Introduction
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing effective support and intervention to children navigating this condition. Level 2 Autism, also known as moderate autism, presents its unique set of characteristics and challenges, particularly in social interaction, communication, and managing changes in routine. However, it's important to recognize that this classification is more about the level of support required rather than defining the individual's qualities or experiences. Each child with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is unique, and their challenges cannot be simplified by a 'level' designation.
Summary
Children with Level 2 Autism require substantial support in various areas of their lives, including verbal and social skills, emotional management, and adapting to changes. Effective interventions such as behavioral and communication therapies, along with early diagnosis and personalized intervention plans, can significantly enhance the child's quality of life. Insights from high needs autism advocates provide a valuable perspective on living with Level 2 Autism.
In this article, we will explore the characteristics and symptoms of Level 2 Autism, the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in supporting these children, strategies for enhancing attention and focus, navigating support services, time management tips for parents, building a supportive community, and the importance of continuous learning in managing Level 2 Autism. By understanding these key points, parents, caregivers, and professionals can provide the necessary support to help children with Level 2 Autism thrive
1. Understanding Level 2 Autism: Key Characteristics and Symptoms
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) manifest in diverse ways, with each individual presenting their own unique set of strengths and challenges. A unique classification within this spectrum is Level 2 Autism, also known as moderate autism. This classification carries its distinct set of characteristics and hurdles, with children often facing significant difficulties in social interaction, communication, and managing changes in routine.
It's essential to remember that this classification is more about the level of support required than defining the individual's qualities or experiences. Each child with ASD is unique, and their challenges, thought processes, and behaviors cannot be summed up simply by a 'level' designation.
Children with Level 2 Autism require substantial support to navigate their daily lives. They often face challenges with verbal and social skills, managing emotions, and adjusting to changes in their schedule or environment.
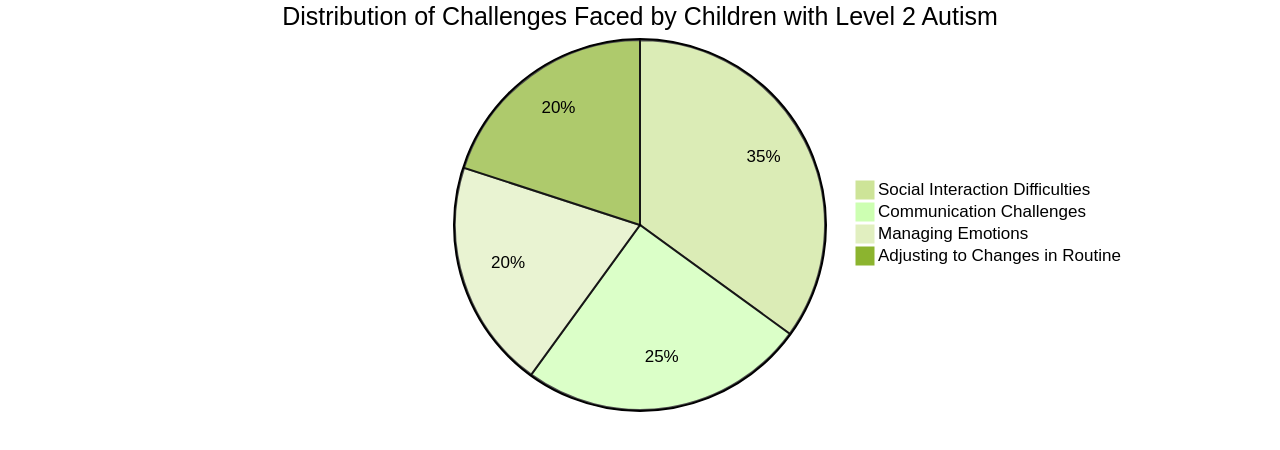
Effective interventions can significantly help children with moderate autism. These interventions can include behavioral and communication therapies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training[^1^]. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to collaborate closely with professionals, such as psychologists, therapists, and special education teachers, to develop a personalized intervention plan that addresses the child's specific needs and challenges[^1^].
