Introduction
Understanding Level 1 Autism is crucial for providing the necessary support to children with this diagnosis. These children possess unique capabilities and face distinct challenges in social interactions and communication. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the need for structured environments and remote learning support. Empathy, understanding, and effective strategies are key to helping these children thrive.
In this article, we will explore practical strategies for supporting children with Level 1 Autism, such as empathizing with the child, seeking assistance from a supportive network, and creating comprehensive plans for events. We will also discuss the role of ABA therapy in enhancing social skills and effective communication techniques in ABA therapy for Level 1 Autism. Additionally, we will explore strategies for managing challenging behaviors and navigating support services in ABA therapy. Finally, we will highlight the importance of building a collaborative and growth-oriented community in the ABA therapy industry.
By providing parents and professionals with the necessary resources and support, we aim to empower them to unlock the full potential of children with Level 1 Autism. Our goal is to create a more inclusive and understanding society that supports the unique contributions of individuals with autism.
1. Understanding Level 1 Autism: The Need for Support
"Children with Level 1 Autism, often recognized as high-functioning autism, possess a unique set of capabilities and face distinct challenges. While social interactions and communication might be daunting for them, they are also gifted with remarkable talents. The key to supporting these children lies in understanding their needs and providing them with suitable resources and strategies that can help them thrive.
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced new obstacles for families dealing with autism, emphasizing the need for a structured and predictable environment, especially for children involved in remote learning. The affection and acceptance from siblings can significantly impact these children's lives. This period has also shed light on the difficulties that special educators encounter in their efforts to assist these families. As we adapt to this new reality, it is crucial to foster an inclusive and understanding environment for individuals with autism and acknowledge their unique contributions to our society.
Understanding the child's perspective and showing empathy are vital when formulating strategies to prepare children with autism for various events and experiences.

Here are some considerations:
- Empathize with your child: Endeavor to see the world from your child's viewpoint. Recognize their behavior as a reaction to overwhelming or unsettling situations. Predict their responses and equip them with preventive measures and compensatory strategies.
- Seek assistance: Build a supportive network of allies who are sensitive to your child's needs. This network could include professionals from the school system, hospitals, private businesses, and airlines who can provide suitable accommodations.
- Draft a plan: Develop a comprehensive list of steps and experiences involved in the event. Predict obstacles, consider the interactions your child might have with unfamiliar people, and pay attention to sensory stimuli and materials that your child will encounter.
- Use social stories: Create short homemade books or slideshows that outline the steps involved in a process. These stories can help your child visualize the event and prepare for it.
- Desensitization and habituation: Gradually introduce tools and sensory experiences associated with the event to alleviate discomfort. Slowly build up to the complete experience to desensitize the child and make the steps routine.
- Normalize the setting: Instead of avoiding challenging locations, seek ways to make them more comfortable. Arrange visits to the location, introduce the child to staff, and use materials like earbuds or masks to block noise or smells.
These insights into the experiences of individuals with autism and the practical strategies provided can equip caregivers to prepare their children for various events. As we express gratitude for the progress made in the field of autism awareness and acceptance, we continue to strive for more inclusive and understanding approaches to support these unique individuals.
There are several effective strategies for supporting children with high-functioning autism.
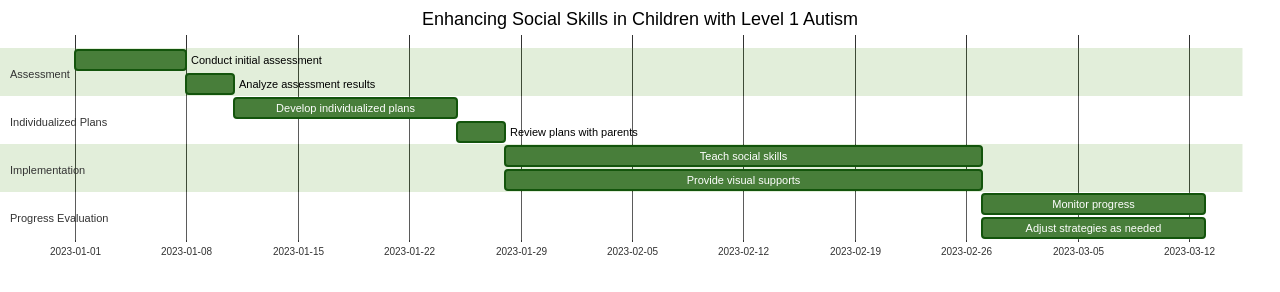
These strategies can help enhance their social skills and promote overall development. Using visual supports like visual schedules and social stories can support their understanding and participation in social situations. Similarly, providing opportunities for social interaction and teaching them social skills through modeling and explicit instruction can greatly benefit these children. It is important to tailor these strategies to the individual needs and preferences of each child, as autism is a spectrum disorder and communication abilities can vary significantly.
