Introduction
Children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism face unique challenges in their social interactions and communication. Understanding the specific traits of Level 2 Autism is crucial in developing effective strategies to enhance social skills. This article provides a brief overview of Level 2 Autism and explores various techniques and interventions that can be employed to support individuals with autism in their social skills development. From social skills training to building a supportive community, this article aims to provide valuable insights and practical strategies for parents, professionals, and caregivers working with children with Level 2 Autism. By implementing these strategies and staying updated on the latest developments in ABA therapy, individuals can ensure they are providing the best possible care and support for children with autism
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: A Brief Overview
Level 2 Autism, a component of the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), presents unique challenges for children, notably in their social interactions and communication. Those diagnosed with this level of autism may exhibit a limited range of interests and struggle with changes in their routines. Understanding the specific traits of Level 2 Autism is the cornerstone in developing effective strategies for the enhancement of social skills.
Children with Level 2 Autism may find social situations intricate. However, it's worth noting that these social skills can be nurtured with time. Comprehending social objectives and values can act as a beacon in this journey. Individuals with ASD may encounter a spectrum of emotions in their quest to enhance their social skills as it might feel like yielding to mainstream norms. Therefore, it's crucial to set clear goals and motivations before embarking on the journey of social skills improvement.
Despite the hurdles, self-acceptance, finding joy in their unique perspective, and maintaining individuality while developing social skills are paramount for individuals with ASD. Several techniques help foster these skills, including social skills training, mentorship, or participation in social skills groups.
Social rules can be complex and may vary depending on the situation. However, individuals with ASD can learn through observation, trial and error, and seeking real-world practice. The use of scripts or rote memorization can be useful tools for navigating social interactions. Understanding one's condition and adjusting expectations can be beneficial for individuals with ASD, as well as for those around them who aim to support their social skills development.
Developing social skills is essential for individuals with ASD.
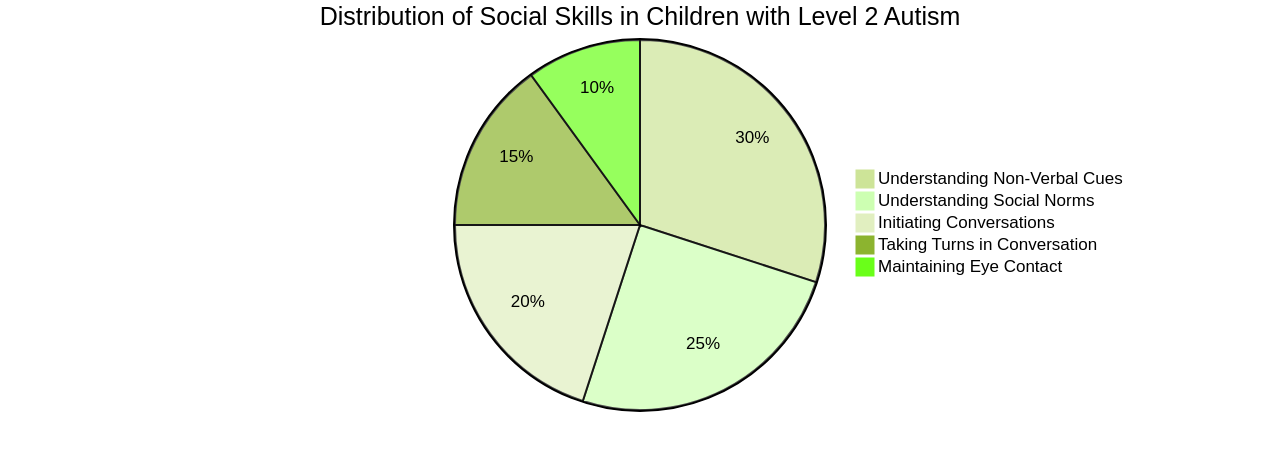
Many children and adults with ASD may need guidance in learning how to behave in various social situations. Regular practice can enhance community engagement and improve outcomes such as happiness and friendships. Teaching social skills to individuals with autism involves direct and explicit instruction, practice in realistic settings, and support from peers and professionals.
