Overview
Navigating the world of picky eating can be particularly challenging for parents of children with autism. Understanding that these behaviors often stem from sensory sensitivities and dietary selectivity is crucial. By recognizing these underlying issues, parents can begin to foster a more positive relationship with food.
One effective strategy is gradual exposure to new foods. This approach allows children to explore different tastes and textures at their own pace, reducing anxiety around mealtimes. Creating a positive mealtime environment is equally important; a calm and inviting setting can encourage children to be more open to trying new foods.
Additionally, seeking professional guidance can provide invaluable support. Nutritionists and therapists can offer tailored strategies, helping parents navigate the complexities of their child’s eating habits. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—many families face similar challenges, and there are resources available to help.
By embracing these strategies, parents can take meaningful steps towards supporting their children. Share your experiences or seek advice from others who understand; together, we can create a nurturing space for our children to thrive.
Introduction
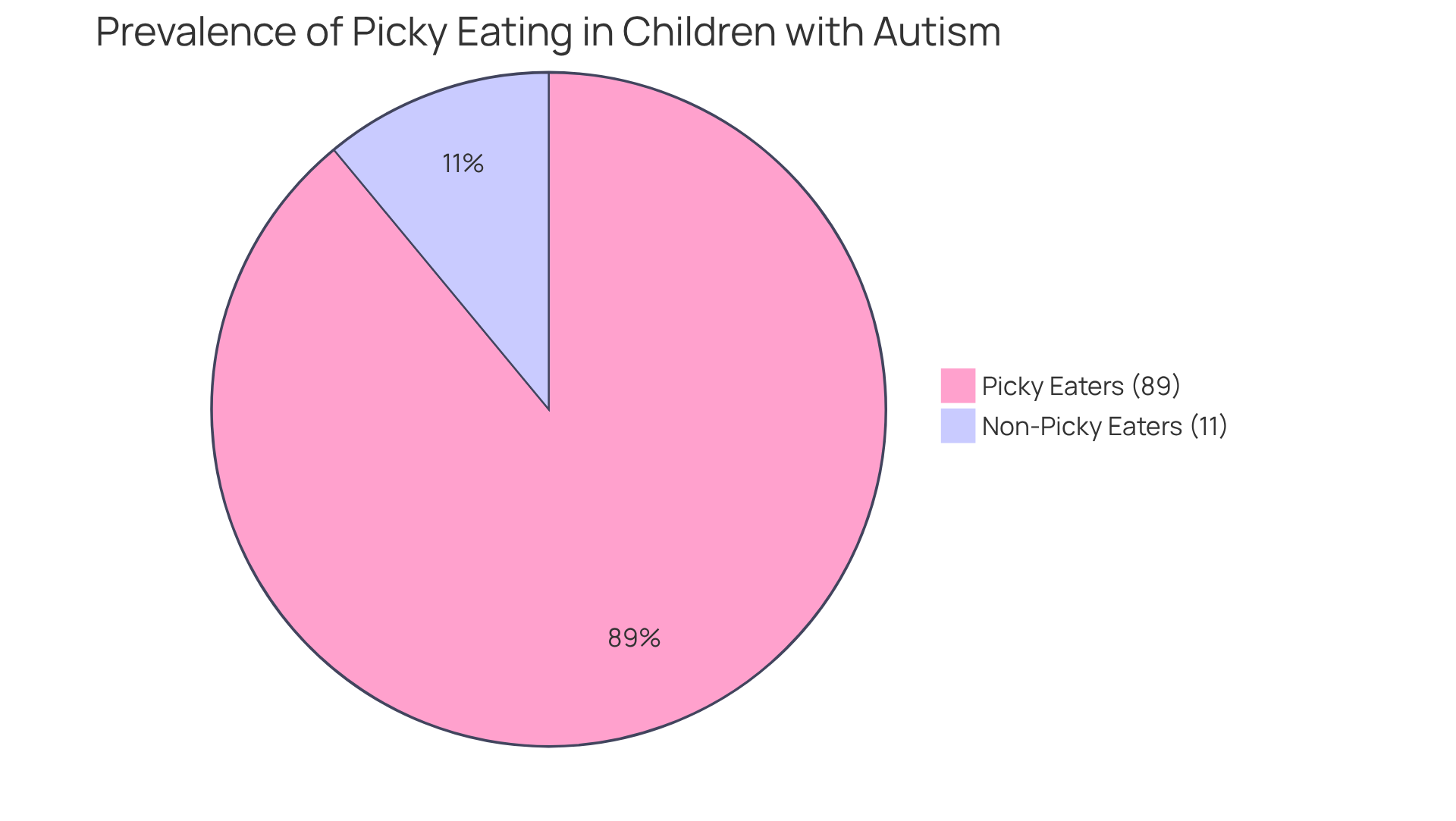
Many parents of children with autism encounter the challenging reality of picky eating, a behavior often stemming from the unique sensory sensitivities of their little ones. Studies suggest that as many as 89% of autistic children display selective eating habits, making it crucial to understand the underlying causes to foster a healthier relationship with food.
