Introduction
Navigating the complexities of communication disorders can be a daunting journey for parents and caregivers. Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) present unique challenges, often overlapping in symptoms yet distinct in their underlying causes. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing the right support and interventions tailored to each child's needs.
As research continues to unveil the nuances between SCD and ASD, it becomes increasingly clear that early identification and effective treatment strategies are essential for fostering meaningful communication and social engagement. This article delves into the characteristics of both disorders, highlights their similarities and differences, and offers guidance on effective treatment approaches, empowering parents to advocate for their children's development and well-being.
Understanding Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder
Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) is fundamentally characterized by challenges in using both verbal and nonverbal communication for interpersonal interaction. Individuals with SCD often find it difficult to interpret cues, engage in meaningful conversations, and modify their communication style to suit varying contexts.
In contrast, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents a broader spectrum of symptoms, including:
- Difficulties with social engagement
- Repetitive behaviors
- Restricted interests
Notably, ASD is frequently linked with sensory sensitivities and a more diverse range of behavioral issues. Understanding these distinctions is vital for parents and professionals alike, as it empowers them to tailor their support strategies effectively.
Recent research indicates that strict diagnostic criteria for SCD may inadvertently lead to the under identification of individuals who could significantly benefit from targeted interventions and support. As noted by Courtenay Frazier Norbury, 'Recognizing the nuances between SCD and ASD is crucial for enhancing the provision of appropriate resources and fostering better outcomes for affected individuals.'
Moreover, Cronbach's α values for assessments related to SCD have ranged from .92 to .97, underscoring their reliability in identifying the disorder. Additionally, a case study involving teacher reports highlighted that teachers provided CCC-2 reports for 321 children, with many identified as having low language, demonstrating real-world implications for understanding and addressing SCD in educational settings.
Identifying Overlapping Symptoms: SCD vs. ASD
Children identified with both Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often display overlapping symptoms, including difficulties in comprehending cues and obstacles in starting or sustaining conversations. For instance, behaviors such as avoiding eye contact or failing to respond to interpersonal overtures can occur in both conditions. However, the reasons behind these behaviors are distinct.
A young person with SCD typically struggles with pragmatic language skills, which affects their ability to use language in social contexts, while an individual with ASD faces broader challenges in social interactions, including difficulties with nonverbal communication and understanding social norms. Understanding these nuances is essential not only for clinicians but also for parents.
As highlighted in recent research, 555 youths (86%) in the ASD group had prior diagnoses, emphasizing the necessity of precise evaluations. Kim et al. highlight that in cases where DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5 ASD diagnoses diverged, many were diagnosed with SCD and other psychiatric conditions, illustrating the significant overlap in service needs between individuals with SCD and ASD.
This overlap is further supported by current studies that examine the similarities and differences in symptoms, reinforcing the importance of tailored interventions. The research titled 'Clinical and Public Health Implications of SCD' emphasizes the need for such interventions to tackle the unique challenges encountered by youth with SCD, ensuring they receive the support necessary for their development.
By identifying these overlapping symptoms and the unique behavioral differences, parents can advocate more effectively for their offspring's needs, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder and Autism
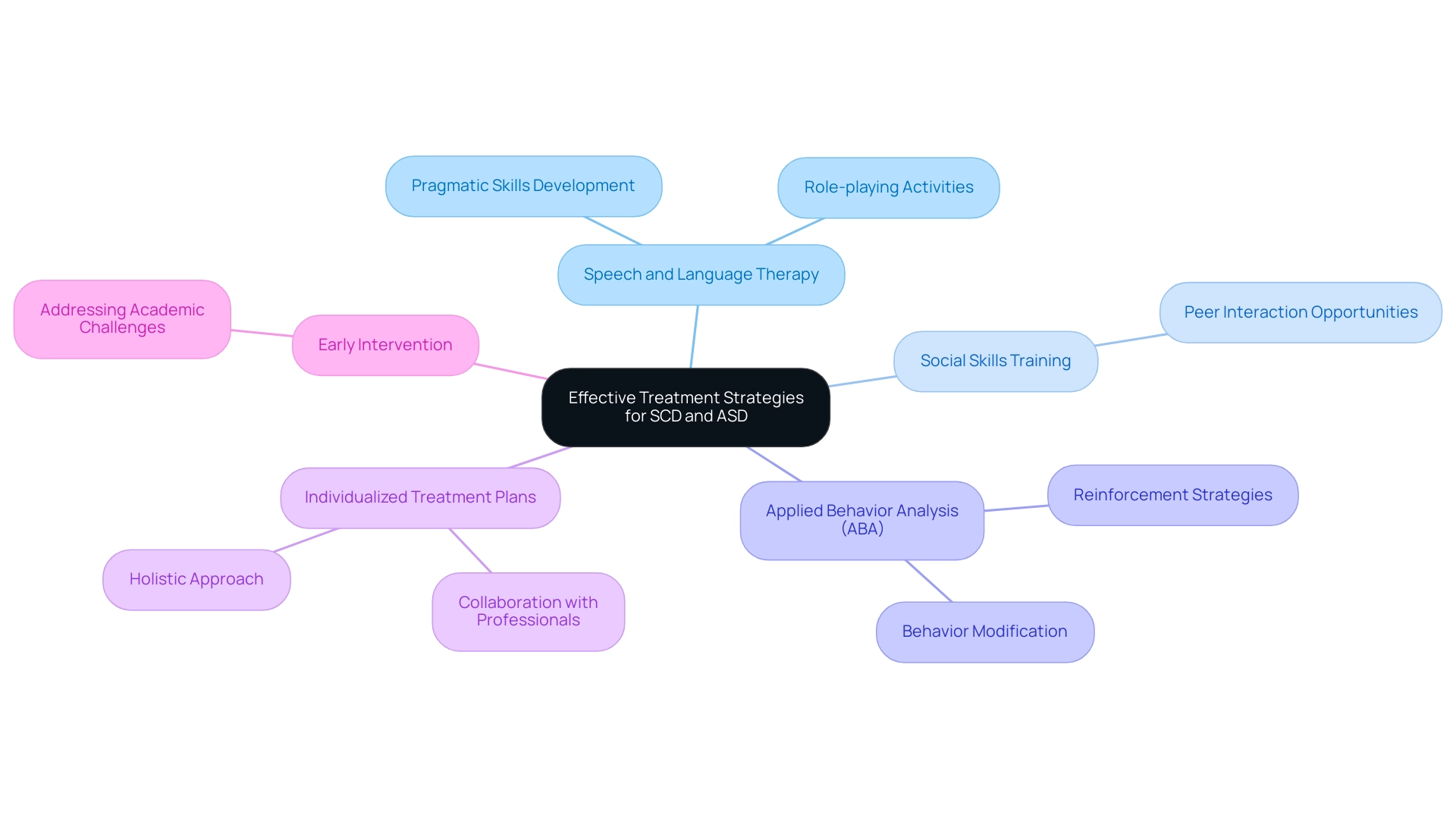
Effective treatment strategies for Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) often prioritize speech and language therapy that enhances pragmatic language skills, social skills training, and role-playing activities to better navigate social contexts.
