Overview
Understanding ADHD is crucial for parents, as it is deeply connected to short-term memory challenges in children. Did you know that approximately 60% of those diagnosed face significant cognitive hurdles? By recognizing these challenges as part of ADHD, parents can better advocate for their children. This awareness opens the door to implementing effective strategies, such as:
- Using visual aids
- Establishing routines
These strategies can significantly enhance a child's learning and memory retention.
As you navigate this journey, it’s important to remember that you are not alone. Many parents share similar experiences and concerns. Consider how visual aids can transform a child's understanding or how a consistent routine can provide the structure they thrive on. These strategies are not just helpful; they can be life-changing.
We encourage you to explore these approaches and share your experiences. What strategies have worked for you? By connecting with others and exchanging ideas, you can build a supportive community that fosters growth and understanding. Together, let’s create an environment where our children can flourish.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between ADHD and memory challenges unveils a landscape rich with both difficulties and opportunities for growth. As research sheds light on the cognitive hurdles faced by children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, it becomes increasingly clear that understanding these memory impairments is essential for both parents and educators.
With around 60% of children diagnosed with ADHD struggling with significant memory issues, it is crucial to recognize that these challenges stem from the condition itself, rather than reflecting a child's intelligence.
This article explores the nuances of memory function in ADHD, offering effective strategies, therapeutic interventions, and lifestyle adjustments that can empower parents to support their children in navigating their educational and social environments.
By fostering a deeper understanding of these connections, parents can advocate more effectively for their children, paving the way for enhanced learning and development.
The Connection Between ADHD and Memory Challenges
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) often brings with it a range of cognitive challenges, particularly concerning short-term memory. It’s important to note that approximately 60% of children diagnosed with ADHD experience moderate to severe symptoms, which can profoundly affect their daily lives. Research has shown that the brains of individuals with ADHD process information differently, leading to significant hurdles in working cognition and recall.
For many young people with ADHD, the struggles are evident:
- They face substantial difficulties in working cognition.
- They experience moderate challenges in phonological short-term retention.
- They have minor issues in visuospatial short-term retention.
This understanding is crucial for parents, as it frames these cognitive challenges as intrinsic to the condition rather than indicative of their child's intelligence or potential.
A recent study, titled "Bifactor Model Application in Attention Research," utilized a bifactor model to delve into the working cognitive performance of youth facing attention difficulties. The findings highlighted the distinct roles of general and specific memory processes, underscoring the complexity of working memory deficits. This suggests that targeted cognitive interventions could offer significant benefits.
Moreover, it's noteworthy that the diagnosis rates of ADHD vary across different demographics. For instance:
- Non-Hispanic Black youth are diagnosed at a rate of 12%.
- White youth follow at 10%.
- Hispanic youth are diagnosed at 8%.
- Non-Hispanic Asian youth at just 3%.
This disparity emphasizes the need for tailored support and understanding for diverse communities.
As Elena Cox, a senior data reporter at Stacker, wisely notes, "Grasping the subtleties of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder can enable caregivers to pursue the appropriate resources and advocate effectively for their offspring." By understanding the connection between ADHD and short-term memory challenges, caregivers can cultivate compassion and understanding as they navigate their child’s educational and social environments. Recognizing that these cognitive difficulties are part of the ADHD experience empowers parents to advocate more effectively for their children and seek the necessary resources and strategies to support their growth.