Social skills groups can be beneficial, where individuals with autism can regularly practice social skills with peers. Effective social skills groups should provide structure, predictability, and multiple learning opportunities. Personalized teaching stories, visual aids, and personalized templates can be used to help individuals with autism understand and navigate different social situations. The aim is to make everyday social situations predictable and provide strategies for effective social interactions.
Community participation and inclusive programs are important for individuals with autism to further enhance their social skills. The more they practice and encounter various social situations, the more adept they become at navigating these interactions. In the end, understanding and accepting one's unique characteristics can be a powerful tool in the journey towards improved social skills.
One of the effective techniques for improving social interactions in children with Level 2 Autism is social skills training. They are taught specific social skills and given opportunities to practice them in controlled settings. Visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules, help children understand social situations and expectations. Peer-mediated interventions, where typically developing peers are trained to provide support and model appropriate social behavior, can also be beneficial.
Various activities can help engage children with Level 2 Autism in social interactions. Strategies such as Social Stories, Role Playing, Social Skills Groups, Visual Supports, and Cooperative Games have proven effective. Remember, tailoring activities to each child's individual needs and preferences and providing a supportive and inclusive environment are vital to their social development.
Managing routines and transitions for children with Level 2 Autism can be aided by providing a visual schedule, using timers or countdowns, and providing clear and consistent instructions. Establishing a predictable routine and providing visual supports can help these children feel more secure and confident in managing transitions.
Working with children with Level 2 Autism requires support and the implementation of effective strategies. Building a structured routine, using visual aids, incorporating sensory breaks, encouraging social interactions, and collaborating with professionals are some of the strategies that can be employed to work effectively with these children.
To find resources for understanding Level 2 Autism and social skills development, it is recommended to explore reputable sources or consult professionals who specialize in autism. Remember, each child with autism is unique, so it is important to tailor strategies and interventions to meet their individual needs
2. The Role of ABA Therapy in Enhancing Social Skills
Applied Behavior Analysis, often known as ABA, is a scientific method that uses our understanding of behavior and its interaction with the environment to aid children with Level 2 Autism in improving their social skills.
