Introduction
Children with Level 2 Autism face specific challenges that can significantly impact their everyday activities. Understanding the key characteristics of Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing effective support and intervention strategies. This article explores the traits and obstacles faced by children with Level 2 Autism, as well as strategies for managing challenging behaviors, enhancing social skills development, and navigating support services. By empowering children with Level 2 Autism and creating a supportive community, we can unlock their potential and help them thrive
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: Key Characteristics and Challenges
Children with Level 2 Autism, or moderate autism, often grapple with specific traits and obstacles that can significantly impact their everyday activities. They may face challenges in communication, social interaction, and exhibit repetitive behaviors. Sensory sensitivities are also common, turning routine situations into overwhelming experiences. Recognizing these traits is the first step towards offering effective support and intervention strategies.

Children with these characteristics may find everyday tasks and environments daunting. Difficulty in expressing their needs and feelings due to communication challenges can be a hurdle. Their inclination towards repetitive behaviors and resistance to change can make adaptation to new routines or environments challenging.
Sensory sensitivities can also present hurdles. Over-stimulation from certain sounds, textures, or lights can cause discomfort or distress, making regular environments, like a bustling classroom or a brightly lit supermarket, overwhelming.
However, understanding these key traits is vital. This understanding guides parents and caregivers in providing the support these children need and in selecting effective interventions and strategies to help their child navigate their world more comfortably.
For instance, recognizing that a child struggles with communication can guide parents towards interventions like visual supports, social stories, structured play activities, and speech and language therapy. These interventions can improve their child's communication skills and promote meaningful interactions.
Understanding their child's resistance to change can help parents create structured routines that make their child feel more secure. A structured routine provides predictability and stability. It can be established by creating a daily schedule that includes specific times for waking up, meals, school or therapy sessions, playtime, and bedtime. Visual supports like pictures, symbols, or written schedules can help children with autism understand and follow the routine.
Recognizing their child's sensory sensitivities can guide parents in creating a sensory-friendly environment. Reducing sensory stimuli, providing visual supports, offering structured routines, incorporating sensory activities, and providing sensory breaks can create a more comfortable and supportive environment.
Understanding these key characteristics of Level 2 Autism is the first step towards empowering these children. It forms the foundation for effective support and intervention strategies and guides parents in their journey of supporting their child with autism
2. The Role of Parents in Supporting Children with Level 2 Autism
Fulfilling the roles and responsibilities as parents of children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism can be multifaceted and extensive. Parents often find themselves at the forefront of their child's development, identifying divergences and initiating the process of seeking professional assistance. Once a diagnosis is received, parents become the champions of their child's needs and rights, advocating for their access to necessary support services and resources.
Creating a nurturing and supportive environment at home is a crucial part of this journey.
This involves establishing routines, providing clear and consistent communication, and implementing visual supports. Incorporating sensory breaks into the child's daily schedule can also be beneficial. Collaborating with professionals such as speech therapists or occupational therapists can further assist parents in implementing strategies tailored to the child's needs.
The advocacy role extends beyond the home environment. Parents are encouraged to actively participate in their child's education and treatment planning, collaborating with teachers, therapists, and other professionals to ensure that their child's individual needs are met. By joining support groups and organizations that focus on autism advocacy, parents can gain access to additional knowledge and resources that can assist them in advocating for their child's rights and needs effectively.
In addition to advocacy, parents are tasked with fostering trust and rapport with their child by enhancing social cognizance and communication abilities, understanding and managing emotional regulation, and promoting flexibility. These efforts are critical to the child's development and overall well-being.
Parents are also encouraged to focus on the strengths and positive aspects of autism while addressing any areas of need. This balanced perspective can foster a positive self-image in the child and cultivate a deeper understanding of autism in the wider community.
Creating a supportive home environment that is tailored to the child's specific needs and preferences is crucial. This can involve establishing a structured routine, designating a quiet space for relaxation, using visual supports, providing clear and consistent communication, creating a sensory-friendly environment, and encouraging independence and self-care skills. Consultation with professionals, such as therapists and educators, can provide additional guidance and support in this endeavor.
Parents are also urged to network with other parents and seek support from autism organizations. These connections can provide valuable resources and a sense of community, which can be a source of solace during challenging times.
