Introduction
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for parents and professionals in order to provide the appropriate support and guidance for children with this diagnosis. Level 2 Autism, also known as moderate autism, presents challenges in social interpretation, communication, and behavior. It is important to recognize the key features and challenges of Level 2 Autism to effectively manage and support these children.
In this article, we will explore the complexities of Level 2 Autism and its impact on social skills development. We will discuss the importance of early intervention and Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in managing the symptoms of Level 2 Autism. Additionally, we will highlight strategies for supporting social skills development and empowering parents as advocates. By understanding the unique needs of children with Level 2 Autism and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can create a supportive and inclusive environment that promotes their growth and development
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: Key Features and Challenges
Comprehending the complexities of Level 2 Autism, or moderate autism, is of paramount importance for both parents and professionals. Children with this type of autism often face challenges in interpreting social situations, and they may struggle with verbal and non-verbal communication. Furthermore, they might exhibit repetitive behaviors and have specific, narrow interests.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition (DSM-5), autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is categorized into three levels. Level 2 Autism, falling in the middle of this spectrum, presents considerable challenges in verbal and nonverbal communication.
These children's responses to social cues may be reduced or abnormal, and they demonstrate a pronounced inflexibility in behavior. Additionally, alterations in routine can cause significant distress, leading to challenging behavior.
In the past, the DSM-IV classified autism into five subcategories, including Asperger's syndrome and severe autism. However, these are now considered outdated diagnoses. The focus has shifted towards the individual's specific challenges and their requirements for support, rather than their diagnosis level.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, a crucial tool for treating ASD symptoms and improving the child's quality of life, requires a formal diagnosis. Early intervention, facilitated by an accurate diagnosis, is key to managing the symptoms of Level 2 Autism effectively. ABA therapy methods, such as visual supports, sign language, and augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, have proven effectiveness in improving communication skills in children with moderate autism. Techniques like discrete trial training (DTT), naturalistic teaching strategies, and social communication interventions are common in ABA therapy. These techniques aim to enhance communication skills by breaking down skills into smaller steps, providing repeated practice, and reinforcing desired communication behaviors.
The Place for Children with Autism, a specialized center, offers services for children aged 2-6. They provide resources, host events, and facilitate enrollment, easing the journey for parents and professionals to provide the necessary support for children with Level 2 Autism.
A crucial aspect of supporting children with moderate autism is fostering their social skills. Strategies such as creating structured and predictable environments, providing social skills training and support, facilitating peer interactions, and promoting positive reinforcement and rewards for social behaviors are effective. It's important to provide individualized support based on each child's unique needs and strengths. This allows children with moderate autism to develop and enhance their social skills, engage in meaningful social interactions, and feel included in their communities.
A guide can be an invaluable resource for parents seeking to understand the unique needs of children with moderate autism. This guide, designed to help parents gain a better understanding of their child's specific needs, offers information and strategies to support their child's development and navigate potential challenges.
In addition, a supportive community for parents and professionals working with Level 2 Autism is essential. Providing access to articles, glossaries, and other educational materials that can help understand and support individuals with Level 2 Autism is a significant step towards building this community. Creating a platform or forum where parents and professionals can connect, share experiences, and seek advice can also contribute to building a supportive community.
In essence, understanding the key features of Level 2 Autism is vital for parents and professionals. This knowledge aids in providing the right support and implementing effective ABA therapy strategies, thereby enhancing the child's quality of life
2. The Role of ABA Therapy in Enhancing Social Skills for Children with Level 2 Autism
ABA Therapy serves as a vital tool in fostering the development of social skills in children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. By implementing the principle of positive reinforcement, this therapy encourages desirable behaviors and works towards reducing challenging ones. This is accomplished by decomposing complex social scenarios into simpler, manageable steps, thus enabling children to grasp a more thorough understanding and making social engagements less daunting.
