Introduction
Navigating ABA therapy for children with Level 1 Autism can be a complex and challenging journey. It requires understanding the key characteristics of Level 1 Autism, the role of parents as advocates, strategies for managing challenging behaviors, accessing support services, enhancing social skills development, building a supportive community, and continuously improving ABA therapy. This article aims to provide valuable insights and guidance for parents and caregivers in supporting their children with Level 1 Autism. From understanding the unique challenges to implementing effective strategies, this article offers a comprehensive overview of the various aspects involved in supporting children with Level 1 Autism through ABA therapy. By embracing these strategies and collaborating with professionals, parents can create a supportive and inclusive environment that nurtures their child's social development and overall well-being.
1. Understanding Level 1 Autism: Key Characteristics and Support Needs
Level 1 Autism, often known as high-functioning autism, presents unique challenges in social interaction, nonverbal communication, and limited, repetitive behaviors. Children with this diagnosis might struggle with understanding others' perspectives, initiating conversations, or adapting to changes in their daily routines. Despite these challenges, they often have a keen interest in social interaction, and with proper, focused support, they can show significant improvement.
To foster social interaction in children with Level 1 Autism, it is crucial to employ effective strategies that enhance their social skills.
Providing opportunities for social engagement, teaching and modeling appropriate social behaviors, and creating supportive and inclusive environments are some of these strategies. Utilizing visual supports, social stories, and social scripts can aid these children in navigating social situations and interpreting social cues. Individualized interventions like social skills training and social communication interventions can further support their social interaction.
Effective interventions designed to support the social skill development of children with autism can significantly enhance their communication and interaction abilities. Strategies such as social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and applied behavior analysis can be particularly beneficial. These interventions address the specific needs and challenges faced by children with autism, offering them the necessary support and guidance for their overall development.
Helping children with Level 1 Autism adapt to changes in their routines requires providing them with adequate support and structure. Visual schedules or aids can prepare them for upcoming changes, while social stories or scripts can help explain the reason for the change and what to expect. Clear instructions and consistent routines can reduce anxiety and facilitate the transition process. Collaborating with professionals, such as therapists or educators specializing in autism, is crucial to develop an individualized plan that meets the child's specific needs.
Improving communication skills in children with Level 1 Autism entails providing them with effective strategies and techniques. Visual supports, social stories, and structured play activities may be included in these strategies. Creating a supportive and inclusive environment where the child feels comfortable expressing themselves is also beneficial. Working with a speech-language therapist who specializes in autism can significantly aid in developing these children's communication skills.
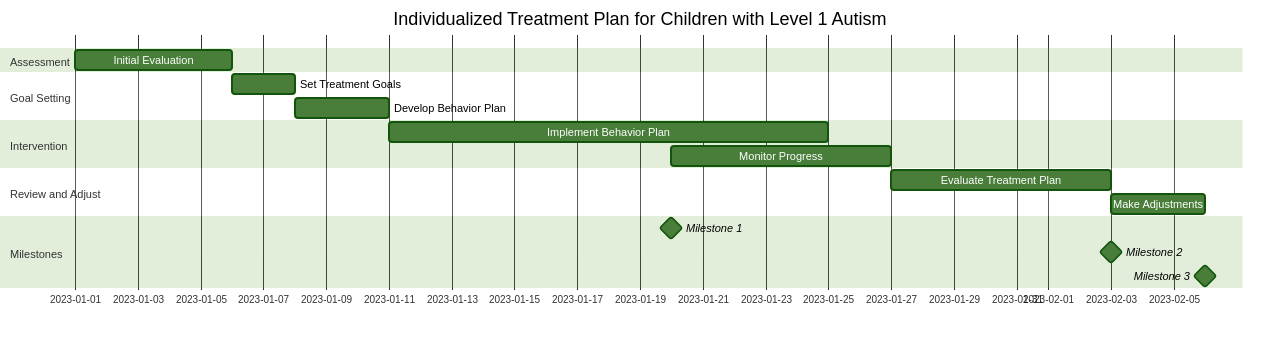
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is a common intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder. It focuses on teaching and reinforcing desired behaviors while reducing problematic behaviors. ABA therapy can be tailored to meet the specific needs of children with Level 1 Autism, who usually have good language skills but may struggle with social interaction and repetitive behaviors. Collaborating closely with qualified professionals is crucial to navigate the ABA therapy process and develop an individualized treatment plan. This process may involve setting specific goals, implementing behavior management strategies, and regularly assessing progress. By following a comprehensive and structured approach, ABA therapy can help children with Level 1 Autism develop vital social skills and enhance their overall quality of life.
