Introduction
In the dynamic realm of child development, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) emerges as a beacon of hope and transformation for children facing autism and ADHD. Grounded in scientific principles, ABA offers a structured approach to understanding behavior and tailoring interventions that can lead to meaningful change.
This article delves into the core tenets of ABA, exploring its practical applications, ethical considerations, and the educational pathways that shape proficient practitioners. As the field evolves, it is crucial for advocates and caregivers to stay informed about the latest advancements and methodologies, ensuring that children receive the most effective support.
By embracing the principles of ABA, families can foster resilience and independence in their children, paving the way for brighter futures.
Fundamentals of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
ABA behavior serves as a scientifically validated method for understanding actions and their interaction with environmental factors. The foundational principles of ABA behavior are crucial for effective intervention, and they include:
- Conduct is learned: Recognizing that actions can be acquired and modified through various techniques, paving the way for meaningful changes.
- Reinforcement: Utilizing positive reinforcement to promote desired actions while simultaneously decreasing undesirable ones—a method supported by recent findings that highlight its effectiveness in various settings.
- Data-driven: The practice relies heavily on the systematic collection and analysis of data, ensuring that progress can be monitored and interventions adjusted as necessary.
- Individualization: Each student's unique needs are paramount; therefore, interventions are tailored to cater specifically to their responses and requirements, reflecting the latest trends in ABA interventions.
- Functional assessment: Understanding the reasons behind specific behaviors is essential, allowing practitioners to construct effective interventions that are grounded in the individual's context.
- Generalization: It is essential that skills learned in therapeutic environments are applicable to daily scenarios, fostering independence and flexibility.
By following these fundamental principles, practitioners are enabled to create effective, tailored interventions using ABA behavior that tackle the unique challenges encountered by individuals with autism and ADHD. Recent studies suggest that ongoing evaluation and tailored treatment strategies significantly improve the effectiveness of ABA behavior interventions, emphasizing the importance of a responsive approach to each individual's journey. Significantly, 10% of individuals who died by suicide were likely to have undiagnosed autism, highlighting the essential need for early intervention through approaches such as ABA behavior.
Weihong Xu emphasizes that 'the principles of ABA behavior are not just theoretical; they serve as practical tools that can lead to significant improvements in the lives of young individuals.' Furthermore, the duration of therapy varies based on individual needs, with 66% of young individuals starting ABA therapy remaining in services for 12 months, but only 46% continuing for 24 months, illustrating the importance of ongoing assessment and tailored treatment plans.
Practical Applications and Techniques in ABA Therapy
Practitioners can implement a range of evidence-based ABA techniques to foster positive behavior changes effectively:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): This structured approach dissects skills into manageable, teachable components. By providing clear instructions and prompt feedback, DTT allows learners to acquire knowledge systematically, establishing a solid basis for various skills. Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention (EIBI) has been demonstrated to positively affect adaptive skills compared to typical treatment methods, emphasizing the significance of structured approaches like DTT within the framework of ABA behavior.
- Natural Environment Training (NET): NET focuses on teaching skills within the natural settings where they will be utilized. This approach not only encourages practical application but also improves skill generalization, enabling young individuals to apply learned actions to daily situations. Case studies have demonstrated that youth engaged in NET show significant improvements in independence and social integration. As Qian Yu notes, "The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose," highlighting the objectivity of the findings in the field.
- Modeling: By demonstrating desired behaviors, practitioners help young learners learn through imitation. This technique is particularly effective for teaching social skills, as young individuals observe and replicate appropriate interactions.
- Social Skills Groups: These organized sessions provide youngsters with opportunities to practice social interactions in a supportive environment. Such groups are instrumental in developing communication skills and building relationships, essential for emotional and social functioning.
- Visual Supports: Utilizing visual aids, such as charts or picture schedules, can significantly enhance understanding and communication. Visual supports cater to diverse learning styles, helping children grasp concepts more effectively.
