Overview
The article delves into the three levels of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)—Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3—each distinguished by different support needs and specific symptoms. Understanding these levels is crucial for parents seeking the best for their children. It highlights the importance of tailored support strategies and early intervention. Research shows that timely assistance can profoundly enhance outcomes for individuals across the spectrum. For instance, early therapy has been linked to improved cognitive and adaptive functioning. This is a reminder that every step taken towards support can make a significant difference. As we navigate these challenges together, let’s explore how we can provide the best resources and encouragement for those on this journey.
Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential in today’s world, where its prevalence is rapidly increasing. Recent statistics reveal that 1 in 36 children in the U.S. are diagnosed with this complex neurodevelopmental condition. ASD manifests in various ways, leading to significant challenges in communication, social interaction, and behavior, which can vary dramatically from one individual to another.
By exploring the three distinct levels of autism, caregivers and professionals can uncover tailored support strategies that truly enhance the quality of life for those affected. However, with such diversity in symptoms and needs, it raises a vital question: how can one effectively navigate the complexities of autism to provide the most beneficial interventions?
This journey requires understanding, compassion, and a willingness to learn. Together, we can foster a supportive environment that addresses the unique challenges faced by individuals with autism and their families.
Define Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Levels
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that can profoundly impact individuals and their families. It is characterized by challenges in interpersonal interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' highlights the diverse range of symptoms and severity levels experienced by those with autism. Understanding the three levels of autism is essential for parents and caregivers who want to provide the best support possible.
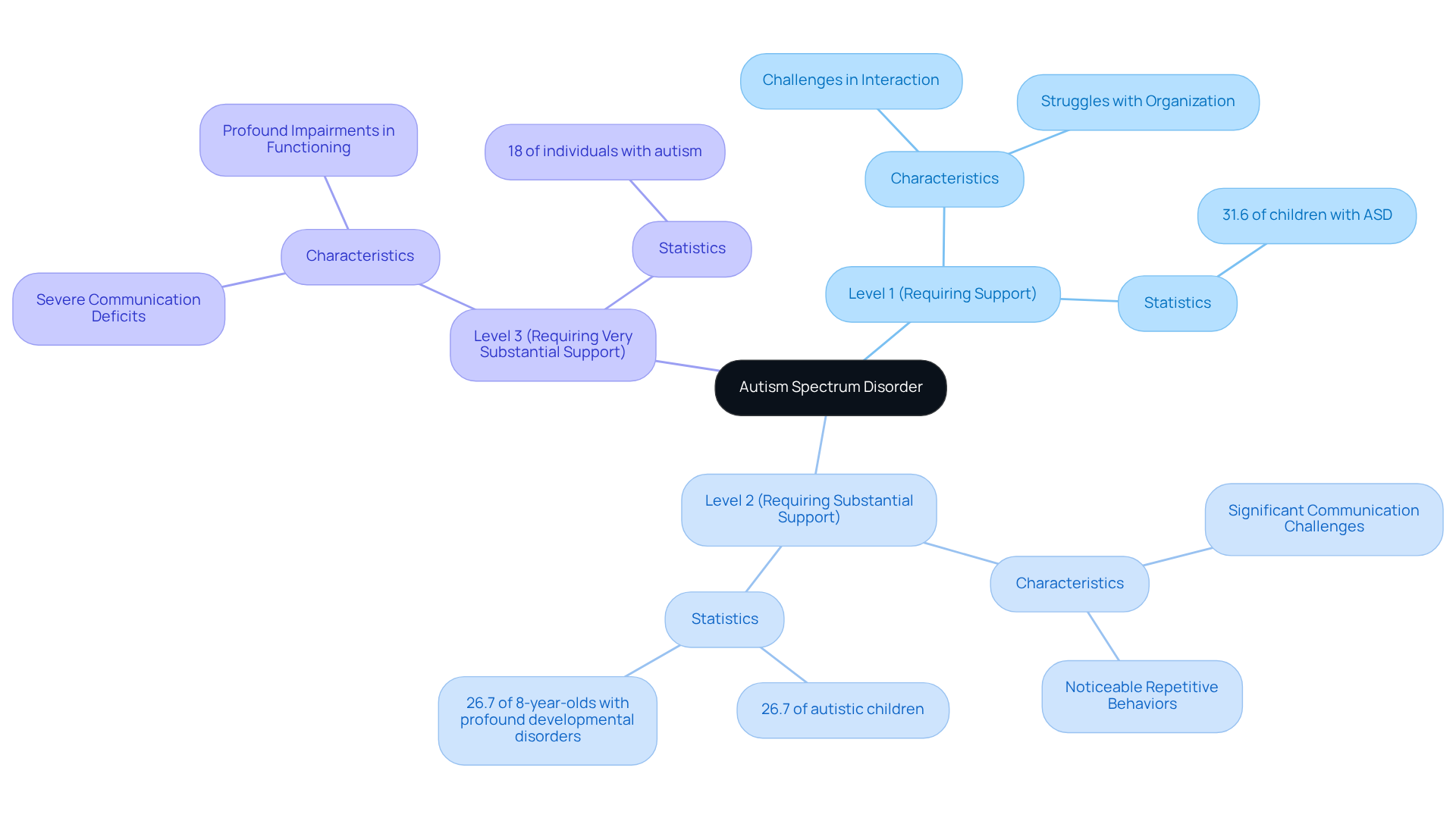
