Introduction
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing the necessary support and creating an inclusive environment for children on the Autism Spectrum. Level 2 Autism presents considerable social and communicative hurdles, impacting the ability to form relationships and adapt to changes. These children face unique challenges that require tailored strategies and support to help them thrive.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Level 2 Autism and explore effective strategies for enhancing social skills development. We will discuss the challenges faced by children with Level 2 Autism, such as cognitive rigidity and sensory issues, and how these challenges can be addressed. Additionally, we will explore the importance of social skills training, visual supports, and other interventions in improving communication and interaction abilities. By understanding Level 2 Autism and implementing effective strategies, we can create a supportive community that nurtures the potential of these children and helps them lead fulfilling lives
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: An Overview
Level 2 Autism, a classification within the broader Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD), presents considerable social and communicative hurdles, necessitating extensive support. Children with this diagnosis might struggle to adapt to changes, comprehend social cues, and demonstrate flexibility in behavior and thought processes. These challenges can greatly impact their ability to form and nurture relationships, making it pivotal to foster social skills.
Living with Level 2 Autism can be likened to navigating a complex video game with unpredictable and challenging controls or residing in a foreign country where the language and cultural norms are unfamiliar.
Cognitive rigidity, a common trait, can make them feel as if they are on a train while everyone else is driving a car. This metaphor illustrates the unique challenges they face and the need for significant support and understanding to navigate their world.
Sensory issues are another common experience for these children. Difficulty in processing sensory information can further complicate their interaction with their environment, underscoring the importance of understanding and supporting these sensory needs to help them thrive.
Children with Level 2 Autism might also grapple with social rejection, impacting their self-esteem and leading to anxiety and depression.
Disciplining can pose challenges due to potential defiant behavior. However, with tailored strategies, such as helping them manage stress, anger, and resistance to change, these challenges can be surmounted.
Effective strategies exist to enhance social skills in children with Level 2 Autism. These strategies focus on providing support and guidance to help children develop and improve their social interactions and communication abilities. Some common strategies include social skills training programs, structured play activities, visual supports, and peer-mediated interventions. It is crucial to tailor these strategies to the specific needs and strengths of each child and to provide ongoing support and reinforcement to ensure continued progress.
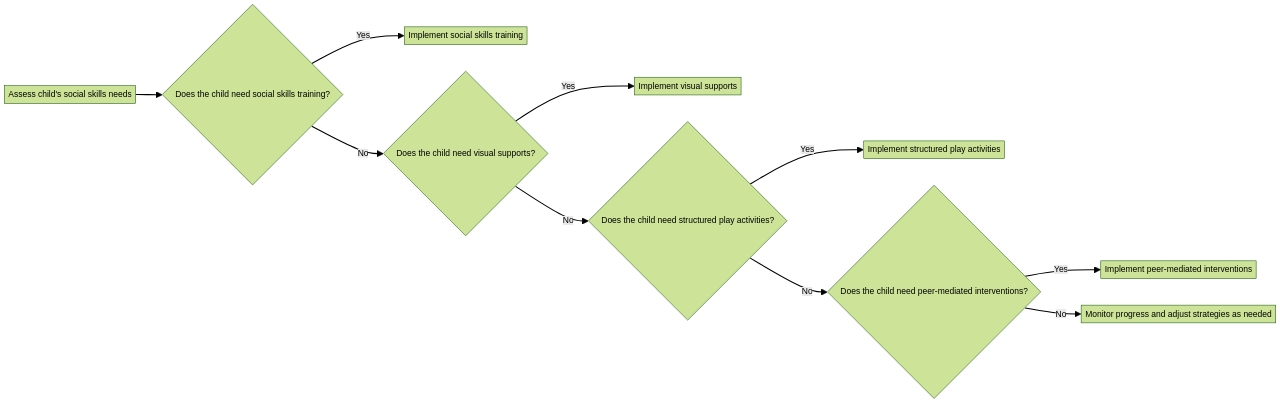
Interventions such as social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and speech therapy can be implemented to enhance social communication. Social skills training teaches individuals with autism how to interact appropriately with others, such as taking turns in conversation and understanding social cues. Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps individuals manage their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in social situations. Speech therapy can assist in improving language and communication skills, including understanding and using nonverbal cues.