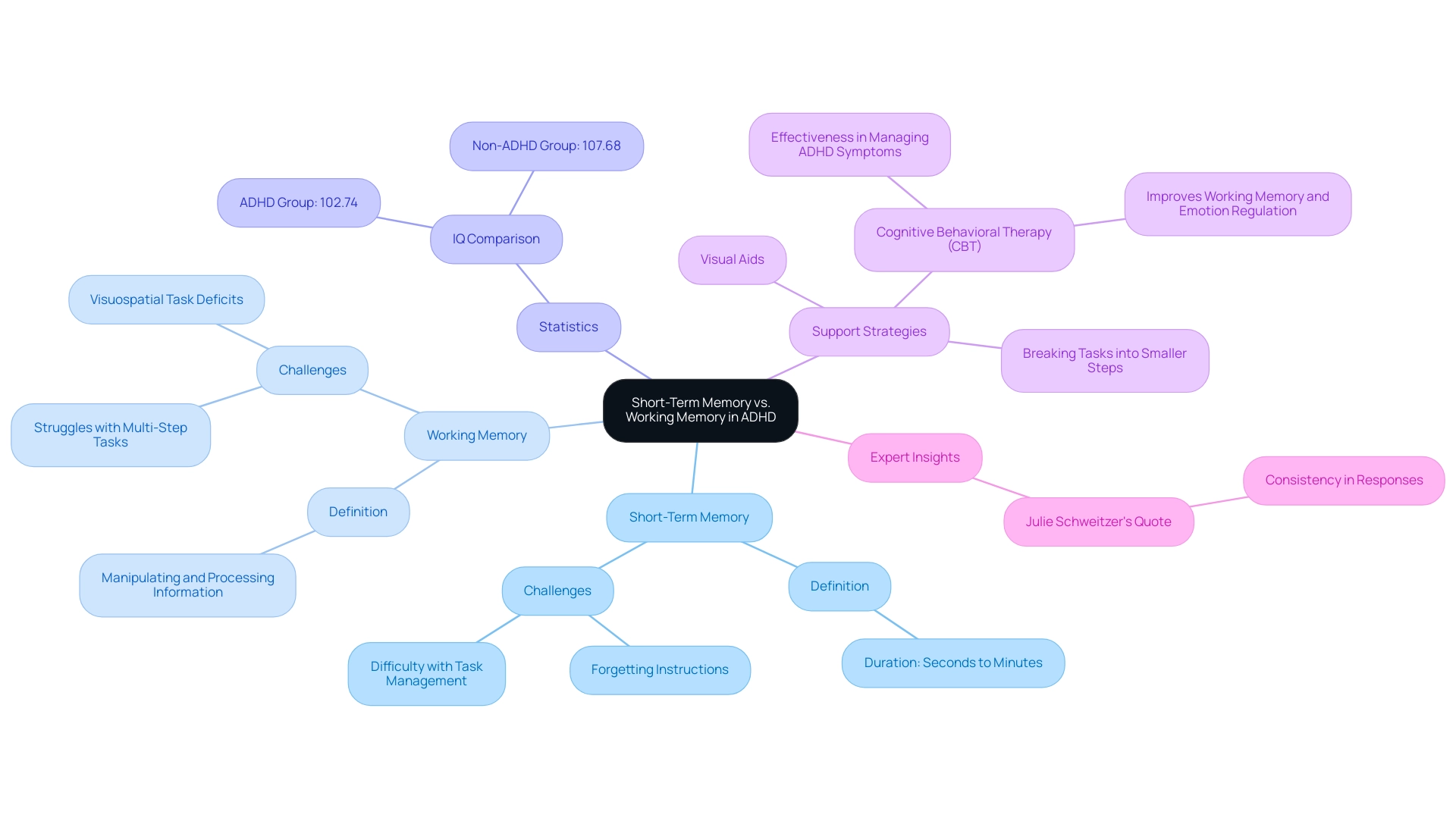
Short-Term Memory vs. Working Memory in ADHD
Short-term retention refers to the ability to hold a small amount of information for a brief period, typically lasting seconds to minutes. In contrast, working cognition not only involves holding information but also manipulating and processing it. This capability is essential for tasks such as reasoning and comprehension. For many children with ADHD, challenges related to short-term memory can significantly impact both their short-term and working cognitive functions.
For instance, a child might forget instructions almost immediately after hearing them, underscoring the difficulties associated with ADHD and short-term memory. Additionally, they may struggle with managing multiple steps in a task, which can indicate challenges with working recall.
Recent findings reveal that youngsters with ADHD and short-term memory challenges often exhibit more pronounced deficits in working cognition compared to short-term cognition subsystems, particularly in visuospatial tasks. This distinction is crucial for caregivers who wish to support their children effectively. By grasping these recall challenges, parents can implement targeted strategies tailored to their child’s unique needs.
