Overview
The article focuses on the relationship between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and stimming, emphasizing that stimming serves as a significant coping mechanism for individuals with ADHD to manage anxiety and sensory overload. This is supported by research indicating that stimming behaviors not only help with emotional regulation but also highlight the importance of understanding and accommodating these behaviors in various settings to promote better outcomes for individuals with ADHD.
Introduction
In a world where the understanding of neurodiversity is evolving, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) emerges as a complex condition that affects millions. At the heart of this condition lies stimming—self-stimulatory behaviors that can serve as vital coping mechanisms for many individuals.
As research reveals the increasing prevalence of ADHD diagnoses, particularly among children, the significance of stimming in managing emotional regulation and sensory experiences cannot be overlooked.
This article delves into the intricate relationship between ADHD and stimming, exploring its characteristics, benefits, and the challenges faced by individuals as they navigate these behaviors in various settings. By shedding light on effective strategies for support and the differences between stimming in ADHD and autism, a deeper understanding of how to foster acceptance and create inclusive environments is achieved.
What is ADHD and How Does Stimming Fit In?
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Within this context, stimming—short for self-stimulatory behavior—describes the repetitive movements or vocalizations that many individuals use to manage sensory input or emotional states. Recent research emphasizes that ADHD and stimming can be especially advantageous for individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, functioning as a significant coping strategy that helps in managing feelings of anxiety, boredom, or sensory overload.
This comprehension is essential, particularly given that over the past twenty years, the proportion of youths diagnosed with attention disorders has almost doubled, with researchers observing a notable rise among girls and minority groups. Furthermore, it's important to acknowledge that 21% of adults with a substance use disorder also have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, underscoring the broader impact of this condition. For youngsters aged 6 years and older, the American Academy of Pediatrics suggests a mix of therapy and medication, which can be enhanced by techniques such as self-stimulation.
Additionally, a 2021 case study revealed disparities in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder care access, showing that children with Medicaid were less likely to receive care from specialists compared to those with private insurance. By acknowledging the importance of self-soothing actions in managing attention disorders and the difficulties in obtaining care, caregivers and advocates can implement more compassionate and knowledgeable approaches to assist individuals dealing with these actions. As one study suggests, self-stimulatory behavior, often associated with ADHD and stimming, can effectively improve emotional regulation, making it a crucial element of coping for individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Identifying ADHD Stimming Behaviors: Characteristics and Examples
Typical stimming actions seen in individuals with ADHD and stimming can include a variety of activities, such as:
- Fidgeting with items
- Tapping fingers or feet
- Humming
- Rocking back and forth
- Performing repetitive movements like hand-flapping
These actions are not uniform; their expression can differ widely among individuals. For instance, one individual may display excessive fidgeting, while another might be inclined to make repetitive sounds.
Significantly, almost 1 in 5 youngsters with Medicaid obtained ADHD-related care from nurse practitioners and psychiatric nurses in 2021, highlighting the necessity for awareness regarding these actions. Recognizing these stimming behaviors is crucial for parents, as it enables them to distinguish between typical manifestations of ADHD and stimming that may indicate the need for additional support. As experts observe, youngsters with attention deficits often display severe symptoms when co-existing conditions, such as anxiety or learning disorders, are present.
This understanding emphasizes the significance of customized interventions that cater to each individual's unique needs. Moreover, it is crucial to acknowledge that sensory-seeking behaviors are not limited to autism; youngsters with ADHD and stimming may also engage in these actions, frequently for various reasons. For instance, while individuals with autism may stim to cope with anxiety or express feelings, youngsters with attention issues might do so to improve concentration.
Additionally, if stimming leads to discomfort or injuries, parents can identify triggers and find strategies to reduce them, ensuring a supportive environment for their kids.
The Purpose and Benefits of Stimming in ADHD
For individuals with ADHD and stimming, it plays a crucial role by serving functions such as self-regulation, sensory input management, and emotional expression. For example, a young person might rock back and forth in moments of stress as a soothing mechanism, while fidgeting with a toy can help them maintain focus during tasks. Anthony explained that he stims 'as often as I’m excited or anxious' in an autism-accepting environment, highlighting the significance of such supportive settings.
Recent discussions emphasize that acceptance of self-stimulatory behaviors in these environments enables children to engage in these actions without fear of judgment, ultimately fostering emotional well-being. Wendy Flottman aptly states,
We are champions
emphasizing the advocacy for acceptance and understanding of self-stimulatory behavior. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Conscious Control of Stimming' reveals that participants learned to intentionally incorporate self-soothing behaviors related to ADHD and stimming into their lives, using these techniques as a proactive strategy to manage anxiety and prevent panic attacks.