Promoting social skills development in children with Level 1 Autism requires effective strategies and enhanced social interactions. Implementing suitable interventions and therapies can improve their communication, socialization, and emotional regulation skills. Tailored programs focusing on social-emotional learning, behavior management, and peer interactions can significantly benefit their overall development. Collaborating with educators, therapists, and parents can create a supportive environment that nurtures social skills and encourages positive social interactions for children with Level 1 Autism.
Understanding the challenges of Level 1 Autism in ABA therapy can be complex. However, the challenges faced by individuals with Level 1 Autism, including difficulties with social interactions, communication, and repetitive behaviors, can be addressed with specific interventions and strategies tailored to the individual's needs. ABA therapists work closely with individuals with Level 1 Autism to identify and address these challenges, promoting positive behaviors and reducing problematic behaviors.
Each individual with Level 1 Autism presents unique challenges and strengths. ABA therapy aims to understand and address these challenges through individualized interventions and strategies, with the ultimate goal of improving the individual's quality of life and overall functioning.
2. The Role of Parents as Advocates in ABA Therapy
Parents play an instrumental role in the Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy process, providing critical support and advocacy to ensure their child's needs are met. Their active engagement in therapy sessions, collaboration with professionals, and application of strategies at home create a comprehensive support system for the child's development.
In the realm of ABA therapy, parents serve as a crucial bridge between the child and the therapy team. Their unique insights into the child's behavior, preferences, and progress significantly enhance the effectiveness of the therapy. One way parents can amplify their advocacy is through the use of innovative resources such as Picture Exchange Communication (PEC) cards. These tools have shown a positive impact on the learning and growth of children with autism.
Parents can also find support in educational advocates when navigating the complex special education system. These advocates guide parents in gathering necessary evidence and information to effectively advocate for their child's education. Parent advisory councils also play a pivotal role in advocating for children with special needs, emphasizing the power of knowledge and the importance of a team approach.
Parents can further participate in ABA therapy sessions by observing the techniques and strategies used by the therapists.
This active participation allows parents to set goals, develop strategies, and implement therapy techniques at home that address their child's specific needs. It also enables parents to provide feedback about their child's progress and any concerns they may have.
At home, parents can create a structured routine and environment for the child, including setting clear expectations, establishing consistent schedules, and providing visual supports. The use of positive reinforcement encourages desired behaviors and rewards for completing tasks or following instructions. It is essential for parents to collaborate with the ABA therapist and follow through with any recommended strategies or interventions at home.
Parents can advocate for their child's needs in the ABA therapy process by actively participating in the therapy sessions and collaborating with the ABA therapist. They can communicate their concerns, goals, and observations about their child's progress to the therapist. Parents can also educate themselves about ABA therapy and the techniques being used, enabling them to make informed decisions and advocate effectively for their child.
Parents can provide valuable insights to the ABA therapy team about their child's behavior by observing and documenting their child's behavior in different settings and situations. They can share information about any specific triggers, patterns, or behaviors that they have noticed. This information can help the ABA therapy team to design a personalized intervention plan and make necessary adjustments to the therapy program for better outcomes.
In conclusion, by embracing their role as advocates, parents can significantly contribute to their child's development and the effectiveness of ABA therapy.
3. Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 1 Autism
Navigating the complex terrain of Level 1 Autism in children requires a proactive, personalized strategy. Effective management of the challenging behaviors often exhibited by these children may involve behavior modification techniques, visual supports, social stories, and structured routines. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional or therapist who specializes in autism to develop an individualized plan that addresses the child's specific needs.
