Introduction
Navigating the challenges of parenting a child with Level 2 Autism can be overwhelming. From understanding the key characteristics and challenges to finding effective support services and developing essential skills, parents need guidance and support. In this article, we will explore various topics related to Level 2 Autism, including understanding the characteristics, strategies for developing executive functioning skills, effective communication techniques, time management tips, building a supportive community, and the importance of continuous learning in ABA therapy. Let's dive in and discover valuable insights and practical advice to support parents in their journey of raising children with Level 2 Autism
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: Key Characteristics and Challenges
Children diagnosed with moderate autism, often referred to as Level 2 Autism, display certain characteristics and encounter specific challenges that can impact their daily routines significantly. They typically need extensive support due to struggles in social situations, communication, and a tendency towards repetitive behaviors.
Understanding these key traits is crucial for providing effective help and devising strategies to boost their executive functioning skills.
One such strategy is executive functioning coaching, a distinct methodology from tutoring. This coaching approach, provided by organizations like Beyond Booksmart, caters to a broad age spectrum, including children with Level 2 Autism.
The executive function coaching approach is research-based and has shown positive results, as seen in client testimonials. This method involves instruction and modeling of these skills, enabling students to achieve greater independence. It's akin to offering a surrogate brain through personalized instruction, guided practice, and visual reminders. Teaching these skills systematically, using real-life contexts, and assisting with working memory overload are also critical components of this approach.
The development of routines, offering repeated opportunities for guided practice, and fostering a supportive and inclusive environment are also stressed. It's about enabling these children to fully express their humanity, creating a safe space for them to communicate their challenges and learn from their mistakes.
Furthermore, resources available through platforms like Beyond Booksmart’s Adult Coaching Client Portal can be very useful. These resources span a wide range of topics, including coping skills for ADHD, improving executive function, parenting a child with ADHD, and developing executive function skills. The availability of a blog, podcast, webinars, and case studies provides a comprehensive support system for those seeking to enhance executive functioning skills in children with Level 2 Autism.
Effective strategies for communication can be implemented to enhance social skills in children with autism. These strategies focus on promoting meaningful interactions and understanding. By using visual aids, such as social stories or visual schedules, children with moderate autism can better comprehend and engage in conversations. Additionally, incorporating visual supports, such as picture cards or communication boards, can assist in expressing needs and wants. Teaching social cues and nonverbal communication through modeling and role-playing can also be effective.
There are effective strategies for managing repetitive behaviors in children with level 2 autism. These strategies can help reduce and redirect repetitive behaviors, allowing children to engage in more functional and meaningful activities. Some common strategies include providing structured routines and schedules, using visual supports and cues, implementing sensory breaks and activities, teaching alternative behaviors, and providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors.
To improve daily life for children with level 2 autism, it's important to focus on enhancing their social skills.
This can be achieved through various strategies, such as providing step-by-step tutorials and effective techniques. By implementing these strategies, children with level 2 autism can develop better social interaction and communication skills, which will ultimately enhance their overall quality of life.
One possible solution for supporting executive functioning skills in children with moderate autism is to provide them with structured routines and visual supports. This can help them understand and follow daily schedules, manage time, and stay organized. Additionally, breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps and providing clear instructions can support their ability to plan and complete tasks. It may also be beneficial to teach and reinforce strategies for problem-solving and decision-making, as these skills are often challenging for individuals with autism
2. The Role of Executive Functioning Skills in Level 2 Autism
Executive functioning skills are a cornerstone for navigating daily life and responsibilities effectively. These cognitive abilities, encompassing planning, organization, impulse control, and time management, are often challenging for children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. However, with tailored strategies and unwavering support, these children can make significant strides in honing their executive functioning abilities, thereby enriching their daily life experiences and unlocking their potential.
Teaching executive functioning skills often involves the gradual release of responsibility approach, a method endorsed by experts like Carol Burmeister and Sheri Wilkins. This approach encourages children to independently learn and apply these skills, fostering greater self-determination and success in both educational and post-educational settings.
