Overview
Navigating the world of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be challenging, especially when it comes to understanding the essential DSM-5 codes that play a vital role in diagnosis and treatment. Among these, code 299.00 stands out as a comprehensive identifier for autism. This code is not just a number; it holds significant importance in ensuring that individuals with ASD receive the right support and care.
Accurate coding is crucial for effective treatment planning and insurance coverage. It paves the way for the development of tailored intervention strategies that can truly enhance outcomes for those affected by ASD. Imagine the peace of mind that comes with knowing that the right resources are being utilized to support your loved one’s unique needs.
As parents, you may often feel overwhelmed by the intricacies of the healthcare system. It’s essential to know that you are not alone in this journey. Sharing experiences and seeking support can make a world of difference. We encourage you to reach out, ask questions, and connect with others who understand the challenges you face. Together, we can foster a community that uplifts and empowers families navigating ASD.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), understanding the nuances of diagnosis and treatment is crucial for families navigating this journey. The DSM-5 has transformed how autism is classified and diagnosed, recognizing it as a spectrum that includes a diverse array of symptoms and severity levels. As we uncover significant disparities in prevalence rates among different demographic groups, the necessity of accurate and informed coding becomes increasingly evident.
This article explores the vital role of the DSM-5 in shaping autism diagnoses and the implications of coding on treatment access and insurance coverage. It highlights the essential responsibilities of healthcare professionals in ensuring that individuals with ASD receive the tailored support they need. By fostering awareness and understanding of these key elements, we empower families and advocates to navigate the complexities of autism care more effectively. Together, let’s work towards a future where every individual with ASD receives the compassionate care and support they deserve.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder and the DSM-5
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition that presents enduring challenges in social communication and interaction, along with restricted and repetitive behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, has transformed the landscape of autism diagnoses by merging previously distinct categories into a singular umbrella classification, known as the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code. This pivotal change reflects a more sophisticated understanding of autism, recognizing it as a spectrum that encompasses a diverse range of symptoms and severity levels.
Recent data highlights the prevalence of ASD, revealing significant variations among different demographic groups. For instance, the CDC's 2023 Community Report on Autism indicates that the prevalence of ASD among non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander children is 33.4 per 1,000 children. Importantly, this report underscores the disruptions in early identification of ASD during the COVID-19 pandemic, which have led to emerging patterns in racial and ethnic differences in diagnosis. It’s essential to note that the data collected applies solely to 8-year-olds, a factor to consider when interpreting these prevalence statistics.
Understanding these foundational concepts is crucial for anyone involved in the care or support of individuals with autism. Accurate diagnosis using the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code is essential, as it informs the development of tailored intervention strategies that can significantly enhance outcomes. The diagnostic manual not only offers a standardized framework for diagnosis but also reflects the latest research and expert opinions on the characteristics of ASD, including a male-to-female ratio of approximately 4:1 according to CDC data. This ratio emphasizes the importance of recognizing gender differences in autism diagnosis, reinforcing the need for a nuanced approach to understanding and supporting individuals on the spectrum.
