Introduction
Understanding extreme autism and the challenges it presents is crucial for providing effective support to children on the spectrum. From limited communication skills to difficulty with social interactions and repetitive behaviors, children with severe autism face unique obstacles. However, a goal-oriented approach to treatment has shown transformative results, highlighting the importance of collaboration and efficiency in improving outcomes. This article explores the characteristics and challenges of extreme autism and the impact of a goal-oriented approach on treatment.
In the journey of advocating for children with extreme autism, parent advocates play a vital role in providing guidance and support. Their multifaceted role involves campaigning for suitable educational provisions, liaising with healthcare professionals, and offering emotional support to both the child and their family. This article delves into the role of parent advocates and their importance in championing the rights of children with severe autism. It also discusses best practices for effective communication techniques and the importance of time management and prioritization for parent advocates
1. Understanding Extreme Autism: Characteristics and Challenges
Navigating the world of severe, or Level 3 autism, requires a deep understanding of the unique characteristics and challenges that define this spectrum. Children with Level 3 autism often have limited communication skills, find social interactions daunting, and exhibit repetitive behaviors. Additionally, they may struggle to adjust to changes in their environment. A thorough understanding of these traits is crucial for developing effective strategies that can empower these children and help them tap into their inherent potential.
A recent case study illuminates the transformative impact of a goal-oriented approach to autism treatment. This innovative shift in perspective is setting the stage for a new paradigm in healthcare and therapy industries. It highlights the importance of collaboration and efficiency, which can greatly enhance treatment outcomes and strengthen the support system surrounding the entire family.
One of the significant hurdles in autism treatment is the delay in diagnosis and access to services, alongside coordinating care across multiple providers. The goal-oriented framework addresses these challenges directly, placing parents at the forefront of the process.
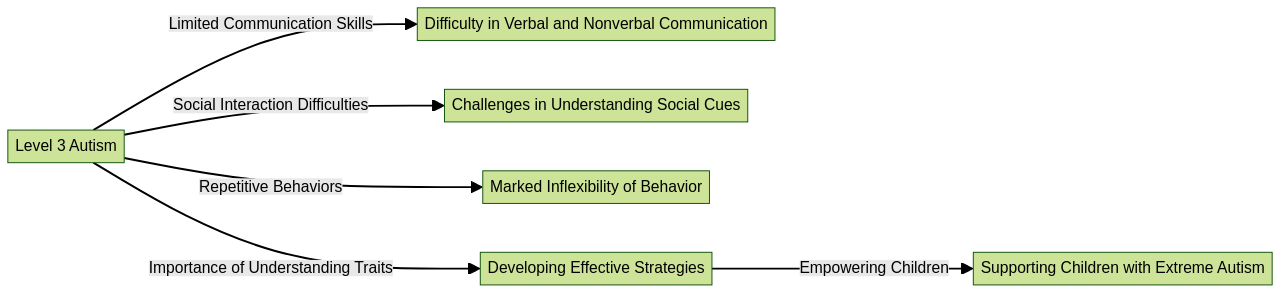
It enlightens them about the importance of long-term support and redirects the focus towards achievable subgoals such as securing insurance authorization and early diagnosis.
The benefits of the goal-oriented approach are extensive. It cultivates happier families, unlocks the potential of the child and the family as a whole, and speeds up access to services. Moreover, it enables the treatment of younger children and reduces administrative tasks, resulting in better outcomes and improved communication among all stakeholders.
The case study emphasizes the importance of continuous optimization and keeping everyone informed about the progress and status of the treatment plan.
The goal-oriented approach promises to bring about a significant industry-wide change, improving the lives of families dealing with autism.
Incorporating strategies to help children with Level 3 autism adapt to changes in their environment is crucial. While effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism exist, it's important to note that the context does not specify whether sensory integration techniques specifically for children with severe autism are discussed. This highlights the need for more comprehensive and tailored strategies in treating severe autism
2. Role of Parent Advocates in Supporting Children with Extreme Autism
Parent advocates are the champions for children with severe autism, providing a guiding light in an often challenging and complex landscape.