An integral part of this individualized approach involves using visual aids to enhance communication. Visual supports such as pictures, symbols, or visual schedules, can facilitate better understanding and communication of needs, thoughts, and feelings in children with Autism. These aids provide a visual representation of concepts, making it easier for the child to process information, thus enhancing their communication skills and promoting a better understanding of social interactions and expectations.
Establishing consistent routines also plays a pivotal role in managing challenging behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism. Providing structure and predictability through routines can make children feel more secure and help reduce anxiety. Tailored routines that consider the specific needs and abilities of each child can foster the development of important life skills, such as self-regulation and independence. Visual supports, like schedules and visual timers, can reinforce these routines and promote understanding and compliance.
Teaching coping skills for handling changes or stressful situations is also beneficial for the overall well-being and development of these children. Providing them with strategies and techniques can equip them to manage their emotions and navigate through challenging situations more effectively.
Positive reinforcement is another key strategy for managing challenging behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism. Rewards or positive consequences for desired behaviors motivate children to engage in appropriate actions. Examples of these rewards could be verbal praise, tokens, or privileges for displaying positive behaviors. Consistent and clear expectations, coupled with immediate reinforcement, can shape and encourage desired behaviors while discouraging challenging ones.
Each child is unique, and therefore, strategies that work for one child might not be as effective for another. Regular assessment of the child's behavior patterns, triggers, and underlying factors contributing to the challenging behaviors is necessary. Once the assessment is completed, strategies can be developed and implemented to address the specific needs of the child and promote positive behavior outcomes. It is essential to regularly review and adjust these strategies based on the child's progress and changing needs.
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often use behaviors to communicate something or achieve a specific function. Therefore, it's vital to see beyond the surface behaviors to discover any unaddressed needs. For the child's safety, consider modifying their schedule to include more preferred activities and creating a safe space within the home for de-escalation.
Finally, providing consistent support and therapies, setting achievable treatment goals, and refraining from punishing ASD children as they may not understand cause and effect is important. Professional help from psychologists or psychiatrists can provide additional tools to manage behavioral difficulties. Remember, patience, consistency, and a supportive environment are key to helping children with ASD manage their behavioral difficulties.
4. Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 1 Autism: A Guide for Parents
"Embarking on the journey of finding support services for children with Level 1 Autism can seem like a challenging task for parents. These services, such as speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, social skills groups, and educational support, play a crucial role in enhancing the child's development and improving their overall quality of life.
In order to navigate through these resources effectively, several strategies can be employed. The first strategy is to educate yourself. A wealth of information is available on reputable websites and resources that specialize in autism support services. These platforms often provide directories or databases of service providers, thereby empowering you to understand each service's offerings and how it can benefit your child.
Secondly, it can be beneficial to seek advice from professionals in the field. Healthcare experts like pediatricians or child psychologists often have a deep understanding of local resources and can offer valuable insights and referrals. They can help you tailor the available support services to meet your child's specific needs.
Another strategy is to be your child's advocate. Asserting your child's needs and rights is a significant part of this journey. Remember, as a parent, your voice can be an influential advocate for your child.
It's also essential to remember that you are not alone in this journey. There are resources and support systems designed to assist you along the way. For instance, free government services for children with autism can be an invaluable resource. Additionally, local autism support organizations or advocacy groups often have information on recommended therapists or clinics in the area.
Creating a personalized treatment plan that caters to your child's unique needs can also be beneficial. This plan could include structured routines, nonverbal ways to connect with your child, and making time for fun and play. It's important to celebrate your child's individuality and progress, rather than comparing them to others.
One crucial insight to bear in mind, as highlighted by experts, is the significance of nonverbal communication in children with autism. Observing and interpreting these cues can offer a deeper understanding of your child's needs and emotions. As one expert aptly puts it, "The best thing you can do as a parent is to start treatment right away and seek help as soon as you suspect something is wrong. Don't wait to see if your child will catch up later or outgrow the problem. Even without an official diagnosis, earlier intervention gives children with autism spectrum disorder a greater chance of treatment success."
Navigating the support services available for children with Level 1 Autism may seem overwhelming, but with the right tools, resources, and support, it is entirely possible to do so effectively.