Key DSM-5 Codes for Autism Spectrum Disorder
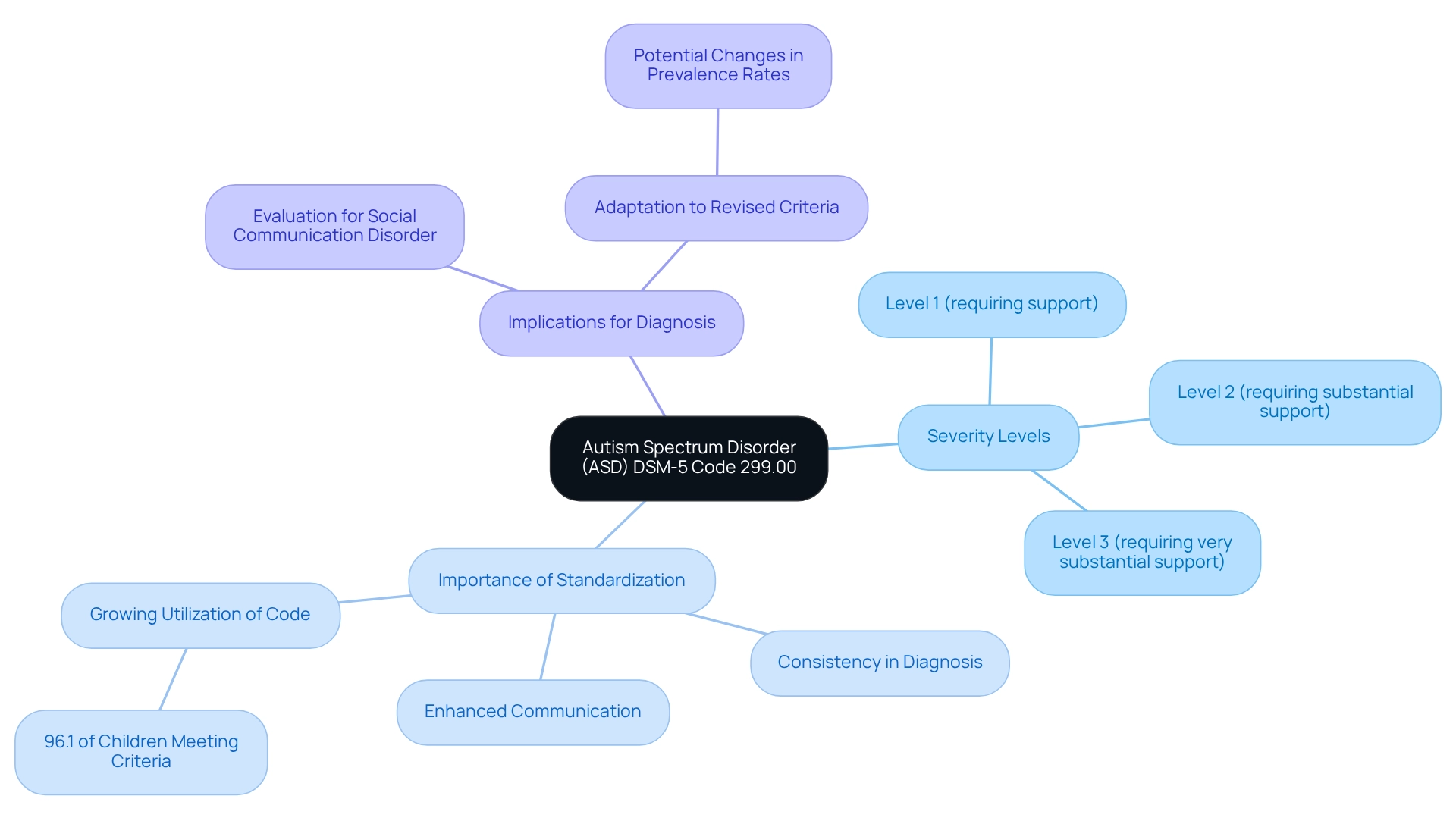
Understanding the classification number for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), which is 299.00, is vital for many families navigating this journey. This code, identified by the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5, serves as a comprehensive identifier for all types of autism within the diagnostic framework. For healthcare professionals, this program is essential; it standardizes diagnosis across various clinical and educational environments, ensuring consistency in treatment and support.
ASD is further categorized into three levels of severity, each indicating the degree of assistance an individual may need:
- Level 1 (requiring support)
- Level 2 (requiring substantial support)
- Level 3 (requiring very substantial support)
Grasping these classifications is crucial not only for precise documentation but also for fostering effective communication among healthcare practitioners, parents, and educators.
Recent statistics reveal that a significant percentage of healthcare providers are now utilizing the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code for diagnosis, reflecting a growing commitment to standardized practices. For instance, when easing the criteria for ASD diagnosis, 96.1% of children met the current ADDM Network ASD case definition. This emphasizes how important these classifications are in recognizing and assisting individuals on the spectrum.
As Eugene Laska, PhD, from the Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, wisely noted, "The incorporation of standardized systems is crucial for enhancing diagnostic precision and guaranteeing that individuals obtain the suitable interventions."