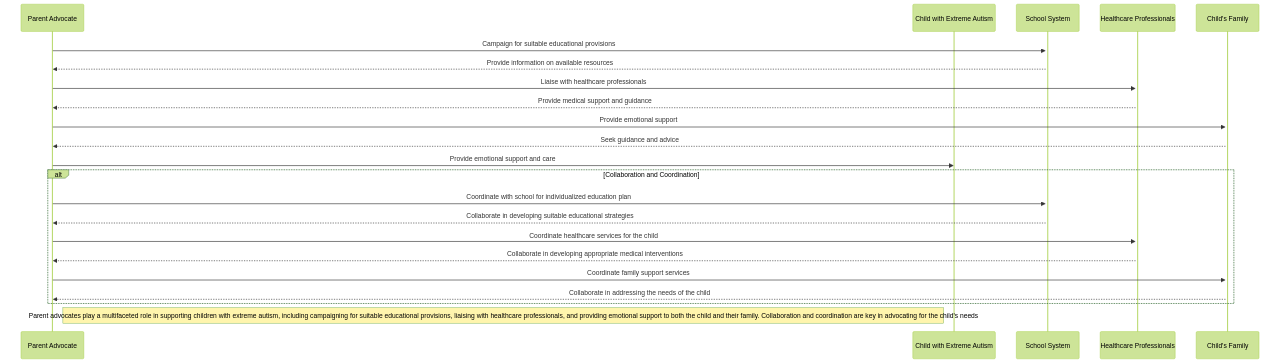
Their role is multifaceted, much like a gemstone, with each facet echoing a different aspect of their advocacy work. From campaigning for suitable educational provisions to liaising with healthcare professionals and providing emotional support to both the child and their family, every aspect of their role is vital.
Similar to a master weaver, parent advocates intertwine the threads of available resources and the unique needs of the child into a woven tapestry of support. This intricate weaving requires a deep understanding of the child's needs and a keen awareness of the resources within reach.
Parent advocates serve as a lighthouse, guiding families safely through the complex world of severe autism. They illuminate the path, shining a light on the resources and services necessary for the child's growth and development, leaving no stone unturned. From education to healthcare, they are the torchbearers that guide families through the darkness.
Their role is a complex ballet, a delicate balance of understanding, advocating, and coordinating. Like a maestro leading an orchestra, they synchronize the various elements of support, ensuring each plays its part harmoniously.
In the heart of support for children with severe autism, parent advocates hold a central position. Their role, though demanding, is crucial in orchestrating the resources and services these children need to thrive, ensuring their voice is heard amidst the world's noise.
In advocating for resources and services for children with severe autism, it is important that parent advocates adhere to best practices. This encompasses educating oneself about available resources and services, establishing connections with professionals and organizations, and joining support groups geared towards parents of children with severe autism.
Documenting the child's needs, challenges, and progress is also a key practice, as these records serve as crucial evidence when advocating for appropriate resources and services. Developing strong communication skills to effectively express the child's needs and concerns is equally important.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals, educators, and therapists involved in the child's care is also a key practice. Building strong partnerships can lead to more effective advocacy and better outcomes for the child. Remember, each child with severe autism is unique, and thus, tailoring the advocacy approach to meet their specific needs and circumstances is of utmost importance
3. Developing Social Skills: Key Strategies for Children with Extreme Autism
The journey to enhance the social competencies of children diagnosed with severe autism is a central focus, one that involves the application of several strategies.