There are also various resources available that can help enhance social skills in children with Level 1 Autism. These resources offer strategies and key terms that promote social skills, fostering the development of these skills in children with autism. Exploring and utilizing these resources can provide much-needed support for these children's development.
By focusing on strategies such as visual supports, social stories, and social scripts, children with Level 1 Autism can improve their ability to communicate and interact with others. Incorporating the use of visual schedules and structured routines can help provide a predictable and organized environment, which can further support their communication development.
To enhance social skills development in children with Level 1 Autism, it's necessary to create a supportive and inclusive environment where children feel safe and comfortable to practice and learn social skills. Some effective strategies may include social stories, role-playing, peer modeling, and social skills groups. Teaching and reinforcing appropriate social behaviors, such as turn-taking, active listening, and empathy, can also contribute to the development of social skills in these children.
Supporting the unique challenges of high-functioning autism requires a comprehensive understanding of the individual's strengths and weaknesses. It involves creating an environment that promotes independence and enhances their social, communication, and organizational skills.
Providing access to specialized therapies and interventions tailored to their specific needs can greatly support their development and overall well-being."
2. Role of ABA Therapy in Enhancing Social Skills
"Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has proven to be an essential resource in cultivating the social abilities of children diagnosed with Level 1 Autism. This therapy, rooted in empirical evidence, is aimed at enriching certain behaviors, inclusive of social interaction, communication, academic competencies, and adaptive learning skills such as punctuality, job proficiency, domestic capabilities, grooming, hygiene, and fine motor dexterity. ABA therapy proves instrumental in aiding children with Level 1 Autism to better apprehend and react to social cues, thereby enhancing their interpersonal exchanges.
A fundamental aspect to the success of ABA therapy in nurturing social skills is the application of visual aids. These visual supports can assist children in understanding and mastering crucial social behaviors such as sharing, taking turns, and managing their voice volume. Practical resources such as choice wheel templates, listening posters, voice level charts, and conversation starters can prove to be invaluable tools in this process. These visual aids also extend to honing phone skills, like answering a call or initiating a video call, thereby widening the child's communication capabilities.
To further reinforce the importance of social skills development, an occupational therapist emphasizes the role of play, understanding non-verbal cues, using visual boundaries, planning low motor activities, directing attention to other children, and participating in social skills groups. These strategies, while advantageous for children with sensory processing disorder (SPD), are equally applicable and effective for children with Level 1 Autism. The meaningful relationships fostered within these social groups can leave a profound influence on the children, contributing positively to their social growth. The role of occupational therapy, in conjunction with ABA therapy, can have a significant impact on a child's social development journey.
In enhancing social skills in children with autism, effective strategies can include the use of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. ABA therapy focuses on breaking down social skills into smaller, manageable steps and teaching them systematically. This can involve using visual supports, role-playing, and providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors. Additionally, incorporating social stories and social scripts can help children with level 1 autism understand and practice appropriate social behaviors in various situations.
ABA therapy, also known as Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is a widely used intervention for children with autism. It focuses on improving various skills, including academic skills, in individuals with autism. By using specific techniques and strategies, ABA therapy aims to teach new skills and decrease challenging behaviors.
Adaptive learning skills development through ABA therapy can be a beneficial approach for children with level 1 autism. It focuses on providing individualized instruction and support based on the child's specific needs and abilities. ABA therapy uses evidence-based techniques to teach various skills, such as communication, social interaction, self-help, and academic skills. By tailoring the therapy to the child's strengths and weaknesses, ABA can help children with level 1 autism develop adaptive skills that will enhance their overall functioning and independence.
There are several strategies that can be used to improve fine motor dexterity in ABA therapy for children with level 1 autism. These strategies often involve activities and exercises that target specific hand and finger movements, such as using tweezers to pick up small objects, stringing beads, or practicing handwriting skills.