Level 1 (Requiring Support): Individuals at this level may find it challenging to initiate interactions with others. They often struggle with organization and planning, which can hinder their independence. Approximately 31.6% of children identified with ASD belong to this group. This emphasizes the necessity for focused assistance to enhance their interaction abilities and everyday functioning.
Level 2 (Requiring Substantial Support): Those in this category face more significant challenges in communication and may exhibit noticeable repetitive behaviors. About 26.7% of autistic children fall into this group, highlighting the need for substantial support to navigate daily life effectively. Structured interventions can foster communication and social engagement, addressing the unique needs of these children. Notably, 26.7% of autistic 8-year-olds in the U.S. experience profound developmental disorders, indicating severe symptoms that require lifelong care.
Level 3 (Requiring Very Substantial Support): Individuals in this category experience severe deficits in both verbal and nonverbal communication skills, leading to profound impairments in functioning. They typically need considerable assistance across all aspects of life, accounting for approximately 18% of individuals diagnosed with autism. This level underscores the critical need for comprehensive care and tailored support strategies that meet their unique challenges.
As the incidence of ASD continues to rise, with recent estimates indicating that 1 in 36 children in the U.S. are diagnosed, it becomes increasingly vital for educational and healthcare systems to adapt to the varied needs of individuals across the spectrum. The prevalence of this condition has surged by 312% since 2000, highlighting the urgency for such adaptations. Moreover, boys are diagnosed with ASD 4.2 times more frequently than girls, pointing to significant gender disparities in diagnosis.
By fostering a deeper understanding of the three levels of autism, parents and professionals can more effectively advocate for essential resources and support. Together, we can improve the quality of life for individuals affected by developmental disorders. If you have experiences or insights to share, please join the conversation in the comments or through our newsletter. Your voice matters in this journey of understanding and support.
Explore Characteristics and Symptoms of Each Autism Level
Understanding the three levels of autism is crucial for both parents and professionals, as each level presents unique characteristics and symptoms that deserve compassionate attention.