The importance of early diagnosis and intervention for children with Level 2 Autism is of utmost importance. The process of obtaining a diagnosis involves multiple visits where the child's abilities and behaviors are closely examined. Seeking diagnosis and treatment as early as possible can significantly enhance the child's quality of life as it becomes increasingly difficult to make advancements in treatment later in life[^1^].
The experiences of high needs autism advocates offer a valuable perspective from within the autism community, especially those with high support needs. Their stories and experiences provide a deeper understanding of what it's like to live with Level 2 Autism[^1^].
For example, the High Needs Autism Advocates (HNAA) community is a platform that allows individuals with high support needs to voice their experiences, thus helping others gain a better understanding of what it's like to have high needs autism[^1^].
The insights shared by these advocates illuminate various aspects of high needs autism such as developmental delays, social skill challenges, sensory processing issues, and cognitive rigidity[^1^]. Personal anecdotes from members of the HNAA community offer a unique perspective on living with high needs autism[^1^].
In understanding Level 2 Autism, the crucial first step is towards providing effective support and intervention. Recognizing the unique challenges these children face and the substantial support they require to navigate their daily lives is paramount[^1^]. The experiences and insights shared by high needs autism advocates further underscore the importance of personalized support and early diagnosis[^1^]
2. The Role of ABA Therapy in Supporting Children with Level 2 Autism
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, an evidence-based intervention, is instrumental in aiding children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. It aims to enhance specific behaviors and skills such as communication, social interactions, academics, and other adaptive learning skills. ABA therapy also assists in developing fine motor dexterity, hygiene, grooming, domestic abilities, punctuality, and job competence.
Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ABA therapy for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), including those with Level 2 Autism. These studies have shown significant improvements in function, challenging the conventional belief of a linear dose-response relationship in ABA therapy. They also highlight the potential of technology-driven innovation in personalizing care and reducing treatment response variance.
ABA therapy uses effective communication techniques to enhance social skills in children with autism. It employs evidence-based strategies to tailor interventions to the specific needs of children. Therapists utilize visual supports, such as picture schedules and visual cues, along with social stories and role-playing activities to facilitate communication and understanding. This consistent application of techniques supports the development of communication skills in children with Level 2 Autism.
To enhance academic skills, ABA therapy implements behavioral techniques to teach and reinforce desired skills. It assists in developing academic capabilities such as reading, writing, math, and problem-solving. Tasks are broken down into small, manageable steps, and consistent positive reinforcement is provided to support academic progress.
Fine motor skill development is a crucial aspect of ABA therapy, improving the child's coordination, dexterity, and control over small movements. Therapists use engaging and motivating activities, such as puzzles, drawing, and manipulating small objects, to develop these skills.
ABA therapy is also effective in teaching domestic capabilities, such as self-care skills, household chores, and independent living skills. By using systematic teaching techniques and individualized strategies, ABA therapists assist children in acquiring these important life skills.
Punctuality skills can be improved through ABA therapy by teaching the concept of time, creating visual schedules and timers, and providing positive reinforcement for punctual behavior. These interventions develop better punctuality skills and improve overall time management abilities.
Job competence training, an important aspect of ABA therapy, focuses on teaching skills essential for employment, such as following instructions, completing tasks, and interacting with coworkers.
ABA therapy is effective in enhancing attention and focus in children with autism. Individualized treatment plans and structured teaching methods help children develop and improve these skills, positively impacting their overall development and daily functioning.
In conclusion, ABA therapy is a comprehensive approach that promotes positive behaviors and reduces challenging behaviors through systematic and evidence-based techniques. It targets specific learning and development goals for each child, improving outcomes such as communication skills, social skills, adaptive skills, and academic skills. ABA therapy has been found to be effective in supporting children with Level 2 Autism in achieving their learning and development goals
3. Strategies for Enhancing Attention and Focus in Children with Level 2 Autism
Enhancing attention and focus in children with Level 2 Autism is multifaceted, necessitating a customized approach that recognizes these children's unique needs and motivations.