Moreover, it’s essential to understand that individuals with marked deficits in social communication who do not meet ASD criteria should be evaluated for social (pragmatic) communication disorder. Case studies suggest that as clinicians become more familiar with the revised diagnostic criteria, they are likely to document additional symptoms. This may lead to a convergence in ASD prevalence rates based on both old and new criteria over time. Such evolution in diagnostic practices underscores the significance of the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code, particularly 299.00, in ensuring that individuals receive the evaluations and interventions they truly need.
Diagnostic Criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder in the DSM-5
The manual provides essential diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), including the DSM-5 code, which underscores the importance of persistent deficits in social communication and interaction across various contexts. It also highlights restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior. These criteria are organized into two main domains:
- Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, which encompass challenges in nonverbal communication and difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships;
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
To confirm a diagnosis under the DSM-5 code, individuals must meet these criteria, emphasizing the vital role of comprehensive assessments by qualified professionals.
Recent data focused on 8-year-olds reveals a concerning prevalence of ASD, indicating that approximately 1 in every 36 children is diagnosed with the disorder. This statistic shows significant variations based on sex and race/ethnicity. For instance, boys are diagnosed at a rate of 4.3%, compared to just 1.1% for girls, highlighting a disparity that invites further exploration. In fact, ASD is 3.8 times more common among boys than girls.
Moreover, Black children are more frequently classified as having intellectual disabilities compared to their Hispanic and White peers, raising important questions about diagnostic practices and access to care. Additionally, girls with ASD are less likely than boys to have cognitive ability data, which points to critical demographic differences in diagnosis.
Understanding the diagnostic criteria, especially the DSM-5 code, along with the associated demographics, is crucial for parents and advocates. This knowledge informs strategies for early identification and intervention. The CDC is dedicated to providing vital data on ASD and developing resources aimed at identifying children with ASD as early as possible. Comprehensive evaluations that consider these factors are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective support for children with ASD.
