Introduction
Understanding Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is crucial for parents and professionals alike. PDA is a behavioral pattern characterized by a strong resistance to everyday demands, often stemming from heightened anxiety levels. This can significantly impact a child's ability to focus and remain attentive. Fortunately, there are resources available to help manage the challenges associated with PDA and ADHD. These resources offer strategies and support for parents and caregivers, enabling them to better understand their child's needs and provide appropriate support. By implementing tailored strategies and seeking guidance from professionals, parents can create a structured and supportive environment that promotes positive behaviors and reduces demand avoidance in children with ADHD and PDA.
1. Understanding Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in Children with ADHD
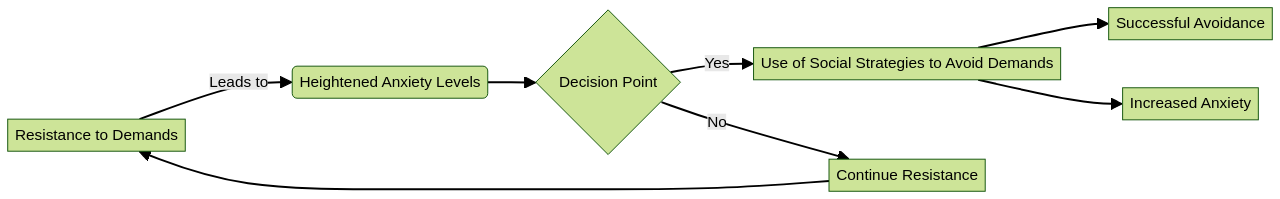
Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) is a behavioral pattern that can be seen in children diagnosed with ADHD. This pattern is characterized by a strong resistance to everyday demands and expectations, which is often a result of heightened anxiety levels. It's not uncommon for children who display PDA to appear socially adept. However, this is often a facade, used as a strategy to resist demands. Understanding PDA is crucial for those dealing with ADHD, as it can significantly impact a child's ability to focus and remain attentive.
Fortunately, there are resources available designed to help manage the daily demands and expectations for children with PDA and ADHD. These resources offer strategies and support that can assist parents and caregivers in navigating the challenges that might arise. By utilizing these resources, parents can acquire the knowledge and tools necessary to better understand the needs of their child and provide appropriate support in various situations.
Subscribe to ASD Media's newsletter for the latest news and unlimited digital access to resources.
It is important for parents to seek advice from professionals and connect with support networks to ensure that their child's unique needs are met.
To aid children with PDA and ADHD in developing genuine compliance and cooperation, it is crucial to provide strategies and support tailored to their specific needs.
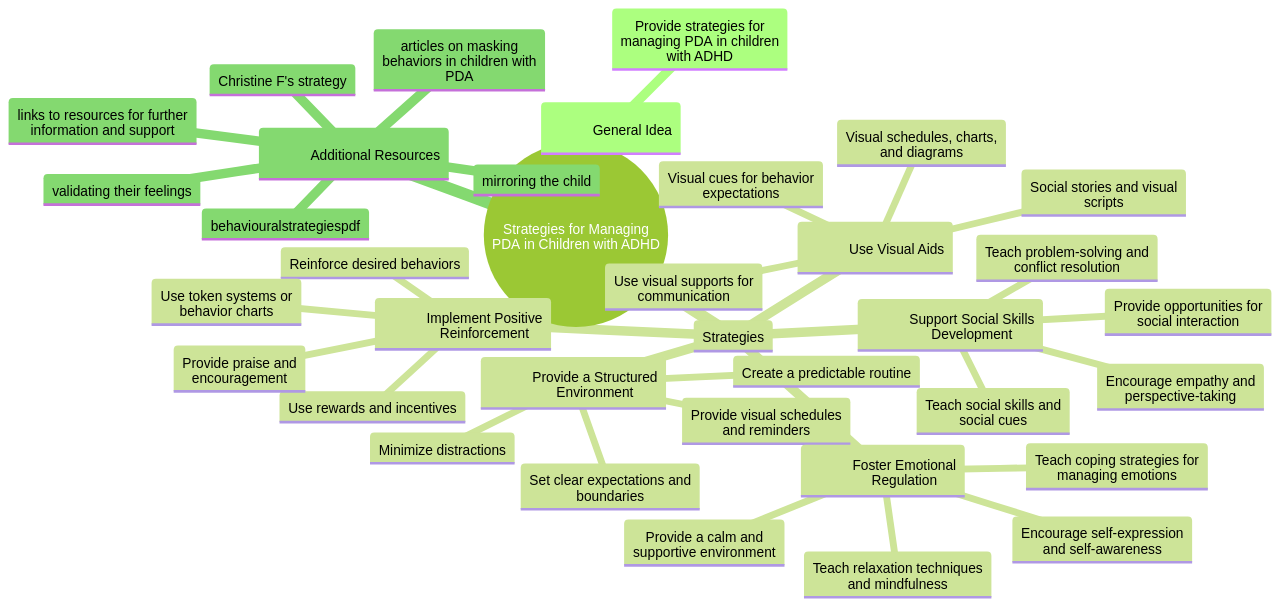
This can include establishing a structured and predictable environment, using visual aids and schedules to help with organization and transitions, and implementing positive reinforcement techniques to encourage desired behaviors. Moreover, the use of social stories, role-playing, and social skills training can assist in the development of appropriate social interactions and communication skills. Collaborating with professionals such as therapists, educators, and behavioral specialists can also be beneficial in creating an individualized plan to address the unique challenges faced by children with PDA and ADHD.