While the journey of parenting a child with Level 2 Autism can be fraught with challenges, it is also filled with unique opportunities for growth and learning. Through effective advocacy and the application of recommended strategies, parents can play a pivotal role in shaping not only their child's future but also the landscape of autism healthcare
3. Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Level 2 Autism
Addressing the challenging behavior displayed by children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism requires a combination of understanding, patience, and effective methodologies. These methods can span across various strategies, including the use of visual aids for improved communication, establishing consistent routines to reduce anxiety, and implementing sensory strategies to manage sensory sensitivities. The use of positive reinforcement, where desirable behavior is rewarded to encourage repetition, should be a primary focus area.
Visual aids such as images, symbols, or written words can significantly enhance communication by aiding children in expressing their needs and wants. These aids can also provide a better understanding of social situations and facilitate engagement in conversations. However, it's critical to remember that every child is unique, and the effectiveness of these strategies can vary from one child to another due to their distinct characteristics and needs.
Creating a predictable and structured environment aids in establishing consistent routines and reducing anxiety in children. A well-defined daily schedule that includes specific times for activities such as meals, therapy sessions, and playtime can be beneficial. Incorporating calming strategies, like deep breathing exercises or sensory breaks, into the routine can help children manage their anxiety.
Sensory strategies can be highly effective for managing sensory sensitivities. These strategies aim to create a sensory-friendly environment and provide sensory input that is calming and regulating for the child. Techniques such as using weighted blankets or vests for deep pressure, incorporating sensory breaks throughout the day, and providing a quiet retreat space can help children manage their sensory sensitivities better and promote a more comfortable and regulated state.
Positive reinforcement techniques can also play a crucial role in promoting good behavior in children. When it comes to managing challenging behaviors, finding the right strategies that work for each individual child is paramount. These strategies can vary depending on the specific needs and characteristics of the child.
The IRIS Center, funded by a cooperative agreement with the U.S. Department of Education, is an excellent resource offering an array of modules focused on addressing challenging behaviors and other related educational topics. These resources include case studies, evidence-based practice summaries, research annotations, and high-leverage practices. However, while the IRIS Center can be a powerful tool, it's essential to remember that the contents of the website do not necessarily represent the policy of the Department of Education, nor do they imply endorsement by the federal government.
Ultimately, the key lies in utilizing these resources as a guide while tailoring strategies to the specific needs of your child. It is often beneficial to consult with professionals such as therapists or behavior analysts who specialize in working with children with autism. They can provide guidance and develop personalized strategies to address challenging behaviors and promote positive outcomes for the child
4. Navigating Support Services: A Guide for Parents
Navigating the intricate web of support services for children with Level 2 Autism can certainly be a daunting task for parents.
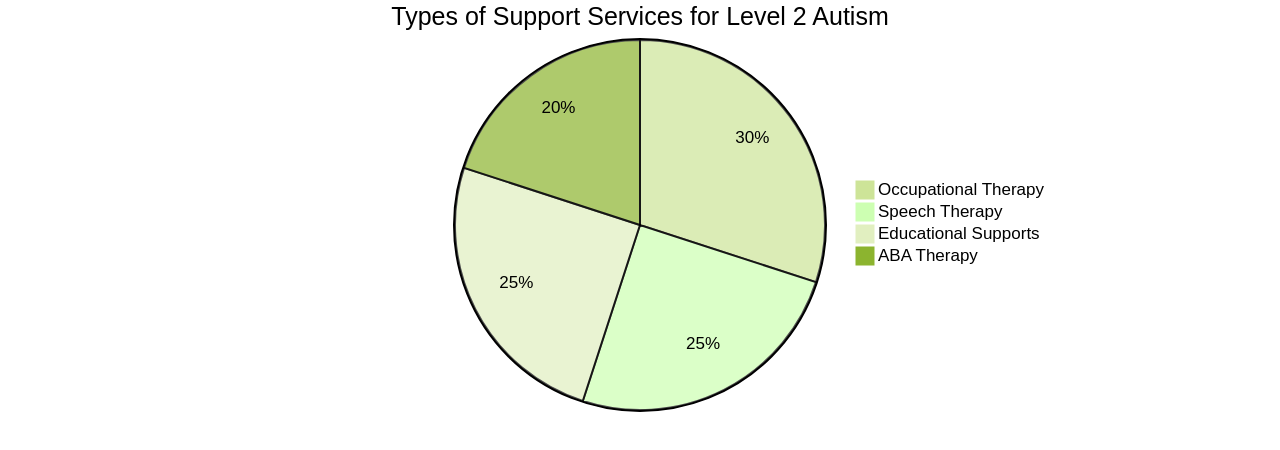
It's fundamental to understand the various services available, like occupational therapy, speech therapy, and ABA therapy, and their role in your child's holistic development.