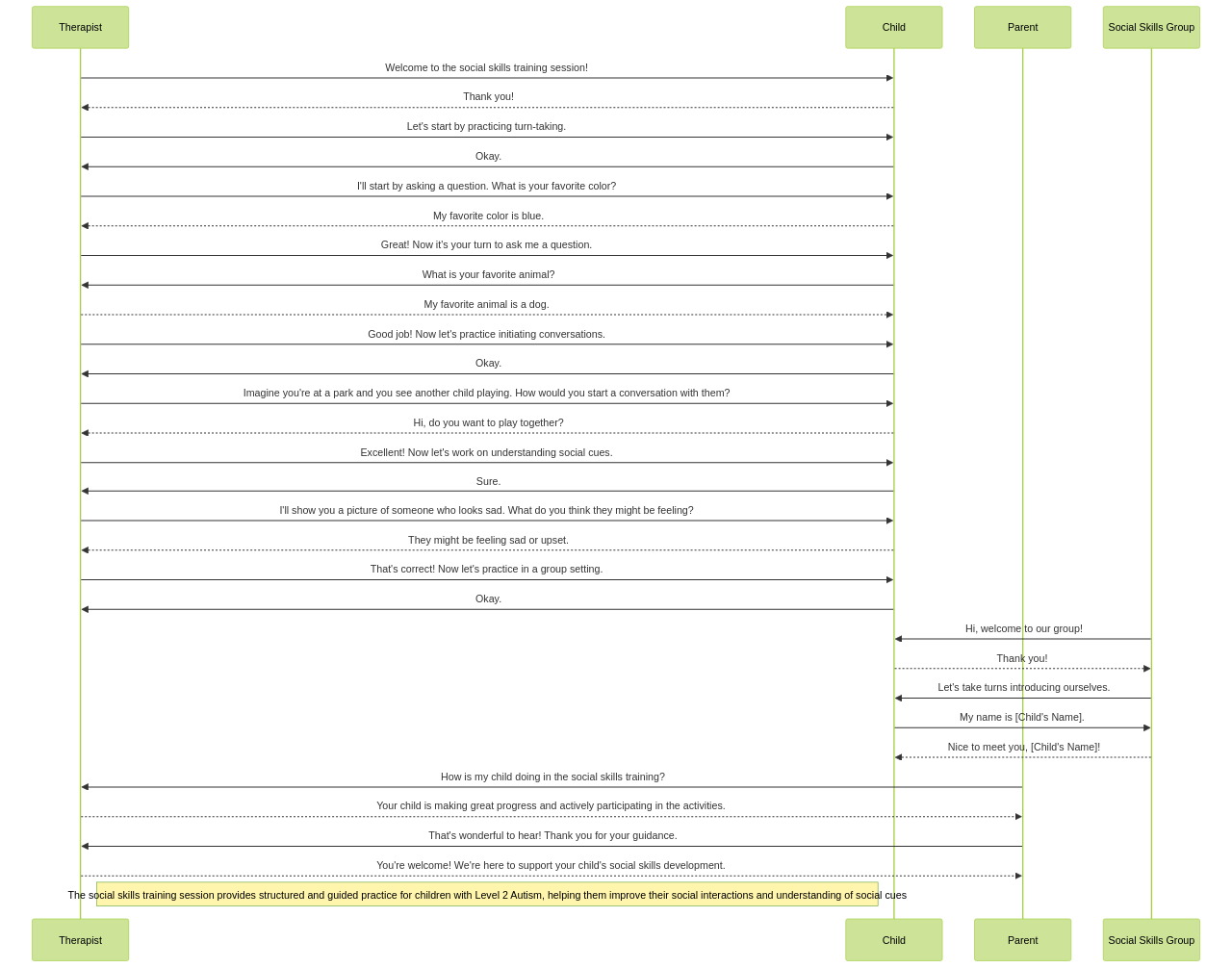
To help children understand social cues, it can be beneficial to provide visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules. Breaking down social interactions into smaller steps and providing clear instructions on how to respond can also be helpful. Practicing social skills through role-playing or social skills groups can help children learn and apply appropriate social cues in real-life situations.
There are resources available for parents and professionals to support social skills development in children with Level 2 Autism. These resources provide guidance and strategies that can help individuals improve their social skills. Utilizing these resources ensures parents and professionals have the necessary tools to effectively support individuals in developing their social skills.