An example of this approach is the use of visual aids such as a choice wheel template, listening posters, and voice level charts. Such tools can significantly boost a child's communication abilities, directing them to articulate their needs and feelings in a more orderly and productive way.
Moreover, a wealth of resources are available for the enhancement of social skills, encompassing activities, concepts, and templates. For children facing difficulties with phone usage, visual supports like tips on answering phone calls, video call sequence strips, and phone call routine booklets can prove to be notably useful.
Programs like the STAR Autism Support curriculum and training schemes have been tailored to highlight social emotional learning. They provide solutions adaptable to both remote learning and classroom environments, accommodating the varied needs of children with Level 2 Autism.
In addition, an array of books and workbooks focusing on nurturing conversation abilities, friendship skills, and social filter skills in children with Autism and social skills challenges are available. These resources offer a step-by-step guide to teaching children with autism how to engage in conversations with peers, keep track of discussion topics, and interpret nonverbal cues. They provide weekly lessons with comprehensive instructions for preparation, execution, and evaluation, making it an all-inclusive resource for both parents and professionals.
To guarantee the acquisition of skills, these resources also include games, crafts, and extended practice sessions. They have garnered positive feedback from users who have found them effective in imparting social skills to children with Autism.
By leveraging these resources and incorporating them into ABA therapy, a more favorable and efficient learning environment can be established for children with Level 2 Autism. This motivates them to actively partake in social interactions and express their needs and emotions in a more constructive and productive manner.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is one such approach that focuses on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors while reducing negative ones. It can use visual supports, social stories, and role-playing to help children with autism understand and practice appropriate social skills. Additionally, structured play activities and social skills groups can be beneficial in promoting social interaction and communication in children with autism.
ABA therapy, a common intervention for individuals with autism spectrum disorder, is particularly effective in breaking down social situations and teaching specific skills to support social skills development. By using behavior analysis techniques, ABA therapists can identify and target specific social skills, breaking them down into smaller, manageable steps. This allows individuals with autism to learn and practice these skills in a structured and systematic way, leading to improved social interactions and relationships. ABA therapy often incorporates visual supports, role-playing, and social stories to further enhance social skills development.
ABA therapy techniques are effective in managing social interactions for children with Level 2 autism. These techniques focus on teaching social skills and promoting positive behaviors. Through ABA therapy, individuals with autism can learn how to initiate and maintain conversations, understand social cues and gestures, and develop appropriate social responses. Additionally, ABA therapy can help children with Level 2 autism improve their non-verbal communication skills, such as eye contact and body language. By implementing ABA therapy techniques, parents and professionals can provide structured support and guidance to help children with Level 2 autism navigate social interactions more successfully
3. Essential Strategies for Supporting Social Skills Development in Children with Level 2 Autism
Children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism often require a variety of strategies to develop social skills.