While it may be challenging, it's essential to remember that every child is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Therefore, it's important to stay patient, flexible, and open to trying different strategies and approaches. By doing so, parents and caregivers can provide the best possible support for their child, ultimately improving their ability to concentrate and remain attentive.
2. Prevalence of PDA in Children with ADHD: A Closer Look at the Statistics
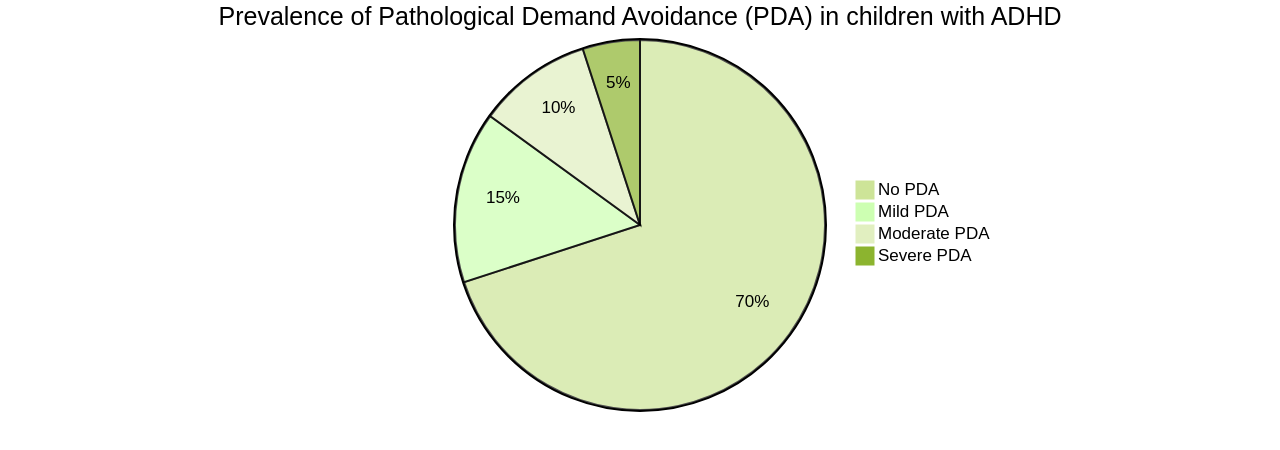
The relationship between Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children is a complex and widely researched subject. While PDA is not exclusive to children with ADHD, a significant correlation between the two conditions is evident. It's been hypothesized that about 14% of children with ADHD display PDA traits, which underscores the need for raising awareness and creating targeted management strategies for this intersection.
ADHD, characterized by chronic inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, is the most common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood. Recent research indicates that the prevalence of ADHD in children and adolescents aged 4 to 17 years in the US remains steady at around 10%. This information was gathered from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), a nationally representative cross-sectional survey.
However, the prevalence of ADHD varies widely based on factors such as age, gender, race, ethnicity, and the family's income-poverty ratio. Interestingly, the estimated prevalence of ADHD in the US exceeds previous global estimates. Therefore, it's crucial to conduct further investigations to identify modifiable risk factors and ensure adequate resources are available for the treatment of individuals with ADHD.
Given these facts, the high prevalence rate of PDA among children with ADHD underscores the importance of comprehensive assessments and targeted interventions.
This is particularly significant considering the high rates of comorbid disorders among children and adolescents with ADHD, with autism spectrum disorder and anxiety disorders being the most common.