In the intricate domain of specialized healthcare needs, multiple pathways can lead to success. These include specialized post-secondary experiences, life skills programs, certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities. It's imperative to assess the student's functioning in areas such as independence, academic skills, and adaptive behavior. The availability of supports and accommodations also play a crucial role.
Mastering organizational and time management skills are vital for success in college. Some colleges offer specific autism support programs. For students who require more assistance in adjusting to college expectations, community colleges provide a beneficial stepping stone. Certificate and technical school programs could be more manageable for students struggling with organizational and time management challenges.
For individuals with lower cognitive functioning, post-secondary day and residential programs concentrating on independent living skills, work skills, and social skills could be the best fit. Some might opt for supported or customized work experiences. It's crucial for parents to be realistic, objective, and flexible when choosing the most suitable pathway for their child's success and happiness.
Furthermore, reaching out to local autism organizations and online communities for recommendations and advice can be exceptionally helpful. For example, the Autism Society Oregon (ASO) is a nonprofit organization that serves as a valuable resource for families seeking information and support related to autism. They offer a comprehensive database of supports, workshops, webinars, and social events.
The Oregon Family to Family Health Information Center aids in understanding insurance systems, accessing financial assistance, and identifying emotional supports. The Swindells Resource Center, located at Providence Health Services, offers a lending library, community presentations, and family support services.
Families can also seek support from state and federal agencies like the Office of Developmental Disabilities Services (ODDS) and the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) program. These agencies provide income, medical insurance, and other supports for eligible children and families.
For families with children aged 5 and above, educational supports can be accessed through county Early Intervention (EI) and Early Childhood Special Education (ECSE) programs. These programs offer services for children with developmental differences and prepare them for school.
Social groups and clubs, such as those sponsored by the Autism Society Oregon, provide opportunities for social interaction, shared interests, and making friends. Another resource is Camp Odakoda, a summer camp specifically designed for the autistic community, offering social activities and opportunities for children to connect, share interests, and make friends.
Finally, remember that you're not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you navigate through it
5. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Level 2 Autism
Children with Level 2 Autism often face challenges developing social skills, but with the right strategies and support, they can make significant strides.
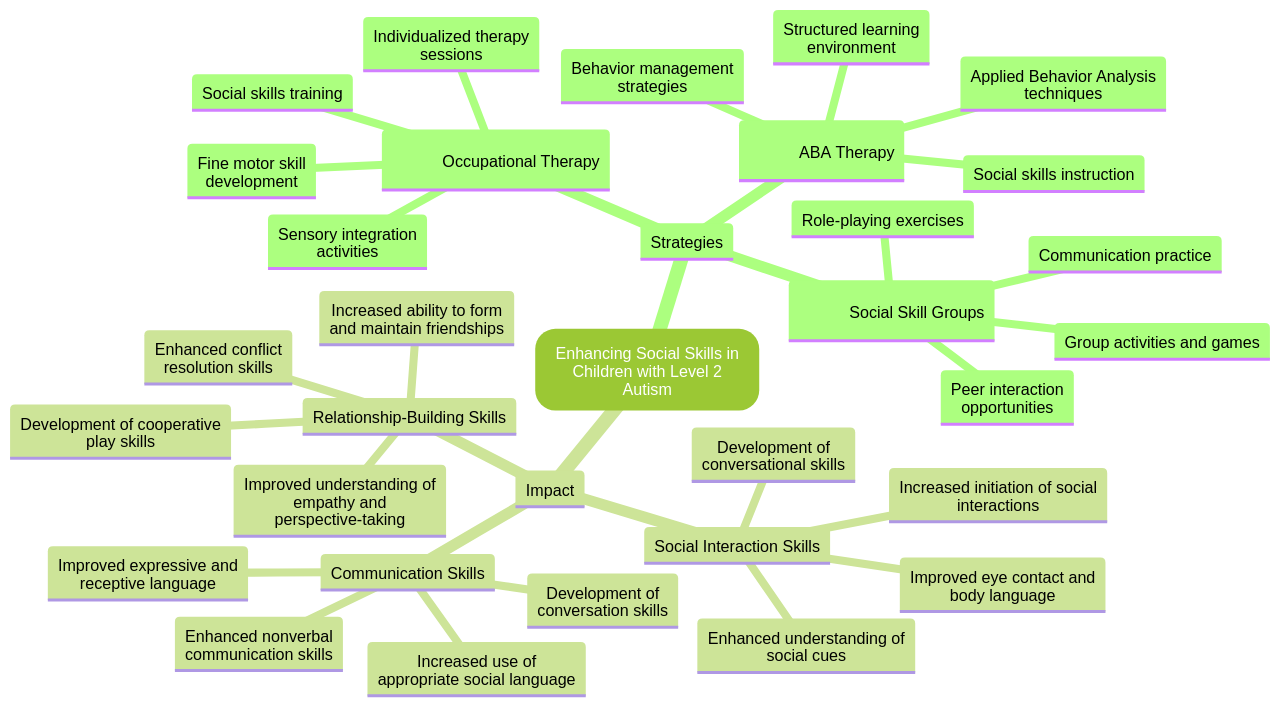
A crucial part of this process involves parents facilitating social interaction opportunities, demonstrating appropriate social behavior, and utilizing social stories to impart social norms.
