Introduction
Children with Level 2 Autism face unique challenges that require significant support and intervention strategies. Understanding the key characteristics and symptoms of Level 2 Autism is crucial for parents and professionals to provide suitable assistance. This article explores the obstacles faced by children with Level 2 Autism in social interaction, communication, and coping with change. It also highlights various intervention strategies, such as social skills training and visual supports, that can enhance their social skills development. Additionally, it discusses the importance of creating a secure and structured environment for these children and the role of parents as advocates in supporting their child's journey. By delving into these topics, this article aims to provide valuable insights and guidance for parents navigating the world of Level 2 Autism
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: Key Characteristics and Symptoms
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a neurodevelopmental variation, exhibits itself in a variety of ways, necessitating different levels of support. A form of ASD, Level 2 Autism, often known as moderate autism, requires significant assistance due to its unique challenges.
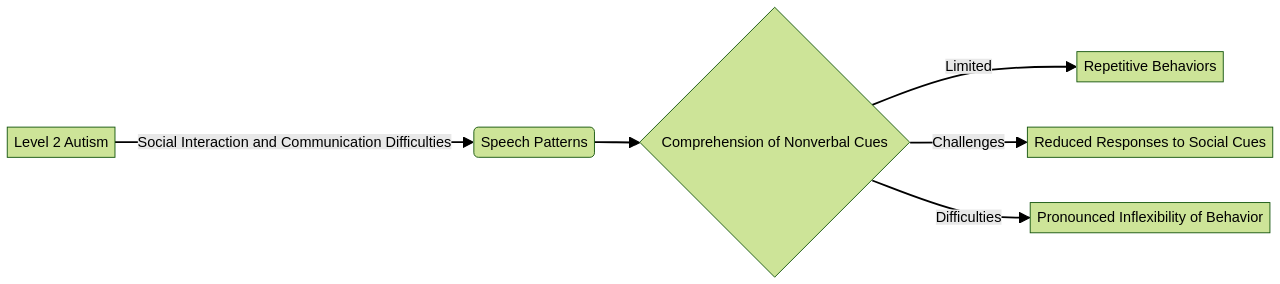
Children with Level 2 Autism typically encounter obstacles in social interaction and communication. Their speech might consist of fewer words or have distinctly different patterns. Difficulty comprehending nonverbal communication cues may lead to unusual social behavior. Repetitive behaviors, often reflected in a limited range of interests, are also common.
Coping with change poses another challenge for children with Level 2 Autism. They often rely on routines for a sense of security and can experience considerable distress when these routines are disrupted. Understanding these key characteristics and symptoms is critical to enabling parents and professionals to offer suitable and effective support and intervention strategies.
To enhance the social skills development of children with Level 2 Autism, there are several intervention strategies available.
These strategies, which include social skills training, social stories, visual aids, and structured play activities, are designed to support and enhance the social skills development of children with autism. Communication strategies such as visual supports, social stories, and social skills training can be used to support the development of communication skills in these children.
Visual supports like visual schedules and communication boards can help children with autism understand daily routines and communicate their needs and preferences. Social stories, brief narratives that describe social situations, can be used to teach children with autism appropriate social behavior and communication skills. Social skills training programs can also be beneficial in teaching children with moderate autism how to initiate and maintain conversations, make eye contact, and understand nonverbal communication cues.
Children with Level 2 Autism might also display repetitive behaviors. To help children overcome these behaviors, implementing structured routines, visual supports, and social stories can be beneficial. Additionally, using positive reinforcement and rewards can help motivate children to engage in alternative behaviors. Collaborating with a team of professionals, such as speech therapists and occupational therapists, can provide individualized support and therapy to address these repetitive behaviors.
Creating a secure and structured environment for children with moderate autism can greatly enhance their development and well-being.
Providing a consistent and predictable routine, clear rules and expectations, and a calming and organized physical space can make children with moderate autism feel more secure and supported. Implementing visual supports, such as visual schedules and social stories, can help them understand and navigate their daily activities. Establishing a positive and supportive relationship with the child, using strategies such as positive reinforcement and effective communication techniques, can also be beneficial.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) provides diagnostic criteria based on functioning in two domains: social communication and restricted interests/repetitive behaviors. It classifies autism into three levels, with Level 2 requiring substantial support.
