Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for parents, professionals, and society as a whole. ASD is a unique neurodevelopmental condition that impacts social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior. The broad range of symptoms and their severity can vary greatly among individuals, making it challenging to identify and recognize signs of ASD. However, early recognition and intervention can greatly improve outcomes for individuals with ASD. In this article, we will explore various aspects of autism, including key signs and symptoms, social communication and interaction skills, restricted or repetitive behaviors, sensory processing issues, challenging behaviors, and navigating support services. By gaining a deeper understanding of these topics and implementing effective strategies, we can create a more inclusive society that supports and values individuals with ASD
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a unique neurodevelopmental condition, characterized by its impact on an individual's social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' denotes the broad range of symptoms and their severity, which can differ greatly among individuals. Identifying signs and symptoms of ASD is crucial, as they can include social difficulties, differences in information processing, sensory processing difficulties, executive dysfunction, issues with fine motor skills, repetitive behaviors, communication difficulties, special interests, and developmental delays. Recognizing these signs in children can be challenging, but early recognition and intervention can greatly improve outcomes.
ASD is a neurotype with which individuals are naturally born. It does not discriminate based on gender and does not dissipate as one ages. Individuals with autism spectrum disorder may also have sensory sensitivities and difficulty with changes in routine. It's important to note that autism is not a disease or an illness that can be cured. It's considered a disability under the American Disabilities Act, and individuals with autism are entitled to reasonable accommodations in school or at work.
While ASD is often characterized by a focus on the self and the internal world, it's crucial to understand that autistic brains are not flawed, but rather they function differently from neurotypical brains. Strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism, such as social skills training, social stories, visual supports, and structured play activities, can improve their social interaction skills. For individuals with limited verbal skills, augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems, such as sign language or speech-generating devices, can be helpful.
The act of masking, or suppressing autistic traits to blend in with neurotypical people, can lead to anxiety, depression, and burnout. To support independence in individuals with ASD, creating a structured environment, establishing clear routines and expectations, and providing visual supports to aid in communication and understanding can be beneficial. Additionally, teaching self-care skills and promoting self-advocacy can empower individuals with ASD to become more independent in their daily lives.
It's also important to acknowledge that girls and women are often underdiagnosed due to the ASD criteria being primarily based on the characteristics observed in young boys. Individuals on the autism spectrum frequently experience co-existing mental health conditions such as ADHD, anxiety disorder, depression, PTSD, among others.
Megan Anna Neff, an autistic psychologist, provides a quote that underscores the importance of understanding autism beyond medical definitions, "As an autistic person in the medical profession, I find this definition inadequate. Instead, I view autism as a form of neurodivergence, diverging from the norms and culture of neurotypicality." This perspective emphasizes the need to understand and appreciate the diverse experiences of individuals with ASD, moving beyond stereotypical representations and embracing the neurodiversity movement.
Finally, it's crucial to create an inclusive environment that supports the needs of individuals with ASD and fosters understanding and acceptance. This can be achieved through education and awareness, providing appropriate support and resources, promoting inclusive practices, and encouraging open communication and dialogue. By implementing these strategies, we can create a more inclusive society that values and supports individuals with ASD
Create an inclusive society that supports individuals with ASD
2. Recognizing Key Signs and Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Deciphering the primary signs and manifestations of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be a profoundly intricate process, as symptoms can differ greatly among individuals. However, some common characteristics often associated with autism include challenges in social interaction, difficulties in communication, and the presence of repetitive behaviors.
Detecting these indicators as early as possible is vital as it can lead to swift intervention.

Researches and initiatives conducted by reputable institutes have highlighted the importance of early detection. It's not just beneficial, but pivotal in managing ASD.
This view is further supported by the broader conversation surrounding autism. The earlier ASD can be diagnosed, the sooner therapies such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy can be initiated. These therapies can play a crucial role in assisting children with autism to learn new skills and realize their full potential. The collective agreement among researchers and healthcare professionals is unambiguous: early intervention can notably improve long-term outcomes for children with autism.