As noted by Williams AR, "Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years — Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020," these findings are invaluable for understanding the demographics of ASD and shaping public health strategies. Together, we can foster a more informed community, supporting each other through the challenges and triumphs of navigating ASD.
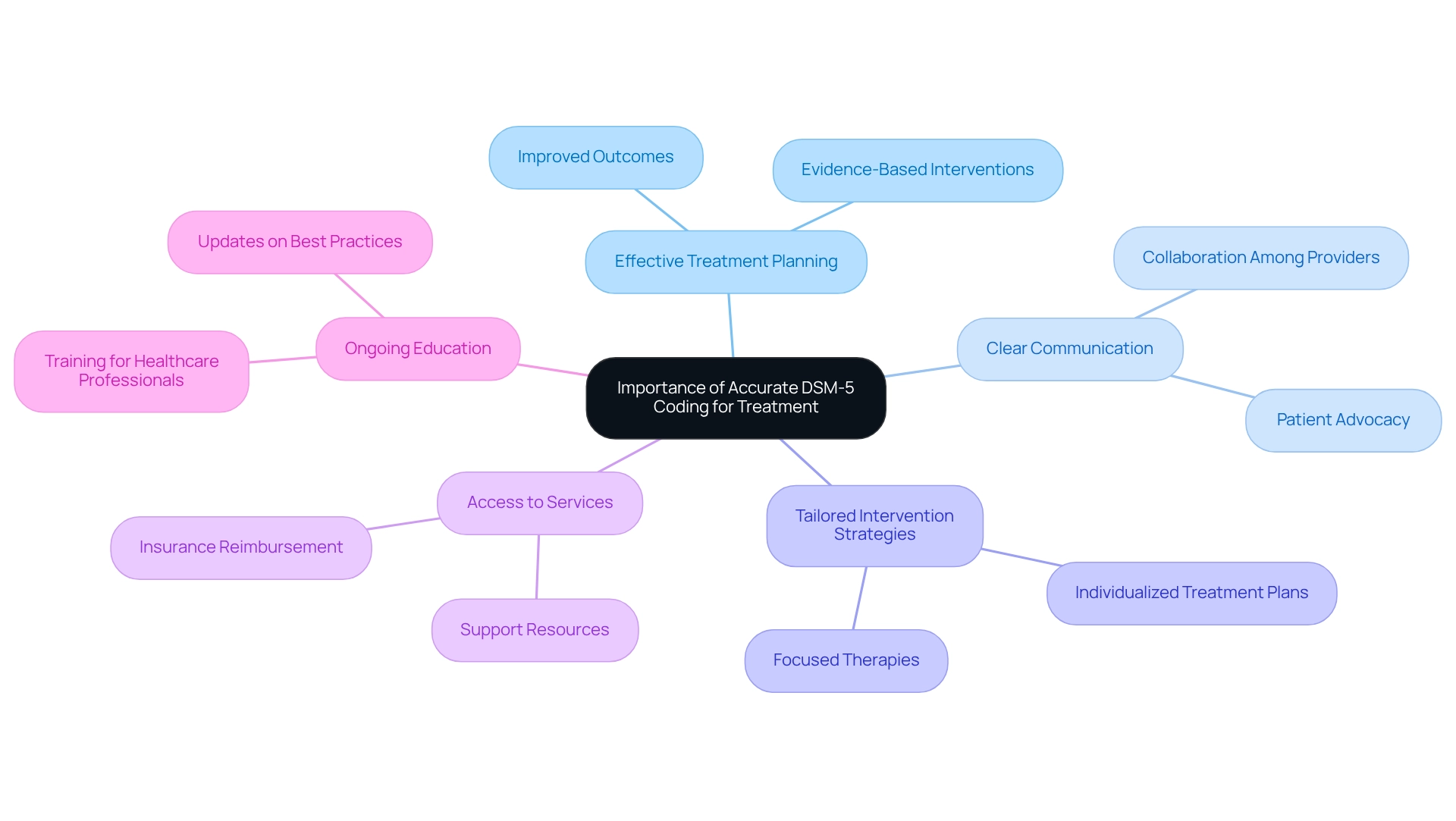
The Importance of Accurate DSM-5 Coding for Treatment
Precise coding, especially the DSM-5 code for autism spectrum disorder, is vital for effective treatment planning and management of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This coding not only facilitates clear communication among healthcare providers about a patient's diagnosis but also plays a crucial role in developing tailored intervention strategies. Moreover, accurate coding is essential for accessing necessary services and support, as many insurance companies require specific identifiers for reimbursement.
Understanding this process empowers parents and professionals to advocate more effectively for the resources and support that individuals with ASD need.
The impact of diagnostic coding goes beyond administrative tasks; it directly shapes intervention strategies. When treatment plans align with the appropriate diagnostic classifications, healthcare providers can implement focused therapies that cater to the unique needs of each individual. This alignment enhances treatment efficacy and ensures that interventions are evidence-based and grounded in the latest clinical insights.
Case studies underscore the importance of precise coding in autism treatment. A recent analysis revealed that practices utilizing accurate coding experienced improved outcomes in their treatment plans, highlighting the connection between coding accuracy and successful intervention strategies. Healthcare professionals emphasize the need for ongoing education about the DSM-5 code for autism spectrum disorder, ensuring practitioners remain informed about best practices in treatment planning for ASD.
As noted by Aich et al., 'Ongoing enhancement of LLMs that include varied real-world clinical data is essential to elevate their precision,' underscoring the need for continual advancements in coding practices.
Statistics indicate that the manual will assist around 200,000 psychiatrists worldwide in providing better care for individuals with mental disorders, showcasing the global significance of precise coding. The 'treatment-prevalence paradox' reveals that even with rising treatment rates, the prevalence of mental disorders has not significantly decreased, illustrating the challenges within the field. As we move forward, refining coding practices related to the DSM-5 code for autism spectrum disorder will be crucial for improving treatment effectiveness and addressing the complexities of ASD.
By prioritizing precise coding from the diagnostic manual, parents and professionals can profoundly enhance the quality of care and support available to individuals with autism.