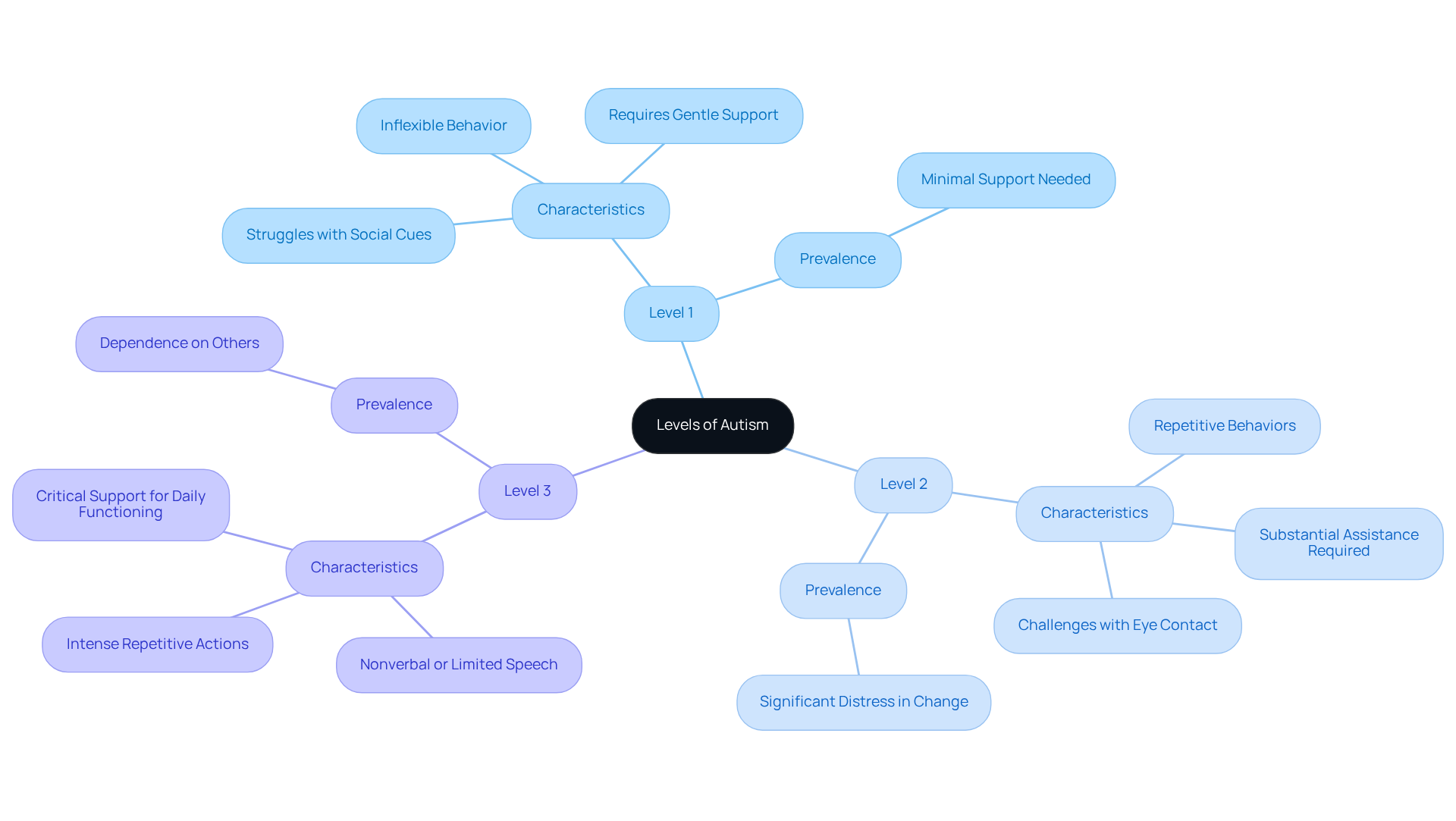
Level 1: Individuals may seem to function well, yet they often struggle with social cues and maintaining conversations. Picture a child who appears engaged but feels overwhelmed by the nuances of social interaction. They may also show inflexible behavior, requiring gentle support to navigate changes in routine.
Level 2: Here, symptoms become more pronounced. Imagine a teenager who finds it challenging to make eye contact and grasp societal norms. They may exhibit repetitive behaviors, and their journey often calls for substantial assistance in daily activities, fostering a nurturing environment for growth.
Level 3: This level can be particularly challenging. Some individuals may be nonverbal or have very limited speech, facing significant hurdles in interpersonal engagement. Visualize a young adult who participates in intense repetitive actions, needing critical support for basic daily functioning and often requiring constant supervision.
Recognizing these symptoms is essential. By understanding the three levels of autism, we can better provide the necessary interventions to support individuals with autism and their families. Let’s come together to share experiences and resources, fostering a community of understanding and compassion.
Identify Support Strategies for Each Level of Autism
Support strategies for autism are crucial and vary significantly across the three levels of autism, with each level requiring tailored approaches to enhance individual outcomes.