Given the complexity, recognizing signs of ASD in children can be challenging. However, some common signs to look out for include difficulties with social interaction, repetitive behaviors, delayed speech or language skills, and sensitivity to sensory stimuli. If you suspect a child may have ASD, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation, proper diagnosis, and guidance on the next steps to support the child's development.
Effective strategies for managing ASD include early intervention, which refers to providing support and services to children with ASD as early as possible.
These interventions may include behavioral therapies, speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. The goal is to address the core symptoms of ASD, such as communication difficulties and social challenges, and help children develop their skills and abilities. Early intervention can have a significant impact on the long-term outcomes for individuals with ASD, improving their social and communication skills, reducing challenging behaviors, and enhancing their overall quality of life
Invest in early intervention for better outcomes in ASD
.
Understanding social interaction challenges in individuals with ASD can be complex. These challenges can make it difficult for individuals with ASD to form and maintain meaningful relationships and navigate social situations effectively. However, with appropriate support, interventions, and strategies, individuals with ASD can develop and improve their social skills and enhance their overall social interactions.
Effective communication strategies for individuals with autism can greatly enhance their social skills. By using visual supports, such as picture schedules or social stories, individuals with autism can better understand and follow conversations. These strategies can promote successful communication and improve social interactions for individuals with autism.
Managing repetitive behaviors in individuals with ASD requires a multi-faceted approach. Some effective strategies may include using visual schedules and social stories to promote predictability and reduce anxiety, engaging individuals in structured activities and routines to redirect their focus, and implementing sensory-based interventions to address sensory sensitivities that may be contributing to the repetitive behaviors.
Early recognition and intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is of crucial importance. By intervening early, individuals with ASD can have better chances of developing important skills, improving communication and social interactions, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Through early intervention programs, individuals with ASD can receive specialized and individualized support to help them develop essential skills and reach their full potential. These programs often focus on providing therapies and interventions that address the unique needs and challenges faced by individuals with ASD. By starting intervention early, individuals with ASD can improve their communication, social interaction, and adaptive skills, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Promoting early intervention for better outcomes in ASD is important for maximizing the potential of children with autism. Early intervention can help address developmental delays and improve social, communication, and cognitive skills. Timely intervention can lead to significant improvements in overall functioning and long-term outcomes for individuals with ASD. It is crucial to provide appropriate support and resources to parents and caregivers to navigate autism support services and access early intervention programs
3. Social Communication and Interaction Skills in Autism
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may experience challenges in social communication and interaction. These challenges can manifest as difficulties in understanding and expressing emotions, interpreting social signals, and maintaining conversations. Such issues can create obstacles in forming and sustaining relationships, emphasizing the importance of understanding these challenges in order to provide effective support and intervention.
Research has examined the impact of an Autism Acceptance Training (AAT) program on social interactions between autistic and non-autistic adults. Results revealed an increased interest in future interactions with autistic individuals among non-autistic adults who underwent the AAT program. However, the quality of interaction and initial impressions did not show significant differences between those who received the training and those who did not. This suggests that while the AAT program can enhance mutual social interest, broader changes are necessary to bridge the social gap between autistic and non-autistic adults.
This research underscores the need to consider the role of non-autistic individuals and their behaviors in the social experiences of autistic individuals. This perspective challenges the traditional deficit model approach that primarily focuses on modifying the behaviors of autistic individuals. Instead, it proposes alternative methods such as improving knowledge and acceptance of autism among non-autistic individuals, in order to alleviate interpersonal difficulties.
In a related context, a step-by-step social skills curriculum called "How to Talk with Friends" has been developed specifically for children with autism. This curriculum is designed to enhance conversation skills and the ability to communicate and interact with peers. It includes weekly social skills lessons that cover a broad range of conversation aspects, from asking about a friend's interests to interpreting nonverbal cues. These lessons are scripted for easy implementation and can be used by parents as well as professionals. User reviews indicate the effectiveness of this curriculum in teaching social skills to children with autism.