"
5. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Level 1 Autism
Building social competencies in children with Level 1 Autism is a critical aspect of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. This process often involves teaching specific social skills, such as maintaining eye contact, reciprocating in conversations, and understanding nonverbal cues. Evidence-based techniques such as role-playing and social stories are powerful tools in this endeavor, providing tangible examples and opportunities for children to practice their skills.
The importance of fostering interaction with peers cannot be overstated, as it offers invaluable practical experiences for children to apply and refine their social abilities. For example, leveraging freely available social skills resources can be a practical approach. These resources provide engaging and interactive activities, visuals, and support for educators and parents alike, specifically designed for special education teachers, speech-language pathologists, and school counselors. With the goal of nurturing social communication skills, social cognition, behavior, emotions, problem-solving, and perspective-taking, these resources are tailored to the unique learning needs of special education students.
Another effective approach is the Social Thinking framework, a versatile teaching method designed to support individuals with autism spectrum disorder and social communication challenges. This framework aims to enhance the understanding and interpretation of the thoughts, beliefs, intentions, emotions, and actions of others within different contexts. It prepares individuals to understand and respond appropriately to social situations, ultimately achieving social goals and positively impacting academics. The framework includes six social thinking strategies: flexible thinking, whole body listening, size of the problem, expected vs. unexpected behavior, mind files, and social detective skills. These strategies are designed to help individuals with autism develop social skills, improve their ability to take perspective, communicate effectively, and build healthy relationships.
By using these resources and strategies, we can equip children with Level 1 Autism with the tools they need to navigate the social world, enhancing their social skills and boosting their confidence in social situations. ABA therapy, in particular, can foster the development of communication, play, and social interaction skills. Through techniques such as visual supports, social stories, and peer modeling, children can learn to understand and respond appropriately to social situations.
Moreover, teaching children to make eye contact can be achieved through various strategies such as using visual cues, positive reinforcement, and gradually increasing the complexity of eye contact tasks. Similarly, teaching children turn-taking in conversation can be effectively done by providing clear instructions, reinforcing appropriate turn-taking behavior, and providing opportunities for practice in diverse social situations.
Nonverbal cues such as gestures, facial expressions, body language, and eye contact can also be incorporated into therapy sessions to improve social interactions and communication skills. Role-playing can also be an effective method for teaching social skills, allowing children to actively participate and experience different social scenarios, which helps them apply these skills to real-life situations.
Furthermore, encouraging peer interaction can be an effective strategy to improve social skills. By providing opportunities for children to interact with their peers in a structured and supportive environment, they can learn important social skills such as turn-taking, sharing, and initiating conversations. Finally, real-world experiences can be beneficial for practicing social skills, as they allow children to apply the social skills they learn in therapy to real-life situations.
These strategies, when implemented effectively, can significantly support the social development of children with Level 1 Autism.
6. Building a Supportive and Inclusive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
The journey of navigating ABA therapy can be challenging, but a supportive environment can make a significant difference. This supportive environment, a sanctuary for parents, is a place where they can exchange experiences, learn from others, and find comfort in the knowledge that they are not alone. Such an environment fosters unity and understanding, which can be vital in the journey of ABA therapy.
One way to find this supportive environment is by joining ABA therapy support groups. These groups can be found through online directories or platforms that specialize in connecting individuals with resources for autism and ABA therapy. Local autism organizations and healthcare professionals who specialize in autism and ABA therapy can also provide information about support groups in your area.
Another resource to consider is online forums for parents of children in ABA therapy. These platforms provide a space for parents to connect, share experiences, ask questions, and seek advice. The sense of community and understanding in these forums can provide valuable insights and encouragement, reducing feelings of isolation and providing a sense of belonging.
In addition to online forums and support groups, there are comprehensive websites dedicated to ABA educational resources. These websites serve as a beacon for families and therapists alike, offering sections such as a "Family Corner" and "Forum" where parents can interact, share experiences, and provide mutual support. They also provide a wealth of resources, programming ideas, and information that can be immensely helpful in navigating the world of ABA therapy.