- Parent Training: Involving parents in the treatment process is crucial. By equipping parents with strategies to reinforce skills at home, the program’s impact extends beyond sessions, fostering a conducive learning atmosphere.
These practical applications not only enhance the effectiveness of ABA behavior techniques but also empower practitioners to create meaningful interventions. The case study titled "Long-Term Benefits of Early ABA Behavior Intervention" illustrates that early and comprehensive ABA behavior intervention leads to long-term benefits, including improved adaptive behavior and social functioning, although the severity of autism symptoms may not always be reduced. As we look toward 2024, the incorporation of these current techniques continues to evolve, ensuring that children receive the most comprehensive support possible.
Expert opinions emphasize that the synergistic application of these methods can result in more substantial changes in ABA behavior, ultimately contributing to the long-term advantages linked to early and comprehensive practices.
Ethical Considerations and Controversies in ABA
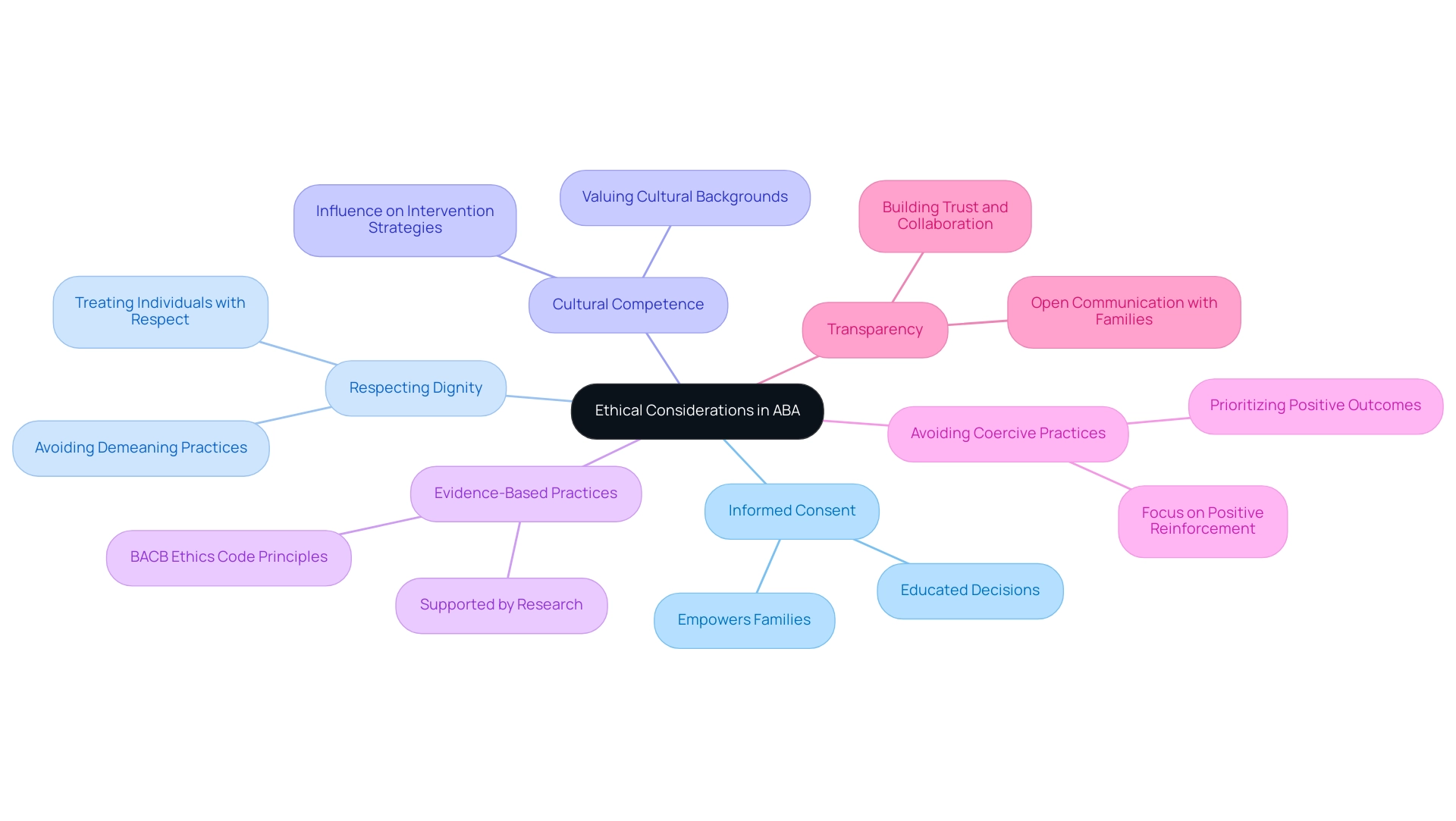
Ethical considerations in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) practices are vital to ensuring that interventions are conducted with integrity and respect for all individuals involved. Key elements include:
- Informed Consent: It is crucial that parents and guardians are fully informed about the methods and goals of therapy before providing consent. This process empowers families to make educated decisions about their child's treatment.
- Respecting Dignity: Practitioners are committed to treating every individual with respect and dignity, avoiding any practices that may be perceived as demeaning or harmful.
- Cultural Competence: Understanding and valuing the cultural backgrounds of clients is essential, as these factors can significantly influence actions and the effectiveness of intervention strategies.
- Evidence-Based Practices: Adhering to interventions that are supported by rigorous research ensures the delivery of the highest quality of care. As noted by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB), "the most recent edition of the Ethics Code for Behavior Analysts begins with a summary of core principles that underlie the code," emphasizing the importance of basing practices on empirical evidence.
- Avoiding Coercive Practices: While recent research has demonstrated the effectiveness of punishment-based procedures in reducing the likelihood of similar behavior occurring, ethical practice must prioritize positive outcomes. Interventions should focus on positive reinforcement rather than coercion or punishment.