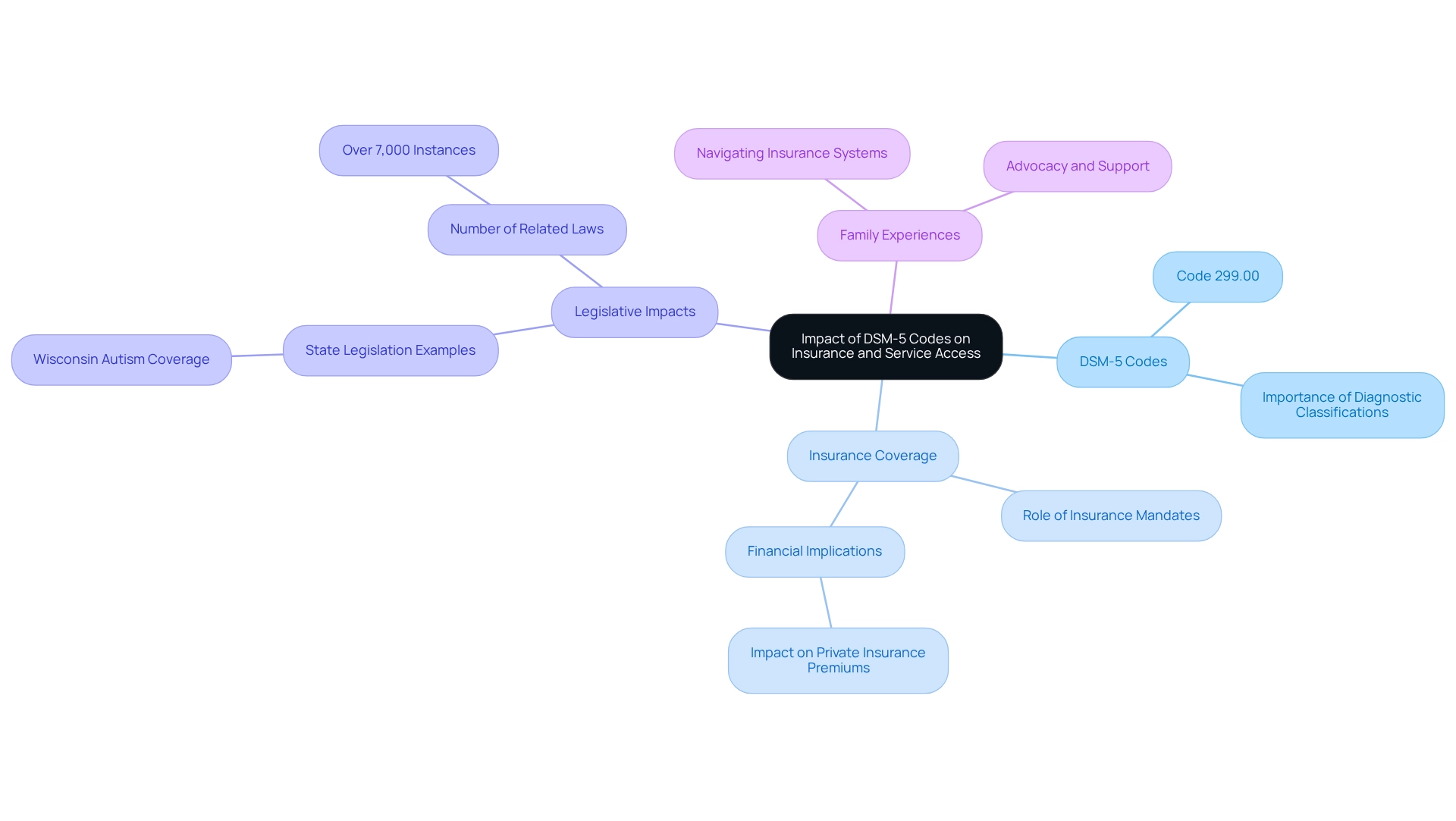
Impact of DSM-5 Codes on Insurance and Service Access
Understanding the DSM-5 code classifications for autism spectrum disorder is essential, especially when it comes to insurance coverage and accessing vital services. Insurance companies often require specific diagnosis identifiers to approve treatment and facilitate reimbursement for healthcare professionals. For families seeking coverage for therapies like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), the number 299.00 becomes crucial.