How can parents effectively navigate these mealtime struggles and inspire their children to embrace a more varied diet? This article explores compassionate strategies and professional insights that can transform mealtime from a battleground into a nurturing opportunity for exploration and growth.
Explore the Connection Between Autism and Picky Eating
Many parents of children with autism notice that their little ones often exhibit picky eating behaviors. This can be attributed to heightened sensory sensitivities that many autistic individuals experience. It’s not uncommon for these children to have strong preferences for specific textures, tastes, and colors, which can lead to a limited diet. In fact, studies reveal that up to 89% of young individuals with autism display some form of dietary selectivity. Understanding this connection is crucial for parents as they navigate mealtime challenges with empathy and patience. It’s important to recognize that their children's aversions are not merely behavioral; they are often linked to sensory processing issues. By embracing this understanding, parents can create a more supportive and nurturing mealtime environment for their children.
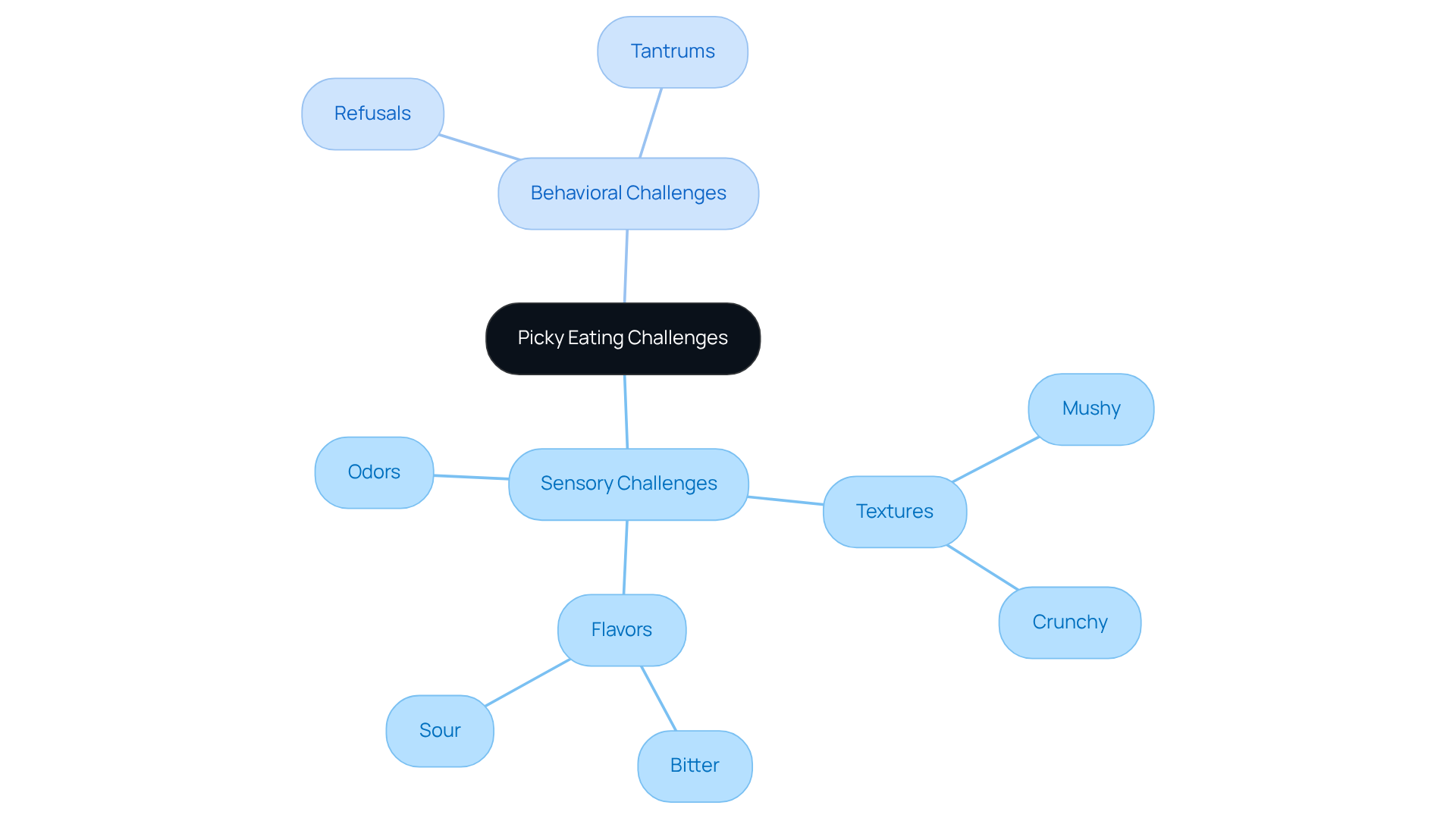
Identify Sensory and Behavioral Challenges in Picky Eaters
To effectively tackle picky eating, parents are encouraged to closely observe their child's responses to various dishes. Sensory challenges often manifest as aversions to particular textures, such as mushy or crunchy items, as well as flavors like bitter or sour, and even specific odors. Behavioral challenges may present as outright refusals to try new foods or tantrums during mealtime, which can be particularly distressing for both child and parent.