- Transparency: Maintaining open lines of communication with families about progress, challenges, and modifications to the treatment plan is essential for building trust and collaboration.
Engaging with these ethical considerations not only upholds the integrity of ABA behavior but also fosters a strong sense of trust within the community. For instance, the case study titled "Smart Homes for Autism Comfort and Energy Savings" illustrates how utilizing smart home technology can enhance comfort and energy efficiency for individuals with autism, demonstrating a practical application of ethical considerations in therapy. As the landscape of ABA behavior continues to evolve, particularly with new insights into informed consent practices and ethical practices, it remains imperative for practitioners to stay informed and committed to these principles.
Educational Pathways and Certification in ABA
The journey to becoming a qualified practitioner in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) involves several educational pathways and certifications that can significantly enhance one’s expertise and impact in the field:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A foundational degree in psychology, education, or a related discipline is essential, serving as the first step towards understanding the principles of analysis of conduct.
- Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Applied Behavior Analysis or a closely related field equips practitioners with specialized knowledge and skills necessary for effective ABA behavior intervention.
- Certification Board for Behavior Analysts (BCBA): Achieving BCBA certification is a mark of professional excellence in ABA behavior, typically requiring both theoretical knowledge and supervised practical experience, underscoring the commitment to best practices in the field.
- Registered Behavior Technician (RBT): This certification is designed for paraprofessionals who implement interventions based on ABA behavior under the supervision of a BCBA, providing essential support in various settings.
- Continuing Education: Engaging in workshops, webinars, and conferences is crucial for staying abreast of the latest research and methodologies in ABA behavior, ensuring practitioners remain effective and informed.
- State Licensure: It’s vital for practitioners to research and comply with state-specific licensure requirements, as some regions mandate licensure to practice ABA legally.