For example, employing visual aids or breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps can significantly enhance retention and task execution.
A case study on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) highlights its effectiveness in managing symptoms of ADHD and short-term memory, especially those related to recall and time perception. CBT has proven to improve working capacity and assist children with attention disorders in better regulating their emotions and actions. This approach underscores the importance of addressing cognitive deficits through structured interventions.
Statistics show that individuals with ADHD and short-term memory difficulties have an average IQ of 102.74, compared to 107.68 for their peers without this condition (p = .02). This difference may be linked to their memory challenges. Understanding these disparities not only empowers guardians but also fosters a supportive environment where young individuals can thrive despite their memory-related hurdles. As Julie Schweitzer, an associate professor at the M.I.N.D. Institute, wisely notes, "Enhancing consistency in how young individuals with attention disorders respond to the environment should aid them in generalizing what they learn in clinical interventions, enhancing their skills across situations."
By focusing on both short-term and cognitive processes, parents can navigate the complexities of attention disorders more effectively, ultimately enhancing their children’s learning and growth.
Effective Strategies to Enhance Memory in Children with ADHD
Enhancing memory in children with ADHD is not just possible; it can be achieved through a range of effective strategies tailored to their unique learning needs. Imagine your child thriving in an environment that understands and supports their journey.
- Utilize Visual Aids: Consider incorporating charts, diagrams, and color-coded notes into your child's learning routine. These tools can significantly assist young learners in visualizing and retaining information. Research indicates that visual aids can improve retention, making learning more accessible and enjoyable.
- Establishing consistent routines can be a game-changer for children with ADHD and short-term memory challenges. Consistency in their schedule not only helps them remember their tasks and responsibilities but also reduces anxiety, enhancing focus. This stability is particularly beneficial, leading to improved performance in recall.
- Chunk Information: Think about breaking down information into smaller, manageable segments. This approach prevents overwhelm and facilitates easier retention. It aligns with cognitive strategies that emphasize processing information in bite-sized pieces, making learning feel less daunting.
- Repetition and practice are vital for those with ADHD and short-term memory issues. Regularly reviewing information and practicing tasks strengthens recall. Studies show that repeated exposure to material enhances neural connections, crucial for improving recall abilities. A small 2012 study even suggested that stimulant medication might help strengthen connectivity in the frontal cortex, further supporting the effectiveness of consistent practice.
- Engage Multiple Senses: Activities that involve touch, sight, and sound create a multi-sensory learning experience. This approach can significantly boost memory retention, as engaging different senses helps solidify information in a young person's mind.
- Incorporate Movement: Did you know that physical activity can enhance cognitive function? Incorporating movement into learning sessions stimulates brain activity, making it easier for young learners to absorb and remember information.
- Employ Mnemonics: Encourage your child to use acronyms or rhymes to remember lists or sequences. This strategy leverages the brain's natural inclination to remember patterns and associations, making learning more effective and fun.
As highlighted by Sherelle L Harmon, Ph.D., in her work on cognitive deficits in attention disorders, addressing these challenges with customized strategies is crucial. By applying these methods, you can nurture a supportive educational atmosphere that enhances recall and enables your child to excel academically and socially. Recent discoveries further emphasize the importance of personalized educational strategies in improving cognitive skills in youth facing attention difficulties.
Moreover, ASD Media's commitment to enhancing ABA therapy execution aligns beautifully with these cognitive strategies, reinforcing community support for youth with attention deficit issues. Together, let's create an environment where every child can flourish.
The Role of Therapy and Support in Managing ADHD-Related Memory Issues
Therapy plays a vital role in addressing cognitive difficulties associated with ADHD and short-term memory issues, providing young individuals with the essential resources they need to navigate their challenges effectively. Behavioral therapies, especially Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), focus on reinforcing positive behaviors and developing coping strategies tailored to memory difficulties. Research shows that ABA therapy can lead to significant improvements for individuals facing ADHD and short-term memory challenges, with effective management strategies enhancing their overall quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is equally important in assisting children with ADHD and short-term memory challenges. It helps them gain insight into their thought processes and develop crucial organizational skills. This dual approach not only tackles immediate cognitive challenges but also encourages long-term cognitive development.