This necessity highlights the importance of grasping how these regulations operate within the insurance landscape, as they directly influence the availability of essential treatments for children.
Professionals in the field emphasize that the leniency of insurance mandates can significantly affect access to services. A leading researcher notes that the extent of coverage provided by these mandates is just as critical as the legislation itself. This insight resonates deeply with families who navigate the complexities of insurance, often facing challenges in obtaining coverage without the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code.
In a recent report by James N Bouder, Stuart Spielman, and David S Mandell, the impact of autism coverage on private insurance premiums is quantified, shedding light on the financial implications of these mandates. Understanding how diagnostic classifications affect service accessibility is vital, as they also influence the overall cost of insurance for families. Statistics reveal that numerous states have enacted laws to enhance coverage for autism therapies, with over 7,000 instances of related legislation documented.
A compelling case study from Wisconsin illustrates this impact: the state mandates that disability insurance policies cover autism treatment prescribed by qualified professionals, ensuring significant financial support for both intensive and non-intensive services. This legislative framework fosters access to essential therapies, demonstrating the tangible benefits of understanding and utilizing diagnostic codes.
Furthermore, an enhanced difference-in-differences specification has been prioritized to analyze the impacts of these mandates, providing a clearer perspective on how the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code influences insurance coverage. Families frequently share their experiences navigating insurance systems, emphasizing how the correct application of diagnostic classifications can unlock access to crucial autism services. By equipping parents with knowledge about these guidelines, ASD Media aims to encourage advocacy and support, ensuring that children receive the comprehensive care they need to thrive.
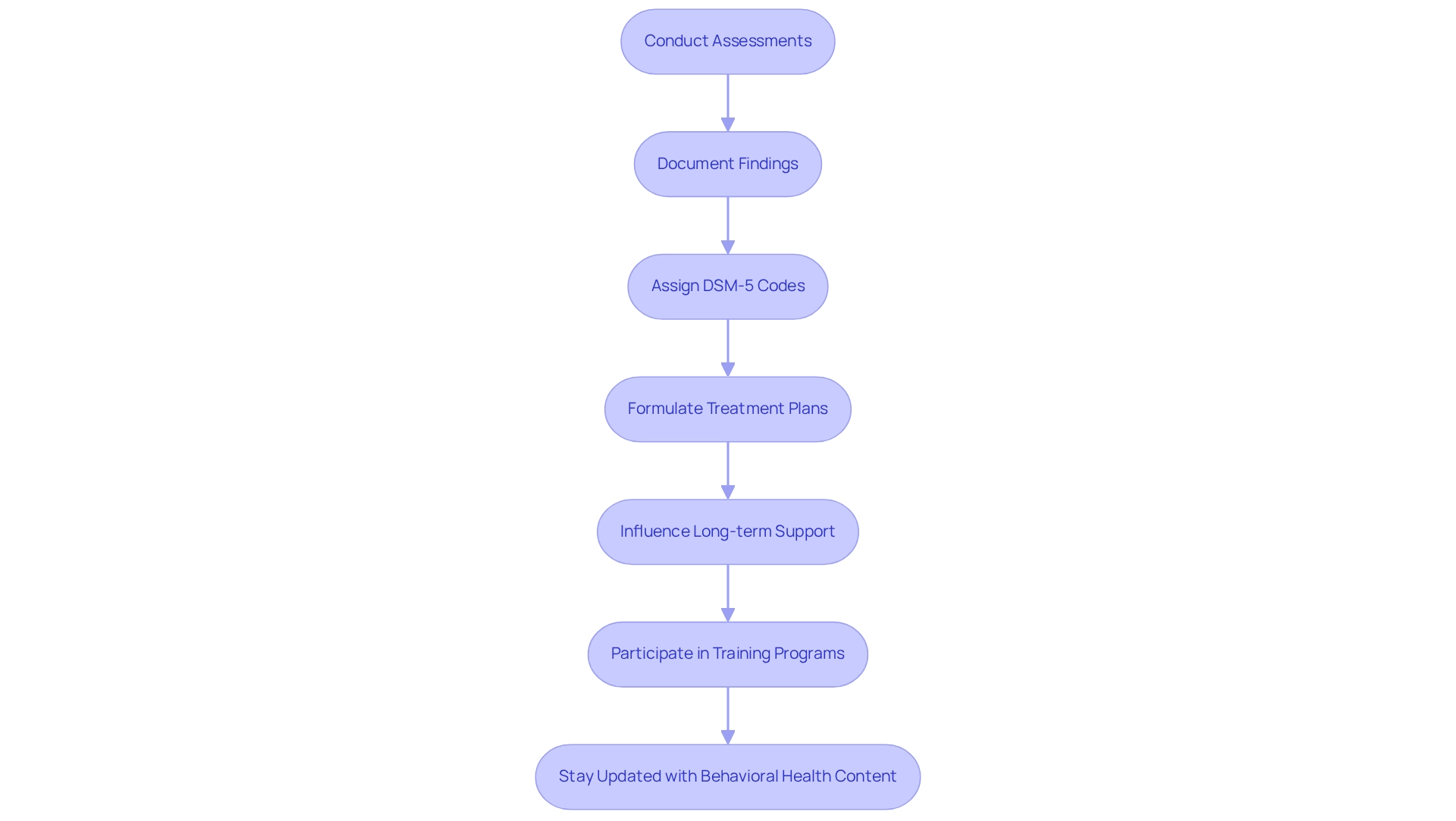
Role of Healthcare Professionals in DSM-5 Coding
Healthcare experts, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and pediatricians, play a vital role in accurately implementing the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code classifications. Their responsibilities involve conducting thorough assessments, meticulously documenting findings, and assigning the appropriate codes, such as the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code. This detailed process not only formulates immediate treatment plans but also significantly influences long-term support and intervention strategies for individuals with ASD.
