individuals facing communication challenges. For those on the autism spectrum, AAC includes valuable resources such as speech-generating devices, communication boards, and mobile applications that facilitate expression. These tools not only provide alternative communication methods but also empower individuals to convey their thoughts, needs, and emotions, significantly enhancing their social interactions and overall quality of life.
Current statistics highlight a growing acknowledgment of AAC's vital role in adult autism treatment, evidenced by a marked increase in its adoption among adults with autism. Research indicates that AAC methods can lead to improved communication outcomes, fostering greater independence and social engagement. For example, a case study titled "Discrimination through Privileging Speech" sheds light on the systemic challenges faced by nonspeaking Autistic individuals who depend on alternative communication methods.
This study emphasizes the necessity for a paradigm shift in valuing communication, advocating for the inclusion of non-speech communication methods in both research and practice.
Expert opinions further validate the effectiveness of AAC tools in overcoming communication barriers. Many professionals in the field stress that AAC not only aids in expressing needs but also enhances social skills development, enabling individuals to engage more fully in their communities. Real-life stories illustrate how AAC has transformed the lives of individuals on the autism spectrum, allowing them to partake in meaningful conversations and forge connections.
As the demand for effective communication strategies continues to grow, the landscape of AAC tools is evolving. Technological innovations are leading to more accessible and user-friendly devices, making it easier for adults with developmental differences to communicate effectively—an essential aspect of adult autism treatment. Notably, between 2010 and 2021, there has been an astonishing 5,852% increase in demand for certified ABA therapists, underscoring the urgent need for effective communication strategies.
Moreover, 94% of researchers rate articles on AAC as excellent or good, reinforcing the credibility of this field. A commitment to respecting various communication styles is crucial in fostering an inclusive environment where everyone can thrive. Additionally, the Reframing Autism team acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands they operate on, reflecting a dedication to inclusivity and respect for diverse cultures.
Sensory Diets: Tailoring Sensory Experiences for Better Outcomes
Sensory diets are personalized strategies designed to meet the unique sensory needs of individuals on the spectrum. These strategies incorporate a variety of sensory activities aimed at enhancing daily functioning. Techniques such as deep pressure, swinging, or fidgeting work to regulate sensory input and reduce the risk of sensory overload. Research indicates that customized sensory diets can significantly improve concentration, emotional regulation, and overall well-being, leading to more positive daily experiences.
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of sensory diets for individuals on the spectrum, showing that they can lead to meaningful improvements in emotional control and behavioral responses. For instance, a recent analysis showed that those who participated in structured sensory activities experienced a notable reduction in anxiety and an enhanced ability to focus on tasks. This finding aligns with results from the Aggression Questionnaire—Short Form (AQ-SF), where total aggression scores ranged from 12 to 60, underscoring the potential of sensory diets in managing challenging behaviors.
Real-world examples vividly demonstrate the beneficial impact of sensory diets. One case study focused on adults with developmental differences who integrated specific sensory activities into their routines, resulting in improved social interactions and a greater sense of community engagement. Participants reported that activities like tactile play and rhythmic movement not only bolstered their emotional stability but also helped them forge connections with peers. This mirrors findings from the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD), which indicated a net benefit score of 2.2 in addressing gastrointestinal symptoms and behavioral concerns, suggesting that dietary interventions can enhance overall health and behavior.
Expert insights further emphasize the critical role of sensory experiences in treating adult autism for individuals on the spectrum. Professionals advocate for the inclusion of sensory diets in therapeutic approaches, highlighting their importance in adult autism treatment and their transformative potential for those on the spectrum. As research advances—demonstrating that therapeutic diets can alleviate symptoms over time—the understanding of how to effectively implement sensory diets is becoming clearer. This progress paves the way for innovative strategies to support individuals with autism in 2025 and beyond.
Expressive Art Therapy: Fostering Emotional Expression and Social Skills
Expressive art practices, such as painting, drawing, and music, empower individuals to articulate their emotions and experiences. For those on the spectrum, this therapeutic method serves as a vital resource for emotional expression and social skill enhancement, offering a non-verbal channel for communication. Engaging in art activities not only fosters personal expression but also cultivates a sense of community and connection, essential for encouraging social interaction and alleviating feelings of isolation.
Current research underscores the effectiveness of expressive art in promoting emotional expression as a treatment for adults with autism. Participants often report increased emotional awareness and improved interpersonal skills following art sessions. A systematic review of existing literature highlights the positive reception of art interventions, yet it also reveals a significant gap in robust research specifically targeting individuals with learning disabilities.