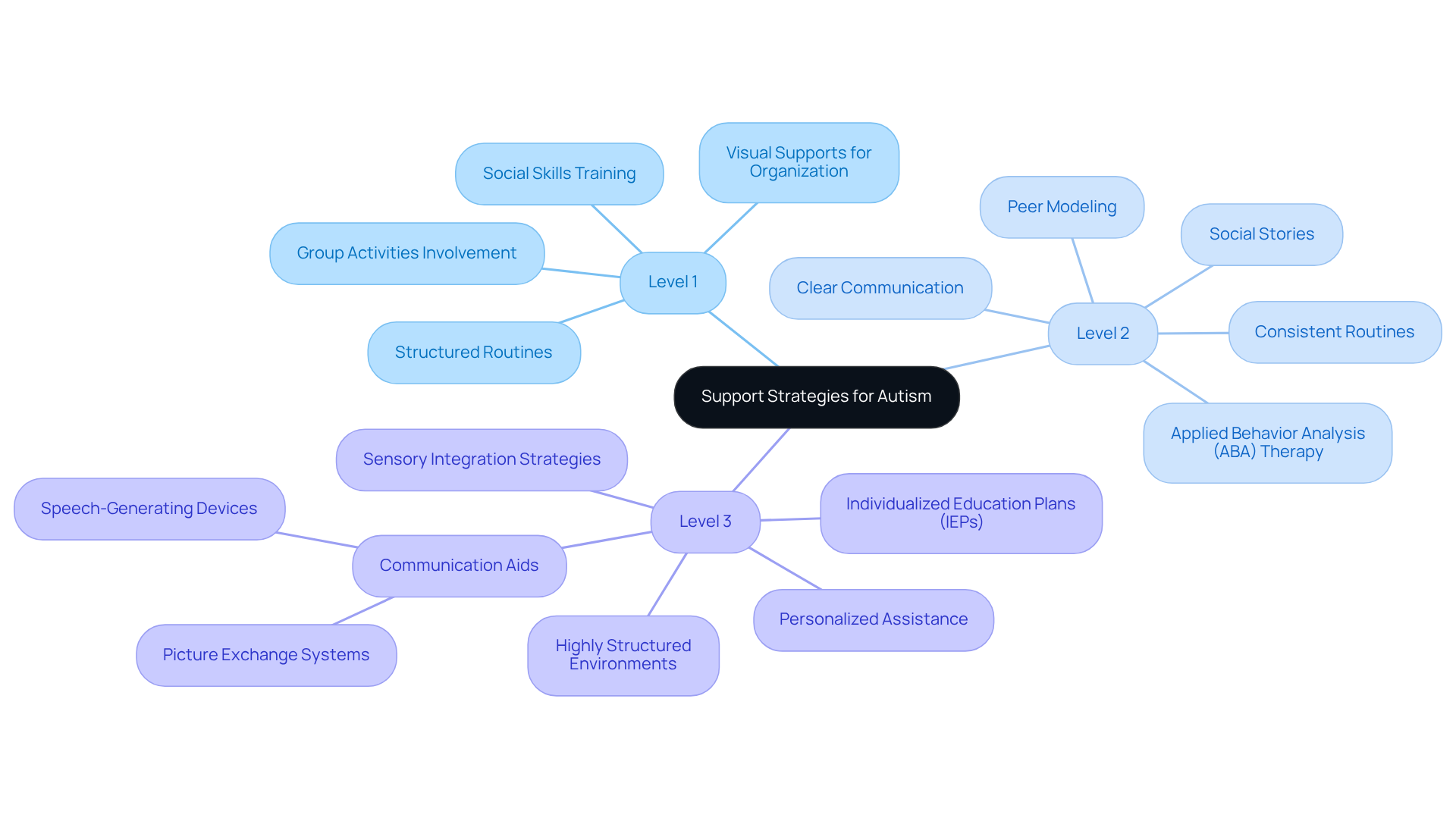
At Level 1, effective strategies include:
- Social skills training
- Visual supports for organization
- Structured routines that facilitate smoother transitions
Promoting involvement in group activities can also enhance engagement, helping individuals form connections and improve their interactions with others.