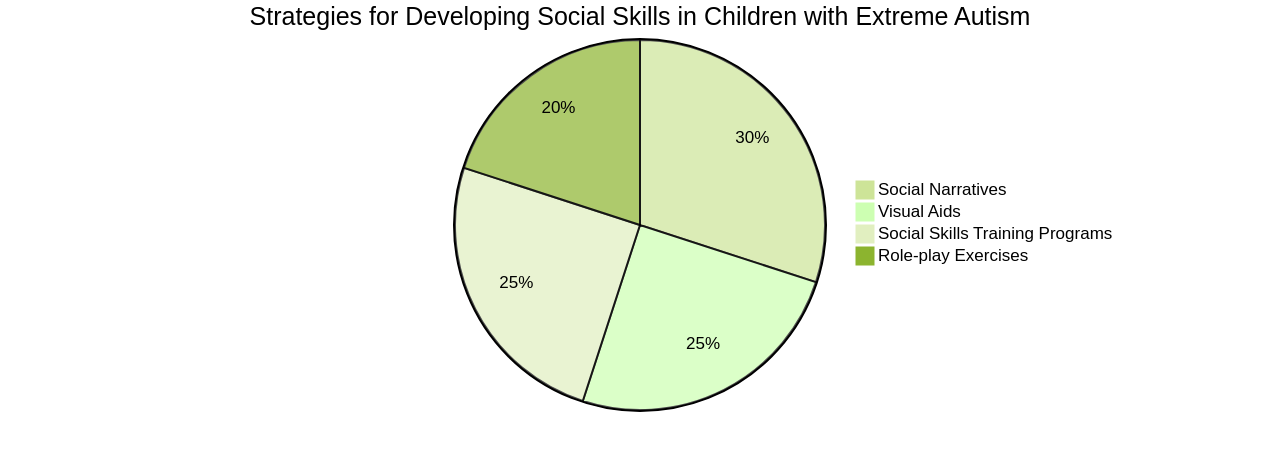
These strategies range from social narratives, role-play exercises, visual aids, and meticulously structured social skills training programs, all of which can significantly assist in teaching these essential skills.
A well-structured social skills training program presents a controlled environment for children to put these skills into practice, thereby improving their effectiveness. For instance, role-playing is a technique that allows children to practice social interactions in a safe and manageable environment. By stepping into different roles and engaging in simulated social situations, children with autism can learn and develop suitable social skills. Role-playing techniques can help children with severe autism understand the perspectives of others, practice turn-taking, and learn appropriate social cues and behaviors. To ensure effectiveness, it is crucial to provide structured and guided role-playing activities tailored to the specific needs and abilities of each child.
The teaching framework known as social thinking is pivotal for the progress of individuals with autism spectrum disorder and social communication challenges. This flexible approach aims to enhance the understanding of thoughts, beliefs, intentions, emotions, and actions of others in different situations, a core requirement for academic success. It employs six main strategies: flexible thinking, whole body listening, understanding the size of the problem, distinguishing expected vs. unexpected behavior, mind files, and social detective skills.
For example, flexible thinking, represented by a group of superheroes known as "the unthinkables," encourages children to view situations from different perspectives. Whole body listening emphasizes the importance of paying attention to someone's brain and body language to understand their thoughts and intentions. The size of the problem strategy introduces a rating scale to help children understand the range of problems and match their reactions accordingly. The expected vs. unexpected behavior strategy helps children understand and follow society's hidden rules. Mind files strategy encourages children to collect information about others for meaningful and engaging conversations. Lastly, being a social detective involves using your ears, eyes, and brain to figure out what to say in a given situation.
These strategies can be practiced and developed through various resources and worksheets, making social thinking a valuable tool for educators, counselors, and parents in supporting individuals with autism. This can help them build healthy relationships and succeed academically.
Furthermore, organizations like the Star Institute offer tailored services such as occupational therapy, speech language therapy, and mental health services for autism. They also provide groups and programs for different age groups. The Star Therapy Approach includes assessments and outcomes with a treatment center and complementary services such as integrated listening therapy and DIR Floortime. The institute also provides home and school services, education, and upcoming summits and symposiums. They offer professional courses and online learning opportunities, including mentorship and certification programs.
By consistently implementing these strategies and participating in well-structured social skills training, children with severe autism can improve their social interactions and build meaningful relationships. This approach not only enhances their social skills but also contributes to their overall well-being and quality of life
4. Effective Communication Techniques for Parent Advocates
The cornerstone of advocacy hinges on the potency of communication. As advocates for parents, the ability to distinctly express a child's needs to various stakeholders, such as educators, healthcare providers, and family members, is of utmost importance. These dialogues serve as a platform to discuss potential strategies, negotiate for resources, and ensure a universal understanding of the child's needs among all involved parties.