Available interventions for addressing PDA in children with ADHD focus on empowering these children to thrive and succeed. These strategies include providing unlimited digital access and offering social skills development programs for children with autism. Such interventions aim to unlock the potential of children with ADHD and equip them with the necessary support and tools to overcome PDA-related challenges.
Further research is necessary to understand the factors contributing to the high rate of comorbidity in individuals with ADHD and to develop effective strategies to manage PDA in the context of ADHD. Studies have found that children with ADHD may also exhibit PDA traits, such as avoiding demands or feeling overwhelmed by everyday tasks. However, it's important to note that not all children with ADHD will have PDA, and vice versa. More research is needed to gain a more profound understanding of the link between these two conditions in children.
3. Identifying Symptoms of Pathological Demand Avoidance in Children with ADHD
Managing Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in children with ADHD can be a challenging task due to the overlap of symptoms, but with a keen understanding of the telltale signs, the journey becomes more navigable. A significant indicator of PDA is the child’s resistance to ordinary demands, not out of rebellion, but an intense aversion linked with anxiety.
Children may also resort to social strategies to dodge demands, utilizing charm, negotiation, distraction, or even feigning illness. These are defense mechanisms to avoid facing demands head-on.
Excessive mood swings, rapid and intense, often spurred by the anxiety and stress of demands, are another symptom of PDA. This emotional volatility complicates the child's ability to effectively regulate their feelings.
Lastly, obsessive behavior, often directed towards people rather than objects, can be an indication of PDA. This obsession can lead to children becoming overly engaged or fixated on specific individuals.
Identifying these symptoms is the cornerstone of managing PDA, facilitating an understanding of the unique challenges faced by these children and the development of effective strategies to support them. Each child is unique, and the manifestation of these symptoms can vary widely.
While PDA is a lifelong trait, it can be managed with a comprehensive understanding and the implementation of supportive strategies and coping mechanisms. The aim is to foster an environment where the child feels safe and understood, alleviating the anxiety associated with demand avoidance.
In this journey of understanding and managing PDA, remember that there are numerous resources and support systems available, such as the PDA Society, which provides valuable information, research, and training courses on PDA. They also offer a platform for sharing experiences and learning from others dealing with similar challenges.
To manage obsessive behaviors in children with ADHD and PDA, implementing strategies and support systems is crucial. This includes the provision of structured routines, clear communication and instructions, and the use of visual aids to enhance understanding. Creating an inclusive environment where these children feel accepted and valued can greatly enhance their social interactions and overall well-being.
Promoting positive behaviors in children with ADHD and PDA can be achieved through various strategies and support systems. Providing a structured and consistent environment, establishing clear expectations, and offering rewards for desired behaviors are some of these strategies. Implementing behavioral interventions, such as social skills training and cognitive-behavioral therapy, can aid children with ADHD and PDA in learning and practicing appropriate behaviors. Collaborating with parents, teachers, and other professionals is also vital in promoting positive behaviors and supporting the overall well-being of these children.
By recognizing the signs and understanding the nature of PDA, we can take a significant step towards providing the right support for children dealing with this condition. It's all about fostering an environment of collaboration, flexibility, and understanding, which will ultimately help these children thrive.
4. The Role of ABA Therapy in Managing PDA: An Overview
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy unfolds a journey akin to gardening when dealing with Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in children with ADHD. It delves into the core reasons that trigger avoidance behaviors in a child, mapping out a route towards fostering more adaptive responses. The fundamental strength of ABA therapy lies in its commitment to nurturing positive behaviors and mitigating negative ones.
Let's visualize ABA therapy as a gardener tending to a young plant. The gardener comprehends the plant's needs for the right balance of sunlight, water, and nutrients to burgeon into a robust tree. In a similar vein, ABA therapy discerns the distinctive requirements of each child and designs strategies tailored to promote more adaptive behaviors.
Just as the gardener bolsters the plant's growth with suitable conditions and trims undesirable sprouts, ABA therapy reinforces positive behaviors and minimizes negative ones. This methodology, mirroring the gardener's caring cultivation, renders ABA therapy a potent instrument in managing PDA in children with ADHD.
ABA therapy paves the way for adaptive responses in children with PDA and ADHD through a variety of strategies. It promotes a structured and predictable environment, offers clear and concise instructions, and utilizes visual aids like schedules and visual cues. By breaking tasks into smaller steps and providing frequent breaks, it alleviates the overwhelming nature of larger tasks. Furthermore, it incorporates social stories, role-playing, and social skills training to aid children in learning appropriate social behaviors and responses. The therapy also emphasizes the importance of positive reinforcement and praise for desired adaptive responses, which serves to motivate children to continue exhibiting these behaviors.