The DSM-5 has resulted in a considerable shift in autism categorization. Previously, autism was classified under pervasive developmental disorders (PDD), including diagnoses like Asperger's syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS), autistic disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD), and Rett syndrome. However, the DSM-5 now recognizes these diagnoses as part of ASD, with the exception of Rett syndrome, which is acknowledged as a separate genetic condition.
Understanding the classification of autism into different levels and the support needs of individuals with autism is fundamental in developing effective treatment plans. It’s also the gateway to therapies like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) which requires a formal diagnosis of autism. This comprehensive overview of the three levels of autism emphasizes the importance of a formal diagnosis for accessing suitable therapy and support
2. The Role of Parents as Advocates in Supporting Children with Level 2 Autism
Parents of children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism are not only caregivers but also their most powerful advocates. These parents often identify the initial signs of autism in their children, which leads them to seek professional help. It is in their capacity as advocates that parents ensure their children have access to the necessary resources and interventions.
Their advocacy role encompasses a collaborative approach with a team of professionals, including therapists and educators. Together, they design and implement a treatment plan tailored to their child's unique needs, often incorporating Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, a method proven effective in managing autism.
However, the parents' advocacy role extends beyond therapy sessions. It entails ensuring their child's rights to services such as insurance coverage and access to parent resources, both crucial for their developmental progress.
The role of parents as advocates is dynamic, involving continuous learning and adaptation, mirroring the field of ABA therapy itself. This includes understanding the importance of clinical integrity and adopting evidence-based practices in ABA therapy.
Parents also play a significant role in making everyday life enjoyable for their child, such as creating a fun and safe environment during occasions like Halloween. Their role as advocates is a testament to the resilience and dedication parents display in ensuring their child's well-being and progress.
In essence, parents are the cornerstone of their child's journey in managing and living with Level 2 Autism. They are the pillars of support, the providers of love, and the driving force behind the interventions and resources that their child needs to thrive.
To be proactive in advocating for their child's needs, parents can take several steps:
- Educate themselves about level 2 autism and its characteristics to better understand their child's needs and communicate effectively with professionals.
- Build a support network by connecting with other parents of children with autism to share experiences, advice, and resources. Joining support groups or online communities can provide valuable emotional support and practical guidance.
- Collaborate with professionals, such as healthcare providers, therapists, and educators, to develop an individualized treatment plan. Regular communication with these professionals can provide insights into the child's progress and any challenges they may face.
- Document their child's needs by keeping a record of their challenges, strengths, and progress. This can be useful when advocating for appropriate services, accommodations, or educational supports.
- Attend Individualized Education Program (IEP) meetings to actively participate in their child's educational planning and contribute their insights and concerns. Collaboration with school staff ensures the IEP addresses the child's unique needs.
- Seek additional resources, such as specialized therapy programs, assistive technology, and community services, to further support their child's development and address specific challenges.
Remember, every child with level 2 autism is unique, so it's essential to tailor advocacy strategies to your child's individual needs and strengths. By actively advocating for their child, parents can help ensure that their child with level 2 autism receives the necessary support, services, and accommodations to thrive and reach their full potential
3. Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 2 Autism
Managing challenging behaviors in children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism can seem daunting, but with the right strategies and resources, parents can effectively guide their children towards improved behavior.
Techniques such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can be instrumental in promoting desirable behaviors. This method focuses on identifying the root causes of challenging behaviors, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable steps, and systematically teaching and reinforcing desirable behaviors.
Creating a well-structured environment that minimizes triggers for challenging behaviors is also essential. By implementing consistent routines and visual supports, parents can provide predictability and structure, thereby reducing anxiety and improving self-regulation.
Moreover, empowering children with self-regulation skills is crucial. This can be achieved by providing clear and consistent instructions along with positive reinforcement and rewards for desired behaviors. Resources such as those provided by the Iris Center can be beneficial in this regard. The center offers a plethora of educational materials, including modules, case studies, evidence-based practice summaries, and research annotations.
In addition, the Iris Center provides high leverage practices (HLPs) and films depicting individuals with disabilities. These resources can be instrumental in teaching children to manage their emotions and behaviors independently, providing them with the tools necessary to navigate their world.
The Iris Center's user-friendly website, complete with navigation videos, can assist users in finding the resources they need. Moreover, a glossary of disability-related terms and a collection of archived resources further enhance the center's offerings. The effectiveness of the Iris Center has been recognized through positive feedback and external evaluations.