To aid learners in building and refining their executive functioning skills, resources such as strategy cards can be utilized. For instance, visual schedules and clear routines can be beneficial in teaching organization and planning. Breaking tasks into smaller steps and offering visual cues or reminders can further assist in this process.
Impulse control, a significant facet of executive functioning skills, can be addressed by implementing strategies to manage impulsive behaviors. Providing clear expectations, setting up structured routines, using visual supports, providing sensory breaks, and teaching self-regulation techniques are some of the strategies that can be employed. Social stories and social skills training can also be beneficial in helping children with autism develop impulse control and appropriate behavior management skills.
Time management, another crucial component of executive functioning skills, can be challenging for children with autism. However, strategies such as visual schedules, timers and alarms, breaking tasks into smaller steps, providing clear and structured instructions, and using visual cues or prompts can aid in improving time management skills. Consistent routines and schedules, as well as positive reinforcement and rewards for completing tasks on time, can also be beneficial.
One noteworthy example of a successful initiative to improve executive functioning skills is the in-school coaching program offered by the Edge Foundation. This program, tailored to each student's unique needs, focuses on addressing executive functioning challenges. A case study involving Giaudrone Middle School, a "turnaround school" in Washington state, showcased the effectiveness of this program. After implementing the Edge Foundation's in-school coaching program, the school saw substantial improvements in the performance of students with executive function impairments, such as ADHD and dyslexia. Their GPAs and behavior improved, and the school's ranking also rose dramatically from the 5th percentile to beyond the 50th percentile within two years. Thus, the program proved to be a game changer, with students matched with specially trained coaches working to enhance their executive function skills, resulting in higher GPAs, improved behavior, and increased graduation rates
3. Practical Strategies for Developing Executive Functioning Skills
Developing executive functioning skills in children with Level 2 Autism necessitates the application of effective strategies that extend beyond traditional methods. These strategies encompass the use of visual aids, structured routines, and task decomposition into manageable steps. Play-based activities that stimulate problem-solving and decision-making abilities are also encouraged.
One of the effective strategies includes breaking tasks into smaller steps, a method that helps children understand and complete tasks more easily. Accompanied by visual aids and clear instructions, this approach can significantly ease the navigation through tasks for children.
Visual aids, such as visual schedules, timers, and checklists, are instrumental in aiding children with autism to better understand routines, manage their time, and complete tasks independently. These aids offer a visual representation of the steps involved in a task or activity, enhancing comprehension and promoting independence. Additional support can be provided through color coding and visual cues, offering clear and consistent visual information.
In terms of structured routines, establishing a predictable and consistent schedule can help children feel secure and reduce anxiety. Visual schedules or cues can provide a clear understanding of the daily routine. Tasks can be broken down into smaller steps with clear instructions. The incorporation of visual supports, such as social stories or visual timers, can promote understanding and facilitate transitions.
In the realm of play-based activities, engaging children in activities that foster their ability to make choices and express preferences can promote decision-making. Visual schedules or choice boards offering clear options allow children to make decisions based on their preferences. Social stories or role-playing activities can teach children how to evaluate different options and make informed decisions. Support and guidance throughout these activities can further enhance their decision-making abilities.
To further emphasize these strategies, a multi-week project provides a robust platform to foster these skills. The project is divided into two distinct units: the teacher passion unit and the carnival unit. The teacher passion unit engages each educator in planning a hands-on activity based on their personal passion. Students are then rotated through these activities, prompting them to reflect on the executive functioning skills utilized.
Subsequently, the carnival unit requires students to design, build, and run carnival games, once again encouraging reflection on the necessary executive functioning skills. These units aim to develop a myriad of executive functioning skills, including but not limited to response inhibition, working memory, emotional control, sustained attention, task initiation, planning and prioritization, organization, time management, goal-directed persistence, flexibility, metacognition, and stress tolerance.
Successful implementation of this project is contingent upon several key elements. These include teacher buy-in, small group size, teacher modeling of metacognition, designated time for meetings, a balance between theory, practice, and fun, intentional reflection tools, and a willingness to revise the program as needed.