Engaging with stakeholders demands certain essential skills. Active listening, empathy, and assertive communication techniques are crucial to this engagement. The principles of active listening are openness, respect, and the suspension of judgment. It entails creating an environment where stakeholders can freely express their views and ensuring these views are accurately documented, promoting transparency and understanding across all parties.
Effective dialogue is another key component of engagement. It can take various forms, including serial monologue, engaged monologue, reflective dialogue, and generative dialogue. Reflective and generative dialogues necessitate empathy, self-reflexivity, and the ability to manage conflict and complexity. These forms of dialogue prove particularly beneficial in long-term collaborations as they effectively address major changes and power differences.
Understanding your audience is a critical aspect of effective communication. This applies not only to researchers communicating their findings to non-scientists but also to parent advocates communicating the needs of the child to various stakeholders. Crafting clear, concise messages that provide additional context and background information is essential.
The use of storytelling can help personify the child's experiences and needs, making them more relatable and understandable to the audience. It is also important to use plain language and active voice, avoiding jargon and acronyms that might confuse the audience. Engaging verbs can make sentences more straightforward and compelling, while revisions and edits can enhance clarity.
One method to build effective communication with family members as a parent advocate is to establish clear and open lines of communication. Regular family meetings or discussions where each member has the opportunity to express their thoughts and concerns can facilitate this. Active listening and empathy are crucial to understanding the perspectives of other family members. Setting goals and creating a shared vision for the advocacy efforts can help unite the family and ensure everyone is working towards a common objective. Regular updates and progress reports can also be shared to keep everyone informed and engaged in the process.
Lastly, seeking feedback from non-experts can ensure understanding and enhance the effectiveness of communication. This not only expands the reach of the message but also builds trust among all parties involved. Ultimately, effective communication is more than just delivering a message; it's about fostering understanding, building relationships, and driving positive change
5. Time Management and Prioritization: Balancing Responsibilities as a Parent Advocate
Being a parent advocate is both rewarding and demanding, often requiring the adept handling of multiple responsibilities. The key to managing these demands lies in effective time management, prioritization, and a well-crafted balance between work and personal life.
Time management is more than just a skill for parent advocates—it's a lifeline. It's about setting clear objectives, organizing tasks based on their importance and urgency, and knowing when to delegate. Think of it as creating a roadmap for your day, week, or even month.
Recognizing and leveraging our peak energy periods during the day can significantly enhance productivity. By scheduling uninterrupted time for necessary tasks during these periods, you can maximize your output and efficiency.
Delegation, although often overlooked, is a powerful tool in time management. Assigning tasks that are low stakes or can be equally handled by others in the household not only lightens your load but also encourages a sense of responsibility among family members.
Minimizing distractions, such as devices, and focusing on one task at a time rather than multitasking can greatly improve focus and efficiency.
Keeping track of time spent on various tasks can provide valuable insights into time usage. These insights can help identify areas for improvement, paving the way for enhanced time management in the future.
Effective stress management is also crucial to productivity. It involves recognizing that stress is a part of life and learning to navigate it rather than letting it impede productivity. Prioritizing self-care, engaging in relaxation techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and establishing a support system are all vital for managing stress. Reaching out to your support network, such as other parent advocates or support groups, can offer valuable guidance and understanding.
Striking a balance between work and personal life can be challenging but is essential. Identifying your top priorities in both areas helps in effective time and energy allocation. Establishing clear boundaries between work and personal life, designating work hours, and ensuring time for self and family are all part of this balance.
Remember, mastering time management and maintaining work-life balance is an ongoing process that evolves with experience and changing circumstances. By making the most of our time, we can set a positive example for our children and help them develop robust time management skills of their own.
Moreover, parent advocates should also remember to take time for self-care and maintain a support network. This can help manage stress, prevent burnout, and ensure they remain effective in their role. After all, a well-cared-for advocate is a more effective advocate
6. Navigating Support Services: Resources and Guidance for Parents
The journey to find support services for children with extreme autism can often feel like navigating a labyrinth. These services, however, are a treasure trove of resources. Parent advocates shine a light on the path, guiding parents through these intricate services which may include educational programs, therapy services, and community resources.