Studies indicate that between 46% to 89% of youngsters who are autism picky eaters face feeding difficulties, highlighting the commonality of these concerns. Furthermore, approximately 25% of all children experience eating problems during their early years, underscoring the importance of monitoring eating behaviors. Keeping a diary of meals can serve as a valuable tool for tracking these reactions and recognizing trends in likes and dislikes. This awareness is crucial for developing effective strategies to encourage a more varied diet.
For instance, gradual exposure to new dishes alongside well-known favorites can help alleviate anxiety about trying new items. As one occupational therapist noted, "Children who are autism picky eaters frequently encounter substantial aversions to meals due to sensory sensitivities, making it crucial to approach new options with patience and understanding."
Engaging with occupational therapists can provide valuable insights into addressing aversions, as they often emphasize the significance of sensory sensitivities in eating habits. By understanding these challenges, parents can create a nurturing mealtime atmosphere that fosters exploration and acceptance of a broader variety of dishes.
Implement Effective Strategies for Encouraging Healthy Eating
- Start Small: Begin by introducing new options gradually, starting with small portions alongside familiar favorites. This approach reduces pressure and allows your little one, often considered an autism picky eater, to explore new flavors at their own pace.
- Create a Positive Mealtime Environment: Make mealtimes enjoyable by adding fun activities, like culinary art or themed meals. This can help alleviate anxiety around trying new dishes and make the experience more inviting.