Moreover, teaching about executive functioning skills can be integrated into various subjects, such as English language arts and math, creating meaningful experiences for the students. This is significant given that the development of these skills can be achieved even with limited support or resources.
In addition to the project-based approach, there are specialized coaching programs available to help foster these skills. For instance, the Edge Foundation offers programs designed for individuals, schools, and communities, focusing on executive functioning challenges. They employ an evidence-based approach, customized to each student. For instance, Giaudrone Middle School partnered with the Edge Foundation to implement their in-school coaching program, which proved to be instrumental in improving student performance. The school's ranking soared from the 5th percentile to beyond the 50th percentile within two years.
The implementation of such programs has a profound impact, resulting in higher GPAs, improved behavior, and increased graduation rates. Thus, the nurturing of executive functioning skills in children with Level 2 Autism can be achieved through a combination of practical strategies, meaningful projects, and specialized coaching programs. Throughout this journey, it's crucial to remember that consistency and patience are integral to the process
4. Navigating Support Services for Level 2 Autism and ADHD
Embarking on the journey to understand and utilize the range of support services available for Level 2 Autism and ADHD can often feel like navigating a complex labyrinth. However, once you gain a deeper understanding of the resources at your disposal, this journey can bring about a transformative difference. These resources span from specialized educational programs to therapy services and community support groups.
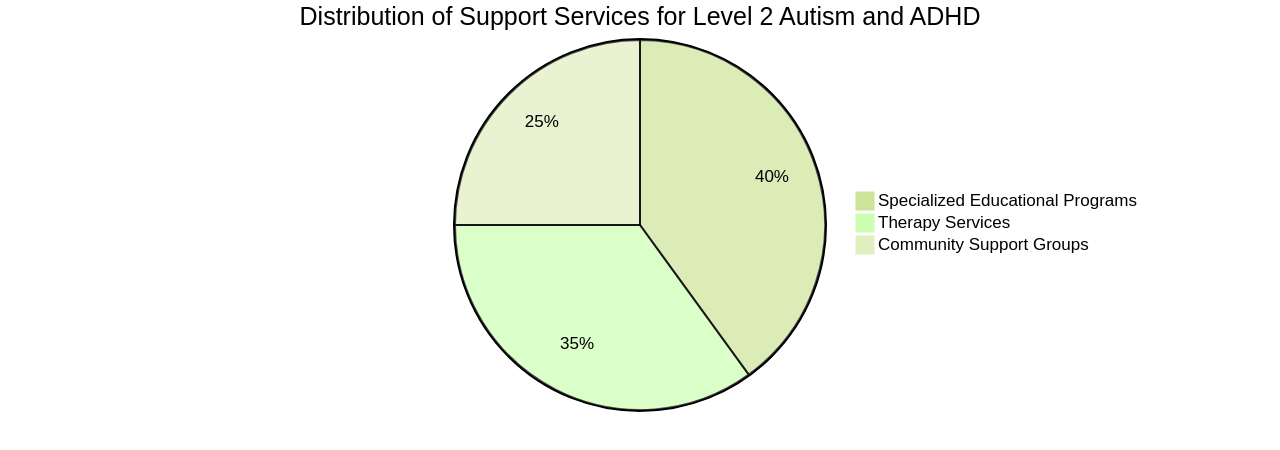
Individuals with Level 2 Autism, often referred to as high support needs autism, face unique challenges, including developmental delays, communication difficulties, sensory processing issues, and cognitive rigidity. These complexities highlight the importance of access to appropriate support services. It's through shared experiences that we can gain a deeper understanding of the reality of high support needs autism, crucial in identifying the most suitable services for your child.
Planning for the future of a child with high support needs autism or ADHD can be particularly challenging. It's a journey that requires a well-thought-out plan, especially when considering post-high school options. The lack of knowledge and support from school personnel can often compound these challenges. Therefore, it is vital to initiate the process of creating a concrete transition plan as part of your child's Individualized Education Program (IEP) as early as possible.