ABA therapy techniques have proven effective in managing PDA in children with ADHD.
These techniques focus on identifying and modifying behaviors through structured and consistent intervention strategies. Visual schedules help children with ADHD and PDA understand and anticipate their daily routines, reducing anxiety and increasing predictability. Opportunities for choice-making give children some control over their environment, decreasing resistance to demands. Task analysis simplifies complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps, making them less daunting for children with ADHD and PDA. Reinforcement strategies, such as rewards or praise, encourage desired behaviors and motivate children to engage in tasks or activities. It is crucial to collaborate with a qualified ABA therapist to create a treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of each child with ADHD and PDA.
It is crucial to remember that every child is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. However, ABA therapy offers a flexible framework that can be adapted to meet each child's unique needs. Just like the gardener, who patiently tends to the sapling, allowing it to flourish, ABA therapy provides the supportive environment necessary for a child to develop more adaptive behaviors and better manage PDA.
5. Implementing Effective Strategies for Managing Demand Avoidance
Managing demand avoidance in children calls for a holistic approach that takes into account the child's unique needs and interests. This involves implementing strategies aimed at reducing anxiety and resistance, making tasks more appealing and manageable for the child.
Part of these strategies involves giving the child an array of choices, thus promoting a sense of autonomy. This can be achieved by setting clear expectations and boundaries, providing alternatives, and using visual supports. These techniques not only give the child control over their environment but also promote cooperation.
Another effective approach is the use of indirect language when presenting demands. This is often achieved by promoting social skills in children with autism, making them understand and respond to requests without feeling overwhelmed or pressured. This approach helps to create a positive and supportive environment where children can thrive and develop their communication skills.
Making tasks more engaging for the child is also essential in managing demand avoidance. This can be achieved by incorporating the child's interests into tasks. By aligning tasks with the child's interests, motivation and engagement are increased, leading to a decrease in resistance or refusal to participate. The child feels a sense of ownership and enjoyment in the tasks they are completing, promoting increased cooperation and a positive attitude towards these activities.
Creating a calm and supportive environment is also crucial in managing demand avoidance. This involves implementing strategies such as providing a structured and predictable routine, creating a designated safe space for the child, using visual aids and schedules to enhance communication and understanding, and implementing sensory breaks or activities. It is also essential to develop a positive and empathetic relationship with the child, understanding their individual needs and preferences, and adapting the environment accordingly. Involving professionals such as therapists or educators who specialize in working with children with demand avoidance can provide valuable guidance and support in creating an optimal environment for these children.
Remember, managing demand avoidance is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It requires techniques tailored to the child's needs, which can include providing clear and consistent expectations, breaking tasks into smaller steps, using visual supports, and providing positive reinforcement. It is also important to create a structured and predictable environment, and to provide opportunities for choice and autonomy whenever possible. Working with a qualified professional, such as a behavior therapist or psychologist, can also be beneficial in developing and implementing individualized strategies for managing demand avoidance in children.
To reduce anxiety and resistance in children with demand avoidance, a supportive approach is to create a predictable and structured environment. This can involve establishing consistent routines and schedules, providing clear and concise instructions, and using visual supports. Providing choices and opportunities for autonomy can also help reduce anxiety and increase cooperation. The environment should also be calm and soothing, using strategies such as sensory breaks or relaxation techniques to help regulate emotions and reduce anxiety. Working with professionals, such as occupational therapists or behavior specialists, can also be beneficial in developing individualized strategies to address anxiety and resistance in children with demand avoidance.
6. Navigating Support Services for Parents and Professionals Dealing with PDA
Support services play a vital role in managing Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA), a developmental disorder that falls under the autism spectrum and affects all areas of a child's development. These services include counselling sessions, parental training programs, and professional development initiatives for educators.
While ASD Media is a significant resource hub, it's worth noting that there's no specific mention of resources for managing PDA on their website. Therefore, exploring other specialized sources or websites for managing PDA is recommended. Also, there's no specific information about effective counseling strategies for PDA from ASD Media. To find such information, it would be best to consult reputable sources that specialize in autism and PDA, such as academic journals, reputable websites, or consult with professionals in the field of autism and counseling.
PDA is a condition first identified in 2003 by Elizabeth Newson. It is often overlooked or unrecognized by many professionals, leading to the use of strategies that are generally helpful for learners with autistic spectrum disorder but may not necessarily be beneficial for those with PDA.