ABA therapy, also known as Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is a widely used intervention for children with autism. It focuses on teaching various skills, including hygiene and grooming skills. These skills are important for promoting independence and self-care in children with autism. By utilizing ABA techniques and strategies, therapists can help children with level 1 autism develop and improve their hygiene and grooming skills.
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is an evidence-based treatment approach commonly used for children with autism. It focuses on improving various skills, including punctuality. There are several techniques that can be used to improve punctuality in ABA therapy for children with level 1 autism.
One possible strategy for job competence development in ABA therapy for children with Level 1 autism is to focus on social skills development. By teaching children with Level 1 autism effective strategies for social skills development, they can improve their ability to interact with others in a work setting.
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is commonly used to help children with autism develop various skills, including understanding social cues. ABA therapy focuses on breaking down skills into smaller steps and using positive reinforcement to teach and reinforce desired behaviors. By using this approach, children with level 1 autism can learn to recognize and understand social cues, such as facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice, which can greatly enhance their social skills and interactions with others."
3. Effective Communication Techniques in ABA Therapy for Level 1 Autism
"Communication is a foundational element in ABA therapy for children diagnosed with Level 1 Autism. The use of clear and precise language, visual aids, and role-playing techniques can notably enhance the understanding and expression of thoughts and feelings in these children. The incorporation of social stories and scripts into the communication strategy can help these children navigate social situations and empathize with others' perspectives more effectively.
There are six practical strategies that can be utilized to enhance communication with children with autism. It's important to remember that the responsibility of effective communication doesn't rest solely on the child with autism. Instead, everyone involved can play a critical role in preventing miscommunications and misunderstandings. This understanding is based on insights from autistic individuals and the collective experiences of families within the autism community.
Moreover, acknowledging the inherent differences in how the brains of children with autism process communication is crucial. Rather than focusing on these differences, tuning into the child's shared feelings and respecting their need for a structured daily routine is more beneficial. Consistent routines and providing choices can alleviate anxiety and foster improved communication.
In addition, using simplified language and engaging in activities the child enjoys, such as scripting from books or shows, can make communication more enjoyable and engaging. Presuming competence in children with autism and offering them patience and choices can strengthen their problem-solving skills and self-esteem.
