Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. As a parent advocate, it's crucial to understand the intricacies of this condition and navigate the complexities of supporting individuals with ASD.
In this article, we will explore strategies for addressing social skill challenges, collaborating with professionals and support networks, and fostering self-advocacy. By empowering yourself with knowledge and resources, you can ensure the well-being and development of your child with autism.
Understanding Autism: A Brief Overview
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a neurodevelopmental disorder, presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior, manifesting in diverse ways across individuals. It's vital for those supporting individuals with ASD to comprehend the intricacies of this condition.
As our understanding expands, we acknowledge the critical role of parents in programs like the University of California's PEERS® for Preschoolers. This evidence-based intervention aids autistic young children grappling with social struggles, with parents reporting an increase in their children's social skills and confidence, and a more profound understanding of their child's development.
ASD, affecting 1 in 36 children, a significant increase from 1 in 44 two years ago, often coexists with other conditions like sleep disturbances and ARFID. These complexities can hinder access to care, especially in the face of social determinants of health.
Providers play an indispensable role in guiding these families through a convoluted healthcare system. Nevertheless, the lack of insurance can limit comprehensive care, necessitating community-based resources and non-profit organizations' support.
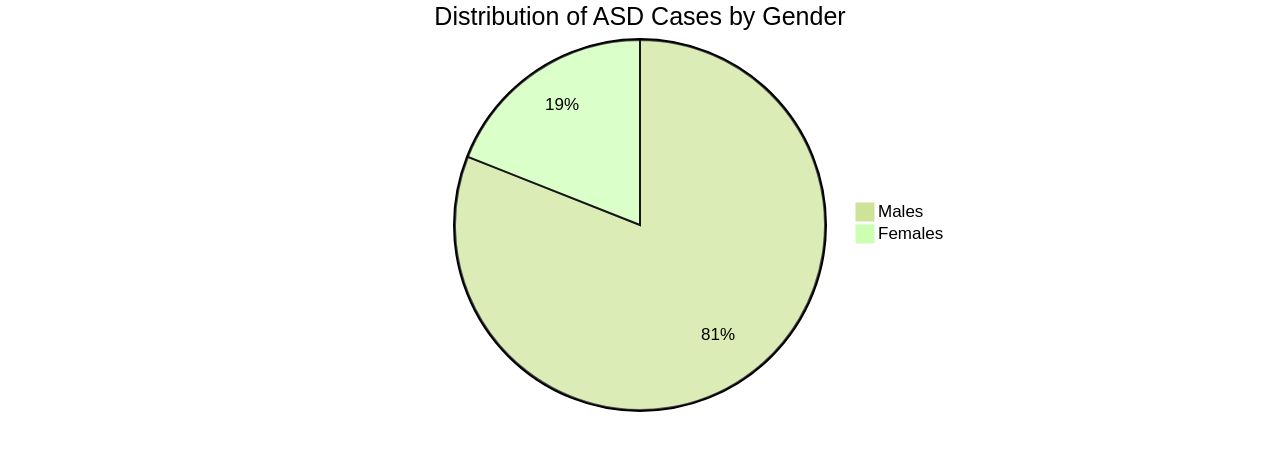
The role of dopamine and serotonin in ASD development has been underlined in recent studies, suggesting potential therapeutic targets that could transform autism treatment. Early diagnosis of ASD, which is characterized by socializing and communication difficulties and repetitive behaviors, can lead to early intervention and optimal outcomes. Despite this, the average age of diagnosis remains at approximately 3 years, underscoring the need for more research on early identification. The journey of caring for autistic individuals can be turbulent, but trusting your instinct as a parent and seeking support can make a significant difference. Remember, you know your child better than anyone else. The rising prevalence of ASD, with males four times more likely to be diagnosed than females, calls for a collaborative approach from policymakers, healthcare professionals, and educators to address the unique needs of those on the autism spectrum.
Identifying Social Skill Challenges in Autism
Navigating the social landscape can be a complex task for individuals with autism, often presenting hurdles in interpreting social cues, expressing emotions, and engaging in reciprocal interactions. This can impede their ability to form friendships, participate in group activities, and navigate social situations.
Recognizing these challenges, parent advocates have become instrumental in identifying these social skill challenges and implementing effective strategies to address them. Programs like the University of California, Los Angeles Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relational Skills (PEERS®) for Preschoolers have shown promising results.
Parents who participated in the program reported increased social skills and confidence in their children and felt more supported and knowledgeable about their child's development. Early intervention is key, as evidenced by Dr. Hannah Schertz's research at Indiana University Bloomington’s School of Education.
Her work focuses on guiding parents in the use of mediated learning practices to promote social communication, addressing concerns early, as signs of autism emerge. The impact of societal changes, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, has also been significant, with online surveys revealing worsened behavior problems in more than one-third of individuals with autism.
This underscores the importance of continuity in educational services and the need for evidence-based procedures to manage challenging behaviors. Advances in research have led to the development of new tools for detection and service delivery models, and routine health care now includes early autism screening and rapid referral.
This has helped connect families to support and services as early as possible. It's also important to recognize the strengths individuals with autism bring to the table. These may include excellent memory, visual thinking, attention to detail, and honesty. A strengths-based approach can help these individuals maximize their potential. Finally, it's crucial to understand that autism is a spectrum, with varied presentations, and some individuals may not receive a formal diagnosis until much later in life. This highlights the importance of understanding the specific needs of each individual, rather than referring them to often unavailable specialists.