Research underscores the necessity of a well-informed healthcare workforce to enhance diagnostic accuracy. For example, a recent survey of 1,764 mental health professionals revealed that most had substantial experience in the field, with an average age of 46.2 years, predominantly male, and primarily from high-income countries. This demographic highlights a strong foundation of knowledge among providers, which is essential for effective coding practices.
Moreover, experts stress the critical importance of accurate documentation in ASD treatment. As noted by Julie Glasgow, MD, "Mental and behavioral health is a critically important area of healthcare, and we’re proud that IMO Health’s behavioral health content supports the providers who care for individuals facing these challenges every day." Understanding the intricacies of diagnostic coding, including the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code, is crucial for delivering high-quality care.
Regular updates to behavioral health content, such as those provided by organizations like IMO Health, ensure that healthcare providers stay informed about the latest changes in mental and behavioral health diagnoses.
Training programs focused on diagnostic coding can significantly enhance the precision of diagnoses using the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code. By equipping healthcare providers with the necessary skills and knowledge, these programs promote better outcomes for individuals with ASD. Efficient coding methods not only streamline the treatment process but also improve access to vital assistance services, ultimately benefiting individuals and families alike.
In summary, the role of healthcare professionals in the coding process for the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code is indispensable. Their expertise and commitment to accurate documentation directly influence the quality of care and support available to individuals with ASD, highlighting the importance of ongoing education and training in this area. Additionally, comprehending the common reasons for using 'residual' categories can help address challenges in coding practices for ASD, further emphasizing the necessity for continuous professional development in this field.
Advocating for Awareness of DSM-5 Codes in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Promoting awareness of the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code classifications is vital for empowering parents and supporters within the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) community. By informing families about the significance of these regulations, they can navigate the complexities of diagnosis, treatment, and insurance coverage more effectively. Unfortunately, research indicates that many parents remain unaware of these guidelines, which can hinder their ability to access essential services.
For instance, a recent study revealed that unemployed parents reported a mean stigma score of 2.40 (SD = 0.60), highlighting the challenges they encounter in seeking support for their children with ASD.