These strategies not only facilitate more effective communication with children with autism, but also serve to strengthen the bond between them and their caregivers or parents. By employing these techniques, we can create an environment that is more understanding, compassionate, and inclusive for children with Level 1 Autism.
ABA therapy techniques are specifically designed to improve communication skills in children with Level 1 autism.
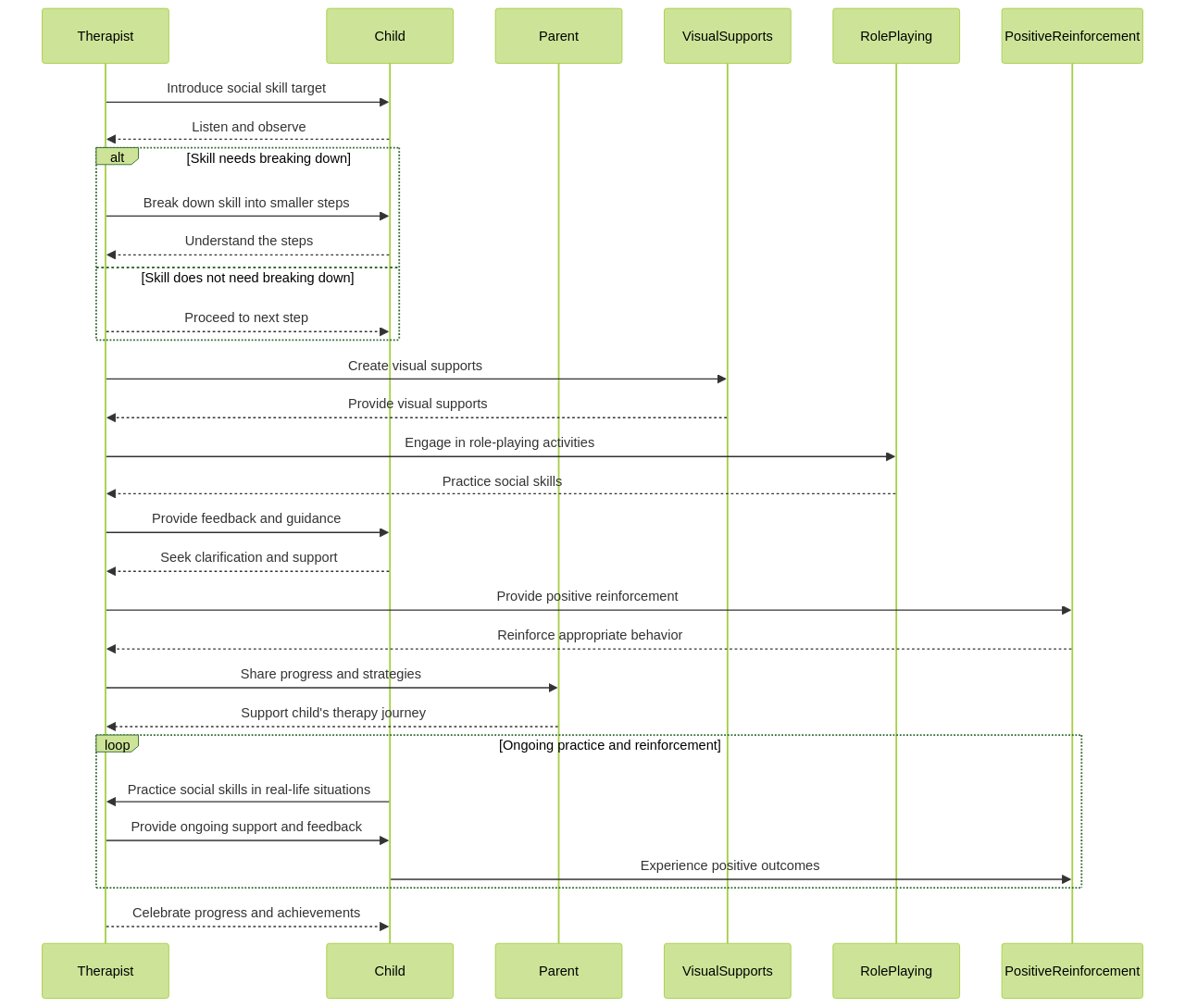
These techniques focus on teaching specific communication skills such as requesting, labeling, and responding to others.
Through structured interventions and reinforcement, ABA therapy aims to increase communication abilities and reduce communication challenges in children with autism.
When working with children with Level 1 autism in ABA therapy, it is important to use strategies that promote clear and concise language. ABA therapists often employ techniques such as visual supports, social scripts, and visual schedules to aid in providing clear and concise instructions and prompts. These strategies help children with Level 1 autism better comprehend and respond to therapy activities and interventions.
Visual aids such as pictures, symbols, or visual schedules can help children with autism understand and process information more easily. These visual supports can be used to teach and reinforce communication skills such as requesting, labeling, and following instructions. By providing visual cues and prompts, visual aids can help children with autism better understand and express their needs and preferences, ultimately enhancing their communication skills.
Social stories are short narratives that describe social situations and appropriate behaviors, helping children with autism understand and navigate social interactions. These stories are created based on the individual needs and goals of each child and are often used to teach social skills and promote social interactions.
Social scripts are pre-written scripts or stories that provide individuals with autism a structured way to communicate and interact in social situations. By using social scripts, children with Level 1 autism can learn appropriate social behaviors, understand social expectations, and practice effective communication skills. This can help them feel more comfortable and confident in social settings, and improve their ability to initiate and maintain conversations with others.
ABA therapy, also known as Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, can be effective in promoting perspective-taking skills in children with Level 1 autism. This therapy focuses on teaching individuals to understand and interpret the thoughts, feelings, and perspectives of others. By using structured and systematic interventions, ABA therapy can help children with Level 1 autism develop social and communication skills, including perspective-taking abilities."
4. Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Level 1 Autism
"Addressing the behavioral complexities associated with Level 1 Autism in children demands a mix of empathy, patience, and targeted strategies.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy offers a comprehensive framework to understand and address these behaviors, arming parents and caregivers with the necessary tools to manage them effectively.