For those at Level 2, more intensive interventions such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy are essential. Studies indicate that 36.5% of autism caregivers utilize ABA therapy, noting favorable outcomes in managing behaviors and enhancing interpersonal skills. Additional strategies include:
- Social stories
- Peer modeling
Consistent routines and clear communication help alleviate anxiety and promote social development.
Individuals at Level 3 within the three levels of autism may benefit from:
- Highly structured environments
- Individualized education plans (IEPs)
- Personalized assistance tailored to their unique needs
Communication aids, such as picture exchange systems or speech-generating devices, can significantly enhance interaction. Furthermore, sensory integration strategies are vital for managing sensory sensitivities, ensuring a more comfortable and supportive environment.
By applying these strategies, caregivers can witness significant enhancements in the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum, enabling them to navigate their environment more effectively. If you have experiences or insights to share, we encourage you to connect with us in the comments or through our newsletter.
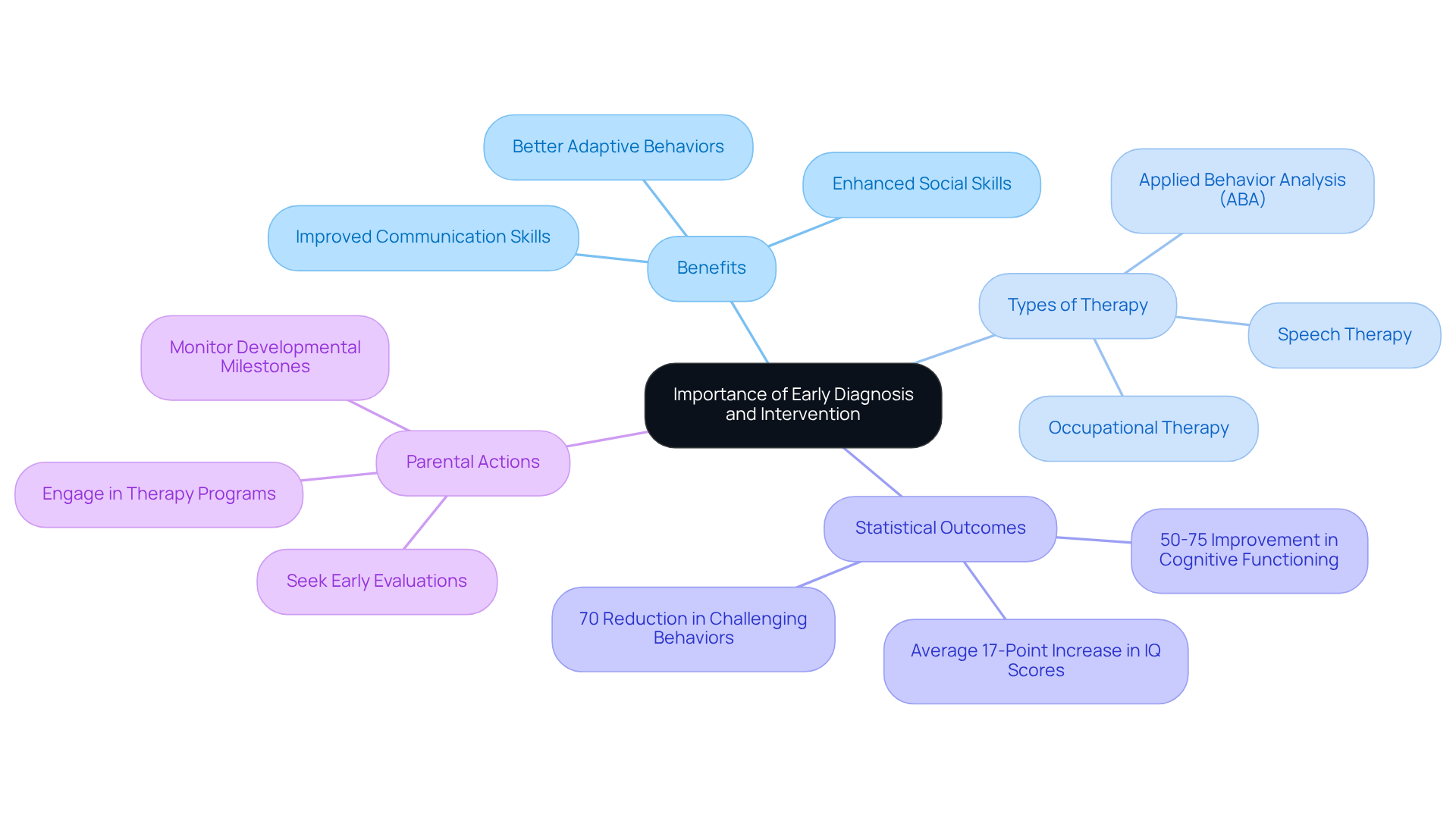
Understand the Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Prompt identification and assistance are essential for children with developmental disorders. Studies consistently show that timely support can lead to significant improvements in communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors. Research indicates that children who receive early support, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy, tend to achieve better outcomes. This is largely due to the brain's increased plasticity during early developmental stages. For instance, research reveals that 50-75% of children who undergo intensive ABA therapy for two or more years demonstrate notable improvements in cognitive and adaptive functioning. Additionally, children engaged in ABA-based early intervention programs have made remarkable progress, with some reducing challenging behaviors by as much as 70% within a year, as seen in Ethan's case, who received a diagnosis at two years old.
Parents are strongly encouraged to seek evaluations if they notice signs of autism, such as delayed communication or limited social interaction. Acting promptly can enhance access to tailored assistance services that cater to each child's unique needs, ultimately leading to better long-term outcomes. Research shows that children who begin therapy before age three often reach more significant developmental milestones. Studies suggest that those who receive early assistance experience an average 17-point increase in IQ scores compared to their peers who start therapy later, underscoring the importance of early support.
By recognizing the significance of early diagnosis and intervention, parents and professionals can take proactive steps to support individuals across the three levels of autism, unlocking their potential and improving their quality of life. As the National Research Council states, 'The sooner a child gets help, the greater the chance for learning and progress.