Families and schools should collaborate to develop a post-graduation plan starting at age 14. This plan could include exploring various options such as 18-21 programs, private transition programs, community colleges with support, and four-year colleges with robust autism support systems. However, it's important to acknowledge the financial challenges that may arise in accessing these options. Thus, the call for more accessible information and support for parents of children with Level 2 Autism and ADHD is louder than ever.
As you begin this journey, it's essential to consult professionals in the field. Reputable organizations, clinics, and healthcare professionals can provide recommendations and referrals to appropriate therapy services. These services may include behavioral therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. In addition, local autism and ADHD organizations often provide resources and information about community support groups catering to individuals with Level 2 Autism and ADHD.
When seeking support services, it's important to ask the right questions to ensure that the services meet the specific needs of individuals with these conditions. Questions about the specific services offered, how services are tailored to meet unique needs, staff qualifications, collaboration with other professionals, strategies used, family involvement, assessment processes, and additional resources can provide valuable information.
Choosing the most suitable services requires considering the specific needs and requirements of the individual. Level 2 Autism and ADHD can vary in severity and symptoms, so it's crucial to find services that address these specific challenges. Consulting with professionals in the field who can provide guidance and recommendations based on their expertise and experience is beneficial.
Understanding the landscape of support services for Level 2 Autism and ADHD can help individuals and families better navigate and access the resources they need.
Researching and connecting with organizations, professionals, and support groups that specialize in providing assistance for individuals with Level 2 Autism and ADHD is essential. Staying informed about the latest research, treatments, and advancements in the field can also be helpful.
Accessing support services can sometimes be challenging. However, various strategies and resources can overcome these challenges. Reach out to local autism and ADHD support organizations, use online resources such as forums and support groups, and consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in autism and ADHD. They can provide recommendations for specific services and interventions that can address the unique needs of individuals with Level 2 Autism and ADHD.
Remember, the road to discovering and understanding these support services starts with research. Your dedication and commitment to finding the best-suited services for your child will be the guiding light in this journey
5. Effective Communication Techniques for Parent Advocates
Navigating the role of a parent advocate necessitates exemplary communication skills. The art of communication in this context is multifaceted, demanding active listening to grasp the distinct needs of each child, expressing empathy, and providing unambiguous and succinct information. The act of communication extends beyond this, necessitating the establishment of open communication channels with professionals involved in the child's life to ensure a unified approach towards shared goals.
A solid rapport with parents is fundamental from the get-go, as it shapes the future relationship. A proactive approach, such as weekly outreach to parents through mass communication, can convey a sense of care and consistency. Moreover, making an effort to connect with individual parents monthly to share positive observations about their child can be a powerful trust-building strategy, fostering a more personal relationship.
Maintaining a healthy balance is vital. Clear boundaries with parents must be set and adhered to for a sustainable work-life balance. These strategies not only improve relationships with parents but also free up time for other responsibilities.
When communicating with children, the approach changes. The key lies in fostering a strong parent-child relationship, which can lead to greater cooperation and feelings of self-worth in the child. This can be achieved through various methods, such as using "door opener" statements to encourage children to express their thoughts and feelings, engaging in two-way conversations instead of merely giving instructions, and using "I statements" to communicate the impact of the child's behavior.
Additional strategies include making clear and specific requests, ensuring you have the child's attention, and providing a reason for the request. It's equally important to avoid using unkind words, ridicule, or shame as these can damage the relationship. Instead, opt for kind words to foster a positive relationship and better communication with the child.
The cornerstone of good communication with children is laying the foundation for them to communicate effectively with others as they grow into adults. As a parent advocate, these communication strategies can be invaluable tools in your journey of providing support and guidance to parents and children alike.
The role of a parent advocate requires effective communication strategies that convey messages clearly and persuasively. Active listening, clear and concise language, empathy, maintaining a calm and respectful tone, and providing evidence-based information to support arguments are all crucial tools. Tailoring communication style to the specific audience and preparing to answer questions and address concerns can also be beneficial.