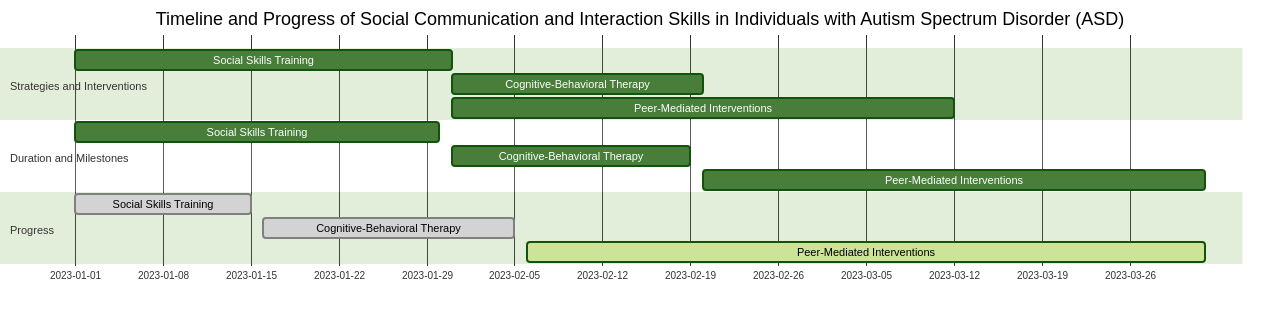
In addition to these interventions, other strategies can be employed to improve social communication skills in individuals with ASD. These strategies include social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and peer-mediated interventions. Visual supports, social stories, and social scripts can aid in teaching individuals with ASD appropriate social behaviors and interactions. Creating structured and predictable environments can also help individuals with ASD feel more comfortable and confident in social situations.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is another effective technique for teaching social skills to individuals with ASD. ABA therapy focuses on breaking down social skills into smaller, manageable steps and using positive reinforcement to teach and reinforce these skills. This can include teaching greetings, turn-taking, sharing, and other social interactions. ABA therapy also emphasizes the use of visual supports and structured teaching methods to help individuals with ASD understand and practice social skills.
Teaching individuals with ASD to read social cues can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help. These include using visual supports, providing direct instruction, practicing in natural settings, using social skills training programs, and fostering peer interactions. Remember, every individual with ASD is unique, so teaching strategies should be tailored to their specific needs and abilities.
In summary, understanding the unique social communication and interaction challenges faced by individuals with ASD is key for the development of effective support mechanisms and interventions. Whether it's through programs like AAT or curriculums like "How to Talk with Friends," or through other strategies and interventions, these efforts can help individuals with ASD navigate their social world more easily
4. Restricted or Repetitive Behaviors or Interests: A Closer Look
A prominent trait of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is the occurrence of restrictive and repetitive behaviors (RRBs). These can manifest in a multitude of ways, such as repetitive motor movements like hand-flapping, or the ordering of objects in a specific manner. Another common RRB is echolalia, which involves the repeated utterance of words or phrases.
Individuals with autism often exhibit a strong preference for consistency, which can be seen in their adherence to specific routines or the manner in which they perform tasks. These routines can provide a sense of predictability and comfort, but they can become detrimental when they disrupt daily activities or impede social interactions.
For instance, a disruption in these routines can result in anxiety or escalate to more severe problem behaviors, such as aggression. Nevertheless, the implementation of behavioral interventions has shown to be effective in managing and reducing the impact of RRBs. By employing these strategies, individuals with autism can participate in a wider array of activities and enhance their social interactions.
Promoting flexibility in individuals with ASD is one of the strategies that can be employed. This strategy aims to help individuals with ASD to develop and improve their ability to adapt to changes and transitions. This may involve the use of visual supports, social stories, and structured routines. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist who specializes in working with individuals with ASD to select the most suitable strategies for each individual.