This gap is particularly concerning given the poor quality of current studies, emphasizing the urgent need for more comprehensive research in this area.
As we look toward 2025, the benefits of expressive art treatment for individuals with developmental disorders, especially in the context of adult autism treatment, continue to gain recognition. Data indicates that this approach can lead to better emotional regulation and enhanced social interaction. Notably, art therapy has been shown to reduce anxiety and improve overall wellness, making it a valuable resource for those navigating the complexities of autism. Interestingly, it is worth noting that 17% of registered art practitioners in the United States are male, comprising around 850 male professionals, which adds a layer of diversity to the field.
Real-life stories illustrate the transformative impact of expressive art techniques. Many individuals have shared how art enables them to convey feelings that are difficult to express verbally. This therapeutic method not only aids in emotional expression but also fosters a supportive environment where individuals can connect with peers, thereby enhancing their social skills and reducing feelings of isolation.
As the field progresses, ongoing discussions among specialists emphasize the importance of integrating expressive art practices into comprehensive support systems for adult autism treatment. Dr. Catherine Carr, with support from the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR), advocates for prioritizing emotional expression through creative outlets. By opening new avenues for connection and understanding, we can ultimately enrich the lives of those affected by this condition.
Additionally, art therapy is typically facilitated by one therapist, though there are instances of co-facilitation involving an art therapist and an assistant psychologist, which can further enhance the therapeutic experience.
The Role of Exercise in Enhancing Well-Being for Adults with Autism
Engaging in regular physical exercise is crucial for enhancing the health of individuals on the autism spectrum. Research shows that exercise not only uplifts mood but also alleviates anxiety and improves social skills. Individual exercise interventions have been shown to produce significantly greater advancements in both motor and social areas compared to group activities.
Activities such as yoga, swimming, and team sports provide important physical and social advantages, nurturing a sense of community and belonging among participants.
The 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans highlight the necessity of consistent exercise across all age groups, stressing its role in bettering health outcomes and lowering the risk of chronic diseases. These guidelines advocate for the incorporation of physical activity into everyday life, which can lead to notable enhancements in mental health and overall quality of life for individuals on the spectrum. Nevertheless, further research is essential to unravel the intricate relationship between physical activity and ASD, emphasizing the ongoing exploration in this domain.
Additionally, various sports, including:
- Swimming
- Minibasket
- Horse riding
- Karate
have demonstrated benefits in improving sensory interaction, motor skills, and even assisting in correcting stereotypical behaviors in children with ASD. As Katrina L. Piercy noted, "Physical activity fosters normal growth and development and can make people feel, function, and sleep better and reduce the risk of many chronic diseases." This underscores the idea that physical activity plays a significant role in enhancing functioning and sleep quality while diminishing the risk of chronic diseases.