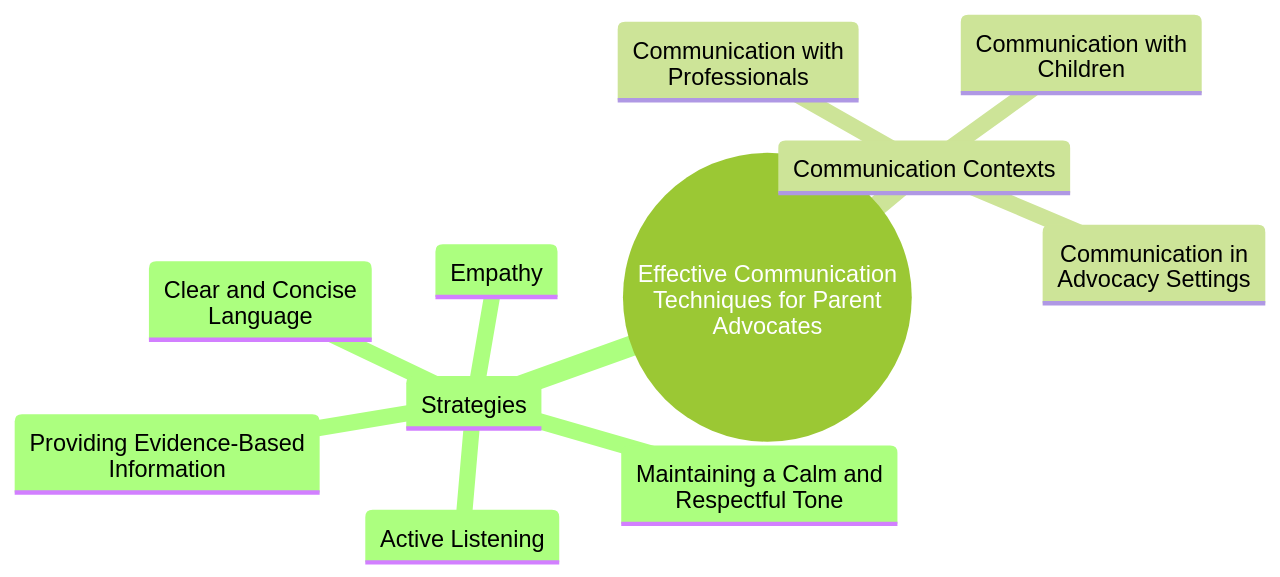
Active listening in parent advocacy allows parents to fully understand and respond to their children's needs and concerns. This involves giving full attention, showing empathy, asking open-ended questions, avoiding interruptions, using non-verbal cues, and summarizing and clarifying to ensure understanding.
Expressing empathy in parent advocacy involves acknowledging parents' challenges and frustrations, offering practical advice and resources, and using inclusive, respectful, and non-judgmental language. This helps to create a safe and supportive environment for parents to express their needs and concerns. Fostering a sense of community among parents can also be beneficial.
Effective communication in parent advocacy can be achieved by using simple and straightforward language, avoiding confusing jargon or technical terms, using visual aids or examples to clarify information, and active listening. Providing written materials or resources that summarize key information can be helpful for parents to refer back to.
Establishing a collaborative and trusting relationship with professionals involved in the child's care is important for open communication. Regularly sharing information, concerns, and updates can ensure everyone is on the same page. Actively listening to professionals' perspectives and expertise is also crucial.
Building collaborative relationships with professionals can empower parents to navigate support services. By working together, parents can gain access to valuable resources, support, and guidance. These professionals can provide information on effective strategies and offer unlimited digital access to resources.
Establishing clear channels of communication and maintaining regular contact with your child's care team is important. This can be done through various methods such as phone calls, emails, or in-person meetings. Actively listening to the care team's feedback and addressing any concerns or questions can foster effective communication and collaboration.
When advocating for your child's needs, it is important to express your concerns, articulate specific needs, and clearly communicate desired outcomes. Using clear and concise language, active listening, and assertive communication techniques can effectively advocate for your child and increase the likelihood of positive outcomes.