It's crucial to understand that their motivation often differs from that of neurotypical children. For instance, high-functioning autistic children tend to respond well to questions that engage their personal interests. Their motivation is often fueled by self-satisfaction, a sense of pride, and the ability to overcome challenges.
Creating a structured environment is an essential strategy. This can be achieved by establishing clear routines and schedules, providing visual supports such as visual schedules and social stories, and creating a designated space for specific activities. The use of visual cues and prompts for organization and transition can also be beneficial in creating a structured environment. Collaborating with professionals such as therapists and educators can also be valuable in creating and implementing a structured environment that meets the specific needs of the child with level 2 autism.
Understanding the common challenges faced by children with ASD, such as boredom and anxiety, is important. Their lack of motivation or perceived irresponsiveness may be linked to anxiety, not laziness. Making the educational process more engaging and connecting it to real-life experiences can help alleviate boredom. This could involve taking studies outdoors or incorporating family outings and activities.
Disorganization is a common issue for children with ASD. Thus, investing time in teaching organizational systems and time management skills can be beneficial. Furthermore, if books or materials needed for homework are left at school, it can indicate that the child is struggling. Communication with teachers and setting up reminders or systems can help address this issue.
Breaking tasks into smaller steps is another crucial strategy. This can make children with ASD feel less overwhelmed. Creating a list of small goals and providing rewards for each completed task can increase motivation. Setting time limits for homework and allowing for breaks can also help children with ASD stay motivated and focused.
Moreover, implementing a "token economy" system, where children earn tokens for completing desired actions, can be effective in increasing motivation. Rewards should be immediate and consistent. Visual representations of progress, such as a paper chain or a calendar, can help children with ASD see their accomplishments and develop a sense of achievement.
Regular physical activity can help to improve concentration and reduce hyperactivity. Additionally, sensory tools, such as movement, fidgets, alternative seating, heavy work, and pressure and weight, can help calm, regulate, organize, and orient the nervous system, leading to improved focus and attention.
Finally, patience is key, as some days may be more challenging than others. It's important to remember that the relationship with the child is more important than the completion of homework. The amount of benefit a child with ASD gets from completing homework may not outweigh the importance of the parent-child relationship. Spending excessive time coercing or cajoling them to do homework can be counterproductive.
Incorporating their interests into learning activities and providing positive reinforcement to encourage their efforts and progress are also essential strategies. Remember, every child is unique and what works for one may not work for another. As Ilana Danneman, a pediatric physical therapist, aptly puts, "Just keeping a few of these tools at your disposal can really impact the effect of your lessons, treatments, or sessions
4. Navigating Support Services for Children with Level 2 Autism
Supporting children with Level 2 Autism necessitates a careful journey through various support services, each tailored to cater to their unique needs and challenges. This includes specialized therapies, such as occupational and speech therapy, as well as training designed to enhance social skills.
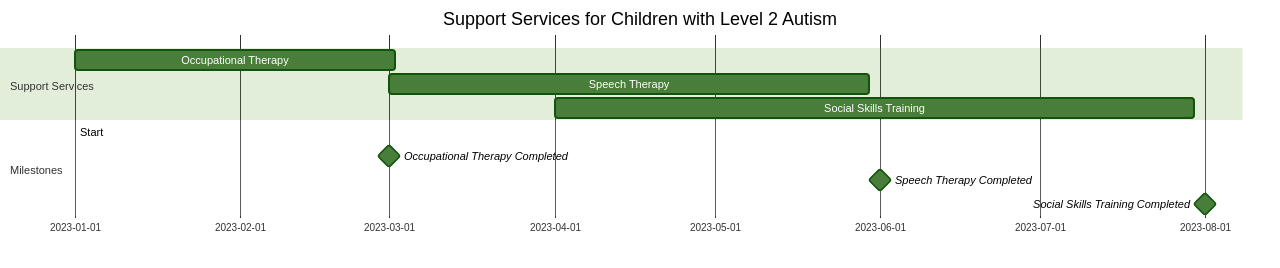
But to truly empower these children to prosper and reach their full potential, we need to move beyond these traditional support services. Drawing from the experiences of parents and professionals, there are several strategies that have proven highly effective in supporting a child with Level 2 Autism.