These advocates are knowledgeable about the complexities involved in accessing these services and provide invaluable guidance to parents. Specialized autism therapy centers and clinics are a noteworthy strategy for accessing therapy services for children with extreme autism. These centers often have a professional team consisting of therapists, psychologists, and speech and language pathologists who can provide a range of therapies and interventions tailored to the unique needs of children with extreme autism.
Online platforms, like MyAspergersChild.com, serve as a robust source of support and information for parents. They offer resources to address the unique challenges faced by children and teens with ASD, such as social rejection and emotional instability. These platforms provide strategies to manage meltdowns, defiant behavior, and resistance to change, acting as a lifeline for parents.
Blogs catering to adults on the autism spectrum and their neurotypical partners offer valuable insights into navigating neurodiverse relationships. They cover topics like coping with grief post-diagnosis, preventing 'Cassandra syndrome', dealing with alexithymia, and achieving emotional reciprocity. These platforms also highlight the importance of social skills for individuals with ASD, providing a list of beneficial skills like active listening, conflict management, empathy, and self-control.
To connect with parent advocates, parents can reach out to various autism support services and organizations. These organizations often have parent advocacy groups or networks that provide support and resources. Online forums or social media groups dedicated to parents of children with extreme autism can also provide a space for connecting with other parents, sharing experiences, and accessing valuable information and resources.
In addition, comprehensive guides can provide a wide range of information and support for parents, including strategies for navigating autism support services, promoting social skills in children with autism, and other key terms related to autism. The website www.asd.media is a recommended resource, as it contains articles and news related to autism support services and social skill development for children with autism.
Throughout this complex journey, parent advocates stand as steadfast allies, providing guidance, resources, and unwavering support to parents navigating the world of ASD. They are the torchbearers in the intricate maze of support services, illuminating the path for parents and ensuring they can access the support they need
7. Building an Inclusive Community: The Importance of Collaboration and Sharing Experiences
Creating an environment that appreciates diversity and champions inclusivity is essential in supporting children with extreme autism and their families.
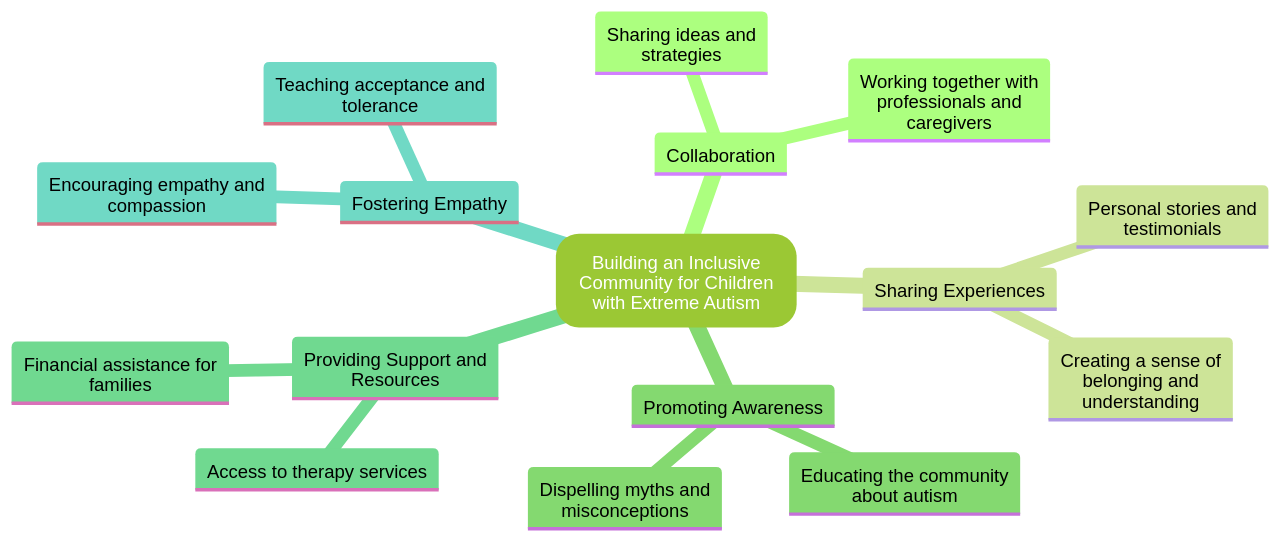
It requires fostering a collaborative spirit that brings parents, educators, and healthcare professionals together to advocate for the child's rights. Moreover, it is vital to create spaces where individuals can share their experiences, learn from others, and feel a sense of belonging.