Real-life examples reveal how structured exercise programs can substantially uplift the mood and mental well-being of individuals on the autism spectrum, reinforcing the importance of integrating physical activity into adult autism treatment.
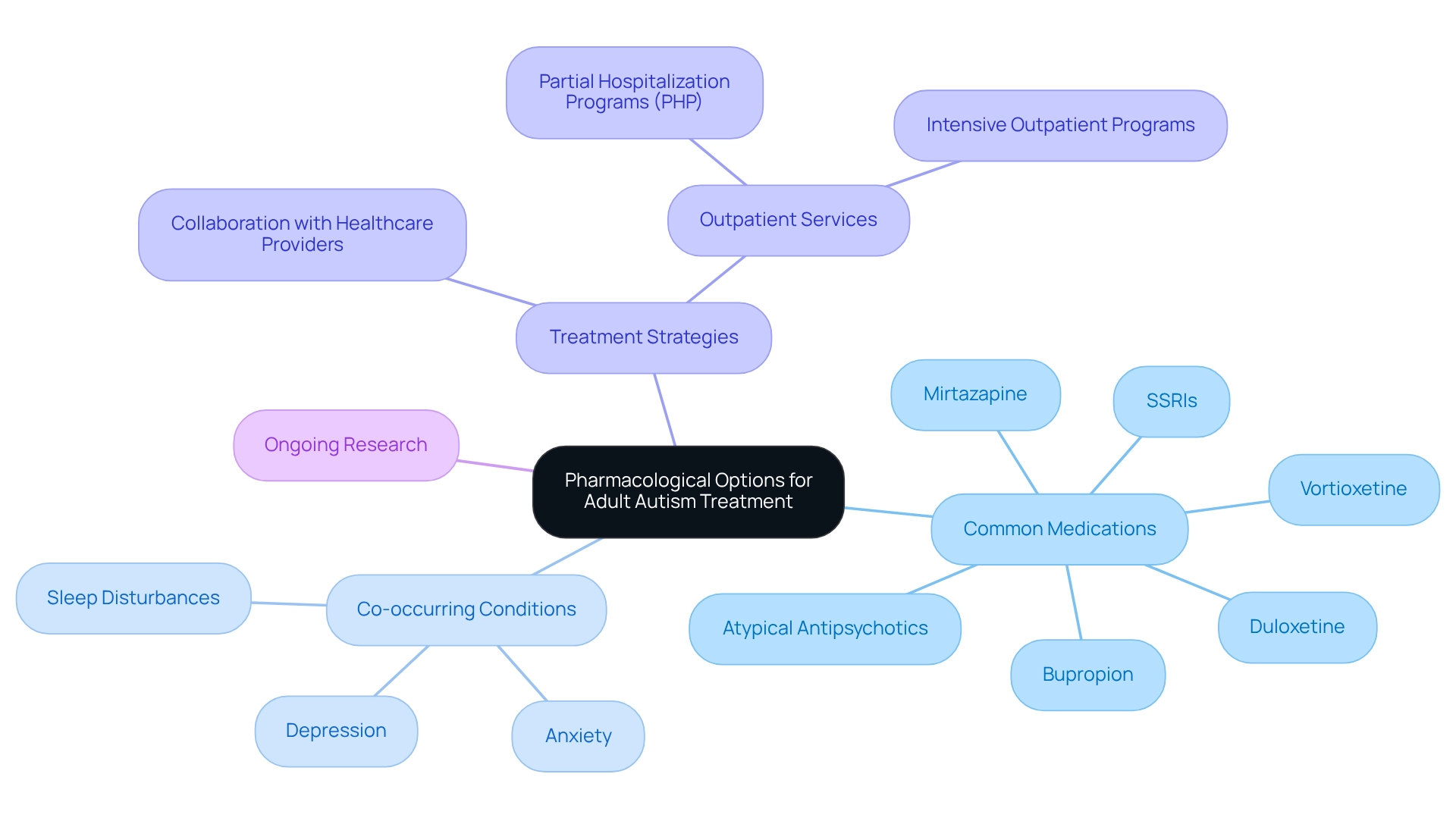
Medical Interventions: Understanding Pharmacological Options for Adults
Adult autism treatment for individuals on the autism spectrum often involves pharmacological interventions designed to alleviate symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and irritability. Among the most commonly prescribed medications are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics, which have shown varying degrees of effectiveness in managing these symptoms. Recent studies suggest that medications like duloxetine, mirtazapine, bupropion, and vortioxetine are now recommended as first-line treatments for depression in people with autism, signaling a shift towards more personalized pharmacological strategies.
As highlighted by ASD Media, these medications are often prioritized over conventional SSRIs, which can sometimes lead to behavioral activation in individuals with autism. It’s important to recognize that around 40% of adults undergoing autism treatment face co-occurring mental health conditions, necessitating careful attention to medication management. Close collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for both patients and caregivers to identify the most suitable pharmacological options, weighing potential benefits against side effects. This teamwork empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment strategies, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
Case studies examining sleep disturbances in individuals with developmental disorders reveal the complexities of managing co-occurring conditions. These studies indicate that sleep issues are significantly more prevalent in this population, affecting both children and adults, and can lead to challenging daytime behaviors that impact the quality of life for both those with the condition and their families. By gaining insight into the relationship between medication and these co-occurring conditions, individuals can more effectively navigate their adult autism treatment options. Furthermore, outpatient services, including Partial Hospitalization Programs (PHP) and Intensive Outpatient Programs, offer flexible treatment avenues that cater to the unique needs of autistic individuals.
As the landscape of developmental disorder treatment continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest pharmacological options and research advancements. This includes ongoing studies into the effectiveness of SSRIs and atypical antipsychotics, which play a significant role in shaping best practices for symptom management. By fostering a collaborative approach to treatment, individuals can unlock the potential for improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
Additional Resources and Tools: Supporting Adults with Autism and Their Families
There is a wealth of resources available to support individuals on the spectrum and their families. Online communities, support groups, and educational materials can make a significant difference. Organizations such as Autism Speaks and the Autism Society offer vital information and resources to help navigate the complexities associated with autism. Recent statistics show that:
- 74% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a diploma, compared to 86% of all students.