The Neurobehavioral Unit (NBU) at the Kennedy Krieger Institute, which is renowned for its comprehensive work with children and young adults suffering from severe behavioral disorders and developmental disabilities, including Level 2 Autism, extensively utilizes this approach.
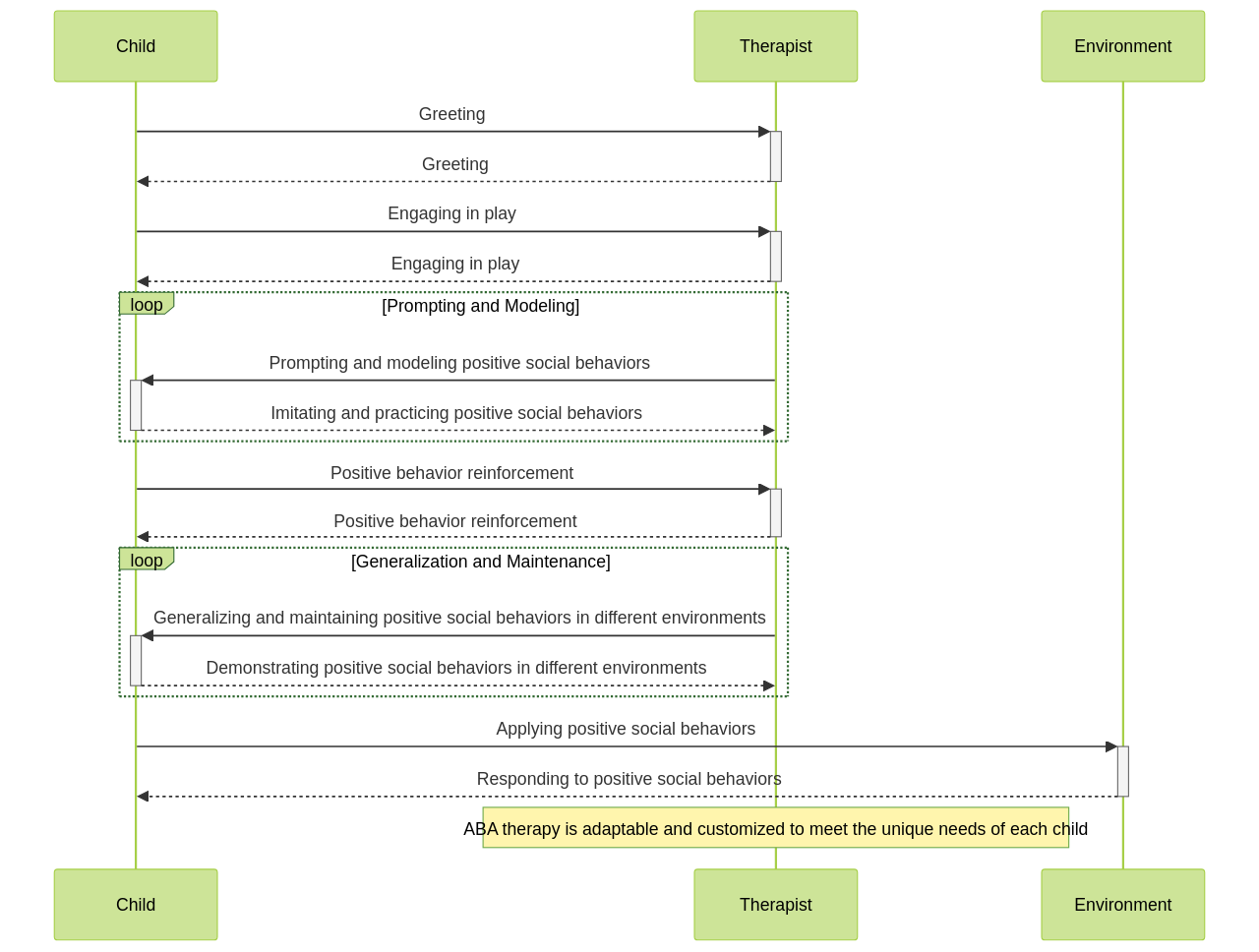
ABA therapy's use at the NBU isn't random; instead, it's a deliberate therapeutic intervention designed to assist these individuals in acquiring new skills and minimizing problematic behaviors. ABA therapy's strength lies in its use of positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. This approach is especially beneficial when addressing social interactions, a typical area of difficulty for children with Level 2 Autism. Social situations can be intricate and overwhelming for these children, but ABA therapy simplifies them by breaking these situations down into manageable steps.
The adaptability of ABA therapy is another of its strengths.
It can be customized to meet the unique requirements of each child, making it a versatile tool in the treatment strategies toolbox. Furthermore, the efficacy of ABA therapy isn't just anecdotal; it's backed by scientific and professional endorsement, with numerous research studies and publications validating its use.
ABA therapy focuses on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors while reducing challenging ones. It employs techniques like positive reinforcement, prompting, and modeling to help children with autism learn and develop social skills. By targeting specific behaviors and providing structured interventions, ABA therapy can help children with Level 2 Autism improve their communication, social interactions, and overall social functioning.
Positive reinforcement, a widely used technique in ABA therapy, enhances social interactions. By providing rewards or incentives for desired behaviors, individuals are encouraged to engage in positive social interactions. This can be achieved by identifying specific social skills that need improvement and designing reinforcement strategies tailored to the individual's needs. Through consistent and targeted use of positive reinforcement, individuals with autism can learn and develop effective social skills.
ABA therapy for children with level 2 autism can involve breaking down complex social situations to help them develop their social skills. By providing step-by-step tutorials and using strategies tailored to their needs, therapists can help children with level 2 autism navigate and understand social interactions more effectively. This can include teaching them how to interpret social cues, understand non-verbal communication, and practice appropriate social behaviors. Through systematic and structured interventions, ABA therapy aims to enhance social skills in children with level 2 autism.
