Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that significantly influences communication, social interaction, and behavior. It is typically identified in early childhood and can profoundly shape an individual's life journey.
In this article, we will explore the early signs of autism in babies, the importance of early identification and intervention, seeking professional evaluation and support, and supporting your baby's development. By understanding these key aspects, parents can navigate the challenges of raising a child with autism and ensure their well-being.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that significantly influences communication, social interaction, and behavior. It is typically identified in early childhood and can profoundly shape an individual's life journey.
ASD is marked by a diverse range of symptoms, which may not fully surface until the child's social demands surpass their ability to cope. While the root cause of ASD remains elusive, we understand that the disorder often appears by age 3.
Early diagnosis and intervention, however, can commence even sooner and prove to be instrumental in managing the disorder effectively. Though significant strides have been made in discerning the early signs of ASD, the average age of diagnosis still hovers around 3 years.
This delay in diagnosis often means missing out on early intervention, a critical window for managing the disorder. Therefore, it is crucial to continuously monitor the child's behavior over time, enabling us to identify early ASD manifestations and chart subtle behavioral changes.
ASD's impact is diverse and pervasive. It affects every aspect of a person's life, from learning to socializing.
While some individuals with high-functioning autism and average or above-average intelligence manage to mask their autistic traits, others may struggle with daily activities. The condition is a significant disability for the majority, with only 10-20 percent of children diagnosed before age 5 capable of living independently as adults.
The prevalence of autism in Australia indicates that males are more likely to be diagnosed with autism than females, with a male-to-female ratio of about 3:1. The increase in autism prevalence in Australia can be attributed to various factors, including broadening diagnostic criteria, heightened awareness and screening efforts, genetic and environmental factors, and increased support and services. Finally, ASD is not a condition that can be 'cured.' Instead, it requires a range of support and intervention strategies to manage symptoms effectively. Since ASD manifests differently in individuals, treatment plans will also vary. These plans aim to reduce symptoms that impact everyday activities and overall quality of life. Studies have proven that early diagnosis and intervention have long-term effects on minimizing symptoms.
Early Signs of Autism in Babies
Identifying early indicators of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in infants is crucial for timely intervention and support. Each ASD child is distinct, exhibiting varying symptoms, but certain common early signs can be observed by parents and caregivers. 1.
Eye Contact: Infants later diagnosed with ASD might struggle with initiating or sustaining eye contact. 2. Communication Delays or Anomalies: ASD infants might display delayed speech or show disinterest in using words or gestures for communication.
- Social Engagement Deficiency: ASD infants might not respond to their name or exhibit interest in social interactions or play. 4.
Repetitive Behaviors: ASD infants might engage in repetitive behaviors, such as hand-flapping, rocking, or spinning objects. 5. Sensory Sensitivities: ASD infants might show hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to certain sounds, textures, or lights.
These signs alone are not definitive for ASD diagnosis. However, if these signs are observed in your child, it is advisable to seek professional healthcare consultation for further assessment and guidance. Research indicates that early diagnosis can improve life quality.
As part of a regular health visit, developmental screenings focused on ASD are recommended at ages 18 and 24 months. This proactive approach can have a significant impact, connecting families to support and services as early as possible. Remember, early detection can lead to better long-term outcomes due to the higher 'plasticity' of younger children’s brains, allowing them to adapt more easily.
The Importance of Early Identification and Intervention
Recognizing autism's early signs and securing appropriate support can fundamentally enhance children's outcomes. Studies indicate that early intervention can boost communication skills, social interactions, and cognitive development in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
However, it's important to note that the intervention strategies and programs available for children with autism vary significantly in philosophy and accessibility. Many are designed for preschool-aged children, and not all are widely known or available.
In fact, there's a lack of empirical studies comparing these various intervention programs. Despite this, there's a professional consensus about the crucial aspects of treatment, including intensity, family involvement, and focus on generalization.
Thanks to recent research, routine screening for autism has been embedded in well-baby checkups, enabling early signs of autism to be identified in children as young as 12–14 months. This advance in healthcare, supported by organizations like the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), has made a significant impact on children and families, connecting them to support and services as early as possible. Autism, a spectrum disorder with a wide variation in symptom type and severity, affects how people interact, communicate, behave, and learn. Therefore, early detection and intervention are vital in supporting children with autism and their families.
Seeking Professional Evaluation and Support
When early signs of autism are noticed in a child, it's crucial to connect with a healthcare professional or a developmental disorders specialist. They can conduct a thorough evaluation to confirm if the child meets the autism diagnosis criteria.
While there's a broad consensus on specific aspects of treatment, such as intensity, family involvement, and focus on generalization, it's essential to note that programs for children with autism vary in philosophy. Most of these programs are designed for preschool-age children, and not all are widely known or accessible.
Research shows that it's possible to train community-based providers to diagnose autism accurately. This can potentially address the challenge of long waits for specialist evaluations, which can take up to a year or more in some regions.
Early detection and intervention can significantly improve child and family outcomes. Screening tools alone cannot confirm developmental delays or result in diagnoses.