Lastly, the Iris Center's commitment to continuous improvement is commendable. The center regularly updates its modules and resources to ensure they remain relevant and beneficial. This ongoing commitment to providing high-quality resources can be a valuable asset for parents navigating the challenges of Level 2 Autism
4. Enhancing Social Skills Development: Effective Techniques for Children with Level 2 Autism
Developing social skills in children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism can be a challenging journey, yet it's one that can yield significant results. Parents can employ a variety of effective techniques and strategies, arming their children with the tools necessary for confident and comfortable social interaction.
Role-playing is one such strategy that has proven instrumental in teaching children about social norms and expectations. Through pretend play scenarios, children can practice and learn socially appropriate behaviors in a safe and controlled environment. This approach allows them to better grasp social cues and develop skills such as empathy and problem-solving, with activities that are customized for specific social situations, such as greetings, turn-taking, and sharing.
In the same vein, social stories serve as a powerful tool for helping children comprehend and navigate diverse social scenarios. These short narratives, written in a specific format, describe social situations and appropriate social behavior. By providing guidance on how to respond and interact with others, social stories can help children with Level 2 Autism understand the expectations and consequences of different social situations, enhancing their understanding of social cues and improving their social skills overall.
A more comprehensive approach involves a specialized curriculum developed specifically for enhancing social skills in children with autism and similar social challenges. This curriculum places a strong emphasis on developing robust conversation abilities and covers key skills such as inquiring about a friend's interests, responding with suitable comments, following the thread of conversation topics, transitioning smoothly between conversation topics, and interpreting non-verbal cues. The curriculum is designed for one-on-one and group settings and includes detailed lesson plans and all necessary materials, providing parents with a structured approach to teaching social skills.
Parents have attested to the effectiveness of the curriculum when used with their children with autism. Their testimonials highlight the tangible progress their children have made after completing the curriculum, which speaks volumes about its efficacy.
Structured play activities and social skills groups offer additional methods to foster social interaction. These platforms provide opportunities for children to practice and generalize their social skills in a supportive environment. Implementing structured activities and routines that encourage social engagement, such as group games or collaborative projects, can be particularly beneficial. Providing clear instructions and visual aids can help children with autism understand and navigate social situations better. Having trained supervisors or therapists present during these interactions can provide additional guidance and support, helping children with autism learn and practice appropriate social skills.
There are also a plethora of resources available online and in print that are dedicated to teaching social skills to children with Level 2 Autism. Parents and caregivers can explore these resources and choose the ones that best suit the needs and preferences of their child.
By adopting these strategies, parents can significantly support their children with Level 2 Autism in honing their social skills, paving the way for them to engage more confidently and comfortably in social settings
5. Navigating Support Services: A Guide for Parents of Children with Level 2 Autism
Exploring the vast array of support services can be overwhelming for parents who have children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. However, with the right guidance and understanding, these resources can be harnessed effectively. This involves knowing the different kinds of support services available, such as therapy sessions, educational assistance, and community resources. It's also vital for parents to be aware of their legal rights and the protective measures in place to ensure their children obtain the necessary support.
A significant phase that often compounds the complexity of navigating support services is the transition from high school to post-secondary education for students with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This transition can be daunting, but there are multiple pathways to success, each custom-fitted to the unique needs and strengths of the individual. These pathways encompass specialized post-secondary programs, life skills programs, certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities.
Conducting a thorough analysis of a child's functioning in key areas such as independence, academic skills, and adaptive behavior is crucial for parents. Coupling this analysis with an assessment of available supports and the demands of the next environment is equally important. For instance, college can be a viable option for students with ASD who exhibit a fair degree of independence and possess the necessary cognitive and adaptive skills. However, success in college would necessitate strong organizational and time management skills.
Community colleges can serve as a useful stepping stone for those who require more support, while certificate and technical schools offer programs that proceed at a slower pace and concentrate on specific content areas. Non-degree seeking programs on university campuses offer opportunities for students with special needs to audit classes and learn skills for independence. Some individuals may prefer post-secondary day and residential programs that focus on independent living skills, work skills, social skills, and executive functioning skills. Others may find supported or customized work experiences with the aid of vocational rehabilitation services beneficial.
While maneuvering through these crucial decisions, it's important for parents to stay realistic, objective, and flexible. Understanding your child’s abilities and support needs will lead to success and happiness. The journey may seem overwhelming, but remember, "There are many different options to achieve a positive outcome".