Understanding Level 2 Autism and its unique challenges is the first step towards creating an inclusive and supportive environment for these children. By doing so, we can help them maximize their potential and lead fulfilling lives
2. The Importance of Social Skills in Children with Level 2 Autism
Navigating the social world presents a complex task for children on the autism spectrum, specifically those classified as level 2. They often struggle to comprehend social norms, interpret non-verbal cues, or engage in meaningful interactions with their peers. Yet, it is crucial to remember that improving their social abilities can greatly enhance their lives. By honing these skills, we can enable them to attain a higher level of independence, cultivate healthier peer relationships, and actively engage in community activities.
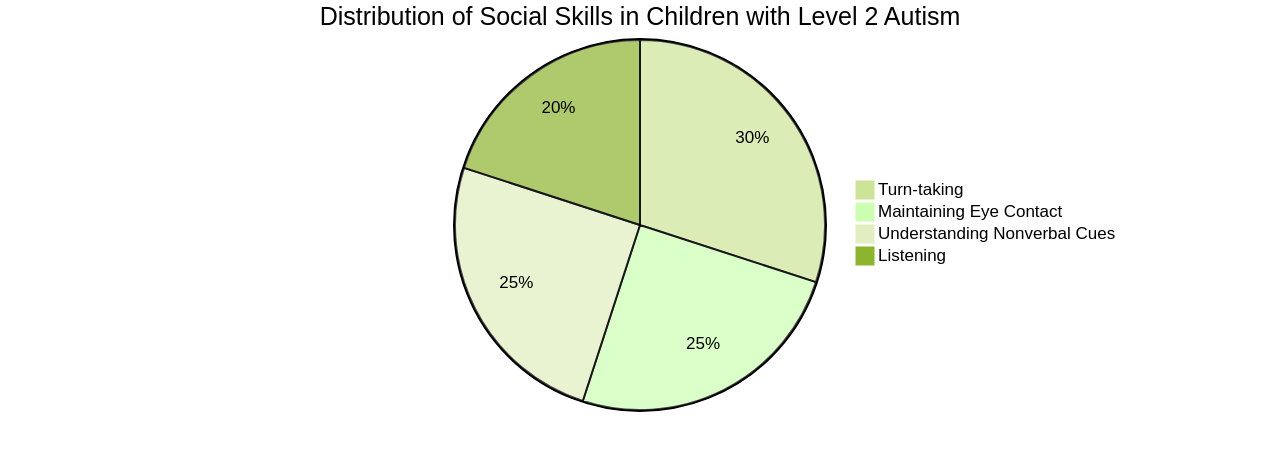
Effective strategies exist for improving the social skills of children with autism spectrum level 2. These strategies, such as social skills training, social stories, visual supports, and structured play activities, can significantly enhance their ability to interact and communicate with others. Social skills training teaches important skills like turn-taking, initiating conversations, and comprehending non-verbal cues. Social stories provide guidance about social situations, while visual supports can aid children in understanding and following social expectations.
The Star Institute, known for its extensive therapy services, has made significant strides in this field. Their autism-specific services are designed to address these social challenges. They also offer a broad range of other services, including occupational therapy, speech language therapy, feeding therapy, and mental health services.
They employ the Star Therapy Approach, which emphasizes outcomes and assessments, making it a valuable resource for children with sensory processing disorders. Complementary services such as integrated listening therapy, DIR Floortime, and Interactive Metronome are also available, providing a well-rounded approach to therapy.
One of their key strategies is the use of play as a medium for learning. This approach focuses on understanding non-verbal communication, using visual boundaries, planning low motor activities, bringing attention to other children, and attending social skills groups. These strategies, shared by Vincentia Ferrari, an occupational therapist at the Star Institute, can play a crucial role in treating sensory processing disorder.
Moreover, the institute possesses a wealth of resources dedicated to sensory processing, including a subject library, research articles, and books. It also offers a sensory integration therapy search and a treatment directory, helping individuals find the appropriate services for their unique needs.
Social skills are more than just a means of communication; they are the building blocks for life skills such as punctuality, discipline, and responsibility. Teachers can foster these skills by creating a welcoming classroom environment, encouraging participation in activities, and modeling good social behavior.
Parents and caregivers can also reinforce social skills training at home through role-playing, watching videos, using social stories, and encouraging interaction with neurotypical children. Games, visual aids, and regular communication with therapists or teachers can be highly effective tools for teaching social skills at home.