In the broader landscape of treatments for autism spectrum disorders, ABA therapy doesn't stand alone. Other evidence-based practices also play a role. However, when it comes to enhancing social skills, ABA therapy has proven its worth time and again, making it a significant component in the treatment regimen
3. Practical Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 2 Autism
Addressing behavioral challenges in children with Level 2 Autism requires a blend of empathy, patience, and actionable strategies.
These children often exhibit disruptive behaviors, not out of defiance, but due to underlying issues such as communication difficulties, sensory processing problems, or struggles with social interactions.
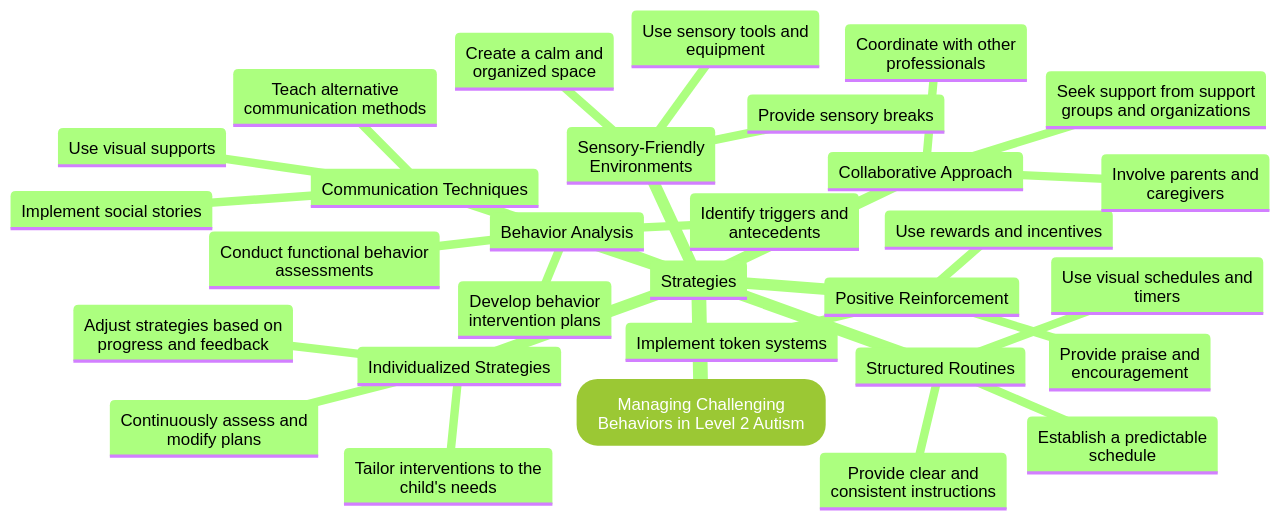
One of the primary factors contributing to these behavioral challenges is communication difficulties. Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may struggle with expressive language and interpretation of non-verbal cues. This struggle can lead to frustration and result in disruptive behaviors. However, a comprehensive behavior management plan that includes strategies such as using clear, concise language and visual aids can help facilitate better communication.
Social interaction can also be a significant challenge for children with ASD. They may find it difficult to understand others' perspectives or adhere to social norms, leading to uncomfortable situations or even bullying. In such cases, using social stories can be an effective strategy to prepare children for these social situations.
Another contributing factor to behavioral issues in children with ASD is sensory processing difficulties. These children might be hypersensitive or hyposensitive to sensory stimuli, leading to reactions that others may find difficult to understand. In such scenarios, creating a calm, sensory-friendly environment can be beneficial in managing these behaviors.
Changes in routine or environment can also trigger behavioral challenges as children with ASD often find it hard to adjust to new circumstances. Maintaining a structured routine can help manage these behaviors. However, every child is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Hence, flexibility and adaptability are critical components of your approach.