One such strategy is creating a structured daily routine. A predictable schedule can instill a sense of security and comfort for these children, aiding them in better managing their day-to-day activities.
Teaching social and problem-solving skills is another vital part of this support structure. Children with Level 2 Autism often grapple with social interactions and understanding social cues. Thus, empowering them with the ability to identify these cues and understand body language can be incredibly beneficial. In addition, teaching them how to identify problems and discuss potential solutions can assist them in effectively navigating challenging situations.
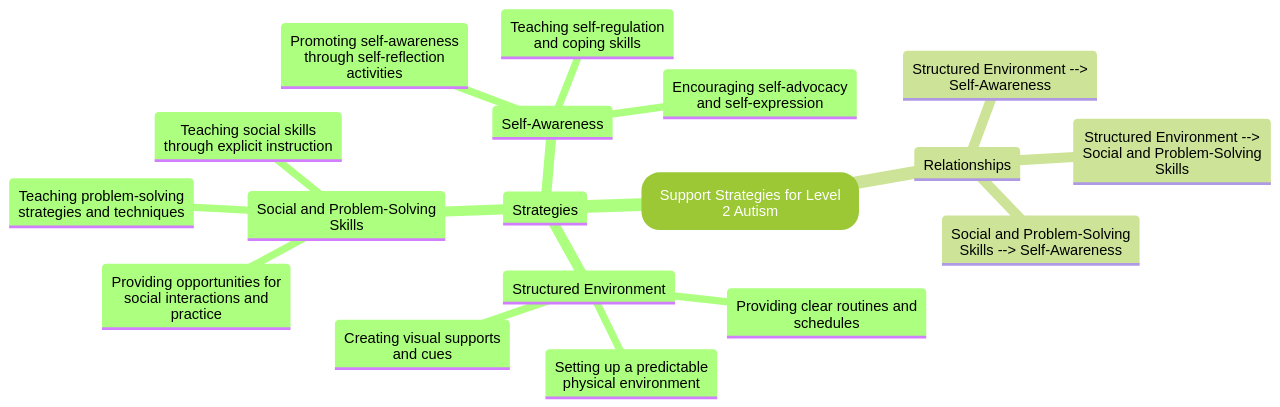
Encouraging self-awareness among these children is also crucial. By helping them identify and understand their emotions, we can help prevent meltdowns and enable them to manage their emotions more effectively.
Another helpful strategy is to provide helpful hints or reminders. This can aid these children in managing social interactions and remembering appropriate behaviors. Recognizing and embracing the unique interests and traits of children with Level 2 Autism can also help them build self-confidence and thrive.
Moreover, establishing a safe word or phrase can be beneficial. This word or phrase can be used by the child to express when they are feeling overwhelmed or find themselves in a difficult situation, thus helping them communicate their needs more effectively.
As a supportive community, it is essential to remember that these strategies require patience, compassion, and love. Navigating the condition can be a challenge, but it's important to remember that Level 2 Autism is not the child's fault and should not define them. Education and helping the child manage the condition with patience, compassion, and love is key.
Looking forward to the transition from high school to post-secondary education, there are various pathways to success for students with Level 2 Autism. These include life skills programs, certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities. It is important to carefully consider the child's functioning in areas such as independence, academic skills, and adaptive behavior when identifying the best pathway for their success and happiness.