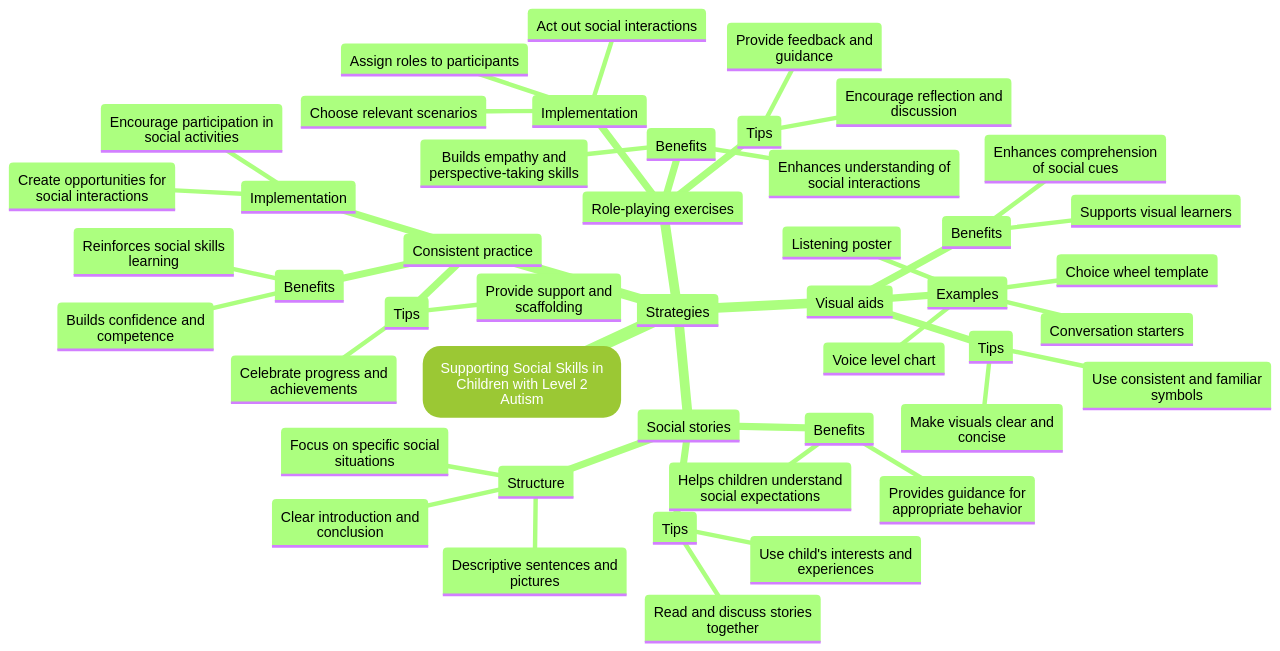
Role-playing exercises are one such strategy that proves to be effective, as they allow children to practice social interactions in a supportive environment. This practice helps children navigate the intricacies of social interactions, boosting their confidence in their ability to handle these situations.
Visual aids are also a powerful tool in helping children understand social cues. These aids can take many forms, such as choice wheel templates, listening posters, and voice level charts. These tools provide a visual representation of abstract concepts, making them more understandable for children. For example, these aids can be used to teach children social skills related to phone usage, such as answering phone calls and making video calls, thus equipping them with the tools necessary for effective communication.
Another potent strategy is the use of social stories. These stories can help children comprehend complex social situations by providing a realistic framework of social norms and expectations. By creating social stories that mirror real-life scenarios, we can help children understand and respond appropriately to social situations, facilitating their engagement with others.
To reinforce these strategies, it's important to provide consistent practice and reinforcement at home. This creates an environment where children can apply their learned skills in real-world situations, which strengthens their understanding and promotes skill generalization.
In addition to these strategies, utilizing established curriculums such as the STAR Autism Support curriculum can provide structured and evidence-based approaches to social skills development. This curriculum provides a comprehensive guide for parents and caregivers, offering resources, videos, and research on autism.
Research has also shown the effectiveness of caregiver-assisted social skills programs, such as the Peers® for Preschoolers (P4P) program. This program aims to improve social skills in young children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) by actively involving caregivers in the intervention. Studies suggest that the P4P program not only improves social skills in children with ASD, but these improvements are also maintained post-intervention.
Overall, supporting the development of social skills in children with Level 2 Autism requires a multi-faceted approach that combines diverse strategies, consistent practice, and caregiver involvement. By implementing these strategies, we can help children with Level 2 Autism navigate their social world with confidence and ease
4. Empowering Parents as Advocates: Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 2 Autism
Parents play a pivotal role in the life of their children, especially those diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. Securing appropriate support services for these children can be a daunting task, yet overcoming these hurdles is a critical aspect of their growth and development. To navigate this journey, parents need to be aware of the various services they can tap into. These include speech and occupational therapy, social skills groups, and special education programs.