It is crucial to understand that a child with ASD uses behaviors to communicate something or achieve a specific function. Therefore, it's essential to look beyond the surface behaviors and discover the unaddressed needs they are trying to convey. This understanding is key in implementing effective strategies to manage behavioral difficulties.
Teaching communication skills to children with ASD is a gradual process. It starts with simple steps and progressively builds up to more complex language strategies. Parents and educators often need additional guidance and support in this area. A well-structured teaching plan, patience, and reinforcing relationships with students can significantly facilitate this learning process.
In managing challenging behaviors in children with Level 2 Autism, it is essential to implement practical approaches such as visual supports, structured routines, positive reinforcement, and social stories. Creating a calm and structured environment, setting clear expectations, and providing consistent and predictable routines can also be effective. It is important to work closely with professionals such as behavioral therapists or psychologists who can provide guidance and support in implementing these strategies.
Lastly, always remember to reinforce positive behaviors and provide clear and consistent instructions. Patience, understanding, and flexibility remain the most powerful tools in this journey
4. Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 2 Autism
Children with Level 2 Autism and their families have access to a myriad of support services encompassing educational assistance, speech and occupational therapy, and social skills groups. Navigating through these resources might seem overwhelming, but remember, you're not alone. ASD Media stands out as a comprehensive repository of necessary resources and information to help you understand and access the required support for your child.
A critical area that often goes unnoticed is planning for the future education of children with autism after high school. As a parent shared in their personal narrative, many parents feel underprepared for this phase due to the lack of guidance from schools. It's crucial to start formulating a concrete post-graduation plan for autistic students as early as age 14, with individual goals aligned with this objective.
School counselors' conventional guidance often falls short in providing information about community colleges or trade schools and special education options for higher-functioning autistic kids. However, there are options available such as 18-21 programs, private transition programs, and specialized programs for students with intellectual and developmental disabilities at community colleges and four-year schools.
For autistic students pursuing college or trade school education, there's a pressing need for improved accommodations and support. One strategy suggested is the layering of options, starting with an 18-21 program, then transitioning to a community college with support, and eventually moving on to a four-year college equipped with a robust autism support system.
As one parent aptly put it, "Educating kids like ours is a marathon, not a sprint." This journey requires patience, perseverance, and the right information. Parents should not hesitate to seek help when needed and leverage resources available, such as ASD Media, to ensure their child's well-being and future success.
For educational support, targeted interventions and resources that cater to children's specific needs are vital. This includes individualized education plans, specialized teaching techniques, and assistive technology. A supportive and inclusive learning environment, with trained professionals and strong collaboration between teachers, parents, and therapists, can greatly enhance the educational experience for children with autism.
Speech therapy can be beneficial for children with autism as it can help improve their communication skills, including speech and language development. Speech therapists use various techniques and exercises to address specific communication challenges that children with autism may face. These may include difficulties with articulation, expressive language, social interaction, and pragmatic language skills.
Social skills groups specifically designed for children with autism can be effective in enhancing their social skills. These groups provide a structured and supportive environment where children can learn and practice social skills with their peers. Activities and exercises can help children develop their communication, social interaction, and problem-solving skills.
Navigating support services for children with autism starts by researching reputable organizations and resources that specialize in autism support. These organizations often provide valuable information, guidance, and resources for parents and caregivers. Local support groups or autism advocacy organizations can be helpful in connecting with other parents who have navigated similar challenges. Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as pediatricians or child psychologists, who can provide guidance and referrals to appropriate support services, is also recommended.
ASD Media, available at www.asd.media, provides resources for support services for children with autism. The website offers a variety of articles and news related to autism support services. Resources like "Unlocking the Potential: Empowering Parents to Navigate Autism Support Services" and a glossary of key terms for promoting social skills in children with autism can provide valuable information and guidance for parents and caregivers seeking support services for children with autism
5. Time Management and Prioritization Tips for Parents
Journeying through the demands of everyday life while providing care and support to a child with Level 2 Autism can be overwhelming. However, with the appropriate approach to time management and task prioritization, it can become significantly more manageable. Creating a well-structured daily routine that includes therapeutic sessions, educational activities, and leisure time can make a significant difference.