Participants like Sally reported that actively using self-soothing techniques helped them manage anxiety and prevent panic attacks, demonstrating that such methods can be both a reactive response to emotional dysregulation and a deliberate coping mechanism. By acknowledging these varied functions, parents can foster settings that welcome self-soothing actions, thereby reducing any guilt or discomfort linked to these instinctive practices.
Navigating the Challenges of Stimming: Benefits and Drawbacks
Stimming behaviors, while often beneficial for emotional regulation and cognitive processing, can present challenges in classroom and social settings. For example, excessive fidgeting may distract peers and contribute to social stigma, making it crucial for parents to navigate these complexities. Research indicates that infants who received less vestibular stimulation engage in more stereotyped movement, highlighting the significance of self-stimulatory behavior for cognitive development.
As mentioned in recent conversations, effective communication strategies for individuals who engage in vocal repetition include:
- Active listening
- Allowing extra processing time
- Utilizing visual aids
- Showing empathy and understanding
These strategies can foster a more inclusive environment. Remington et al. highlight that including relevant visual information in the background display in the classroom can actually be beneficial for all students, not just students with ASD.
This viewpoint emphasizes the necessity for educational methods that incorporate self-stimulatory behaviors, particularly in the context of ADHD and stimming, as a natural aspect of cognitive dynamics, especially for neurodivergent youth who frequently encounter marginalization. Insights from the case study 'Stimming as Thinking' emphasize that peripheral sensorimotor stimming activities, such as rocking and fidgeting, are intrinsic to adaptive functioning and cognitive dynamics, particularly in the context of ADHD and stimming. By acknowledging the dual nature of stimming—its supportive role in emotional regulation and its potential to distract—parents can assist in guiding their offspring on when and where certain actions may be more suitable.
This balanced approach not only supports the individual's needs but also promotes the development of essential social skills, ultimately leading to more effective management strategies in various contexts.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stimming in Daily Life
To effectively manage sensory behaviors, providing alternative sensory outlets is crucial. Tools like stress balls and fidget toys serve as beneficial resources in appropriate settings, allowing young individuals to channel their energy productively. Creating consistent routines can promote a sense of predictability, assisting young individuals in feeling secure and, consequently, diminishing anxiety-driven behaviors.
Stimming, which is often associated with ADHD and stimming, can occur in response to various emotions such as excitement, happiness, boredom, stress, fear, and anxiety, making it essential for parents to understand these triggers. Parents play an essential role in educating their offspring to recognize when specific repetitive actions may not be appropriate, encouraging self-regulation methods such as deep breathing and mindfulness techniques. These strategies not only empower young individuals to manage their responses but also enhance their overall quality of life by improving social interactions.
As one autistic adult insightfully expressed, "I quickly become overwhelmed [in social situations]. Is it surprising that I then feel like blocking the world out and literally putting my thoughts back in order?" This quote highlights the natural response to overwhelming situations and emphasizes the need for effective sensory outlets.
Moreover, management strategies for sensory-seeking actions in children with ADHD and stimming involve understanding the triggers and reasons behind the conduct, as highlighted in the case study on the management of sensory-seeking actions. Promoting self-discipline instead of trying to eliminate the actions completely can result in better social interactions and an enhanced quality of life for individuals who partake in repetitive movements.