Speech therapy, for instance, is tailored to address the specific needs and abilities of each child. Professionals such as speech-language pathologists or autism specialists can guide parents on the most effective speech therapy approaches and interventions. Occupational therapy, on the other hand, focuses on improving motor skills, sensory integration, and daily living activities. Occupational therapists use a variety of techniques to help children develop and enhance these skills.
Social skills groups provide a structured environment where children with Level 2 Autism can work on their social interaction, communication, and relationship-building skills. This experience helps them better understand social cues, maintain conversations, and navigate social situations more effectively.
Parents also need to comprehend their rights and responsibilities to ensure their children receive the necessary support. This includes being aware of personalized coaching services that cater to different age groups, providing resources, tips, and strategies for improving executive function, time management, emotional regulation, and more.
Parents should also familiarize themselves with the role of educational advocates. These advocates provide guidance on conflict resolution, monitoring a child's progress, and understanding the rights of children with learning differences. They can also provide resources and tips for working with educational advocates.
However, it's crucial to remember that each child with autism is unique, so the advocacy efforts should be tailored to the child's specific needs and strengths. Parents should gather evidence, understand their child's specific needs, and reach out to parent training and information centers, as well as special education parent advisory councils, for further support and resources.
Moreover, there are resources available that provide tips for managing online distractions, making friends, study skills, self-advocacy, and more. These resources can be particularly useful for parents dealing with homework battles, tutoring vs. academic coaching, and homework refusal.
In this journey, parents should remember they are not alone. Numerous resources, advocacy groups, and services are available to assist them. As a team, parents, educational advocates, and service providers can ensure that children with Level 2 Autism are supported and make effective progress
5. Time Management and Prioritization Tips for Parents of Children with Level 2 Autism
Managing time and tasks for parents of children with Level 2 Autism is a lifeline, not just a necessity. Structuring a consistent routine that includes therapeutic sessions, academic pursuits, and leisure activities is essential to add predictability and stability to their lives. Visual schedules and timers help children understand the concept of time and manage tasks independently.
High-functioning autistic children often find tasks more engaging when they align with their interests. A simple linguistic shift, such as replacing 'homework' with 'study', can eliminate negative connotations and motivate children to engage in academic tasks.
The challenge of boredom and anxiety in children with autism can hinder their willingness to complete school assignments. Therefore, it's important to make learning more engaging and relevant to their interests. Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable ones can make them less daunting and achievable. Setting time limits for tasks can encourage children to work efficiently and purposefully.
Disorganization can be challenging for children on the autism spectrum. Teaching them organizational skills, such as using visual aids and representations of progress, can foster a sense of order and control. Tools like calendars, planners, and apps can be instrumental in managing time effectively.
Token economies, where children earn tokens for completing desired actions, can serve as powerful motivators. However, it's essential to remember that homework should not be left until the last minute. Parents need to assist their children in planning and prioritizing their work to prevent procrastination and last-minute rushes.
In the face of homework meltdowns, patience is paramount. Each day presents a fresh opportunity to teach study skills and foster resilience. While the benefits of finishing homework are significant, they may not always outweigh the importance of the parent-child relationship. Therefore, it's crucial to strike a balance between pushing children to complete their homework and understanding their unique challenges.
Children on the autism spectrum may struggle with certain subjects or tasks. In such instances, it may be necessary to advocate for individualized education plans (IEPs) or accommodations. Rewards and incentives, like computer time or special activities, can also serve as potent motivators.
Lastly, considering the individual needs and strengths of children on the autism spectrum is crucial when it comes to homework and schoolwork. Each child is unique, and understanding their distinct challenges and capabilities can help tailor strategies that best support their development. Parents should prioritize self-care and set aside time for themselves to prevent burnout and ensure they can effectively support their child.