Another possible strategy for supporting individuals with ASD is providing them with a variety of coping mechanisms. This could include teaching them relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises or mindfulness. Additionally, introducing them to sensory tools or activities that help regulate their sensory input could also prove beneficial. It's important to customize these coping mechanisms to cater to each individual's specific needs and preferences as what works for one individual with ASD may not necessarily work for another.
While the context doesn't provide specific strategies for managing intense interests in individuals with ASD, it is recommended to seek advice from professional sources or consult with professionals who specialize in ASD for strategies on managing these behaviors. It's also advised to explore reliable sources to better understand the impact of routines in ASD and techniques for promoting flexibility in daily routines for individuals with ASD
5. The Role of Sensory Processing Issues in Autism
Sensory processing difficulties are a significant aspect of the experiences of those on the autism spectrum.
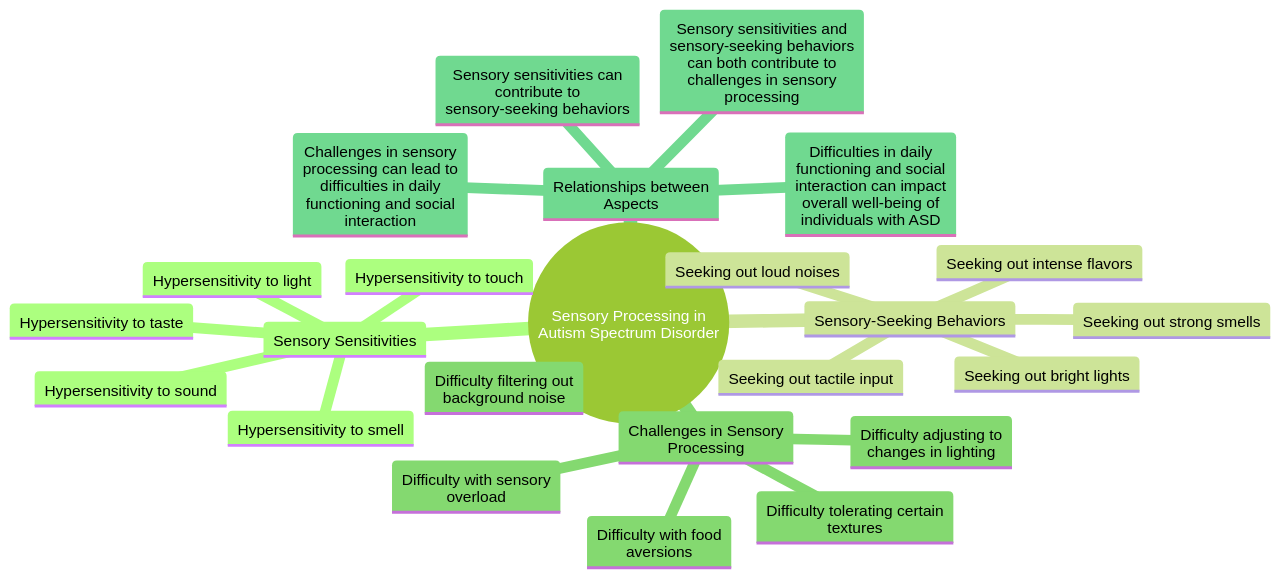
These individuals may demonstrate heightened sensitivity to certain sensory stimuli, such as light or sound, or may actively seek out sensory encounters. These sensory experiences can manifest in behaviors that may seem unusual or confusing to others.
Despite their importance, discussions about autism often overlook sensory processing difficulties. This oversight can lead to a lack of understanding and recognition of the experiences of autistic individuals. We must strive for a more comprehensive understanding of their sensory needs, rather than focusing solely on encouraging them to conform to non-autistic norms.