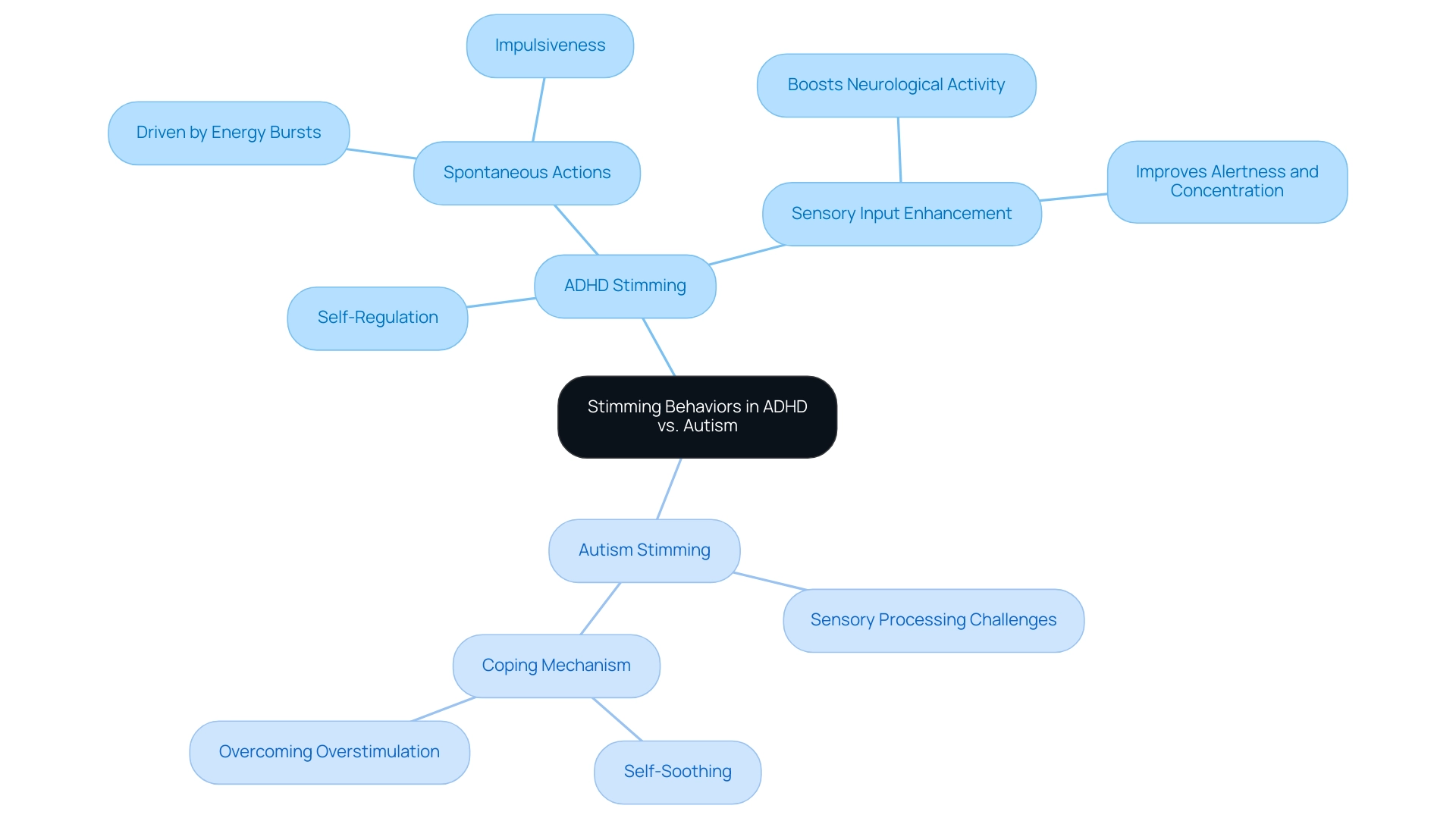
ADHD Stimming vs. Autism Stimming: Key Differences
Stimming behaviors are observed in both ADHD and stimming disorders, yet they arise from different motivations and take on varied forms. In the context of ADHD and stimming, repetitive movements often serve as a self-regulation tool or a technique to improve concentration, usually happening spontaneously, fueled by surges of energy and impulsiveness. Rachael Young notes that ADHD and stimming help to boost sensory input and activate neurological activity, which can improve alertness and concentration.
Conversely, in autism, self-stimulatory behavior is frequently tied to sensory processing challenges or as a strategy to cope with overwhelming stimuli. For instance, an individual with autism may resort to repetitive movements or vocalizations to self-soothe during overstimulating experiences. Grasping these differences is essential for parents; it enables them to more effectively understand their offspring's self-soothing actions and react suitably.
Recent studies further demonstrate these distinctions, emphasizing that while stimulant medications do not worsen repetitive actions in youngsters with both ADHD and stimming, the fundamental reasons for these actions remain crucial for customizing effective interventions. The case study titled 'Stimming and Medication: A Complex Relationship' emphasizes that while stimulants may assist with attention-related issues in some individuals with autism, they do not significantly influence core autism symptoms, suggesting a need for careful evaluation of medication benefits and limitations. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize the distinctions between ABA therapy and other therapeutic methods, as this comprehension can enhance the approach to interventions for repetitive actions.
By understanding the subtle reasons behind repetitive behaviors, parents can create a more nurturing atmosphere for their kids.