Occupational therapists and ABA therapists play a pivotal role in this journey. Both these professionals help children enhance their social interaction skills through group activities and structured teachings. ABA, or Applied Behavior Analysis, is a therapeutic approach that focuses on understanding and modifying behavior patterns through positive reinforcement and systematic teaching strategies. It can help children with autism develop and improve their social skills by breaking down complex social interactions into smaller, manageable steps. ABA therapists use techniques such as modeling, role-playing, and social scripts to teach appropriate social behaviors and responses.
Social skill groups provide a nurturing environment where children can find common interests and build on them, fostering stronger connections. These groups focus on improving social interaction, communication, and relationship-building skills in a supportive and structured environment. They allow children with Level 2 autism to develop a better understanding of social cues, improve their ability to initiate and maintain conversations, and learn how to navigate social situations more effectively.
Building social skills in children with SPD involves a multifaceted approach. Key strategies include promoting play, understanding non-verbal communication, employing visual boundaries, organizing low-motor activities, drawing attention to other children, and ensuring regular attendance at social skills groups. This approach is further strengthened by individualizing these strategies based on the specific needs and strengths of each child, as well as to provide ongoing support and reinforcement to ensure continued progress.
Furthermore, the Social Thinking framework can be an invaluable tool for children with autism spectrum disorder and social communication difficulties. This framework enables children to better comprehend and interpret the thoughts, beliefs, intentions, emotions, and actions of others. It offers six strategic areas: flexible thinking, whole body listening, size of the problem, expected vs. unexpected behavior, mind files, and being a social detective. These strategies empower children with autism to cultivate flexible thinking, understand the significance of paying attention to the whole body when listening, distinguish between large and small problems, adhere to social rules, engage in meaningful conversations, and analyze social situations.
Though the journey of social skill development can be gradual, each step forward signifies progress. As parents, it's crucial to remember that every bit of advancement is a victory in itself. By implementing these strategies and seeking professional support, you can contribute significantly to your child's social development. Each small victory in social skills development should be celebrated as it boosts the child's confidence, reinforces their progress, and encourages them to continue working on their social skills
6. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Creating a supportive environment is crucial for parents maneuvering the challenges of raising children with Level 2 Autism. This supportive network, which can be formed through local support groups, online forums, or social media communities, is a beacon of strength. The shared experiences and collective wisdom of these communities offer invaluable insights and remind parents they are not alone.
Engaging with others who are on the same journey can lead to a deeper understanding and discovery of effective strategies from their experiences. The sentiment of a parent, Coffeefirst, resonates with many, "I’ve struggled, especially to see girls her age get on with life and get easier with time." This highlights the importance of a supportive network.
Another parent, Libbyalum, reached out with a supportive message, "I wanted to check in and see how you're getting on and if there's anything else I can do to help." This simple act of reaching out underlines the role of a community as a support system, offering help and resources when needed.
Although there might be no specific data or facts mentioned, the collective wisdom of the community becomes its own form of evidence. The shared experiences, advice, and encouragement from others who are facing similar challenges provide a wealth of knowledge and understanding.
For parents of children with ADHD and autism, the world continues to evolve, but their challenges remain constant. However, the power of a supportive community provides a safe space for parents to express their fears, share their victories, and find comfort in the shared journey.
To connect with other parents of children with Level 2 autism, consider joining online forums or support groups specifically designed for parents of children with autism. These platforms provide a space for parents to share their experiences, seek advice, and connect with others who are going through similar situations.