Occupational therapy is one method of supporting individuals with autism in managing sensory processing difficulties. It equips them with the tools to navigate their sensory experiences in a respectful and non-invasive way. Additionally, adopting accommodations and sensory regulation strategies, such as sensory breaks and a sensory diet, can help create more accessible and inclusive environments for autistic individuals.
Understanding sensory processing disorders (SPD) can be challenging. SPD, which involves difficulty processing or interpreting sensory input effectively, can feel like trying to navigate with a malfunctioning compass. The significance of awareness, understanding, and appropriate treatment in assisting these individuals to regain control of their bodies, minds, and self-esteem cannot be overstated.
Moreover, sharing perspectives from adults with SPD can enable educators and caregivers to better empathize with children facing these challenges. Early identification and treatment of SPD is key to preventing potential obstacles in learning, self-esteem, and relationships.
In our considerations, we must prioritize the experiences and needs of those dealing with sensory processing issues, whether from autism or SPD. By doing so, we can help them live fulfilling lives and access the necessary support they need. This can be achieved by creating sensory-friendly environments, using visual supports, and gradually introducing new sensory experiences.
Some strategies include noise reduction through noise-canceling headphones or earplugs, designating sensory-friendly spaces with soft lighting and textures, and working closely with therapists, educators, and caregivers. It's crucial to remember that every individual with ASD is unique, and their sensory needs may vary.
Sensory integration therapy is another possible solution. This therapy gradually exposes individuals to sensory inputs that trigger hypersensitivity in a controlled and supportive environment. Activities such as deep pressure massages, brushing techniques, and sensory play can help desensitize individuals and regulate their sensory responses.
Understanding the impact of sensory issues on behavior in individuals with ASD is crucial for providing effective support and intervention. Sensory processing difficulties may lead to sensory overload or sensory seeking behaviors, which can manifest as challenging behaviors or self-stimulatory behaviors.
Identifying sensory-seeking behaviors requires a comprehensive understanding of their specific needs and triggers. Implementing appropriate strategies can address and redirect the sensory-seeking behaviors towards more appropriate activities. This may include providing alternative sensory experiences or offering sensory breaks to help regulate their sensory input.
Finally, promoting understanding and acceptance of sensory differences in individuals with ASD involves providing education and awareness about sensory processing difficulties. This can involve sharing information about the sensory challenges experienced by individuals with ASD and offering strategies to support them in various environments
6. Effective Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Autistic Children
Addressing behavioral challenges in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be daunting, yet there are several effective strategies at our disposal such as behavior modification techniques, social skills enhancement, and sensory integration therapy. Understandably, each child is unique, thus the effectiveness of these strategies will vary.
Children with ASD often struggle with expressive language and comprehension of verbal communication, which can lead to frustration and challenging behaviors. Social situations can be a minefield for these children, as understanding others' perspectives and adhering to social norms can be overwhelming. These difficulties can result in social isolation and instances of bullying. Moreover, children with ASD may find unstructured time overwhelming and struggle with sensory overload, which can cause difficulties in processing sensory stimuli.
In dealing with these behaviors, parents and caregivers need to identify the unmet needs that the child may be trying to communicate. Keeping a "behavior diary" can help identify patterns and triggers for challenging behaviors. Effective strategies to support children with ASD include the use of clear and concise language, the application of visual supports, creation of social stories to prepare them for upcoming social situations, and the use of visual aids to help them identify and manage their emotions.
Creating a calming environment, free from sensory irritants like flickering lights and loud noises, can help children with ASD. Positive reinforcement techniques, such as praise and rewards, can encourage desired behaviors. However, it's crucial to adapt the form of praise to the child's preferences. In some cases, seeking professional help from psychologists or psychiatrists can be beneficial in managing behavioral challenges.