When to Seek Professional Help for Stimming Behaviors
Parents should actively contemplate seeking professional intervention for actions related to ADHD and stimming when they notice significant distress for their offspring, interference with daily activities, or potential safety risks. A qualified behavioral therapist or psychologist can provide personalized strategies and interventions tailored to the individual's unique needs. Research shows that the average score of the Suspected Autistic group on the RAADS-R was 34.43, with a standard deviation of 5.98, emphasizing the prevalence of such actions in neurodivergent youth.
If self-stimulatory behavior associated with ADHD and stimming escalates or evolves into harmful actions, seeking immediate professional assistance is vital to safeguard the child's well-being. Furthermore, suppressing preferred stims in relation to ADHD and stimming has been linked to negative cognitive effects, such as lack of concentration and confusion, underscoring the importance of addressing these actions rather than ignoring them. As Rebecca poignantly states,
angry that they’ve been told a thousand times why I do it, the reason behind it, that it’s not affecting anyone.
This highlights the necessity for enhanced comprehension and acceptance of self-soothing actions. Furthermore, case studies indicate that young individuals who encounter acceptance in their surroundings, such as Anthony, frequently feel free to express their self-regulatory actions without fear of judgment. Furthermore, Greg's experience demonstrates that support from family and friends can greatly improve a young person's ease with their self-soothing behaviors in different environments.
Recognizing signs that behaviors related to ADHD and stimming require intervention, such as increased frequency or intensity, is crucial in fostering a supportive atmosphere and ensuring the child's overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between ADHD and stimming reveals the vital role these behaviors play in emotional regulation and sensory management for individuals affected by this condition. As highlighted throughout the article, stimming serves as a significant coping mechanism for many, allowing children and adults alike to navigate their experiences with anxiety, boredom, and sensory overload. Recognizing the characteristics and motivations behind stimming behaviors is crucial for parents and caregivers, as it enables them to provide tailored support that respects the unique needs of each individual.
While stimming can present challenges in social and educational settings, it is essential to promote acceptance and understanding of these behaviors. By fostering inclusive environments that embrace stimming, caregivers can help individuals feel more comfortable expressing themselves, ultimately enhancing their emotional well-being. Implementing effective strategies, such as providing alternative sensory outlets and establishing consistent routines, can empower individuals with ADHD to manage their stimming in ways that support their overall quality of life.
In conclusion, the dialogue around ADHD and stimming should focus on empathy and informed strategies that recognize the benefits of these behaviors. By differentiating the motivations behind stimming in ADHD versus autism, parents and educators can ensure that interventions are appropriately tailored. Seeking professional help when necessary can further enhance support for those navigating the complexities of ADHD. Through understanding and advocacy, a more inclusive and accepting environment can be cultivated, allowing individuals with ADHD to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
What is stimming and how is it related to ADHD?
Stimming, short for self-stimulatory behavior, refers to repetitive movements or vocalizations that individuals use to manage sensory input or emotional states. It can serve as a significant coping strategy for individuals with ADHD, helping them manage feelings of anxiety, boredom, or sensory overload.
How has the diagnosis of ADHD changed over the years?
Over the past twenty years, the proportion of youths diagnosed with attention disorders has almost doubled, with a notable increase among girls and minority groups.
What is the relationship between ADHD and substance use disorders?
Approximately 21% of adults with a substance use disorder also have ADHD, highlighting the broader impact of this condition.
What treatment options are recommended for children with ADHD?
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests a combination of therapy and medication for children aged 6 years and older, which can be enhanced by techniques such as self-stimulation.
What disparities exist in ADHD care access?
A 2021 case study found that children with Medicaid were less likely to receive care from specialists compared to those with private insurance, indicating disparities in ADHD care access.
What are some typical stimming actions seen in individuals with ADHD?
Typical stimming actions can include fidgeting with items, tapping fingers or feet, humming, rocking back and forth, and performing repetitive movements like hand-flapping.
How can parents recognize stimming behaviors in their children?
Parents can distinguish between typical manifestations of ADHD and stimming by observing their child's behaviors, noting that stimming actions can vary widely among individuals.
Why is it important to understand stimming behaviors in children with ADHD?
Understanding stimming behaviors is crucial for parents, as it helps them identify when their child may need additional support, especially when ADHD coexists with other conditions like anxiety or learning disorders.
Can sensory-seeking behaviors occur in children with ADHD?
Yes, sensory-seeking behaviors are not limited to autism; children with ADHD may also engage in stimming for various reasons, such as improving concentration.
What should parents do if stimming leads to discomfort or injuries?
Parents can identify triggers for stimming behaviors and find strategies to reduce them, ensuring a supportive environment for their children.