To maximize the benefits of these support services, parents should explore resources that provide information and assistance. These resources may include websites, online platforms, or organizations that specialize in autism support. By visiting these websites and platforms, parents can access a wide range of information, strategies, and tools to help enhance the social skills and overall well-being of children with Level 2 autism. Additionally, it may be beneficial to connect with local autism support organizations or seek recommendations from healthcare professionals who specialize in autism.
Parents can also find educational support options to empower them in navigating the challenges their children face. Resources such as online courses, workshops, and support groups specifically designed for parents of children with autism can provide valuable information and strategies to enhance their child's educational experience. Local schools, autism organizations, and community centers can offer guidance and support in accessing appropriate education services for their child.
To ensure your child receives the necessary support for Level 2 autism, start by understanding the specific needs and challenges associated with this condition. Reach out to professionals, such as doctors, therapists, and educators, who specialize in working with children with autism. They can provide guidance, support, and recommendations for appropriate interventions and therapies. Collaborate with your child's school to develop an Individualized Education Program (IEP) or a 504 plan, which can outline specific accommodations and support services your child may require in an educational setting. Connecting with support groups and organizations that focus on autism can provide valuable information, guidance, and a sense of community. Remember, every child with autism is unique, so tailor the support and interventions to meet your child's specific needs
6. Building a Supportive and Inclusive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Creating an inclusive and supportive community is a crucial aspect of the journey for parents of children with Level 2 Autism.
This community acts as a beacon of hope, offering parents a platform to exchange experiences, learn from each other, and garner emotional backing. Parents can engage in local support groups, participate in online discussions, and attend community events to create connections with others navigating similar paths. The sense of community thus built can alleviate feelings of isolation and empower parents in their advocacy roles.
To find local support groups, parents can search online or reach out to local autism organizations or healthcare professionals specializing in autism. These resources may provide information on local support groups in the area. Online forums and support groups specifically designed for parents of children with autism can also provide a safe and understanding space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive advice from other parents facing similar challenges.
Beyond immediate parent groups, this community extends to professionals in the field of autism, such as therapists and educators who work with Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). These professionals have access to a plethora of resources including blog posts, videos, and podcast episodes that provide practical advice and tips for addressing various challenges such as sensory processing issues, language delays, and the development of social skills.
Among the resources available, the podcast "All Autism Talk" serves as a valuable resource, offering enlightening discussions with experts, authors, and individuals from the autism community. It covers a multitude of topics spanning from research and treatment options to practical tips for families dealing with autism. The podcast features a range of guests including David Friedman, founder and CEO of AutonomyWorks, and Dr. Hanna Rue, who regularly discusses the latest research and treatment options for individuals on the autism spectrum. Other notable guests include Molly Ola Pinney, founder of the Global Autism Project, and researchers Susan White and Carla Mazefsky who have shared insights on their book and ongoing projects related to autism and co-occurring disorders.
In a supportive community for individuals with Level 2 Autism, parents play a crucial advocacy role. They actively engage in advocating for their child's needs and rights, as well as promoting awareness and understanding of autism within the community. By being vocal about the challenges faced by individuals with Level 2 Autism and the support services they require, parents help create a more inclusive and accommodating environment.
Creating a sense of belonging in a community for parents of children with Level 2 Autism can be achieved through various means. Support groups or online forums where parents can connect with others who are facing similar challenges can provide a space for parents to share their experiences, seek advice, and offer support to one another. Organizing regular meetups or events specifically for parents of children with Level 2 Autism can help foster a sense of community and belonging. These gatherings can provide opportunities for parents to network, share resources, and build relationships with others who understand their unique circumstances.
The importance of an inclusive community also resonates with the mission of Learn Behavioral, an organization dedicated to ensuring success for every child in their care. Learn Behavioral offers services such as diagnosis of autism, ABA therapy, and other resources, all structured around the understanding that each child with autism is unique and requires a personalized approach to treatment. They extend their support through various platforms, offering practical advice and updates on raising children and teenagers with autism.
Building a supportive and inclusive community is not a solitary effort. It requires the collaboration of parents, professionals, and organizations, all united by the common goal of empowering every child with autism to reach their full potential
7. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation in the Field of ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is an ever-evolving field, especially when it comes to Level 2 Autism. It's crucial for parents to stay informed about the latest developments. This doesn't only involve absorbing new research and strategies, but also critically evaluating existing practices and providers.