A daily schedule with specific times for waking up, meals, activities, and bedtime can offer a sense of predictability for the child. This consistency can help them feel more secure and enhance their understanding of what is expected of them. A tool that can aid in creating this daily routine is an Excel spreadsheet, where you can document individualized education program (IEP) goals for your child. It's a common practice in special education classrooms and can be adapted for home use. Remember to include non-negotiable times such as meals and breaks in your schedule.
Consider incorporating activities that not only serve as therapy but also provide an element of play. This makes the learning process more enjoyable for your child. Visual supports such as visual schedules, timers, and calendars can also be helpful in time management. These tools can help the child understand the passage of time, manage transitions, and stay organized.
Prioritizing tasks based on their importance and urgency can help manage time effectively. Breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable ones can also make them feel less overwhelming. Realize that it's okay to seek assistance and delegate tasks when necessary. There may be times when you'll have to make difficult decisions and trust your instincts. It's okay to make mistakes and learn from them. Understand that you won't always make the right choices and forgive yourself when you falter.
Among all these, it's equally crucial to maintain your identity outside of being a parent, and to allow yourself time for self-care. This personal time will help you rejuvenate, enabling you to lend the best support to your child. Self-care is crucial for parents who are supporting a child with level 2 autism. Taking care of oneself physically, mentally, and emotionally allows parents to better support their child's needs. It helps parents maintain their own well-being and prevents burnout, which is common in caregivers of children with special needs.
Remember that parenting a child with special needs is akin to a marathon, not a sprint. Celebrate your child's small accomplishments, and refrain from comparing their progress with others. Engage in extracurricular activities that offer therapeutic benefits and make time to create beautiful memories. After all, although parenting a child with special needs comes with its unique set of challenges, it also brings its own special rewards
6. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Creating a supportive and nourishing environment for both parents and professionals who cater to children with Level 2 Autism is pivotal.
This involves facilitating the exchange of experiences and wisdom, which aids in fostering invaluable insights and emotional support. It's important to remember that this exchange isn't a single-sided process, but rather a mutual one where each member can contribute and benefit.
A significant part of this communal interaction involves understanding the unique communication patterns of children with autism. Since the brain of a child with autism interprets communication differently, it's crucial to focus on shared feelings and respect their need for a structured routine. Consistent routines and the provision of choices can help alleviate anxiety and foster better communication. It's also fundamental to assume competence in autistic children, providing them the autonomy to make decisions, and nurturing a sense of control.
Creating engaging and enjoyable communication processes can be achieved by implementing scripting activities and adopting the child's communication style. Though every autistic individual has a unique way of communicating, recognizing and expressing emotions is a common thread that binds them together. Even nonverbal individuals with autism can contribute meaningfully to society despite their communication challenges. Acknowledging this is a step towards creating a more inclusive environment.
The High Needs Autism Advocates (HNAA) community is a commendable platform that enables high-support needs autistic individuals to narrate their stories and advocate on their own behalf. This community sheds light on various aspects of high-needs autism such as developmental delays, social skill challenges, sensory processing issues, and rigidity. Personal accounts from community members add authenticity to these discussions.
But the HNAA community isn't solely about spreading awareness; it also provides tools for advocacy, fostering a better understanding, and representation of severely autistic individuals. As a community member aptly put it in a Reddit post, "Our experiences are unique, yet we share a common thread - the need for understanding and representation."