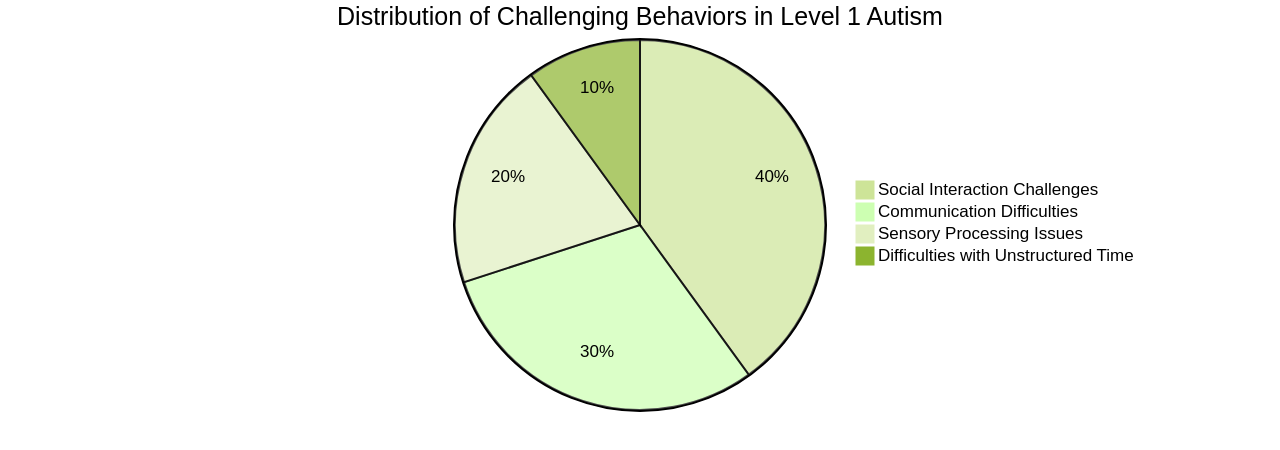
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often face numerous behavioral challenges. It's crucial to keep in mind that these are not intentional, but rather indicative of underlying struggles with communication, social interaction, and sensory processing. Communication issues can appear as challenges with expressive language or interpreting non-verbal cues, potentially leading to frustration and problematic behaviors.
Social difficulties extend beyond communication, encompassing issues in understanding others' perspectives and adhering to social norms. This can result in feelings of social isolation and instances of bullying. Furthermore, children with ASD might find it difficult to handle unstructured time and routine alterations due to difficulties in sequencing activities.
Sensory processing issues are another critical aspect, which can cause children to become overwhelmed by sensory inputs such as loud noises or touch, leading to strong reactions or concentration difficulties. It's vital to understand that these behaviors often serve a purpose for the child, such as a means to communicate or fulfill a specific function.
Managing these behavioral challenges involves a multi-pronged approach. Keeping a behavior diary to identify triggers, introducing changes gradually, employing visual aids, crafting social stories, and imparting relaxation techniques are some of the strategies that can be beneficial. As one article quote emphasizes: "Understanding causes and root causes of behavioral difficulties generally follows difficulties in communication. Children with ASD typically struggle with expressive language and understanding, said picking up non-verbal communication cues, understandably become quite frustrating and provoke problem behaviors."
Consistency in approach and availing supportive therapies can assist children with ASD in managing their frustration and learning new behaviors. In more complex situations, or when informal support proves insufficient, seeking professional help from a psychologist or psychiatrist is advisable.
Moreover, ensuring safety at home is of the utmost importance. This can be achieved by modifying the environment, creating a safe space for de-escalation, and using protective equipment. It's also crucial to formulate a safety plan and involve all family members to manage a behavioral crisis effectively.
In essence, dealing with the behavioral difficulties of children with Level 1 Autism is an ongoing journey. It necessitates patience, understanding, the right strategies, and the support of ABA therapy. ABA therapy, which focuses on understanding and modifying behaviors using techniques such as positive reinforcement, prompting, and shaping, can be effective in teaching and reinforcing appropriate behaviors while reducing challenging ones.
It's important to establish a structured routine, use visual supports like schedules, visual cues, and social stories, provide clear and consistent instructions, and use positive reinforcement. Teaching children with Level 1 autism alternative ways to cope with challenging situations can also be beneficial.
Remember, every child with Level 1 autism is unique, so it's important to tailor strategies to their individual needs and strengths. Working closely with a healthcare professional or therapist who specializes in autism to develop an individualized plan is crucial.
Through these methods, we can create a consistent and predictable environment, reducing anxiety and confusion in children with Level 1 autism. These strategies help children better understand and navigate their environment, leading to a reduction in anxiety and confusion. Furthermore, ABA therapy can help children develop social skills and improve their ability to communicate, further reducing anxiety and confusion in social situations.
The journey of dealing with behavioral difficulties in children with Level 1 Autism is ongoing and requires patience, understanding, the correct strategies, and the support of ABA therapy."