Parents can also seek support from other parents or support groups with experience with children on the autism spectrum. Sharing experiences and learning from others can be a great source of support and guidance
6. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Creating a supportive and collaborative community is integral for parents and professionals engaged in ABA therapy. The community serves as a haven for sharing experiences, acquiring knowledge, and providing mutual support on this journey. Such a community fosters collaboration and learning opportunities, enabling parents and professionals to navigate the challenges of ABA therapy more effectively and ultimately improve outcomes for individuals with autism.
It's essential to join this community with an open mind, ready to receive and process various perspectives on ABA therapy, which can sometimes be critical. Immersing oneself in articles, blogs, and groups discussing ABA therapy can be beneficial. However, before participating in any discussions, it is recommended to observe and absorb for at least a month. This period allows for reflection on initial reactions and understanding why certain techniques or practices evoke specific emotions. It's also a time to respect the experiences of those sharing their stories.
After this period of reflection and understanding, individuals are encouraged to participate in discussions, ask questions, and seek clarity. However, the intention should be to enhance understanding, not to defend oneself or the practice of ABA. Any feedback received should be seriously considered and used to alter behavior, even if it's delivered in a straightforward manner.
In addition to these discussions, the community also provides a blog that collaborates with families to help children with autism flourish. It provides thoroughly vetted and expert-approved information about raising a child with autism and pursuing a career in ABA. The blog encourages reader contributions, shares strategies for navigating holidays with kids on the autism spectrum, and highlights the valuable skills developed as a behavior technician. It emphasizes the importance of clinical integrity in ABA therapy and the potential of early intervention in improving socialization, communication, behavior, and academic success for children with autism.
The community provides a wealth of resources for parents, including insurance information, a location finder, and a video podcast. It provides insights about the mission and offers a newsletter for the latest information on raising kids and teens with autism. This community serves as a supportive and informative hub for everyone involved in the journey of ABA therapy. To connect with others in ABA therapy, it is important to create an environment that promotes social skills development in children with autism. This can be achieved by implementing industry insights and strategies to overcome challenges and improve outcomes in ABA therapy. By utilizing key terms and promoting social skills in ABA therapy, professionals can facilitate meaningful connections and interactions between individuals in the therapy setting. This approach can enhance the effectiveness of ABA therapy and support individuals in developing their social skills.
To find a supportive network for ABA therapy, it is important to connect with organizations and communities that specialize in autism support services. These networks can provide valuable resources, information, and a sense of community for individuals and families seeking ABA therapy. Additionally, reaching out to local autism support groups, online forums, and social media communities can also help connect with others who have firsthand experience with ABA therapy and can offer support and guidance
7. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning for Parent Advocates
The path of a parent advocate is an ongoing journey of evolution and education. Staying updated with the latest discoveries, techniques, and resources is crucial for providing the best possible support to your child. Various methods exist for staying informed, such as subscribing to newsletters, participating in webinars, or attending workshops.
Institutions like Beyond Booksmart serve as invaluable sources of support and knowledge. This organization offers coaching services to people across all age groups, assisting them in developing critical life skills and boosting academic success. Their services are supported by comprehensive research and reviews, ensuring that you're accessing trustworthy information. They cover an extensive array of topics on their blog, from cultivating good habits to providing support for children with ADHD.
Beyond Booksmart also provides a plethora of resources specifically designed for parents. These include tips for promoting executive function, managing ADHD, and addressing mental health issues. They also offer resources to assist parents in navigating the intricacies of the special education system. Their website provides information on locating an educational advocate or consultant, understanding your child's rights, and advocating for specific supports and services. They also offer resources for identifying educational advocates, underlining the importance of teamwork in ensuring children are supported and making strides towards their educational objectives.
Understanding the concept of a growth mindset, as described by Stanford researcher Carol Dweck, is another crucial component of continuous learning. This concept encourages individuals to believe that they can enhance their intelligence by overcoming challenges. Encouraging children that their brains can grow and their skills can develop through effort and persistence can aid in cultivating this mindset. It's also crucial to foster children's innate curiosity and interests for their cognitive growth.