Creating a supportive community for parents in ABA therapy can have several benefits. Regular parent support groups, educational resources, open communication, social events, and parent training workshops are some strategies to consider. These elements can foster a sense of community, provide opportunities for parents to build relationships with others who are going through similar experiences, and offer resources to support their child's progress.
Overall, joining a community for parents navigating ABA therapy can provide a supportive network and valuable resources to help you on your journey. With the right resources and community, parents can find the fortitude, insight, and assurance needed to traverse their journey, fostering a sense of unity and understanding, and ultimately empowering them to advocate for their child's needs.
7. Continuous Improvement in ABA Therapy: The Importance of Collaboration and Growth
The journey of employing ABA therapy is a continuous process of evolution and refinement. To ensure the effectiveness of this approach, it is critical to regularly assess and modify strategies based on the child's growth and development. This process is underpinned by a commitment to staying abreast of the latest research and advancements in the field. This can be achieved by regularly seeking out the latest research, attending conferences and workshops, and networking with other professionals in the field. The use of technology and new techniques can also serve to enhance the implementation and outcomes of ABA therapy.
The combined efforts of parents, therapists, and other professionals are invaluable in this journey. Effective collaboration between these parties ensures a comprehensive understanding of the child's needs and development. Parents and therapists can share information, set goals, and develop strategies that are tailored to the unique needs of the child. This collaborative approach allows for a more comprehensive and holistic approach to therapy, ensuring that the child receives consistent support and reinforcement both at home and in therapy sessions.
Parents play a pivotal role in contributing to positive outcomes in ABA therapy. Their active participation can greatly enhance the effectiveness of the treatment. Parents can reinforce and generalize the skills learned in therapy to real-life situations, provide valuable insights and observations about their child's progress, and implement the strategies learned during therapy sessions in their daily interactions with their child.
In the pursuit of an ABA provider, it's essential to be conscious of certain warning signs indicating outdated or potentially harmful practices. An excessive focus on reducing "stimming," teaching sustained eye contact, a rigid view of compliance, recommendation of an extensive number of therapy hours without a clear rationale, the use of food as a primary reinforcer, and a refusal to collaborate with other providers, all serve as red flags.
Additionally, the issue of burnout in the field of ABA needs to be addressed. Factors such as age, workplace conflict, lack of support, and prolonged job-related stress contribute to burnout. Implementing strategies to prevent and manage burnout is crucial. These strategies include self-evaluation, assessing values and alignment with the work environment, and advocating for necessary modifications.
It is paramount to thoroughly research potential ABA providers and ask questions to ensure their practices align with current ethical standards and best practices in the field. The individual needs and preferences of the client should always be the top priority, with the ultimate goal of enhancing their well-being and quality of life.
Conclusion
Navigating ABA therapy for children with Level 1 Autism can be a complex and challenging journey. It requires understanding the key characteristics of Level 1 Autism, the role of parents as advocates, strategies for managing challenging behaviors, accessing support services, enhancing social skills development, building a supportive community, and continuously improving ABA therapy.
From understanding the unique challenges to implementing effective strategies, this article offers a comprehensive overview of the various aspects involved in supporting children with Level 1 Autism through ABA therapy. By embracing these strategies and collaborating with professionals, parents can create a supportive and inclusive environment that nurtures their child's social development and overall well-being.
The main points discussed in this article include: - Understanding the characteristics of Level 1 Autism and the role of parents as advocates. - Strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism. - Navigating support services for children with Level 1 Autism. - Enhancing social skills development in children with Level 1 Autism. - Building a supportive and inclusive community for parents navigating ABA therapy. - The importance of continuous improvement in ABA therapy through collaboration and growth.
The broader significance of this topic is that it provides valuable insights and guidance for parents and caregivers in supporting their children with Level 1 Autism. It emphasizes the importance of understanding their child's unique needs, advocating for appropriate support services, implementing effective strategies to manage challenging behaviors, promoting social skills development, and creating a supportive community.
In conclusion, by embracing these strategies and collaborating with professionals, parents can create a nurturing environment that supports their child's social development and overall well-being. By continuously improving ABA therapy through collaboration and growth, parents can ensure that their child receives the best possible care. Start now to create a supportive environment for your child's journey through ABA therapy.