ASD Media also nurtures such a community, offering a platform where individuals can connect, share, and learn. Remember, this journey is not one you have to walk alone. A supportive community stands ready to lend a hand, sharing your experiences and offering the necessary support. This support includes providing resources, information, and opportunities for connection and collaboration, such as creating online platforms or forums. Organizing support groups or workshops that bring parents and professionals together can facilitate networking and the sharing of strategies and resources. Providing access to educational materials and training opportunities for parents and professionals to enhance their knowledge and skills in supporting children with level 2 autism is also a key part of this support. By fostering a sense of community and collaboration, parents and professionals can feel supported and empowered in their efforts to provide the best possible care for children with level 2 autism
7. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning and Improvement in ABA Therapy
ABA therapy continues to evolve, with new research and strategies constantly emerging. This is vital in offering effective support to children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. One of the recent advancements is the use of data-driven, client-centric ABA treatment dose optimization, aiming to enhance functional outcomes for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
This approach is significant because it challenges the existing belief in a linear dose-response relationship in ABA therapy. By adjusting the treatment dosage to fit individual client needs, we may observe better functional progress. This method emphasizes the importance of personalization in therapy, implying that the amount of therapy may not be the sole determinant of outcomes.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also induced a shift towards telehealth, affecting the delivery of ABA therapy. The full impact of this shift is still under investigation, but preliminary findings suggest that the method of supervision, whether in-person or via telehealth, contributes significantly to determining functional outcomes.
As a recent study stated, "Findings challenge prior research that demonstrated a linear dose-response relationship and suggest that by tailoring treatment dosage to individual clients' needs, providers may be able to better maximize functional progress for each client and preserve family time and utilize health plan dollars more efficiently."
To navigate the challenges and celebrate the successes of the journey with Level 2 Autism, continuous learning and improvement are vital. This includes staying updated on these developments. It's essential to access reliable sources and organizations that focus on autism research and treatment. They often publish studies, articles, and reports on the latest developments in ABA therapy. By reading these sources, you can stay informed about the latest research findings and understand how they can enhance the implementation of ABA therapy for individuals with autism.
Navigating the challenges of Level 2 Autism can be complex and requires a comprehensive approach. It's crucial to seek professional guidance and support from experts in the field. A blend of therapies, such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral therapy, may be recommended to address specific areas of difficulty. Establishing a structured and predictable environment, setting clear routines, and providing visual supports can help individuals with Level 2 Autism navigate daily challenges more effectively.
As we continue to understand and adapt to these changes, we also acknowledge the potential benefits of using technology and data analytics in personalizing care and aligning provider and payer goals. Therefore, it's crucial to stay informed about ABA therapy developments by regularly accessing reputable sources of information in the field. This can include websites, online publications, journals, and professional organizations specializing in autism and ABA therapy. By staying updated with the latest research, industry insights, and advancements in ABA therapy implementation, individuals can ensure they are offering the most effective and evidence-based interventions for those with autism
Conclusion
Children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism face unique challenges in their social interactions and communication. Understanding the specific traits of Level 2 Autism is crucial in developing effective strategies to enhance social skills. This article provides a brief overview of Level 2 Autism and explores various techniques and interventions that can be employed to support individuals with autism in their social skills development. From social skills training to building a supportive community, this article aims to provide valuable insights and practical strategies for parents, professionals, and caregivers working with children with Level 2 Autism. By implementing these strategies and staying updated on the latest developments in ABA therapy, individuals can ensure they are providing the best possible care and support for children with autism.
The main points discussed in this article include understanding the traits of Level 2 Autism, the role of ABA therapy in enhancing social skills, practical strategies for managing challenging behaviors, navigating support services for children with autism, time management and prioritization tips for parents, building a supportive community, and the importance of continuous learning and improvement in ABA therapy.
The broader significance of this article's topic lies in the impact it can have on improving the lives of children with Level 2 Autism. By understanding their unique challenges and employing effective strategies, we can help these children develop their social skills, manage their behaviors, access necessary support services, create a nurturing environment at home, foster a supportive community, and stay updated on advancements in ABA therapy.
In conclusion, by implementing the strategies discussed in this article and staying informed about the latest research and developments in ABA therapy, parents, professionals, and caregivers can provide the best possible care and support for children with Level 2 Autism. It is through our collective efforts that we can make a positive difference in the lives of these children. Start now by accessing reputable sources like ASD Media to further expand your knowledge and resources Start now