For individuals on the Autism Spectrum, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out as a prominent approach, focusing on behavior modification through carefully structured reinforcement strategies.
Recent findings indicate that individuals exhibiting abnormal language and cognitive screenings have a significantly elevated risk for future academic challenges, underscoring the necessity for early intervention.
Both SCD and ASD can greatly benefit from participation in social skills groups, which create opportunities for peer interactions within structured environments.
As one expert points out, these young individuals often struggle with the functional aspects of communication, highlighting the need for targeted strategies.
Furthermore, speech therapy plays a crucial role in treating SCD, assisting young individuals in developing essential communication skills.
Parents are encouraged to work closely with professionals to develop individualized treatment plans that cater to their children's unique needs, ensuring a holistic approach to their development and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Social Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for parents and caregivers navigating the complexities of communication challenges. Both disorders present overlapping symptoms, such as difficulties with social cues and conversation, yet they stem from different underlying issues. Recognizing these nuances allows for more accurate diagnoses and tailored interventions that can significantly enhance a child's communication skills and social interactions.
Effective treatment strategies play a critical role in the development of children with SCD and ASD. From speech and language therapy focused on pragmatic skills to behavioral approaches like Applied Behavior Analysis, early intervention is paramount for fostering meaningful communication and social engagement. Active participation in social skills groups also provides invaluable opportunities for practice and growth in a supportive environment.
Ultimately, empowering parents with knowledge and resources is vital in advocating for their children's needs. By understanding the unique characteristics of SCD and ASD, and implementing appropriate interventions, parents can help pave the way for their children's success and well-being. The journey may be challenging, but with the right support and strategies in place, positive outcomes are within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD)?
Pragmatic Communication Disorder (SCD) is characterized by challenges in using both verbal and nonverbal communication for interpersonal interaction, making it difficult for individuals to interpret cues, engage in meaningful conversations, and adjust their communication style to different contexts.
How does SCD differ from Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
While SCD primarily involves difficulties in pragmatic language skills and social communication, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a broader range of symptoms, including difficulties with social engagement, repetitive behaviors, and restricted interests, along with sensory sensitivities.
Why is it important to understand the differences between SCD and ASD?
Understanding the distinctions between SCD and ASD is crucial for parents and professionals to tailor support strategies effectively, ensuring that individuals receive appropriate resources and interventions based on their specific needs.
What recent research findings highlight issues with diagnosing SCD?
Recent research suggests that strict diagnostic criteria for SCD may lead to under-identification of individuals who could benefit from targeted interventions. This emphasizes the importance of recognizing the nuances between SCD and ASD for better outcomes.
What do Cronbach's α values indicate about assessments related to SCD?
Cronbach's α values for assessments related to SCD have been reported to range from .92 to .97, indicating high reliability in identifying the disorder.
What overlapping symptoms do children with SCD and ASD exhibit?
Children with both SCD and ASD may display overlapping symptoms such as difficulties in comprehending cues and challenges in starting or maintaining conversations, including behaviors like avoiding eye contact.
How can understanding the unique differences between SCD and ASD benefit parents and clinicians?
Recognizing the distinct reasons behind similar behaviors in SCD and ASD can help clinicians and parents advocate more effectively for appropriate interventions and support tailored to each child's unique needs.
What treatment strategies are effective for individuals with SCD?
Effective treatment strategies for SCD often include speech and language therapy to enhance pragmatic language skills, social skills training, and role-playing activities to navigate social contexts.
What approach is commonly used for treating individuals on the Autism Spectrum?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a prominent approach for individuals with ASD, focusing on behavior modification through structured reinforcement strategies.
Why is early intervention important for individuals with SCD and ASD?
Early intervention is crucial as individuals showing abnormal language and cognitive screenings are at a significantly elevated risk for future academic challenges, highlighting the need for timely support.
How can social skills groups benefit children with SCD and ASD?
Participation in social skills groups can create opportunities for peer interactions within structured environments, which can enhance social communication skills for both SCD and ASD individuals.
What role do parents play in the treatment of children with SCD and ASD?
Parents are encouraged to work closely with professionals to develop individualized treatment plans that cater to their children's unique needs, ensuring a holistic approach to their development and overall well-being.