Learning from other parents of children with Level 2 autism can provide valuable insights and support. They can share tips and experiences that can be helpful in navigating autism support services and enhancing social skills in children with autism. Resources such as articles, tutorials, and digital access to relevant content can also assist in gaining knowledge and guidance from other parents who have faced similar challenges.
Effective strategies for parents of children with Level 2 autism can involve a combination of various approaches. It is important for parents to work closely with professionals, such as therapists and educators, to develop an individualized plan that addresses the specific needs and challenges of their child. Seeking support from support groups or other parents who have similar experiences can be beneficial for sharing resources, advice, and emotional support.
For support and insight, consider visiting reputable websites that specialize in providing resources for autism support. These websites often offer articles, guides, and forums where parents can connect with others facing similar challenges and gain insights from their experiences. Local support groups or organizations dedicated to autism support can provide an invaluable network of individuals who can offer guidance, resources, and a sense of community for parents navigating the unique needs of children with autism
7. Empowering Your Child: Unlocking the Potential of Children with Level 2 Autism
Empowering a child with Level 2 Autism is a multidimensional endeavor that revolves around harnessing their unique strengths, fostering a sense of independence, and creating opportunities for them to thrive. This empowerment process can be achieved by setting realistic goals tailored to their abilities and needs, providing structured choices, and leveraging their interests to enhance their motivation and engagement.
To unlock their potential, it is critical to concentrate on their personal desires and interests. Children with high-functioning autism are most responsive when motivations are intrinsic rather than externally imposed. This responsiveness can be amplified by adjusting the language used, such as replacing the term "homework" with "study" to diminish negative associations and enhance motivation.
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) frequently encounter challenges such as boredom and anxiety, which can impede their motivation and academic performance. To counteract this, it is advantageous to equip them with organizational skills and time management strategies. The use of visual aids and tangible rewards can serve as potent motivators for these children.
Moreover, segmenting tasks into manageable steps and setting achievable goals can prevent feelings of overwhelm and boost motivation. As an eloquent quote from the article puts it, "High-functioning autistic kids respond best when the answer to the question 'What's in it for me?' is something they desire."
Maintaining a positive and supportive relationship with the child is of utmost importance, as the rewards of completing tasks should not overshadow the significance of the parent-child relationship. With the right support and opportunities, your child can indeed reach their full potential. This support can be provided through specialized educational programs, behavioral therapies, and social skills training, all of which can be customized to the child's specific needs and challenges.
Creating a supportive and predictable environment that promotes routine and consistency can greatly benefit their development and well-being. Visual supports, such as schedules and visual cues, can assist children with autism in understanding and navigating their daily activities. Moreover, creating a sensory-friendly environment by minimizing sensory overload and providing sensory breaks can help children with autism feel more comfortable and regulated.
Additionally, using structured choices can be an effective strategy to empower children with level 2 autism. By providing clear and organized options, children with autism can feel more in control of their environment and decisions, which can help reduce anxiety and promote independence.
In conclusion, children with Level 2 Autism can indeed flourish with the right support, opportunities, and environments. By focusing on their strengths, fostering independence, and creating engaging and supportive environments, we can empower them to reach their full potential
Conclusion
Children with Level 2 Autism face specific challenges that can significantly impact their everyday activities. Understanding the key characteristics of Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing effective support and intervention strategies. This article explores the traits and obstacles faced by children with Level 2 Autism, as well as strategies for managing challenging behaviors, enhancing social skills development, and navigating support services. By empowering children with Level 2 Autism and creating a supportive community, we can unlock their potential and help them thrive.
The main points discussed in this article include understanding the key characteristics of Level 2 Autism such as communication challenges, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Strategies for managing challenging behaviors include the use of visual aids, establishing consistent routines, implementing sensory strategies, and utilizing positive reinforcement. Navigating support services involves understanding the available resources such as therapy options and educational programs. Enhancing social skills development can be achieved through occupational therapy, ABA therapy, social skill groups, and utilizing the Social Thinking framework.
The broader significance of this article's topic is that it provides valuable information and guidance to parents and caregivers of children with Level 2 Autism. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing and understanding the unique needs of these children in order to provide effective support and intervention strategies. By implementing these strategies and seeking professional support, parents can play a pivotal role in shaping their child's future.
In conclusion, by empowering children with Level 2 Autism through understanding their needs, implementing effective strategies, and creating a supportive community, we can help unlock their full potential. Let us all work together to create an inclusive society where every child with autism can thrive. Start now by accessing resources at ASD.media to continue your journey of supporting your child with autism