Learning new concepts can be daunting, but children are capable of doing hard things, and the discomfort is a catalyst for growth. Remember, intelligence is not fixed; it can be developed. Resources like ASD Media and Beyond Booksmart can assist parents in staying informed and empowered on this continuous journey.
Based on the provided context information, another way to stay updated on the latest research for parent advocates is to regularly visit reliable websites or online platforms that concentrate on providing information and resources related to autism support services and promoting social skills in children with autism. These websites may post articles, studies, and other pertinent content to keep parent advocates informed about the latest research findings. Additionally, subscribing to newsletters or joining online communities or forums dedicated to autism support can also be beneficial in staying updated on the latest research in this field
8. Unlocking Potential: Celebrating Progress and Successes in Social Skills Development
Each progression a child achieves in the realm of social skills development, regardless of its magnitude, is a victory worth acknowledging. By celebrating these milestones, we reinforce the child's self-confidence and foster their enthusiasm to further grow. This practice also serves as a meaningful reminder to parents of the importance of their efforts and the untapped potential within their children. It is essential to keep in mind that every child has their unique growth journey, and each triumph, irrespective of its scale, brings them a step closer to unveiling their inherent abilities.
The Star Institute's approach, providing a range of therapy services such as occupational, speech-language, and mental health services, illustrates the importance of an all-encompassing support system. Their focus on fostering social skills in children with sensory processing disorder (SPD) and their provision of guidelines for parents exemplify this. They also highlight the significance of social cognition, communication, and problem-solving skills through social skills groups[^1^].
In addition to children, the Star Institute extends its resources to adults with SPD, offering a treatment directory and a sensory processing and sensory integration process for identifying sensory differences. This inclusivity embodies the Institute's mission to promote self-regulation and its dedication to providing therapy services[^2^].
The journey of social skills development is an ongoing process, as illustrated by the personal experience of an author who has successfully enhanced their social skills. Their journey was marked by several key changes such as challenging insecure thoughts, initiating friendships, giving potential friends a chance, and making a deliberate effort to practice social skills. Their experience of backpacking in Australia and being continually surrounded by people played a pivotal role in their social development. This underscores the importance of exposure to diverse social situations in enhancing social skills[^3^].
The author's transformation also encompassed becoming well-rounded, improving their fashion sense and appearance, and learning to accept aspects of the social world. This story highlights that the journey to improved social skills is not linear, but rather a gradual and continual process[^4^].
In conclusion, each small victory in a child's social skills development journey is a testament to their potential and a cause for celebration. While the journey may be filled with diverse experiences, every step forward is a stride towards unlocking their untapped potential. The comprehensive approach of the Star Institute and the personal experiences of individuals who have successfully improved their social skills serve as sources of inspiration and guidance on this journey[^5^]
Conclusion
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for parents and professionals in order to provide the appropriate support and guidance for children with this diagnosis. Level 2 Autism, also known as moderate autism, presents challenges in social interpretation, communication, and behavior. It is important to recognize the key features and challenges of Level 2 Autism to effectively manage and support these children.
The main points discussed in this article include the complexities of Level 2 Autism, the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in managing symptoms, strategies for supporting social skills development, empowering parents as advocates, and the importance of continuous learning. By understanding the unique needs of children with Level 2 Autism and implementing evidence-based strategies such as ABA therapy, visual aids, social stories, and structured environments, we can create a supportive and inclusive environment that promotes their growth and development.
In conclusion, understanding Level 2 Autism is essential for parents and professionals to provide the necessary support for children with this diagnosis. By implementing strategies such as ABA therapy, visual aids, and social skills groups, we can help children with Level 2 Autism develop their social skills and navigate social interactions more successfully. Continuous learning and staying connected with supportive communities are also crucial for parents in advocating for their child's needs. Let's work together to create a supportive environment that celebrates each milestone in a child's social skills development journey.