ASD Media is a valuable resource in this journey, offering a wealth of information to help parents and professionals navigate these services and strategies. By leveraging resources such as ASD Media, parents can ensure that their children receive the support they need to thrive, both now and in the future. ASD Media's resources cover a range of topics, including strategies for communication, behavior management, and accessing appropriate services. The resources are designed to empower parents and professionals by providing them with the necessary tools and information to effectively support individuals with Level 2 Autism. By visiting their website, parents can find valuable guidance and advice to help them navigate the challenges associated with Level 2 Autism
5. Time Management Tips for Parents Supporting Children with Level 2 Autism
Supporting a child with Level 2 Autism is a multifaceted endeavor, requiring an intricate blend of patience, understanding, and effective time management. The journey isn't solely about meeting deadlines or organizing your day; it's about fostering an environment that caters to your child's needs without inducing unnecessary stress.
Prioritizing tasks based on importance is the first step. By creating a daily schedule with specific time slots for different activities, you can focus on what truly matters. Remember, though, to maintain adaptability. Life is unpredictable, and being able to adjust plans when unexpected situations arise is key.
Establishing routines is crucial as well. Routines offer structure, which is comforting for children with Level 2 Autism. These routines need to be fluid, adaptable to the child's comfort levels, and needs. Visual aids such as timers or clocks can be helpful tools in maintaining these routines and helping your child understand the schedule.
When possible, delegation can be a game-changer. It's not about shirking responsibilities, but about ensuring that you're not overly burdened to the point of exhaustion. Remember, you can't pour from an empty cup. Setting aside time for self-care is a necessity, not a luxury. It helps manage stress, prevent burnout, and maintain a positive mindset, enabling you to provide the best possible support for your child.
One of the challenges children with Level 2 Autism often face is disorganization. Teaching them organizational systems and time management skills can be beneficial. Not only does this help them in the present, but also equips them with skills that will serve them well in the future.
Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable parts is another essential strategy. This can help children with Level 2 Autism feel less overwhelmed and more in control. Utilizing a "token economy" system, where they earn tokens for completing desired actions, can also be a powerful motivator.
Patience is key. There will be good days, and there will be challenging days. Remember, the bond with your child is more important than the completion of tasks. Respecting their pace and providing them with the support they need can do wonders for their overall development.
In essence, effective time management is a multifaceted approach. It involves prioritization, flexibility, establishing routines, delegation, self-care, and above all, patience and understanding. By adopting these strategies, parents can provide the necessary support to their children without feeling overwhelmed
6. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
For those dedicated to the well-being of children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism, the creation of a supportive and understanding environment is essential. This network goes beyond merely sharing experiences and learning from one another; it offers a sense of belonging and understanding that empowers individuals to confront and overcome the challenges they face.
A prime example of such a supportive community, The Autism Project, is a unique collaboration between parents, professionals, and community members. It provides a comprehensive support system for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and their families. The Autism Project offers essential resources like family support, social groups, summer camps, and access to medical home portals.
The Autism Project places a strong emphasis on education, offering training for caregivers, first responders, educators, and the broader community. This extends to understanding the unique neurology of autistic individuals, such as the tendency of the autistic brain to think in absolutes rather than relatives, which can significantly enhance the support provided.
Moreover, the importance of predictability and structured routines is highlighted, which can alleviate anxiety and support smoother transitions for autistic children. The use of visual supports like schedules and visual cues is promoted to provide predictability, improve understanding, and foster independence.
Another critical aspect of their work is understanding and supporting sensory needs, given the commonality of sensory processing difficulties in autistic individuals. The organization encourages the development of interoceptive awareness - the ability to recognize and interpret bodily sensations, a skill that can significantly aid emotional regulation.
The Autism Project also acknowledges that caregivers need care too. Their resources and support extend to the caregivers, ensuring their well-being and enhancing their ability to effectively support their child.
The organization also emphasizes the importance of focusing on the strengths and positive qualities of autistic individuals, such as their visual learning abilities and long-term memory. This perspective fosters a positive environment that celebrates the unique abilities of each individual with ASD.
In line with their mission of creating communities where individuals with ASD can thrive, The Autism Project offers opportunities for others to donate, volunteer, and get involved. They respect individual choice by using both person-first language and identity-first language. Their affiliation with Gateway Healthcare, the largest provider of behavioral health care services in Rhode Island, further strengthens their commitment to providing comprehensive support services.