As we look ahead to 2025, the effectiveness of ABA therapy for ADHD and short-term memory challenges remains well-supported by statistics, indicating that stimulants are effective in approximately 70% of patients with these conditions. However, integrating behavioral therapies can further bridge the gap between science and practice, ensuring that children receive comprehensive interventions that address both their behavioral and cognitive needs. As Anil Chacko highlights, "Enhancing access and availability of evidence-based psychosocial interventions remains essential to ensure that the substantial efforts made over decades in developing and evaluating interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder result in population-level benefits for youth with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder."
The case study titled 'Treatment Approaches for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder' emphasizes that treatment primarily involves the use of stimulants and psychotherapy, aimed at managing symptoms and improving functioning. Early intervention is crucial to reduce the risk of comorbid conditions, underscoring the need to address ADHD and short-term memory issues promptly.
Parents are encouraged to seek professional guidance to tailor interventions that meet their child's unique needs. Additionally, support groups for caregivers can be invaluable resources, offering shared experiences and fostering a sense of community. These networks empower parents to advocate for their children, ensuring they receive the necessary support and strategies to thrive.
How Lifestyle Factors Influence Memory in ADHD
Lifestyle elements play a crucial role in shaping the cognitive performance of youngsters facing ADHD and short-term memory challenges. By understanding and addressing these factors, we can significantly enhance cognitive function in our children. Let's explore some key areas of focus:
- Quality Sleep: A good night's sleep is essential for consolidating information. Many children with ADHD struggle with sleep issues, which can hinder their ability to recall information. Establishing a consistent bedtime routine and creating a calming sleep environment can greatly improve sleep quality, leading to better retention of information.
It's important to note that sleep disorders are often linked to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, as highlighted in research on physical health outcomes related to this condition.
- Nutrition: A well-balanced diet is fundamental for optimal brain health. Diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and whole grains have been shown to support cognitive function. Parents should prioritize nutritious meals that promote brain development, ensuring their children receive the essential nutrients necessary for effective learning.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity has been proven to enhance recall and focus in children with ADHD. Encouraging activities that your child enjoys not only promotes physical health but also stimulates brain function. Daily exercise can lead to improved focus and information retention, particularly for those experiencing ADHD and short-term memory challenges.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can impede recall performance. Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help young individuals manage anxiety and boost their cognitive abilities. These practices foster a calm mind, which is beneficial for enhancing cognitive function.
Moreover, adults with ADHD and short-term memory difficulties often face challenges in their close relationships, potentially linked to recall and cognitive issues. This highlights the importance of stress management for overall well-being.
By actively addressing these lifestyle elements, parents can create a supportive environment that enhances recall abilities and overall health for their children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The seriousness of ADHD is underscored by the statistic that approximately 25.5% of individuals with this condition end up in prison, emphasizing the need for effective strategies to support children in overcoming these challenges. As noted by Joel T. Nigg, PhD, researchers are encouraged to explore genetic mechanisms that may influence response inhibition, further illustrating the complexity of ADHD and its impact on recall.