To enhance communication with professionals in parent advocacy, it is important to establish clear and effective channels of communication. This can be achieved by maintaining open lines of communication through various means such as email, phone calls, or in-person meetings. Building a collaborative relationship with professionals can help parents effectively advocate for their children's needs.
To effectively communicate in parent advocacy, employ strategies that promote clear and concise messaging. This can include active listening, using non-verbal cues, and choosing the appropriate communication channels. Building relationships and establishing trust with other parents, educators, and professionals can greatly enhance the effectiveness of parent advocacy efforts
6. Time Management Tips for Parents: Balancing Responsibilities and Support
Parenting a child with Level 2 Autism can be a demanding task, requiring a delicate balance of responsibilities. Effective time management is a crucial tool in managing these demands. Prioritizing tasks, setting realistic goals, and maintaining an organized daily routine can significantly alleviate stress. However, it is equally important to remember that your personal well-being matters. The saying, "you cannot pour from an empty cup," is particularly relevant here. It is vital to ensure self-care is an integral part of your routine.
Understanding the unique motivations and challenges faced by children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is instrumental in managing time and tasks effectively. For instance, children with high-functioning autism often respond better once they understand the personal gain associated with completing a task. Linking tasks to their individual interests or offering rewards that resonate with their motivations can prove beneficial.
Altering terminology from "homework" to "study" can shift perspective and reduce resistance. Establishing a designated study space and time can further help in creating a routine. Recognizing that what may appear as lack of motivation or laziness might, in fact, be anxiety is critical. Introducing methods to make learning more engaging and anxiety-reducing can significantly improve motivation.
Teaching organizational skills and offering support in time management can be particularly helpful for children with ASD, who often struggle with disorganization. Breaking down tasks into smaller steps and creating a list of goals makes tasks more manageable and can increase motivation.
Communicating with teachers is pivotal to ensure necessary materials are brought home. Setting up a system and regularly reminding the child about what they need can help prevent frustration. Implementing a token economy system, where the child earns tokens for completing desired actions, can effectively increase motivation. However, it is essential to focus on positive reinforcement and gradually introduce the concept of delayed gratification.
Planning ahead and creating a visual representation of completed tasks can give children with ASD a sense of accomplishment. However, patience is key, as some days may be more challenging than others. The relationship with the child is more important than the completion of homework.
As children with ASD transition from high school to college, parents can help them develop effective time management skills to navigate the increased freedom and responsibilities. Encouraging self-awareness and planning by discussing their energy levels and preferences for studying at different times of the day, helping them identify their ideal work environment and minimize distractions, and teaching them to set boundaries and say "no" to social activities that may interfere with their academic commitments can be beneficial. Gradually stepping back and allowing them to make their own time management decisions, while still providing guidance and support when needed, can better prepare them for the challenges of college and promote their academic success.
Remember, every child with Level 2 Autism is unique. What works for one may not work for another. It is important to tailor your strategies and expectations to your child's individual strengths, challenges, and interests
7. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Others
Building a supportive network can be a transformative tool, offering a sense of understanding and shared experiences. This can be achieved through various channels such as local support groups, online directories, and social media communities. Engaging in these networks allows for the exchange of experiences and the opportunity to learn from others who are navigating similar challenges. This can provide fresh perspectives, new strategies, and the comforting reassurance of not being alone.
Consider the case of a Facebook group, "Sarah's Book Picks". Initially, a small circle of 50 friends, it has grown into an international community of 7,200 members from 32 countries. This group serves as a platform for members to recommend books and engage with other book enthusiasts in a supportive and respectful environment. It's a testament to how communities can be built around shared interests and objectives, whether for problem-solving, forming new friendships, or sharing passions.
Creating a community, however, requires thoughtful planning. Your goals and motivations should be clear, and the timing must be right. It's important to include a mix of online and face-to-face interactions to cater to different preferences and circumstances. For example, you might find local support groups for autism and ADHD through online directories and databases that specialize in connecting individuals with support services. You could also contact local healthcare providers, community centers, and advocacy organizations for information about support groups in your area.