The core features of PDA include a need to resist everyday demands made by others to manage acute anxiety. Learners with PDA may use social skills to manipulate, but this is often at a functional and logical level rather than at a deeper emotional level.
In managing PDA, practitioners and parents can adopt various helpful approaches, such as individualized and less direct methods, using calm and level emotions, implementing novelty and variety, using visual structures and disguising demands, reducing anxiety, and depersonalizing demands.
Getting a diagnosis for PDA involves completing a checklist and seeking a referral to a local pediatrician or team specializing in autism spectrum disorder. Support and advice can be sought from organizations such as the Elizabeth Newson Centre, the PDA Society, and the NAS Helpline.
Safeguarding is a key priority across all children's services. Together, we can navigate this journey and improve the lives of children living with PDA.
7. Enhancing Social Skills Development to Mitigate PDA Challenges
Developing social skills in children with ADHD, especially those grappling with Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA), can significantly alleviate associated challenges. A key instrument in this process is empowering these children with methods to manage anxiety, thereby enhancing their capability to interact successfully with others. This approach can lead to a reduction in avoidance behaviors and an improvement in their focus and attention.
Children with ADHD often struggle with social skills, due to a variety of factors such as weak executive functions, lack of practice, and lagging maturity. The social distancing measures introduced during the pandemic have compounded these challenges, making social interactions even more taxing. However, parents can play a crucial role in helping their children enhance their social skills.
Identifying the root cause of these difficulties and practicing solutions can be of enormous help. Direct instructions, combined with real-world practice, can aid children with executive function weaknesses in learning to self-regulate and actively participate in social scenarios. Assigning a mission or specific behavior to practice during playdates can also help children to work on particular skills.
Social skills training plays a vital role in managing anxiety in children with PDA. By providing structured and targeted interventions, this training can help children develop necessary skills for managing their anxiety and effectively engaging in social interactions. Strategies such as providing clear, structured instructions, breaking tasks into smaller steps, using visual supports and schedules, and providing opportunities for choice and control can be particularly effective.
Gradually increasing demands while providing support and reinforcement can also be beneficial. Additionally, incorporating social stories, role-playing, and modeling appropriate behavior can be very useful in teaching and reinforcing social skills. It's crucial to create a supportive and understanding environment that encourages and rewards positive social interactions and gradually increases the child's comfort and confidence in engaging in social situations.
Social skills training can provide several benefits for children with PDA, such as improving their communication, empathy, and cooperation skills. It can also enhance their ability to navigate social situations, understand social cues, and build meaningful relationships with others. This type of training can also boost their self-confidence and self-esteem, as they learn to interact effectively with their peers and adults.
Implementing social skills training for children with PDA requires adherence to best practices such as creating a structured and predictable environment, providing clear and explicit instructions, using visual supports, incorporating social stories and role-playing, and offering plenty of opportunities for practice and reinforcement. It's also important to tailor the training to meet the specific needs of each child, and to regularly monitor progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Organizations like the ADD Coach Academy (ADDCA) offer coach training and resources for ADHD education and support. Similarly, the Star Institute provides services like occupational therapy, speech language therapy, feeding therapy, and mental health services. They also offer home and school services, as well as education and professional courses for therapists. Their research center focuses on sensory processing and sensory integration, with a particular emphasis on SPD research. They offer social skills groups for children, where they work on social interaction skills and build common interests.
In summary, enhancing social skills in children with ADHD is a multifaceted process that requires a comprehensive approach. By identifying the root causes of their difficulties and implementing appropriate strategies, we can help these children overcome the challenges of PDA and improve their ability to focus and pay attention.
8. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Establishing a nurturing environment for managing Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) is paramount, and this task is being championed by ASD Media. They have created an interactive space that allows caregivers and professionals to share ideas, learn from each other, and provide essential support. This symbiotic setting nurtures understanding and encourages the development of effective strategies for managing PDA.
This community does more than offer emotional support; it also provides a wealth of resources for its members. The platform is organized into different sections like announcements, feedback, urgent support, recommendations, and a lounge for informal discussions. New members are encouraged to introduce themselves and find the help they need. The community extends its support to various mental health challenges, such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, eating disorders, abuse, bipolar disorder, attention deficit, addictions, personality issues, relationship problems, grief, parenting, and aging. Special discussion topics range from dealing with mental illness within the family to cognitive reframing, creating a safe space for open conversations and shared experiences.