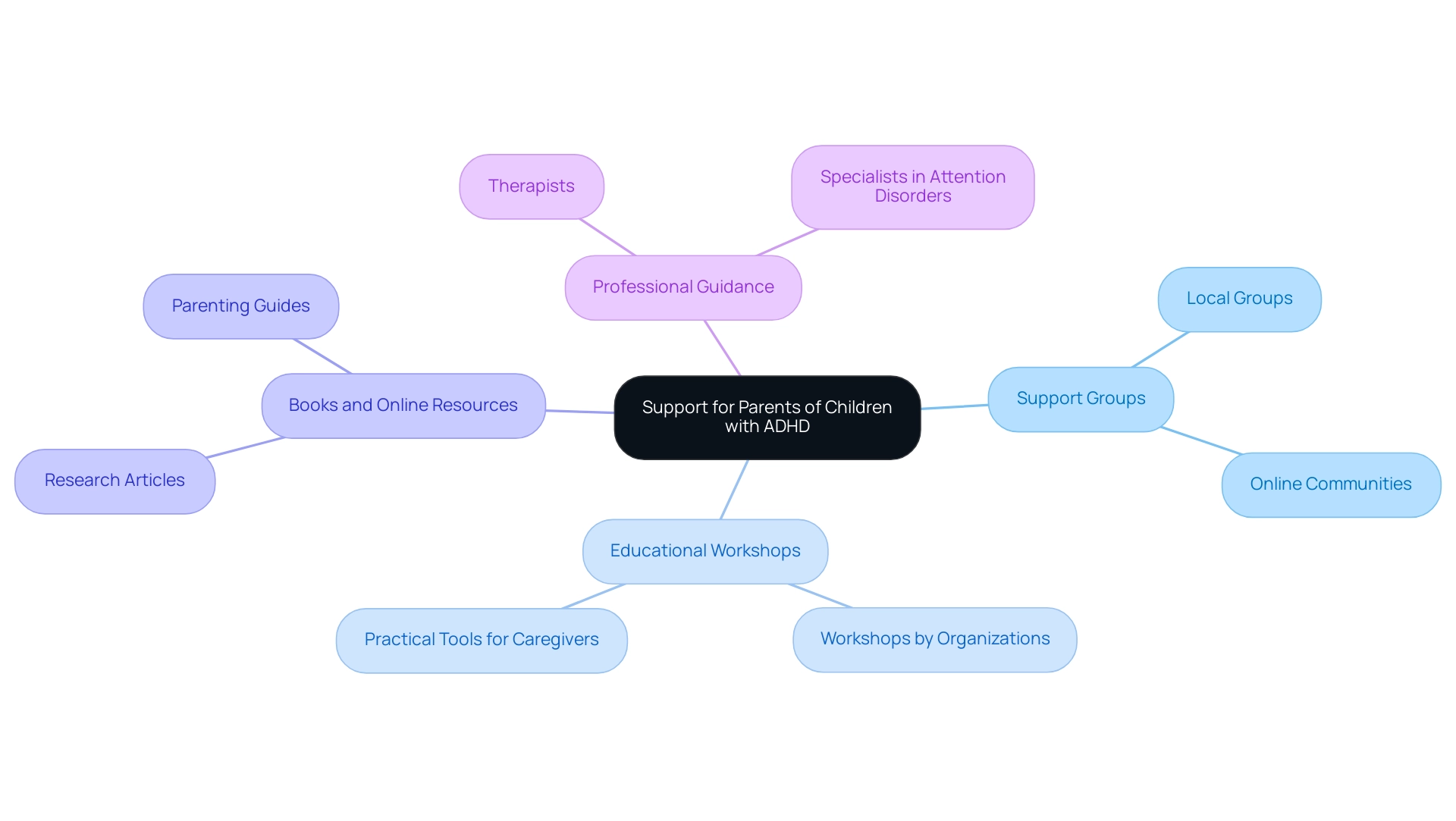
Navigating the Journey: Support and Resources for Parents
Navigating the challenges of ADHD and short-term memory can feel overwhelming for guardians. However, a wealth of resources is available to provide essential support. Approximately 6 in 10 children experience moderate to severe ADHD, underscoring the importance of effective strategies and community support.
- Support Groups: Joining local or online support groups allows caregivers to connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups become vital platforms for sharing experiences, strategies, and emotional support, fostering a nurturing sense of community among caregivers.
- Educational Workshops: Various organizations offer workshops specifically focused on managing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. These sessions provide valuable information and practical tools that empower caregivers to implement effective strategies at home.
- Books and Online Resources: A plethora of books and websites dedicated to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and memory strategies assist parents in staying informed about the latest research and techniques. This knowledge enables them to better support their children.