- Involve Your Offspring: Engage your children in meal planning and preparation. Allowing them to choose and help prepare dishes can ignite their enthusiasm for tasting new items.
- Using visual aids such as schedules or charts can assist autism picky eaters in understanding what to expect at mealtimes, offering a sense of predictability that many autistic individuals thrive on.
- Be patient and persistent, as it may take several introductions to a new dish before your child, who is an autism picky eater, is ready to try it. Maintain a calm demeanor and encourage small tastes without forcing them to eat.
- Model Healthy Nutrition: Demonstrate nutritious habits by enjoying a variety of dishes yourself. Children often imitate adult behaviors, so showing enthusiasm for new foods can inspire them to try as well.
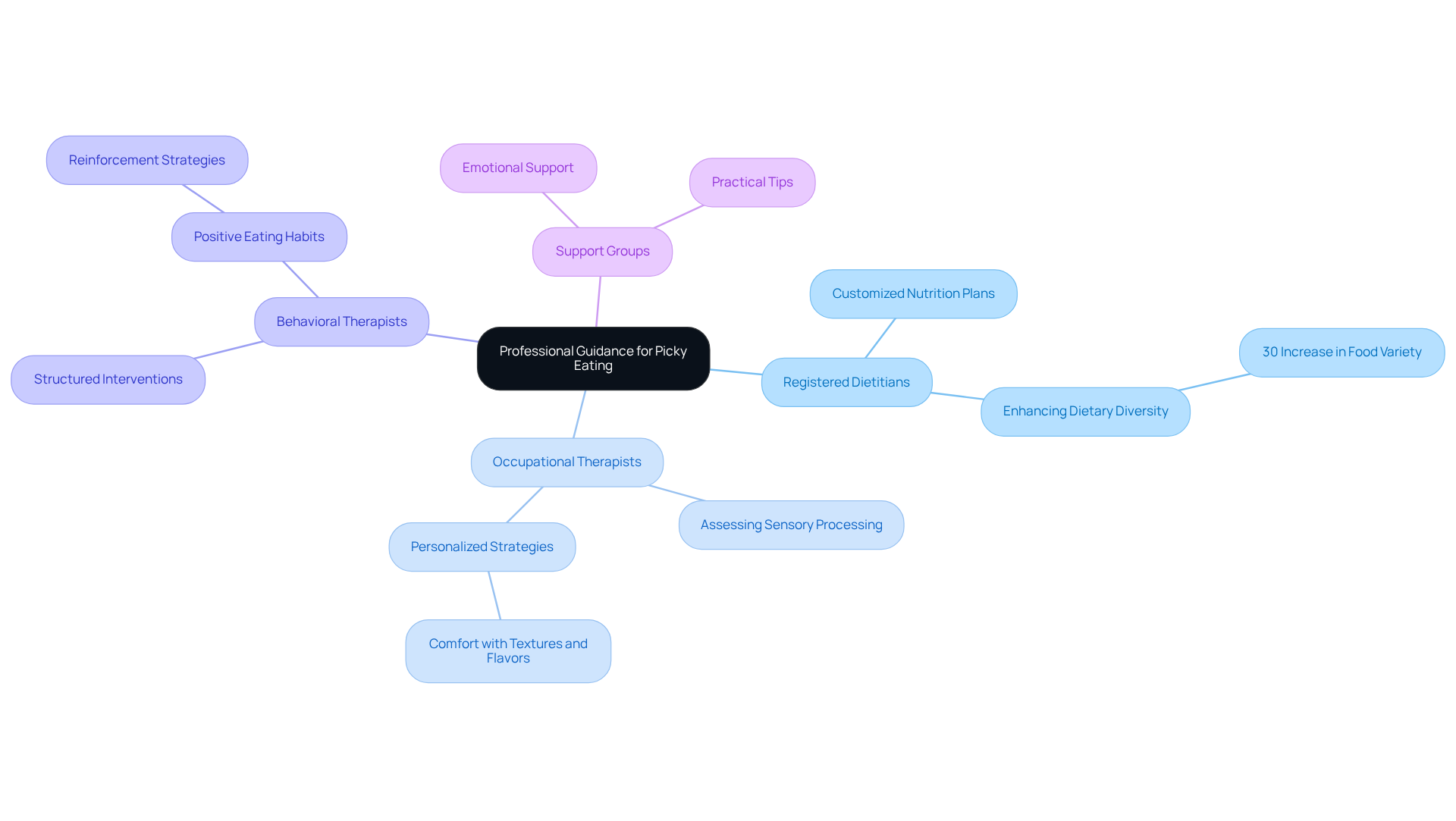
Seek Professional Guidance and Support for Picky Eating
When selective food preferences persist despite your best home strategies, seeking professional guidance can be essential. It's important to know that you're not alone in this journey, and there are experts who can help.