- 19% of autistic students earn a certificate, while 8% do not finish high school, in contrast to 5% of all students.
These figures underscore the critical need for robust educational support systems. Local organizations also play a pivotal role in fostering a sense of community and shared experiences, allowing individuals and families to connect in meaningful ways.
The impact of online communities is profound; they provide a platform for adults with developmental differences to share their stories, seek guidance, and build relationships. These virtual spaces can serve as lifelines, particularly for those who may feel isolated in their daily lives. For example, supervised apartments offer a practical solution for individuals striving for independence while still needing some support.
In this model, professionals visit several times a week to assist residents, enabling them to manage daily tasks with periodic oversight. This balance of autonomy and guidance not only promotes personal independence but also incorporates community members, colleagues, and friends into the support network, enhancing overall quality of life.
Community assistance is vital for families of adults with developmental disorders, especially when it comes to accessing adult autism treatment. It provides both emotional support and practical resources. Engaging with support groups can lead to valuable insights and strategies for navigating challenges. As the landscape of autism support evolves, staying informed and connected remains essential for empowerment and ongoing support throughout the autism journey.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by adults with autism is not just important; it is essential for fostering a more inclusive and supportive society. The complexities of autism spectrum disorder call for a multifaceted approach that encompasses effective therapies, community support, and tailored interventions. From Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Interoception Therapy to Expressive Art Therapy and Applied Behavior Analysis, a variety of strategies are available to empower individuals and enhance their quality of life.
Recognizing co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety and depression, is crucial, as they significantly impact the well-being of adults on the spectrum. By prioritizing comprehensive treatment plans that include both therapeutic and medical interventions, we can effectively address the diverse needs of this population. Moreover, the role of community resources, support groups, and online networks is vital in creating an environment where individuals with autism feel connected and understood.
As awareness and understanding of autism continue to grow, so does the potential for positive change. By embracing tailored approaches and fostering open dialogue, we can enhance the experiences of adults with autism, allowing them to thrive and contribute meaningfully to their communities. The journey towards inclusivity and support for individuals with autism is ongoing, and our collective efforts will pave the way for a brighter, more equitable future. Let us work together to ensure that every adult with autism feels valued and supported, making their voices heard in our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main characteristics of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by difficulties in social interactions, communication challenges, and heightened sensory sensitivities. Individuals on the spectrum often struggle to understand social signals, resulting in feelings of isolation and anxiety.
What co-occurring conditions are common among individuals with autism?
Many individuals with autism experience co-occurring conditions such as anxiety and depression, which can complicate their daily experiences.
What is the prevalence of ASD among women in different states?
The prevalence of ASD among women ranges from 0.72% in Arkansas to 0.97% in Virginia, indicating the need for increased awareness and tailored support services.
How does age affect the prevalence estimates of ASD?
A sensitivity analysis revealed that individuals aged 6–17 years have a higher estimated prevalence of 2.38% compared to 2.21% in the 3–17 years age group, highlighting the importance of age selection in understanding the characteristics of the condition.
What treatment methods are effective for adult autism?
Effective treatment methods for adult autism include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Interoception Therapy, and Expressive Art Therapy, each addressing specific challenges associated with neurodevelopmental disorders.
How does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) help individuals with autism?
CBT helps individuals with autism by altering negative thought patterns and behaviors, particularly in managing anxiety and improving daily life coping strategies. It has shown sustained effectiveness over time.
What role does Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) play in autism treatment?
ABA is a cornerstone treatment for autism, supported by numerous studies that highlight its importance in early intervention and adaptability for adult populations.
What is Interoception Therapy, and how does it benefit individuals with autism?
Interoception Therapy helps individuals develop awareness of their internal bodily signals, enhancing emotional regulation and self-management, which is particularly beneficial for adults who struggle to identify and respond to their emotional states.
How does Expressive Art Therapy assist individuals with autism?
Expressive Art Therapy provides a creative outlet for self-expression, allowing individuals to communicate feelings and experiences that may be difficult to articulate verbally, thereby facilitating emotional healing and improving social skills.
What is the significance of personalization in autism treatment interventions?
Personalization in interventions is crucial for effectively meeting the unique needs of individuals on the spectrum, as tailored approaches can enhance engagement and treatment outcomes.
What ongoing research is being conducted in the field of autism treatment?
Research is ongoing to develop more effective and personalized treatment options for adults with autism, addressing existing gaps in interventions and focusing on the unique challenges faced by this population.