- Professional Guidance: Consulting with therapists or specialists in attention disorders can yield tailored strategies and interventions suited to individual youth. Such professional insight is crucial for addressing specific challenges and enhancing the overall management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
In 2021, a significant portion of ADHD care for U.S. children aged 3-17 was provided by primary care clinicians. Nearly half of privately insured children and about 25% of Medicaid-covered children received care from pediatricians. This reliance on primary care providers highlights the importance of incorporating ADHD management into general pediatric practices, while also exposing potential gaps in access to specialized care. Parents may find it particularly challenging to navigate these gaps, especially in areas where mental health resources are limited. In fact, 19% of U.S. counties lack adequate mental health resources, correlating with higher rates of challenges faced by families.
As Elena Cox, a senior data reporter, poignantly notes, 'You think you have adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Now what?' This statement underscores the ongoing journey many families encounter in understanding and managing ADHD.
By leveraging these resources, parents can cultivate a supportive network that enhances their ability to effectively manage their child's ADHD and memory challenges. This ultimately leads to improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between ADHD and memory challenges is essential for fostering a supportive environment for affected children. This article has explored the significant cognitive hurdles faced by children with ADHD, emphasizing that these memory difficulties are inherent to the condition and not reflective of a child's intelligence. By recognizing the distinctions between short-term and working memory impairments, parents can better tailor their approaches to meet their children's unique needs.
Effective strategies to enhance memory retention include:
- Utilizing visual aids
- Establishing consistent routines
- Engaging multiple senses
These strategies can significantly empower children with ADHD. Additionally, therapy plays a crucial role in addressing these memory issues, with interventions like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Applied Behavior Analysis proving beneficial in promoting positive outcomes.
Lifestyle factors also contribute significantly to memory performance, highlighting the importance of:
- Quality sleep
- Nutrition
- Physical activity
- Stress management
By proactively addressing these factors, parents can create a nurturing atmosphere that enhances cognitive function and overall well-being.
Navigating the journey of ADHD requires a robust support system. By utilizing available resources, such as:
- Support groups
- Educational workshops
- Professional guidance
Parents can effectively advocate for their children and foster an environment conducive to growth and learning. Emphasizing understanding, compassion, and targeted strategies can pave the way for children with ADHD to thrive academically and socially, ultimately leading to improved quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What cognitive challenges are commonly associated with ADHD?
Individuals with ADHD often face significant difficulties in working cognition and experience moderate challenges in phonological short-term retention, along with minor issues in visuospatial short-term retention.
How prevalent are ADHD symptoms among children?
Approximately 60% of children diagnosed with ADHD experience moderate to severe symptoms, which can significantly impact their daily lives.
What does recent research indicate about the memory processes of youth with ADHD?
A study using a bifactor model highlighted the distinct roles of general and specific memory processes, suggesting that targeted cognitive interventions could be beneficial for those facing attention difficulties.
Are there demographic disparities in ADHD diagnosis rates?
Yes, diagnosis rates vary by demographic: Non-Hispanic Black youth at 12%, White youth at 10%, Hispanic youth at 8%, and Non-Hispanic Asian youth at 3%.
How does short-term retention differ from working cognition?
Short-term retention refers to the ability to hold information briefly, while working cognition involves holding and manipulating information, which is crucial for reasoning and comprehension.
How can ADHD-related short-term memory challenges affect children?
Children with ADHD may forget instructions soon after hearing them and struggle with managing multi-step tasks, indicating difficulties with both short-term and working recall.
What strategies can parents use to support children with ADHD and memory challenges?
Parents can implement strategies such as using visual aids and breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps to enhance retention and task execution.
What role does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) play in managing ADHD symptoms?
CBT has been shown to improve working capacity and assist children with ADHD in better regulating their emotions and actions, addressing cognitive deficits through structured interventions.
What is the average IQ of individuals with ADHD and short-term memory difficulties compared to their peers?
Individuals with ADHD and short-term memory challenges have an average IQ of 102.74, compared to 107.68 for peers without these challenges.
How can understanding memory challenges in ADHD empower parents?
By recognizing these cognitive difficulties as part of the ADHD experience, parents can seek appropriate resources and advocate effectively for their children, fostering a supportive environment for their growth.