In the words of Temple Grandin, a renowned author and autism advocate, children with autism should learn social skills to help them become more independent. With the assistance of qualified experts, educators, and a supportive community, children with autism can acquire these essential social skills, paving the way for a fulfilling and independent life.
To promote reciprocal conversations in children with autism spectrum level 2, it is important to provide effective strategies for enhancing social skills.
This can include using specific techniques and interventions tailored to the needs of the child. Additionally, creating a supportive and inclusive environment that encourages communication and social interaction can also be beneficial.
Community activities can also help children with autism spectrum level 2 to improve their social skills. Engaging in group activities such as sports teams, art classes, or music groups can provide opportunities for social interaction and cooperation with peers.
Lastly, resources are available for parents to support the social skills development of children with autism spectrum level 2. These resources can provide guidance and strategies to help children with autism develop their social skills. It is important for parents to actively engage with their child and seek out resources that are specifically tailored to the needs of children with autism spectrum level 2. By utilizing these resources, parents can play a crucial role in supporting their child's social skills development journey
3. Strategies for Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Level 2 Autism
Children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder can face significant hurdles in social skills development, but with the right strategies tailored to their specific needs and challenges, they can make considerable strides. A structured intervention, such as the use of social stories, visual supports, and social scripts, can be a game-changer. These tools offer a structured environment for the children to learn and practice appropriate social behaviors in different situations, making abstract social concepts more concrete and understandable.
Role-playing exercises, while not directly addressed in the context, can be inferred as an effective tool for enhancing social skills. By acting out various social scenarios, children can explore different responses and outcomes, which helps them understand social dynamics better. This practice can also help them become more comfortable with social interactions, reducing anxiety and hesitation.
Visual aids, such as pictures, charts, and diagrams, can be incredibly beneficial in teaching social norms and expectations. These aids provide clear and concrete information, which can help children with autism process and remember social rules and expectations more easily. Moreover, they can also help children generalize their social skills to different contexts and settings.
Incorporating the child's interests into social skills training can significantly increase their engagement and motivation. For instance, if a child is interested in dinosaurs, a social skills training session could involve a role-playing exercise where the children pretend to be paleontologists working on a dig. This approach not only makes the training more enjoyable for the child but also makes the learned social skills more likely to generalize to other settings.
Consistent practice and reinforcement, both at home and in various social settings, are crucial for the child to effectively apply the social skills they learn in training to their everyday interactions. Parents, teachers, and other key figures in the child's life should provide ample opportunities for the child to practice these skills and give positive reinforcement when the child uses these skills appropriately.
Each child is unique, with their own strengths and weaknesses, and therefore, social skills development strategies should be personalized to fit the child's specific needs and abilities. With patience, understanding, and the right strategies, children with Level 2 Autism can achieve significant improvements in their social skills, enhancing their quality of life and their ability to form meaningful connections with others. Working closely with professionals, such as speech therapists and behavior analysts, who specialize in autism spectrum disorders can provide guidance and support in implementing these strategies effectively
4. Role of Parent Advocates in Supporting Social Skills Development
As a supportive ally in the journey of nurturing children with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder, we comprehend the importance of social skills development. These skills enable our children to communicate, empathize, and interact with their environment. Parent advocates become the crucial link in this process, providing the necessary support, resources, and advocacy that these children need.
In today's vast digital world, numerous resources can assist parent advocates in this endeavor. Websites offer an abundance of free social-emotional learning activities tailored for elementary and middle school students. These comprehensive activities cover an array of skill areas, such as communication, cooperation, emotion regulation, empathy, and impulse control, critical for children with Level 2 Autism.
These resources extend beyond worksheets and lesson plans to game-based online programs and interventions. These offer a fun and interactive way for children to practice and improve their social-emotional skills. Moreover, these resources can be customized based on the child's age and specific social-emotional learning needs, making them an ideal tool for parent advocates.
Among the standout resources is the "Feelings Wheel," designed to assist individuals in understanding and expressing their emotions. It categorizes 135 emotions into different sections, helping children identify, understand, and articulate their feelings better. Tools like these can be instrumental in teaching children about self-awareness, active listening, impulse control, and more.
Developing social skills in children is not a one-time event; it's a continuous process that evolves as the child grows. Everyday activities, like reading books and discussing the characters' emotions and behaviors, can serve as practical teaching moments. Role-playing specific social skills, like maintaining eye contact or joining group activities, can be especially beneficial for children who struggle with these aspects.