Consider consulting with:
- Registered Dietitians: These specialists can design customized nutrition plans that ensure your child receives adequate nourishment while addressing selective eating habits. Research shows that interventions by registered dietitians can significantly enhance dietary diversity and nutritional intake in children identified as autism picky eaters. For instance, studies indicate that youngsters who participated in structured dietary programs experienced a 30% increase in the variety of foods they consumed.
- Occupational Therapists: They assess sensory processing challenges and develop personalized strategies to help your child feel more comfortable with different textures and flavors. As Virginia Stoffel, AOTA President, beautifully puts it, "Occupational therapy practitioners ask, 'what matters to you?' not, 'what's the matter with you?'" This compassionate approach allows children, particularly autism picky eaters, to gradually expand their food preferences through tailored strategies that resonate with their unique needs.
- Behavioral Therapists: ABA therapists can introduce structured interventions that promote positive eating habits through reinforcement strategies. Their expertise in behavior modification can lead to lasting changes in dietary habits, fostering a healthier relationship with food.
- Support Groups: Connecting with other parents facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical tips. Resources like ASD Media offer valuable community support, helping families navigate the complexities of picky eating together. Sharing experiences can lighten the load and create a sense of belonging.
Remember, seeking help is a proactive step towards nurturing your child's growth and well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between autism and picky eating is essential for parents striving to support their children through mealtime challenges. Recognizing that picky eating behaviors often stem from sensory sensitivities allows parents to approach the situation with greater empathy and patience. This foundational knowledge fosters the creation of a nurturing environment that encourages exploration and acceptance of diverse foods.
Throughout this article, various strategies have been highlighted to assist parents in managing picky eating effectively. From gradually introducing new foods to creating positive mealtime experiences, these approaches emphasize the importance of patience and persistence. Seeking professional guidance from registered dietitians, occupational therapists, and behavioral therapists can provide tailored support that addresses both dietary and sensory needs, ultimately fostering a healthier relationship with food.
Navigating picky eating in children with autism is not merely about overcoming food aversions; it’s about understanding the unique challenges these children face and responding with compassion and creativity. By implementing the strategies discussed and seeking appropriate support, parents can transform mealtime into an enriching experience that promotes not only nutritional diversity but also emotional well-being. Embracing this journey together can lead to profound growth and connection, making each meal an opportunity for exploration and joy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do many children with autism exhibit picky eating behaviors?
Many children with autism exhibit picky eating behaviors due to heightened sensory sensitivities, which lead to strong preferences for specific textures, tastes, and colors.
How common is picky eating among children with autism?
Studies indicate that up to 89% of young individuals with autism display some form of dietary selectivity.
What should parents understand about their children's aversions to food?
Parents should recognize that their children's aversions are often linked to sensory processing issues rather than being purely behavioral.
How can parents support their children during mealtime challenges?
By understanding the connection between autism and picky eating, parents can create a more supportive and nurturing mealtime environment for their children.