The iGEM competition, a long-standing beacon of inclusivity within the scientific community, is a prime example. Their Diversity and Inclusion Committee is dedicated to breaking demographic barriers and nurturing a diverse and inclusive scientific community. Their method includes the fair distribution of roles and responsibilities and ensures everyone's voice is heard, promoting a sense of belonging and inclusivity.
In a similar vein, the Better Allies™ approach encourages the formation of more inclusive online communities by providing actionable steps each week. They underscore the importance of mentorship in transmitting knowledge and experiences that can guide individuals to thrive within a community. They also address bias by clarifying the experience necessary for various roles, thereby fostering an objective evaluation of prospective members.
Language also holds a significant place in inclusivity. Communities should endeavor to eliminate non-inclusive or harmful terms and encourage discussions regarding alternatives. They emphasize the importance of redirecting questions to the most qualified subject matter expert, regardless of gender, challenging power dynamics and promoting inclusivity.
Effective strategies for building an inclusive community for children with extreme autism are available. These strategies focus on creating an environment that is accepting, understanding, and accommodating to the unique needs of individuals with autism. Such strategies include promoting awareness and education about autism, fostering empathy and understanding among community members, providing sensory-friendly environments, and offering support and resources for families and caregivers. The primary aim is to create a community where children with extreme autism can feel valued, included, and supported in their daily lives.
Additionally, there are also collaborative approaches available for supporting children with extreme autism. These approaches involve working together with professionals, caregivers, and educators to create a comprehensive support system. They may include therapies such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. Creating an individualized education plan (IEP) and involving the child's family in their educational and therapeutic journey can also be beneficial.
The iGEM blog and Better Allies are valuable resources for best practices in developing inclusive communities and diverse teams. They encourage individuals to collaborate and work together to make their communities more diverse and inclusive. In the words of Better Allies, "Being an ally is a journey." As we aim to build an inclusive community for children with extreme autism and their families, let's remember that the journey towards inclusivity is ongoing, and every step we take brings us closer to our goal
8. Continuous Improvement: Driving Positive Outcomes through ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis, often referred to as ABA therapy, has been recognized as a successful strategy in aiding children with extreme autism.

The unique aspect of this therapy is its play-based approach, which facilitates the learning of new skills whilst managing the challenges of the condition in an engaging manner.
The therapy is built on the principles of positive and negative reinforcement, both essential tools in shaping behavior and promoting desired actions. Positive reinforcement involves associating rewards, such as verbal praise or tangible items, with desired behaviors. This association increases the likelihood of the child repeating these behaviors. In contrast, negative reinforcement involves the removal of an unwanted or unpleasant situation to boost the chances of desired behaviors being displayed.
Despite the implications of the term, negative reinforcement in ABA therapy does not mean punishment. Rather, it involves the removal of an undesirable condition to reinforce appropriate behavior. The balance of positive reinforcement, to increase desired behaviors, and negative reinforcement, to reduce problem behaviors, establishes an effective strategy to promote behavioral change and help individuals with ASD reach their fullest potential.
ABA professionals are mindful of the use of punishment procedures and typically reserve them as a last resort to avoid severe detrimental behaviors. It's also important to select rewards that motivate the individual receiving treatment and to use positive reinforcement frequently but not excessively to avoid satiation. Gradually fading reinforcement once the desired behavior is learned allows the individual to perform the behavior without being rewarded every time.
However, common mistakes in using positive reinforcement include selecting rewards that are not motivating, using reinforcement too frequently and for too long, and failing to fade reinforcement gradually. In the case of negative reinforcement, overuse can lead to feelings of overwhelm and stress, and it should not be used for behaviors that are not genuinely problematic.