In New Jersey, there are currently 1,804 ABA therapist jobs available, with an average salary of $39,905, which provides insight into the job market and financial prospects in this field. However, it's important to note that the lowest average salary for ABA therapists is found in South Dakota at $26,952, highlighting regional disparities in compensation.
By navigating these educational pathways and obtaining relevant certifications, practitioners not only enhance their qualifications but also play a pivotal role in advancing ABA behavior in the field. A practical application of this knowledge can be seen in the case study titled "Crafting Tranquil Spaces for Autistic Individuals," which focuses on creating calming environments for autistic individuals in various settings. This initiative promotes well-being and comfort through thoughtfully designed spaces, showcasing how education and certification can lead to impactful outcomes.
As Baer et al. stated, the continued examination of analytic applications to solve problems of social significance will help assist in their refinement and, possibly, their replacement by better applications, emphasizing the ongoing need for skilled professionals dedicated to improving outcomes for individuals in need.
The Evolution and Future of Applied Behavior Analysis
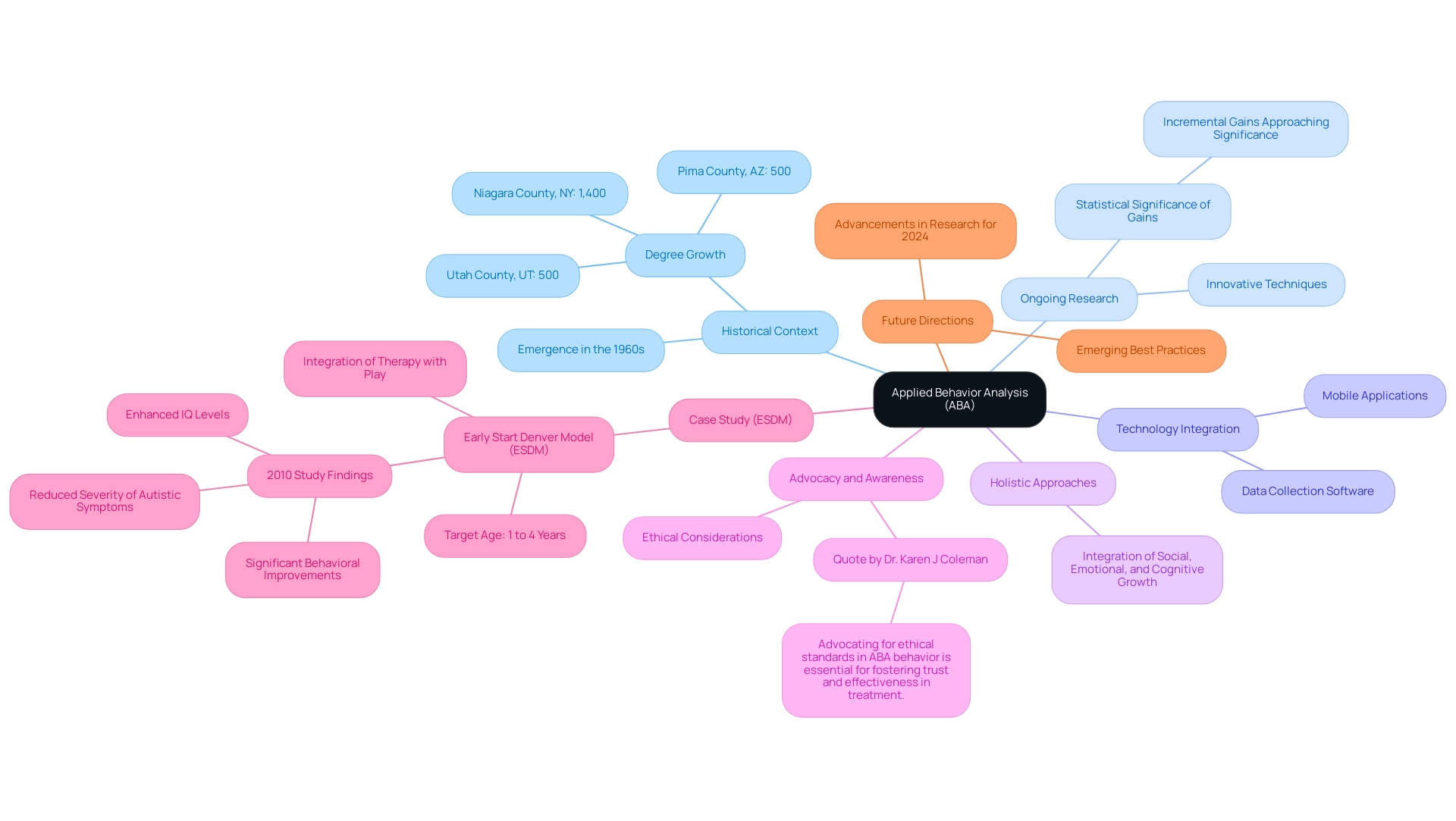
The field of ABA behavior has undergone a remarkable transformation since its inception, shaping the way we approach therapeutic interventions for autism and other developmental disorders.
- Historical Context: Emerging in the 1960s, ABA behavior has evolved into a widely recognized therapeutic strategy due to its effectiveness. As the discipline has matured, it has garnered significant support, particularly in counties like Niagara County, NY, where the number of degrees awarded in ABA surged by an astonishing 1,400%. Additionally, Pima County, AZ, and Utah County, UT, have also seen impressive growth in ABA degrees awarded, each increasing by 500%. This growth reflects a broader recognition of the importance of ABA behavior in the field.
- Ongoing research has led to innovative techniques and a more nuanced understanding of action modification, particularly in the context of ABA behavior. Recent studies indicate that, while time in ABA and receiving a full dose of treatment were not significantly associated with changes in behavior for the overall population, incremental gains observed over each 12-month period are approaching statistical significance, highlighting the need for continued investigation in this area.