As one expert aptly stated, "It’s vital for parents and caregivers to understand that these behaviors are not the child's 'fault' but rather symptoms of underlying difficulties". It's important to remember that children with autism can struggle with managing their behavior, even high-functioning children can meltdown in situations that would be only mildly challenging to a typical peer. Just as it's challenging to predict the response of an autistic person, interpreting autistic reactions to difficult emotions can also be difficult.
In essence, understanding and supporting children with ASD who experience behavioral difficulties is crucial. By addressing the underlying causes and employing appropriate strategies, parents and caregivers can help these children manage their behaviors and improve their overall well-being.
There are several online resources available for social skills training for children with ASD. These resources offer effective strategies and techniques to enhance social skills in children with ASD. Exploring these resources to find appropriate training programs can help children with ASD develop their social skills.
One of the effective strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with ASD is sensory integration therapy. This therapy provides sensory experiences to help children with ASD better integrate and process sensory information. Activities that stimulate their senses, such as touch, movement, and sound, can help children with ASD learn to regulate their behaviors and emotions.
Addressing challenging behaviors in children with ASD includes a variety of approaches. It's important to develop a behavior support plan tailored to the specific needs of the child. This may involve implementing visual schedules, using social stories to teach appropriate behaviors, and providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors. Clear and consistent expectations, visual supports such as visual cues or visual prompts can be helpful. Collaborating with professionals, such as behavioral therapists or psychologists, can be beneficial in developing and implementing effective strategies.
Establishing a structured routine and setting clear expectations for the child can be helpful. Providing visual supports, such as visual schedules or social stories, can also be beneficial in helping them understand and navigate their daily routines. Additionally, using positive reinforcement strategies, such as praise or rewards, can encourage desired behaviors. Teaching the child alternative communication skills, such as using visual aids or sign language, to express their needs and wants can also be helpful.
There are resources available for managing challenging behaviors in children with ASD. These resources provide effective strategies and techniques for parents and caregivers to address and manage these behaviors. Seeking guidance from professionals and organizations specializing in the field of autism to access these resources can be beneficial. They may offer training programs, workshops, online materials, and support networks that can provide valuable information and strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with ASD.
To address challenging behaviors in children with autism, implementing effective strategies for enhancing their social skills is important. By focusing on social skills development, children with autism can learn appropriate behaviors and responses in various situations. Providing unlimited digital access to resources and materials that target social skills development can be beneficial in addressing challenging behaviors
7. Navigating Support Services for Parents and Professionals
Navigating the realm of support services for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be a complex endeavor. However, numerous resources exist to aid parents and professionals in this journey. One such resource is ASD Media, an online platform providing industry insights and effective strategies to overcome obstacles and improve outcomes.
A key resource explored on ASD Media is the support available for adults on the autism spectrum and their neurotypical (NT) partners. This includes a variety of options such as online group therapy, individual counseling, and blogs for individuals and couples impacted by high-functioning autism and Asperger's. The resources cover a wide array of topics including challenges faced by NT spouses, managing grief following an autism diagnosis, preventing the "Cassandra syndrome," and the critical components of emotional intelligence for adults with ASD. In addition, they offer guidance on enhancing social skills, managing anger control issues, handling meltdowns, and fostering emotional reciprocity in relationships.
Another critical transition that demands careful navigation is the progression from high school to post-secondary education for students with ASD and their parents. Various pathways to success are available including specialized post-secondary experiences, certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities. Parents need to assess their child's abilities in areas such as independence, academic skills, and adaptive behavior thoroughly. The availability of supports and accommodations should also be considered when choosing the appropriate pathway. Colleges' disability departments provide accommodations for disabled students, with some even having specific autism support programs. Community colleges can act as a stepping stone for students who need more support in adapting to college expectations. Certificate and technical schools may be suitable for students who are not candidates for a college degree but require a slower pace of instruction. There are also programs for non-degree seeking students that provide a college campus experience and skills for independence. Those who need higher levels of support can consider post-secondary day and residential programs that focus on independent living skills, work skills, social skills, and executive functioning skills. Some individuals may opt for supported or customized work experiences with the help of vocational rehabilitation departments. Parents need to be realistic, objective, and flexible in navigating the transition to adulthood, understanding their child's abilities and support needs to find a pathway to success and happiness.