A detailed evaluation by a trained provider can determine the need for treatment and early developmental intervention services. For children aged 0-3 years, referrals to early intervention programs can be made, while children aged three years and older can be directed to special education services for developmental evaluation. Remember, parents are reliable sources of information about their child's development. Therefore, they play an essential role in monitoring their child's progress. It's also worth noting that autism typically appears by age 3, but for some children, symptoms may not fully manifest until social demands exceed their capacity to cope with them. Hence, early detection and intervention are key to managing the impact of autism on family dynamics.

Supporting Your Baby's Development
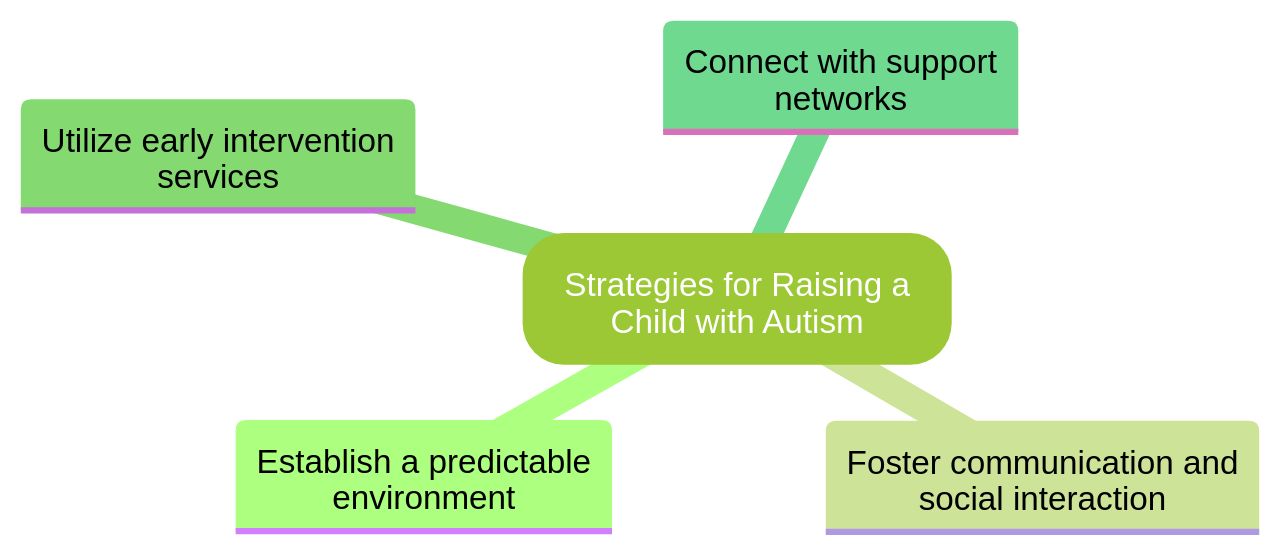
Navigating the journey of raising a child with autism can be complex. However, you can positively influence your child's development with these steps:
1.
Establish a predictable environment: Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often flourish in settings with defined routines and expectations. 2.
Foster communication and social interaction: Engage your child in activities that enhance social engagement and communication. This could be through reading, singing, or playing games.
- Utilize early intervention services: Programs such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, which are designed for children of preschool age, can offer personalized support to address your child's needs and encourage their growth.
However, it's important to note that not all these programs are widely known or available, and there's a lack of research comparing the various intervention programs. 4.
Connect with support networks: Participating in support groups or connecting with other parents of children with autism can offer valuable resources, advice, and emotional support. Remember, each child with autism is unique, and their needs can differ. By recognizing early signs and seeking suitable help, you can play a crucial role in helping your child reach their full potential. As a caregiver, if you notice any developmental delay at any age, consult a doctor for an evaluation to identify any underlying causes and recommend supportive services if necessary. Additionally, using communication aids such as eye contact gestures, pictures, or symbols can help convey what you're saying to your child. Allow extra time for your child to understand what you say to them and consider using other communication tools such as Makaton or the Picture Exchange Communication System. Seek additional help from a speech and language therapist if necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, early identification and intervention are crucial for effectively managing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Recognizing the early signs of autism in babies, such as difficulties with eye contact, communication delays, social engagement deficiency, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities, is vital.
Parents and caregivers should seek professional healthcare consultation if they observe these signs in their child. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, enhancing communication skills, social interactions, and cognitive development in children with ASD.
Routine screenings during well-baby checkups have made it possible to identify early signs of autism as young as 12-14 months. This connects families to support and services at the earliest stage.
When noticing early signs of autism, connect with a healthcare professional or developmental disorders specialist for a thorough evaluation. They can confirm the diagnosis criteria and recommend suitable treatment options.
Intervention programs for children with autism may vary in philosophy, so finding the right program is essential. As parents and caregivers, you play a vital role in supporting your baby's development.
Establish a predictable environment with defined routines and expectations. Engage in activities that foster communication and social interaction. Utilize early intervention services like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy and seek support from speech and language therapists when needed. By recognizing early signs of autism and seeking appropriate help, you can make a significant impact on your child's development. Remember that each child with autism is unique, so their needs may differ. Stay proactive in monitoring their progress and utilize various communication tools to aid understanding. With early detection and intervention, you can help your child reach their full potential and navigate the challenges of living with autism successfully.