In extreme autism cases, the implementation of ABA therapy requires additional techniques and strategies to ensure its effectiveness. This includes a highly structured and individualized approach where the therapy is tailored to the specific needs and abilities of the individual. Breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable steps and providing frequent reinforcement can increase engagement and progress. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team, including speech therapists, occupational therapists, and educators, can also enhance the success of ABA therapy.
To adjust ABA therapy based on individual needs, strategies such as conducting thorough assessments to identify specific strengths and areas for improvement, setting individualized goals, using reinforcement techniques that are meaningful to the individual, implementing visual supports or social stories to enhance comprehension, providing consistent and clear instructions, and regularly monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments to the therapy plan are key. By personalizing the therapy approach, practitioners can effectively address the unique needs of each individual and promote positive outcomes.
It is crucial to enhance outcomes in ABA therapy for children with extreme autism by providing effective strategies for enhancing social skills. By incorporating step-by-step tutorials and providing unlimited digital access to resources, therapists can offer comprehensive support to children with autism. Utilizing evidence-based techniques and personalized approaches can further improve outcomes in ABA therapy for children with extreme autism.
To support stakeholders in the implementation of ABA therapy for extreme autism, it is essential to provide resources and industry insights. This can help overcome challenges and improve outcomes for individuals with extreme autism. By enhancing ABA therapy implementation, stakeholders can navigate autism support services more effectively and empower parents to access the necessary services for their children.
To maximize the benefits of ABA therapy for children with extreme autism, the therapy should be tailored to their specific needs and challenges. ABA therapy should focus on addressing the individual's unique behaviors, communication difficulties, and social skills deficits. It is also crucial to provide a structured and consistent environment for the child, with clear expectations and rewards for positive behaviors. Involving parents and caregivers in the therapy process can help reinforce skills learned during therapy sessions and extend the benefits of ABA therapy to the child's daily life.
The integration of positive and negative reinforcement in ABA therapy can lead to longer-lasting results and help create stronger associations between desired behaviors and positive consequences. It's worth noting that ABA therapy is an evidence-based approach recommended by many medical professionals and is covered by insurance. Organizations like the ABA Centers of America offer autism therapy services and provide cutting-edge treatment to children with autism spectrum disorder.
The implementation of ABA therapy should involve regular monitoring of progress, adjusting strategies based on the child's needs, and incorporating feedback from parents and other stakeholders. This ongoing customization and adjustment of the therapy ensure that the unique strengths, needs, and interests of each learner are catered to, thereby driving positive outcomes for children with extreme autism
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding extreme autism and the challenges it presents is crucial for providing effective support to children on the spectrum. From limited communication skills to difficulty with social interactions and repetitive behaviors, children with severe autism face unique obstacles. However, a goal-oriented approach to treatment has shown transformative results, highlighting the importance of collaboration and efficiency in improving outcomes. By focusing on achievable subgoals and involving parents as advocates, the goal-oriented approach addresses the delay in diagnosis and access to services that children with severe autism often face. It cultivates happier families, unlocks the potential of the child and the family as a whole, and speeds up access to services.
The impact of parent advocates in supporting children with extreme autism cannot be understated. Their multifaceted role involves campaigning for suitable educational provisions, liaising with healthcare professionals, and offering emotional support to both the child and their family. Parent advocates serve as a guiding light in an often challenging and complex landscape, weaving together available resources and the unique needs of the child into a tapestry of support. By championing the rights of children with severe autism and prioritizing effective communication techniques, parent advocates play a vital role in ensuring that these children receive the necessary support and opportunities for growth. It is crucial for parent advocates to continuously educate themselves about available resources, establish connections with professionals and organizations, document the child's needs and progress, and collaborate with healthcare professionals, educators, and therapists involved in the child's care.
To make a positive impact on children with extreme autism, it is essential for individuals to start now by becoming informed allies. By supporting parent advocates, advocating for appropriate resources and services, promoting awareness about extreme autism within communities, building inclusive environments that celebrate diversity, sharing experiences to foster understanding, implementing evidence-based strategies like ABA therapy tailored to individual needs, prioritizing effective communication techniques, managing time effectively as parent advocates while balancing responsibilities, accessing support services through reliable resources like ASD.media - we can collectively create a more inclusive society where every child has an equal opportunity to thrive.