- The integration of technology within ABA behavior practices is revolutionizing delivery methods. Tools such as mobile applications and data collection software are streamlining the monitoring of client progress, providing real-time feedback that enhances the effectiveness of interventions.
- Focus on Holistic Approaches: There is a notable shift towards holistic treatment strategies that integrate ABA behavior to address the entire child. This includes concentrating on social, emotional, and cognitive growth alongside traditional behavioral interventions, ensuring a well-rounded approach to treatment.
- Advocacy and Awareness: Growing public awareness and advocacy efforts are crucial in shaping the perception of ABA behavior. Ethical considerations are now more prominent, driven by advocates who emphasize the importance of respectful and informed practices in treatment. As Dr. Karen J Coleman aptly puts it, "Advocating for ethical standards in ABA behavior is essential for fostering trust and effectiveness in treatment." This insight emphasizes the need for practitioners to uphold ethical practices as they navigate the complexities of ABA behavior.
- Case Study: A significant example of an effective ABA behavior approach is the Early Start Denver Model (ESDM), which is tailored for individuals aged one to four. This model integrates therapy with play to enhance social and communication skills. A 2010 study found that participants in the ESDM program exhibited significant behavioral improvements, including enhanced IQ levels and reduced severity of autistic symptoms, illustrating the practical application of ABA techniques.
- Future Directions: The landscape of ABA is ever-evolving, and practitioners must stay informed about emerging best practices to provide optimal support for youth. Looking ahead to advancements in research set for 2024, it is vital for advocates to engage with these developments, ensuring they can effectively navigate the changing landscape of ABA behavior.
By understanding the historical context and future trajectory of ABA behavior, practitioners are empowered to embrace innovative methods that enhance the quality of life for children with autism and ADHD.