Parent advocates can have a significant impact on the social skills development of children with autism spectrum level 2. Through their advocacy efforts, parents can ensure that their children receive appropriate support and interventions to enhance their social skills. This may include accessing specialized services, therapies, and educational programs that specifically target social skills development. Additionally, parent advocates can collaborate with educators, therapists, and other professionals to create individualized plans and strategies that address the unique needs of their children.
Remember, positive reinforcement can go a long way in helping children improve. Verbal rewards and praises for handling social situations well can motivate them to continue practicing and improving.
Lastly, resources like "The Child Code" by Danielle Dick, a tenured professor of psychiatry at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, can provide insightful strategies for helping children develop social skills. Such resources can serve as a guide for parent advocates, equipping them with the knowledge and strategies to effectively support their child's social skills development
5. Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 2 Autism
Navigating the path to securing support services for children with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be intricate, yet with a comprehensive understanding of available resources, the process can be significantly eased. Resources such as therapeutic interventions, educational support, social skills training, and specialized interventions tailored to their specific needs can play a pivotal role in the child's development.
Transitioning from high school to post-secondary education can seem overwhelming for students with ASD. However, it's crucial to remember there are multiple paths to success. These could include specialized post-secondary experiences, life skills programs, certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities.

A critical analysis of the student's abilities, including their independent living skills, academic prowess, and self-care capacities, can aid in determining the most suitable post-secondary options. Organizational and time management skills are essential for college success, and students with ASD may require additional support in these areas.
Colleges often have disabilities departments that provide accommodations for disabled students. Some colleges even offer specific autism support programs. Community colleges can be an excellent starting point for students aiming for college, as they tend to have smaller class sizes and accommodate students who have challenges adjusting to college expectations.
Certificate programs and technical schools offer more focused instruction in specific content areas and may be more manageable for students with organizational and time management challenges. Some universities have special programs for non-degree seeking students with special needs, providing opportunities to audit classes, live on campus, and learn skills for independence.
Individuals who require higher levels of support may consider post-secondary day and residential programs that focus on honing independent living skills, recreational skills, work skills, social skills, and executive functioning skills. Some individuals may choose to pursue supported or customized work experiences with the help of vocational rehabilitation services.
As parent advocates, it's vital to be realistic, objective, and flexible when considering post-secondary options for the child with ASD. Understanding their abilities and support needs is key in finding the right pathway to success and happiness. By researching options, coordinating services, and advocating for the child's needs, parent advocates play a pivotal role in this journey.
With the help of tools such as the website www.asd.media, parents and caregivers can access a wealth of information and resources related to autism support services. This includes articles focusing on unlocking potential and empowering parents to navigate autism support services, as well as a glossary of key terms for promoting social skills in children with autism.
Coordinating services for children with ASD can be a complex task that requires careful planning and collaboration. It is important to ensure that the services provided are tailored to meet the specific needs of each child. This involves working closely with healthcare professionals, educators, and support organizations to develop an individualized plan that addresses the child's unique challenges and goals. Regular communication and coordination between all parties involved is crucial to ensure that the child receives the necessary support and interventions to thrive and reach their full potential
6. Building a Supportive Community for Parents and Professionals
Crafting a nurturing and inclusive community is vital for parents and professionals involved in the care of children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder. Such a community serves as a haven where experiences can be exchanged, collective knowledge can be gathered, and emotional support can be found.
Online platforms and forums are effective means to establish such communities. They allow parents and professionals to connect, share their experiences, and exchange resources. One such digital support group is Other Parents Like Me, specifically designed for parents of teenagers grappling with mental health issues. It offers a wealth of resources, including support groups, toolkits, curated articles, books, podcasts, and a comprehensive glossary of mental health terms. Parents are also introduced to various organizations, schools, and professionals who can aid them on their journey.
In addition to offering resources, these online platforms often host workshops, seminars, and support groups, creating opportunities for networking, collaboration, and knowledge exchange. For instance, Other Parents Like Me goes a step further by offering recordings of talks by guest speakers and industry experts. This provides parents with firsthand insights and information on mental health. Personal narratives from the community are also shared on the blog, offering a raw, unfiltered, and insightful look into the experiences of other parents.