ASD Media, with its digital access to unlimited resources, is a beacon of support in this challenging journey. By subscribing to their services, parents and professionals can gain insights and strategies on navigating support services effectively. This includes conducting thorough research to identify available services, building a network of contacts, attending workshops and training sessions, collaborating with professionals, and advocating for their child or client's needs. With these strategies, individuals with autism can receive the necessary support for their unique needs, and parents can become empowered in accessing these services. This wealth of information and guidance is available at the click of a button, making ASD Media a valuable tool in navigating the landscape of autism support services
8. Enhancing Social Skills Development: Practical Approaches
Enhancing social abilities is a key aspect of supporting those with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). There are several effective strategies that can be implemented to improve their understanding and navigation of social situations.
Structured social skills training techniques are one such strategy, often employing visual supports, structured learning experiences, and social scripts. These tools assist individuals with ASD in learning and practicing their social skills. Role-playing exercises, another effective technique, allow individuals with ASD to practice various social scenarios in a controlled environment. This helps enhance their communication and social interaction skills, and reduces anxiety in social situations.
Another helpful tool is social stories, short narratives that provide specific information about social situations. They guide individuals on how to behave in these situations, helping them understand and improve their social interactions and communication abilities.
In the words of Ronald E. Riggio, Ph.D., emotional and social intelligence are critical for forming successful relationships and excelling in various professional fields. These skills, which include emotional and social communication, are key to achieving success. Observing others, understanding one's emotional behavior, honing conversational skills, and participating in public speaking are some effective strategies to develop these skills.
Drawing from personal experiences, challenging insecure thoughts can be an effective way to improve social skills. Realizing that a single conversation does not define one's social worth can help individuals with ASD manage negative thoughts about their social abilities. Taking the initiative in making friends and actively improving social skills can enhance their social experience.
Moreover, becoming more well-rounded can make it easier for individuals with ASD to relate to others and engage in meaningful conversations. Improving their appearance can also lead to better first impressions and boost their confidence, further enhancing their social skills.
It is crucial to remember that every individual's situation is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Therefore, it is important to explore different strategies and find what works best for the individual with ASD. It is also essential to tailor the social skills training approach to their specific needs and abilities, and regularly evaluate and adjust the training program to ensure progress and success
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for parents, professionals, and society as a whole. ASD is a unique neurodevelopmental condition that impacts social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior. The broad range of symptoms and their severity can vary greatly among individuals, making it challenging to identify and recognize signs of ASD. However, early recognition and intervention can greatly improve outcomes for individuals with ASD.
Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of autism, including key signs and symptoms, social communication and interaction skills, restricted or repetitive behaviors, sensory processing issues, challenging behaviors, and navigating support services. We have discussed effective strategies for managing these challenges and promoting social skills development in individuals with ASD.
Recognizing the signs of ASD in children is vital for early intervention and support. By understanding the unique challenges faced by individuals with ASD, we can provide appropriate strategies to enhance their social skills, manage challenging behaviors, address sensory processing issues, and navigate support services effectively.
The broader significance of this article's topic lies in creating a more inclusive society that supports and values individuals with ASD. By gaining a deeper understanding of autism and implementing effective strategies, we can foster an environment that embraces neurodiversity and provides equal opportunities for individuals with ASD to thrive.
To create this inclusive society, we must take action. We can start by educating ourselves about autism spectrum disorder and advocating for increased awareness and acceptance. We can support organizations like ASD Media that provide valuable resources to parents and professionals in navigating the complexities of supporting individuals with ASD.
Let us work together to create a world where individuals with ASD are valued for their unique abilities and contributions. Start now by accessing the resources available at ASD Media to gain insights on supporting individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by ASD