Conclusion
The exploration of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) reveals its profound impact on the development and well-being of children with autism and ADHD. By grounding interventions in scientific principles, ABA emphasizes the importance of understanding behavior as a learned phenomenon, allowing for tailored approaches that meet each child's unique needs. The core tenets of ABA, including reinforcement, data-driven practices, and functional assessments, equip practitioners to foster meaningful behavior changes that can lead to greater independence and resilience.
In practical terms, the diverse techniques employed within ABA—such as:
- Discrete Trial Training
- Natural Environment Training
- the use of visual supports
demonstrate the adaptability of this approach. These methods not only enhance learning but also empower parents to reinforce skills at home, ensuring the benefits of therapy extend beyond the clinical setting. Ethical considerations remain paramount, as informed consent, respect for dignity, and evidence-based practices guide practitioners in delivering compassionate and effective interventions.
As the field evolves, the educational pathways leading to certification in ABA highlight the commitment to professional excellence. This dedication, coupled with ongoing research and technological advancements, signals a bright future for ABA practitioners and the families they serve. By embracing innovative strategies and maintaining a focus on ethical practices, advocates can navigate the complexities of child development, ultimately paving the way for brighter futures for children facing the challenges of autism and ADHD.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ABA behavior and its significance?
ABA behavior is a scientifically validated method for understanding actions and their interaction with environmental factors. It is significant for effective intervention in individuals with autism and ADHD.
What are the foundational principles of ABA behavior?
The foundational principles include: 1. Conduct is learned. 2. Reinforcement is used to promote desired actions. 3. Data-driven practices ensure progress monitoring. 4. Individualization tailors interventions to unique needs. 5. Functional assessment identifies the reasons behind behaviors. 6. Generalization ensures skills learned are applicable in daily life.
How does reinforcement work in ABA behavior?
Reinforcement in ABA behavior involves using positive reinforcement to encourage desired actions while decreasing undesirable ones, supported by findings that highlight its effectiveness in various settings.
Why is data collection important in ABA practices?
Systematic data collection and analysis are crucial in ABA practices as they allow for monitoring progress and adjusting interventions as needed.
How are interventions tailored in ABA behavior?
Interventions are individualized to meet each student’s unique needs, reflecting their specific responses and requirements.
What is the role of functional assessment in ABA?
Functional assessment helps practitioners understand the reasons behind specific behaviors, allowing them to create effective interventions based on the individual's context.
What does generalization mean in the context of ABA?
Generalization refers to the application of skills learned in therapeutic environments to daily scenarios, promoting independence and flexibility.
How does ABA behavior address the needs of individuals with autism and ADHD?
By following the principles of ABA behavior, practitioners can create effective, tailored interventions that address the unique challenges faced by individuals with autism and ADHD.
What are some evidence-based ABA techniques?
Evidence-based techniques include: 1. Discrete Trial Training (DTT) 2. Natural Environment Training (NET) 3. Modeling 4. Social Skills Groups 5. Visual Supports 6. Parent Training.
What is Discrete Trial Training (DTT)?
DTT is a structured approach that breaks skills into manageable components, providing clear instructions and prompt feedback to help learners systematically acquire knowledge.
How does Natural Environment Training (NET) differ from other methods?
NET focuses on teaching skills in natural settings, which encourages practical application and improves skill generalization to daily situations.
What is the importance of social skills groups in ABA?
Social skills groups provide opportunities for youngsters to practice social interactions in a supportive environment, essential for developing communication skills and relationships.
How do visual supports enhance learning in ABA?
Visual supports, such as charts or picture schedules, cater to diverse learning styles and help children understand and communicate concepts more effectively.
Why is parent training included in ABA interventions?
Parent training is crucial as it equips parents with strategies to reinforce skills at home, extending the program's impact beyond therapy sessions.
What are the long-term benefits of early ABA behavior intervention?
Early and comprehensive ABA behavior intervention leads to long-term benefits, including improved adaptive behavior and social functioning, although it may not always reduce the severity of autism symptoms.