When creating a social media group for parents of children with autism and ADHD, it's crucial to foster a supportive and inclusive environment. Clearly communicate the purpose of the group, establish guidelines for participation, choose the right platform, and promote the group through relevant channels. Encourage active participation, share relevant resources, and ensure respectful and on-topic discussions. This will create a valuable support network and a positive community for parents facing similar challenges.
On the other hand, if you're looking to join an online community for autism and ADHD support, search for reputable platforms that cater to individuals and families affected by these conditions. Websites, forums, and social media groups dedicated to autism and ADHD can provide a space for individuals to connect, ask questions, and share resources.
In the end, whether you're building a community or seeking to join one, remember that you're not alone. Cultivating a community that uplifts and supports you can have a significant positive impact on your life and overall well-being
8. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning in ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a dynamic field that requires consistent vigilance and the pursuit of updated knowledge. The continuous evolution of research, strategies, and best practices necessitates an active engagement with the field and its professionals.
Staying informed is a critical part of being an effective parent advocate. It's not just about attending professional development workshops or subscribing to newsletters; it involves using reputable sources like academic journals, professional conferences, and recognized experts' publications. These sources provide the latest advancements, research findings, and innovative strategies for implementing ABA therapy.
Professional development opportunities tailored for ABA therapy professionals can offer valuable industry insights. Participating in workshops, seminars, conferences, and online courses can enhance skills, keep you updated with recent research and advancements, and provide a platform for networking with other professionals in the industry.
When choosing an ABA provider, awareness of certain red flags indicative of outdated practices is crucial. These could include a heavy focus on reducing self-stimulatory behavior, teaching sustained eye contact, recovering or curing autistic individuals, relying on forced compliance, recommending high therapy hours without justification, using food as a primary reinforcer, and refusing to collaborate with other providers.
Most providers do not intend harm, but it's vital to research providers proactively and ask questions to ensure their practices align with the clients' best interests. This is also a chance to encourage providers to update their practices in line with current, evidence-based strategies.
ABA therapy doesn't only focus on the child's development. It also has transformative potential for the family dynamics, socialization, communication, behavior, and academic success of the child. Understanding the importance of early intervention and the benefits of partnering with families can help children with autism to thrive.
Continuous learning is an essential aspect of ABA therapy. It allows therapists to stay updated with the latest industry insights, overcome challenges, and improve outcomes. By continuously learning and adapting their techniques, ABA therapists can provide the best possible care for individuals with autism.
Remember, the journey of a parent advocate is not a solitary one. There's a wealth of knowledge to be gained from others' experiences, professionals' insights, and the stories shared within the community. By staying connected and informed, and continuously learning, you are not only empowering yourself but also ensuring the best possible outcomes for your child
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of parenting a child with Level 2 Autism can be overwhelming. From understanding the key characteristics and challenges to finding effective support services and developing essential skills, parents need guidance and support. In this article, we explored various topics related to Level 2 Autism, including understanding the characteristics, strategies for developing executive functioning skills, effective communication techniques, time management tips, building a supportive community, and the importance of continuous learning in ABA therapy.
We learned that understanding the key traits of Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing effective help and devising strategies to boost executive functioning skills. Strategies such as executive functioning coaching and the gradual release of responsibility approach can make significant strides in honing these skills. Effective communication techniques, including using visual aids and social stories, can enhance social skills in children with autism.
Time management tips, such as breaking tasks into smaller steps and creating routines, can help parents balance their responsibilities effectively. Building a supportive community is essential for sharing experiences and learning from others who are navigating similar challenges. And lastly, continuous learning in ABA therapy is vital for staying updated with the latest research and best practices.
In conclusion, by understanding the characteristics of Level 2 Autism and implementing effective strategies for developing skills, communicating effectively, managing time, building a supportive community, and continuously learning in ABA therapy, parents can provide valuable support to their children. Remember that you are not alone in this journey. Connect with others who share similar experiences and seek professional guidance when needed. Together, we can create a nurturing environment that helps children with Level 2 Autism thrive. Start now by accessing valuable resources at ASD.media