5. Navigating Support Services for Parents and Professionals in ABA Therapy
Navigating the complexities of Level 1 Autism can be both challenging and rewarding. A shining source of support and guidance in this journey is ASD Media. This platform serves as a reliable fountain of industry insights, effective strategies to conquer obstacles, and a nurturing community where individuals can share experiences and learn from one another.
Understanding the apprehensions parents often face when trying to find the right Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy facility for their children, ASD Media equips parents with a set of questions to ask potential ABA facilities. These questions cover a broad range of topics, from preventing meltdowns and handling food-related issues to parent training requirements and staff qualifications.
A frequent contributor to ASD Media, Cassie Hauschildt, an advocate for autistic children and a mother to an autistic son, shares her personal experiences, providing support to parents navigating similar pathways.
ASD Media also bravely addresses controversial topics, understanding that ABA therapy can be a double-edged sword. While it can help reduce self-injurious behaviors and enhance communication skills, it can also be perceived as abusive and traumatizing for autistic individuals. The platform emphasizes the importance of harm reduction and trauma-informed approaches in ABA therapy, particularly for BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, and People of Color) families who often face systemic racism and ableism.
ASD Media's resources, accessible via their website, provide valuable support for individuals with Level 1 Autism and their families. Strategies to enhance social skills and promote communication and interaction, such as visual supports, structured routines, social stories, and social skills training, are among the resources available. Tailoring these strategies to each child's needs and strengths, as well as providing a supportive and inclusive environment, is a key focus. Collaboration with professionals such as therapists and educators can also be beneficial in developing effective strategies.
Subscribing to the ASD Media newsletter allows individuals to stay updated on these crucial discussions, gain unlimited digital access to a wealth of resources, and join a community that advocates for nuance and understanding in the conversation around ABA therapy. The newsletter may include articles, tips, and strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism, as well as a glossary of key terms for promoting social skills in children with autism. This subscription can be a valuable tool for individuals at Level 1 Autism, offering informative content and resources to support their needs. By leveraging the resources available on ASD Media's platform, parents, caregivers, and educators can access effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism, contributing to positive outcomes in their development.
6. Building a Collaborative and Growth-Oriented Community in ABA Therapy Industry
Building a collaborative and growth-oriented community is paramount to enhancing the quality of care and outcomes in the Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy sector. This can be achieved by providing necessary resources and support to parents and professionals, thereby empowering them to unlock the full potential of children with Level 1 Autism.
Recognizing "green flags" in ABA providers is a key aspect of this commitment. These indicators of ethical and effective practices serve as a guide for parents and professionals in selecting an ABA provider that best suits the child's needs. Such green flags include individualization of therapy plans, respect for the child's assent and withdrawal, balanced Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) caseloads, prioritizing parent training and support, naturalistic teaching strategies, and BCBA-owned agencies.
However, these indicators are not exhaustive. They primarily highlight essential aspects of ethical and effective practices in ABA. To further cultivate a collaborative and growth-oriented community, regular networking events, online forums, and support groups can be beneficial. These platforms provide opportunities for ABA therapists to share experiences, exchange ideas, and seek advice. Moreover, joint research projects, workshops, and training sessions can foster a spirit of teamwork among ABA therapy practitioners.
Professionals in the ABA field often face challenges such as burnout, largely due to factors like large caseloads, lack of support or supervision, personal feelings of ineffectiveness, and lack of control over job duties. Addressing this requires a supportive work environment and realistic job expectations - antecedent strategies that can help prevent burnout.
Furthermore, consequent strategies like self-evaluation, assessing personal values, and advocating for necessary modifications in the work environment are also crucial in managing and overcoming burnout. While the journey to overcoming burnout can be challenging, with support and proactive measures, it is certainly achievable.
In addition to fostering collaboration, it's important to establish regular communication channels among professionals. Regular meetings, conferences, and online forums where practitioners can share experiences, exchange ideas, and collaborate on research and best practices can enhance the sense of community. Partnerships and collaborations with other related industries, such as healthcare or education, can also foster collaboration and create opportunities for interdisciplinary approaches to ABA therapy.
Promoting a growth-oriented community in ABA therapy involves following certain best practices. These include promoting collaboration and communication among therapists, caregivers, and clients, encouraging ongoing professional development and training for therapists, providing a supportive and inclusive environment for clients and their families, and regularly evaluating and adapting treatment plans based on individual client needs and progress.