The fostering of a supportive community like The Autism Project provides a platform where individuals can share their experiences, learn from each other, and receive the support they need, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for children with Level 2 Autism and their families
7. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning in Managing Level 2 Autism
Maintaining an up-to-date understanding of Level 2 Autism is vital for the effective support of children navigating this condition. This involves continuous learning which enables parents, caregivers, and professionals to offer the most beneficial assistance. Staying informed can be achieved by regularly referring to reputable sources such as scientific journals, research institutes, and organizations dedicated to autism research. These sources often publish the latest findings and advancements in the field. Additionally, attending conferences, workshops, and seminars related to autism research can provide valuable insights and opportunities to connect with experts in the field. Online forums or communities where professionals and individuals with expertise in autism research share information and discuss new developments can also be beneficial.
The understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) has undergone significant changes over time. Previously, ASD was categorized into levels 1, 2, and 3, with level 3 being the most severe. However, this linear model often fails to encapsulate the diversity of experiences within autism, possibly leading to unfair comparisons. Consequently, researchers now advocate for a pie chart model. This model represents individual autism traits in different sections, offering a visual representation of the unique experiences of autistic individuals. This model simplifies the understanding of autism while acknowledging that autism comes in different forms and sizes. It allows for a fluid understanding of autism, recognizing that symptoms may change and develop over time, and provides a clearer visual representation of the uniqueness and complexity of autistic individuals.
Fostering a growth mindset is another crucial aspect of managing ASD. This mindset, the belief that abilities can improve through effort and persistence, can be particularly beneficial for children with autism. Children with a fixed mindset may struggle with making mistakes and persevering through challenges, which can hamper their educational progress. Conversely, a growth mindset can help children with autism become more comfortable with taking risks, making mistakes, and displaying effort, leading to greater learning confidence and success in school.
Parents and caregivers can cultivate this mindset through various strategies. They can model the growth mindset by responding positively to mistakes, embracing mistakes as teachable moments, and demonstrating that taking risks with effort and persistence is valuable. Exposing children to examples of individuals who take healthy risks, ask for help and show that it's a positive thing, engage in physical activities that require effort, and discuss the importance of effort in accomplishing goals can also be beneficial.
In essence, staying updated with the latest research on ASD, understanding the unique experiences of autistic individuals, and fostering a growth mindset can significantly enhance the support provided to children with Level 2 Autism
Conclusion
Understanding Level 2 Autism is crucial for providing effective support and intervention to children navigating this condition. Level 2 Autism, also known as moderate autism, presents its unique set of characteristics and challenges, particularly in social interaction, communication, and managing changes in routine. However, it's important to recognize that this classification is more about the level of support required rather than defining the individual's qualities or experiences. Each child with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is unique, and their challenges cannot be simplified by a 'level' designation.
Children with Level 2 Autism require substantial support in various areas of their lives, including verbal and social skills, emotional management, and adapting to changes. Effective interventions such as behavioral and communication therapies, along with early diagnosis and personalized intervention plans, can significantly enhance the child's quality of life. Insights from high needs autism advocates provide a valuable perspective on living with Level 2 Autism.
In this article, we explored the characteristics and symptoms of Level 2 Autism, the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in supporting these children, strategies for enhancing attention and focus, navigating support services, time management tips for parents, building a supportive community, and the importance of continuous learning in managing Level 2 Autism. By understanding these key points, parents, caregivers, and professionals can provide the necessary support to help children with Level 2 Autism thrive.
The Supportive Ally is a compassionate and encouraging persona who stands by parents and offers unwavering support. They understand the struggles parents face and provide a safe space for them to share their experiences and find solace.
To continue learning about supporting children with Level 2 Autism and accessing valuable resources, visit ASD Media. Stay informed, stay connected, and together we can make a difference in the lives of children with Level 2 Autism. Start now!