Conclusion
Understanding the three levels of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for providing effective support to individuals and their families. By recognizing the varying degrees of challenges faced by those on the spectrum, caregivers and professionals can tailor their approaches to meet the unique needs of each individual, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
The article highlights the characteristics of each autism level:
- Level 1: where individuals require support in social interactions
- Level 2: where substantial assistance is necessary due to pronounced communication challenges
- Level 3: which involves very substantial support for severe deficits in communication and functioning
It also emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and intervention, showcasing how timely support can lead to significant improvements in developmental outcomes.
In conclusion, fostering a deeper understanding of autism levels and advocating for early intervention can empower families and professionals to make informed decisions. By sharing experiences and resources, the community can work together to create a more inclusive environment for individuals with autism, ensuring they receive the support they need to thrive. Taking proactive steps today can unlock the potential of those on the spectrum, paving the way for a brighter future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in interpersonal interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. It is referred to as a 'spectrum' due to the diverse range of symptoms and severity levels experienced by individuals with autism.
What are the three levels of autism?
The three levels of autism are: - Level 1 (Requiring Support): Individuals may struggle with initiating interactions and organization, affecting their independence. - Level 2 (Requiring Substantial Support): Individuals face significant communication challenges and exhibit noticeable repetitive behaviors. - Level 3 (Requiring Very Substantial Support): Individuals have severe deficits in both verbal and nonverbal communication, requiring considerable assistance in all aspects of life.
How prevalent is Autism Spectrum Disorder in children?
Recent estimates indicate that 1 in 36 children in the U.S. are diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder, with the prevalence having surged by 312% since 2000.
What percentage of children with ASD fall into each level?
Approximately 31.6% of children with ASD are categorized as Level 1, 26.7% as Level 2, and 18% as Level 3.
What gender disparities exist in the diagnosis of ASD?
Boys are diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder 4.2 times more frequently than girls, indicating significant gender disparities in diagnosis.
Why is understanding the levels of autism important for parents and caregivers?
Understanding the three levels of autism is essential for parents and caregivers to provide appropriate support and advocate for necessary resources tailored to the unique challenges faced by individuals across the spectrum.