In essence, the continuous improvement and positive outcomes in ABA therapy are heavily reliant on building a collaborative and growth-oriented community. By fostering such an environment, we ensure that both parents and professionals are empowered to unlock the full potential of children with Level 1 Autism.
7. Empowering Parents and Professionals: Unlocking the Potential of Children with Level 1 Autism
"In our pursuit to uplift parents and professionals working with children diagnosed with Level 1 Autism, we aim to equip them with effective strategies that can help manage challenging behaviors, guide them towards accessing the right support services, and enhance social skills development. These strategies encompass behavior modification techniques, visual supports, social stories, and structured routines, all designed to meet the unique needs of every child. Our ultimate objective is to unlock the inherent potential of these children, fostering their growth and enabling them to lead fulfilling lives.
Parallel to our initiative, Practicewise, an organization dedicated to improving children's lives, provides evidence-informed tools and resources for mental health practitioners. Their services extend across various sectors, including hospitals, mental health centers, government agencies, private practices, child welfare, higher education, and the public school system. Their primary goal aligns with ours - to address common youth mental health problems and enhance outcomes through the use of evidence-based interventions.
Practicewise utilizes a modular approach to therapy for children, known as the "Modular Approach to Therapy for Children" (MATCH). This approach enables practitioners to tailor interventions to suit the specific needs of each child. Fundamental tools in this approach include clinical dashboards, the Practitioner's Workbench (PWEBs) database, and practitioner guides.
In addition to these tools, Practicewise offers resources such as books, guides, courses, and webinars to assist practitioners in managing and adapting their practice. They underscore the significance of tracking and measuring treatment outcomes to gauge effectiveness. To broaden their impact, they have initiated a telehealth practice, concentrating on the right clients for online mental health services. They recently welcomed a new CEO, Heather Brennan, and made their presence known at the APA Convention and Florida Behavioral Health Conference.
Practicewise's mission statement, "Practicewise is focused on improving children's lives by putting evidence-informed tools and resources into practice," strongly aligns with our commitment to empowering parents and professionals to unlock the potential of children with Level 1 Autism. As we endeavor to provide the right support and resources, we draw inspiration from organizations like Practicewise, who bridge the gap between research and practice to ensure the best outcomes for children.
In the same spirit, ASD Media, an online platform dedicated to autism-related news and information, offers insights and resources to support parents and professionals. Their articles and educational materials, accessible through their website, provide valuable guidance on managing challenging behaviors and promoting social skills in children with Level 1 autism. By empowering parents and professionals, ASD Media contributes significantly to improving the lives of children with Level 1 Autism."
Conclusion
Understanding Level 1 Autism is crucial for providing the necessary support to children with this diagnosis. These children possess unique capabilities and face distinct challenges in social interactions and communication. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the need for structured environments and remote learning support. Empathy, understanding, and effective strategies are key to helping these children thrive.
In this article, we explored practical strategies for supporting children with Level 1 Autism, such as empathizing with the child, seeking assistance from a supportive network, and creating comprehensive plans for events. We also discussed the role of ABA therapy in enhancing social skills and effective communication techniques in ABA therapy for Level 1 Autism. Additionally, we explored strategies for managing challenging behaviors and navigating support services in ABA therapy. Finally, we highlighted the importance of building a collaborative and growth-oriented community in the ABA therapy industry.
By providing parents and professionals with the necessary resources and support, we aim to empower them to unlock the full potential of children with Level 1 Autism. Our goal is to create a more inclusive and understanding society that supports the unique contributions of individuals with autism.
Navigating the complexities of Level 1 Autism can be challenging, but platforms like ASD Media provide valuable resources and support for parents and professionals. With insights on green flags in ABA providers, controversial topics surrounding ABA therapy, and strategies for managing challenging behaviors, ASD Media offers guidance to those on this journey.
Building a collaborative community is essential in enhancing the quality of care in ABA therapy. Regular networking events, online forums, and support groups provide opportunities for professionals to share experiences and exchange ideas. Practicewise also contributes to this community by offering evidence-informed tools and resources for mental health practitioners working with children.
Empowering parents and professionals is key to unlocking the potential of children with Level 1 Autism. Through empathy, understanding, effective strategies, collaboration, and access to valuable resources, we can create an inclusive society that supports these unique individuals.
To continue your journey of supporting children with Level 1 Autism, visit ASD Media now!