One more notable community is Transforming Family, a Los Angeles-based family support group. This organization is dedicated to creating a positive environment for children, adolescents, and their families dealing with issues of gender identity. It offers support not just for transgender, nonbinary, and gender expansive youth, but also for their parents, caregivers, and siblings.
Transforming Family provides a variety of services, such as peer support, training, education, and family events, to cater to each family member's unique needs. Founded by parents and professionals with personal experiences with gender identity issues, the organization firmly believes in the power of collective support and advocacy for the best interests of youth.
The importance of fostering a supportive community for parents and professionals is immense. These communities not only provide a platform for sharing experiences and learning, but also serve as a beacon of hope and support in the challenging journey of parenting a child with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder
7. Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 2 Autism: Effective Strategies for Parent Advocates
Managing the intricate behaviors displayed by children with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder requires a well-rounded and comprehensive strategy. As someone standing alongside parents, it is essential to understand the root causes of these behaviors, encourage positive behavior, and ensure consistent strategies across diverse environments.
The IRIS Center provides a range of resources focused on evidence-based practices and high leverage practices, offering support materials such as modules, case studies, and activities centered around disabilities and inclusive education. One notable resource is their module on addressing challenging behaviors in elementary schools. This module, forming part of a two-part series, focuses on understanding the acting-out cycle and provides strategies for teachers to prevent and address such behaviors, particularly relevant for children with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Alongside understanding and addressing behaviors, establishing a collaborative relationship with professionals to create and execute a behavior support plan is equally critical. This collaboration not only aids in managing challenging behaviors but also promotes the development of social skills in children with Level 2 Autism.
The goal remains constant: to encourage positive behavior and provide an environment conducive for the child to grow and thrive. The resources and strategies offered by the IRIS Center can significantly contribute to achieving this objective.
To manage such challenging behaviors effectively, it is vital to implement a range of strategies tailored to each child's individual needs. These strategies could include:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): This approach involves breaking down behaviors into smaller components and using positive reinforcement to teach new skills and reduce problem behaviors.
- Visual Supports: Visual aids like visual schedules and social stories provide a clear structure, reduce anxiety, and help manage challenging behaviors.
- Communication Strategies: Implementing communication strategies can help children communicate effectively and reduce frustration.
- Sensory Regulation: Providing sensory breaks, using sensory tools or techniques, and creating a sensory-friendly environment can help manage challenging behaviors related to sensory issues.
- Social Skills Training: Teaching and reinforcing appropriate social skills can help children navigate social situations more effectively, thus reducing challenging behaviors.
These strategies focus on providing structure, consistency, and positive reinforcement. It is crucial to work closely with professionals, such as behavior analysts or therapists, to develop and implement individualized behavior management strategies.
Implementing consistent strategies for behavior management can be beneficial for the overall development of children with Autism Spectrum Level 2. By using consistent strategies, caregivers and educators can create a structured and predictable environment that supports the child's needs.
Promoting positive behaviors can be achieved through various strategies, such as focusing on enhancing their social skills. It is crucial to create a supportive and structured environment that encourages social interactions and provides opportunities for practicing and reinforcing appropriate social behaviors.
Finally, it's important to remember that every child with autism is unique, and what works for one child may not work for another. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with professionals and create an individualized behavior management plan based on the specific needs and strengths of the child
Conclusion
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing the necessary support and creating an inclusive environment for children on the Autism Spectrum. Level 2 Autism presents considerable social and communicative hurdles, impacting the ability to form relationships and adapt to changes. These children face unique challenges that require tailored strategies and support to help them thrive.
By delving into the world of Level 2 Autism and exploring effective strategies for enhancing social skills development, we can create a supportive community that nurtures the potential of these children and helps them lead fulfilling lives. Strategies such as social skills training, visual supports, and interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy and speech therapy play a vital role in improving communication, interaction abilities, and overall well-being. It is important to tailor these strategies to each child's specific needs and strengths, providing ongoing support, reinforcement, and collaboration between parents, professionals, and educators.
To support social skills development in children with Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder, it is crucial for parents and professionals to access available resources. Websites like www.asd.media provide a wealth of information on autism support services, including articles focusing on unlocking potential and empowering parents. By utilizing these resources, parents can actively engage with their child's development journey and play a crucial role in supporting their social skills development.
Start now by accessing available resources at www.asd.media to enhance your understanding of Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder and discover effective strategies for supporting social skills development in children with autism. Together, we can create an inclusive community that fosters the growth and well-being of these children