Strategies for Addressing Social Skill Challenges
Parent advocates play a crucial role in fostering social skills development for children with autism. Their active engagement in various strategies ensures a supportive environment for their children. One such strategy is the use of Social Stories, which are visual and written narratives that elucidate social situations and expected behaviors.
This approach aids children in comprehending social norms and responding appropriately. Another practical strategy is Role-playing, where parents and children engage in pretend play scenarios that enable practice of social interactions and development of communication skills. Parents model suitable behaviors that their children can emulate.
Organizing Structured Playdates is another effective method, where children get opportunities for social interaction in a controlled environment. This allows them to practice social skills while the parent advocate facilitates and provides guidance. Enrolling children in Social Skills Groups or therapy programs designed for social skill development can be beneficial.
These groups provide a structured and supportive environment for children to learn and practice social skills with their peers. Finally, the use of Visual Supports such as schedules, charts, and social scripts can be helpful. These aids help children understand and follow social routines and expectations, thus reducing anxiety in social situations.
The strengths-based approach, which focuses on the positive skills and attributes of children with autism, such as excellent memory, developed visual thinking, attention to detail, and honesty, can be an effective solution to help these children reach their full potential. Moreover, parent involvement in these programs is essential, as they can apply the learned intervention strategies outside of sessions. This involvement reduces parenting stress through empowerment, knowledge, and social support.
One such program is the University of California, Los Angeles Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relational Skills (PEERS®) for Preschoolers. Parents reported an increase in their children's social skills and confidence after participating in this program. They also felt more positive, supported, and gained a greater understanding of their child's development.
Collaborating with Professionals and Support Networks
For those advocating for parents of autistic children, it is crucial to establish strong connections with professionals and utilize the influence of supportive networks focused on autismo. Collaboration with therapists, educators, and other experts can provide invaluable autismo insights and resources, thereby enhancing the ability to address social skill challenges in a more effective autismo manner. Specialized networks, such as parent support groups and online communities, provide a safe haven of acceptance and understanding for individuals with autism.
These platforms offer a space for sharing personal experiences, acquiring knowledge from others navigating similar paths, and fostering a collective strength in the context of autism. The growing need for comprehensive support systems is underscored by the increase in autism diagnoses, attributed in part to improved screening and heightened awareness. Families often face significant time, energy, and dedication in dealing with the complex nature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
The stress of families dealing with autismo can be alleviated by social support and peer support, which is reinforced by hope, leading to enhanced mental well-being, improved family dynamics, and reduced anxiety and collective stress. Furthermore, by employing a strengths-based approach, children with autismo can harness their potential, utilizing their remarkable memory, astute visual thinking, meticulous attention to detail, and unwavering honesty. Remember, every day brings a new beginning and a new ending, and remaining hopeful that tomorrow will be better has proven to be a valuable mindset.
Celebrating Progress and Fostering Self-Advocacy
When it comes to supporting children with autism, it's crucial to adopt a strengths-based approach, focusing on their unique abilities such as excellent memory, developed visual thinking, and attention to detail. Acknowledging and celebrating even the smallest milestones can significantly enhance their self-esteem and motivation.
It's important to empower them with self-advocacy skills, like expressing their needs and preferences, enabling them to navigate social situations independently. Parent advocates play a pivotal role in creating a conducive environment for learning and fostering positive relationships.
Their support and guidance are crucial, not just for the child's mental and physical health, but also for their own wellbeing. As expressed by a parent, 'ASD parents will always need support & guidance to support their child, regardless of how well they respond to their children's needs.
We may be ticking all those boxes, but we don't stop to think of the parents' mental health & wellbeing & to see what THEIR needs may be.' In the journey of nurturing children with autism, every day brings a new beginning and a new ending, as one parent shared.
This perspective underscores the value of remaining hopeful that the next day will be better. With this positive mindset, parents can effectively facilitate their child's progress, reducing stress and bolstering long-term child functioning. It's also worth noting that early intervention, mediated through parents, plays a key role in improving social communication in toddlers with autism. Dr. Hannah Schertz, a professor at Indiana University Bloomington’s School of Education, emphasizes the importance of guiding parents in the use of mediated learning practices to promote social communication. This approach targets the core autism challenge and addresses concerns early, as signs of autism emerge. In sum, the role of parent advocates in fostering self-advocacy skills and celebrating progress, combined with a strengths-based approach and early intervention, can enhance the social skills of children with autism, helping them reach their maximum potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as parent advocates for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), it is crucial to understand the complexities of this condition and empower our children to reach their full potential. Strategies such as early intervention, social skill development programs, and a strengths-based approach play key roles in supporting individuals with autism. Identifying and addressing social skill challenges through programs like PEERS® for Preschoolers and mediated learning practices can significantly contribute to their social development.
Early intervention is essential for optimal outcomes and improved long-term functioning. Collaboration with professionals and support networks provides valuable insights and resources. Joining parent support groups and online communities offers acceptance, understanding, and collective strength.
Celebrating progress and fostering self-advocacy are vital for our children's growth. By focusing on their unique strengths and empowering them with self-advocacy skills, we enhance their self-esteem, motivation, and independence in social situations. With knowledge, resources, collaboration, celebration of progress, and the fostering of self-advocacy skills, we ensure the well-being of our children with autism and help them maximize their potential on the spectrum.