To stay updated on advancements in ABA therapy, parents can regularly check reputable websites and online platforms specializing in autism and ABA therapy. These platforms often publish articles and resources discussing the latest research, techniques, and advancements in the field. Additionally, subscribing to newsletters or email updates from organizations or professionals specializing in ABA therapy can provide regular updates on advancements and new findings. Attending conferences, workshops, and seminars focused on autism and ABA therapy can also be a valuable way to stay informed about the latest advancements and connect with experts in the field.
Some cautionary signals suggest outdated or potentially harmful practices, such as an excessive focus on reducing self-stimulatory behavior, teaching sustained eye contact, the idea of 'curing' autism, forced compliance, recommending a high number of therapy hours without appropriate justification, using food as a primary reinforcer, or refusal to collaborate with other providers.
While ABA is considered the "gold standard" in intervention for children with autism, it's essential to remember that it should be tailored to the needs, values, and culture of each child and family. Parents' goal should be to ensure that the therapy respects the dignity, individuality, and self-expression of their child.
An essential aspect of staying updated in the field of ABA therapy is listening to and learning from the experiences of adults who have undergone ABA therapy. This firsthand knowledge can provide invaluable insights into how the therapy can be approached, thus ensuring the well-being and autonomy of individuals with autism.
In the evolving field of ABA therapy for level 2 autism, it's important to stay up-to-date with the latest industry insights and research.
Stay informed about the latest industry insights and research in ABA therapy for Level 2 Autism.
This can involve attending continuing education courses, conferences, and workshops that focus on advancements in ABA therapy. Additionally, collaborating with other professionals in the field and joining professional organizations can provide opportunities to learn from and share experiences with others. It's also beneficial to regularly review and update treatment plans based on new research and best practices.
Parents of children with level 2 autism can benefit from continuous learning to better support their child's needs. By staying informed about the latest research, interventions, and strategies, parents can enhance their understanding of autism and develop effective ways to navigate support services. Continuous learning can involve attending workshops, webinars, or support groups specifically tailored to parents of children with autism.
To stay informed about new research and strategies in ABA therapy for level 2 autism, it's important to regularly access reliable sources of information. This can include visiting reputable websites, subscribing to newsletters or publications that focus on autism and ABA therapy, and following trusted social media accounts or blogs that provide updates in this field.
In essence, continuous learning and adaptation in the field of ABA therapy involve more than just keeping up with the latest research. It's about critically examining existing practices, listening to firsthand experiences, and ensuring that your child's therapy is tailored to their unique needs and respects their individuality. This diligent approach ensures that parents provide the best possible support to their children with Level 2 Autism
Conclusion Children with Level 2 Autism face unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and coping with change. Understanding the key characteristics and symptoms of Level 2 Autism is crucial for parents and professionals to provide suitable support and intervention strategies. This article has explored the obstacles faced by these children and highlighted various intervention strategies, such as social skills training and visual supports, that can enhance their development. It has also emphasized the role of parents as advocates in supporting their child's journey.
By delving into these topics, this article aims to provide valuable insights and guidance for parents navigating the world of Level 2 Autism. It is important for parents to educate themselves, build a support network, collaborate with professionals, document their child's needs, attend meetings, seek additional resources, and tailor advocacy strategies to their child's individual needs.
Furthermore, managing challenging behaviors requires effective strategies such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), creating a structured environment, empowering children with self-regulation skills, and utilizing resources like the Iris Center for assistance. Enhancing social skills development involves techniques such as role-playing, social stories, specialized curricula, structured play activities, and social skills groups.
Navigating support services requires knowledge of available resources, understanding legal rights, and making informed decisions about post-secondary education options. Building a supportive community involves connecting with other parents through support groups or online forums and engaging with professionals who offer resources like podcasts or organizations dedicated to autism support.
Staying updated in the field of ABA therapy is essential for parents. They can achieve this by regularly checking reputable websites and platforms specializing in autism and ABA therapy, subscribing to newsletters or email updates from professionals in the field, attending conferences or workshops focused on autism, critically evaluating practices and providers for potential red flags or outdated methods.
In conclusion, this article provides a comprehensive understanding of Level 2 Autism and offers practical guidance for parents supporting their children. By staying informed, connecting with others in similar situations, advocating for their child's needs, implementing effective strategies for behavior management and social skills development, accessing appropriate support services, building a supportive community, continuous learning from reliable sources about ABA therapy advancements - parents can empower themselves to provide the best possible support for their child's journey with Level 2 Autism.
Start now!