Ongoing educational initiatives play a crucial role in demystifying the coding process. Programs designed to educate families about the diagnostic criteria can enhance their advocacy skills, enabling them to articulate their children's needs more effectively. As the landscape of autism support evolves, fostering awareness and understanding of diagnostic classifications becomes increasingly important.
This knowledge not only empowers parents but also nurtures a more informed community that can advocate for improved resources and support.
Case studies have illustrated that perceived stigma can significantly affect health service utilization among families of children with ASD. The study titled "Perceived Stigma Among Families of Children with ASD" developed a brief, validated measure of stigma perceived by parents, examining variations in stigma by demographics and exploring the association between perceived stigma and ASD service use. By addressing these perceptions through education, advocates can enhance access to essential services.
The American Psychiatric Association's recent revisions to the DSM-5-TR clarify diagnostic criteria, stating that the phrase 'manifested by the following' was revised to read 'as manifested by all of the following' to improve clarity. This change underscores the importance of parents staying informed about these updates. As advocates highlight the necessity of educating families about the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code, they are paving the way for a more supportive environment in which individuals with ASD can receive the comprehensive care they deserve.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and the role of the DSM-5 is crucial for families and advocates alike. This article highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis and coding, which serve as the foundation for effective treatment planning and access to necessary services. The DSM-5 not only provides a standardized framework for diagnosing autism but also reflects evolving research and insights into the diverse manifestations of the disorder across different demographic groups.
The implications of DSM-5 coding extend beyond the clinical setting, directly influencing insurance coverage and access to therapies that can significantly improve the lives of individuals with ASD. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in this process, as their expertise in applying these codes ensures that individuals receive the appropriate support tailored to their unique needs. As parents and advocates, increasing awareness and understanding of DSM-5 codes empowers you to navigate the often-complex landscape of autism care more effectively.
Ultimately, fostering a comprehensive understanding of the DSM-5 and its impact on ASD diagnosis and treatment is essential for advocating for the rights and needs of individuals on the spectrum. By working together to raise awareness and ensure accurate coding practices, families and professionals can contribute to a future where every individual with autism receives the compassionate care and support they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition characterized by enduring challenges in social communication and interaction, as well as restricted and repetitive behaviors.
How has the DSM-5 changed the classification of autism?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) has merged previously distinct categories of autism into a singular classification known as autism spectrum disorder, reflecting a more sophisticated understanding of autism as a spectrum with a diverse range of symptoms and severity levels.
What does recent data say about the prevalence of ASD?
The CDC's 2023 Community Report on Autism indicates significant variations in the prevalence of ASD among different demographic groups, with non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander children having a prevalence of 33.4 per 1,000 children. The report also highlights disruptions in early identification of ASD during the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is the importance of the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code?
The autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code, classified as 299.00, serves as a comprehensive identifier for all types of autism within the diagnostic framework, essential for standardizing diagnosis and ensuring consistency in treatment and support across clinical and educational environments.
How is ASD categorized in terms of severity?
ASD is categorized into three levels of severity: Level 1 (requiring support), Level 2 (requiring substantial support), and Level 3 (requiring very substantial support).
Why is understanding ASD classifications important?
Understanding ASD classifications is crucial for precise documentation and effective communication among healthcare practitioners, parents, and educators, which can enhance the support provided to individuals on the spectrum.
What percentage of healthcare providers are using the DSM-5 code for ASD diagnosis?
A significant percentage of healthcare providers are now utilizing the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code for diagnosis, with 96.1% of children meeting the current ADDM Network ASD case definition when easing the criteria for diagnosis.
What should be considered for individuals with social communication deficits who do not meet ASD criteria?
Individuals with marked deficits in social communication who do not meet ASD criteria should be evaluated for social (pragmatic) communication disorder, as clinicians may document additional symptoms with familiarity of the revised diagnostic criteria.
What is the significance of the evolution in diagnostic practices for ASD?
The evolution in diagnostic practices underscores the importance of the autism spectrum disorder DSM-5 code in ensuring that individuals receive the evaluations and interventions they truly need, potentially leading to convergence in ASD prevalence rates based on both old and new criteria over time.