Meanwhile, Warriors Connect is a private community that provides peer support for individuals diagnosed with mental health conditions and their caregivers. They maintain a members-only site filled with resources, including resilience stories, shared achievements, recommended resources, and archived conversations. The community also organizes public events, with video recordings available for later viewing. WhatsApp subgroups encourage focused discussions on specific topics. Members have access to emergency helplines for immediate assistance during periods of mental distress. The community covers a wide range of mental health conditions, from depression and anxiety to ADHD and handling comorbidities. They also offer support for various life aspects, including professional life, relationships, and holistic life.
To join Warriors Connect, individuals can send a request if they or someone they care for has been diagnosed with a mental health condition. Existing members can access the members-only site. Contact information for Warriors Connect, including a WhatsApp number and email address, is readily available.
In essence, these supportive communities foster a sense of belonging, understanding, and mutual support that is crucial for managing PDA. The exchange of experiences and ideas promotes effective PDA management strategies, lightening the load for everyone involved. Building such supportive communities involves providing resources and information about PDA to parents and caregivers, creating online forums for networking, promoting collaboration among professionals, and raising awareness about PDA through events and campaigns. These strategies not only reduce stigma but also promote understanding and acceptance, making the journey to effective PDA management a little less daunting.
9. Continuous Improvement and Positive Outcomes: The Impact of Collaborative Efforts on Managing PDA
The transformative power of collective action is a vital tool in addressing the challenges of Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in children with ADHD. It is through the unity of communities, pooling their insights, experiences, and strategies, that a dynamic environment is created. This environment fosters growth and facilitates effective management of PDA.
Drawing parallels from the healthcare sector, a multidisciplinary approach has been highly effective in managing complex health conditions. A similar collaborative approach can be beneficial in promoting effective social skills development in children with ADHD experiencing PDA. It involves working together with parents, educators, and other professionals to create a supportive and structured environment for the child. By implementing consistent routines, clear expectations, and providing visual aids, children with ADHD and PDA can better manage their impulsivity and social interactions. Additionally, incorporating sensory breaks and offering choices can help reduce anxiety and promote self-regulation.
Effective approaches for managing PDA can vary depending on the specific needs and challenges of the individual. Some common strategies may include creating a structured and predictable environment, using visual supports and schedules, providing clear and concise instructions, offering choices and flexibility, and implementing strategies to reduce anxiety and sensory overload.
During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, a university community partnership was formed to manufacture medical personal protective equipment (PPE). This collaborative effort led to four types of participants: connectors, coordinators, consultants, and contributors. The initiative underscored the importance of early coordination, communication, and bringing together the right people. It also highlighted the potential of such relationships formed during crisis response for future disaster response efforts.
Translating these lessons to the context of managing PDA, it's clear that the collective effort of parents, professionals, and the wider community is a potent force in driving positive outcomes for children with ADHD experiencing PDA. By bringing together multiple stakeholders, such as educators, therapists, and parents, a comprehensive and holistic approach can be developed. This approach may include individualized strategies, such as creating a structured environment, providing clear expectations and instructions, and offering choices and flexibility. Additionally, implementing interventions that focus on building trust and rapport, promoting self-regulation skills, and addressing sensory sensitivities can also be valuable in managing PDA. Regular communication and coordination among all involved parties are crucial for the success of collaborative efforts in managing PDA.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is crucial for parents and professionals. PDA is a behavioral pattern characterized by a strong resistance to everyday demands, often stemming from heightened anxiety levels. This can significantly impact a child's ability to focus and remain attentive. Fortunately, there are resources available to help manage the challenges associated with PDA and ADHD. These resources offer strategies and support for parents and caregivers, enabling them to better understand their child's needs and provide appropriate support. By implementing tailored strategies and seeking guidance from professionals, parents can create a structured and supportive environment that promotes positive behaviors and reduces demand avoidance in children with ADHD and PDA.
The broader significance of understanding PDA in children with ADHD lies in the potential for improved outcomes and quality of life for these individuals. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by children with PDA, parents and professionals can develop effective strategies to support their social skills development, manage anxiety, and create an inclusive environment. This not only helps the child navigate daily demands but also enhances their overall well-being by promoting positive behaviors and reducing stress levels. Additionally, raising awareness about PDA within the community can reduce stigma, foster empathy, and encourage collaboration among stakeholders. By working together and sharing experiences, we can create a supportive network that empowers parents, professionals, and individuals with ADHD and PDA to navigate this journey of understanding and managing PDA.
Start now to access valuable resources and support for managing PDA in children with ADHD.




