Overview
The article titled "Navigating Your Path to Applied Behavior Analysis Certification: A Compassionate Step-by-Step Guide" offers a heartfelt exploration of the vital steps and considerations for obtaining certification in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). It highlights the educational pathways available, the various certification options, and the practical experience requirements that are essential for aspiring behavior analysts. Additionally, it provides strategies for effective exam preparation, while underscoring the importance of ethics and continuing education. Understanding these elements is not just a checklist; it is crucial for those who wish to support individuals facing behavioral challenges with compassion and expertise.
Introduction
In the heart of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), understanding its core principles and practices is vital for practitioners who aspire to make a meaningful difference in the lives of individuals facing behavioral challenges. Imagine the foundational concepts of positive and negative reinforcement, intertwined with the ABC model—these principles are the essential building blocks for effective intervention strategies. As the field evolves, the focus on comprehensive training and ethical standards is more important than ever. This ensures that practitioners are equipped not just with knowledge, but with the compassion needed to provide effective care.
Let’s explore the multifaceted world of ABA together, illuminating the educational pathways to certification, the diverse professional roles available, and the ongoing importance of education and ethical practices in nurturing positive outcomes for clients. Your journey in understanding ABA can lead to transformative changes, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding Applied Behavior Analysis: Core Principles and Practices
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientific discipline dedicated to understanding and modifying actions through systematic techniques. The core principles of ABA are essential for practitioners and form the foundation for effective intervention strategies. These principles include:
- Positive Reinforcement: This principle involves encouraging preferred actions by providing rewards or incentives. Recent studies have shown that positive reinforcement significantly enhances adaptive actions, with statistical evidence indicating a notable effect size (F(1, 80.033) = 8.272, p = 0.005, η² = 0.066). This underscores the effectiveness of reward-based strategies in promoting positive behavioral changes.
- Negative Reinforcement: Contrary to common misconceptions, negative reinforcement strengthens actions by removing aversive stimuli. For instance, when a child finishes a task and is freed from an unpleasant situation, the probability of that action being repeated increases. Real-world examples illustrate how this principle can be effectively applied in various therapeutic settings.
- Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence (ABC) Model: This model is essential for understanding the dynamics of actions. It highlights the significance of recognizing triggers (antecedents) that result in specific actions and the outcomes that ensue. By analyzing these components, practitioners can develop tailored interventions that address the root causes of challenging actions.
- Data Collection: Systematic recording of behavior is vital for informed decision-making. Accurate data collection allows practitioners to track progress, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and make necessary adjustments. This practice is not only essential for ABA qualification but also for ensuring the best outcomes for clients.
The significance of these principles is further highlighted by recent developments in ABA, which advocate for prioritizing comprehensive training for parents and professionals in intervention workshops. This approach aims to enhance the overall effectiveness of ABA therapy, particularly in light of findings that indicate high rates of ABA discontinuation and low dosing can diminish potential benefits, even with mandated insurance coverage.
A relevant case study titled "Enhancement of Daily Living Skills via ABA" examined the impact of the ABA program on improving daily living skills among children with autism. The research demonstrated that by breaking tasks into smaller components, the ABA method effectively enhanced daily living skills, leading to positive behavioral changes and improved performance in daily activities. This case study exemplifies the practical application of ABA techniques and underscores the importance of comprehensive training for parents and professionals.
In summary, mastering these core principles is not only fundamental for effective practice but also essential to the qualification process in ABA. As Ralph Moller aptly stated, "The importance of customization in autism therapy cannot be overstated," emphasizing the need for personalized approaches that leverage these foundational principles. Additionally, other ABA professionals have noted that "Positive reinforcement is key to fostering long-term behavioral change," further supporting the critical role of these principles in effective ABA practice.
Educational Pathways to ABA Certification: Degrees and Programs
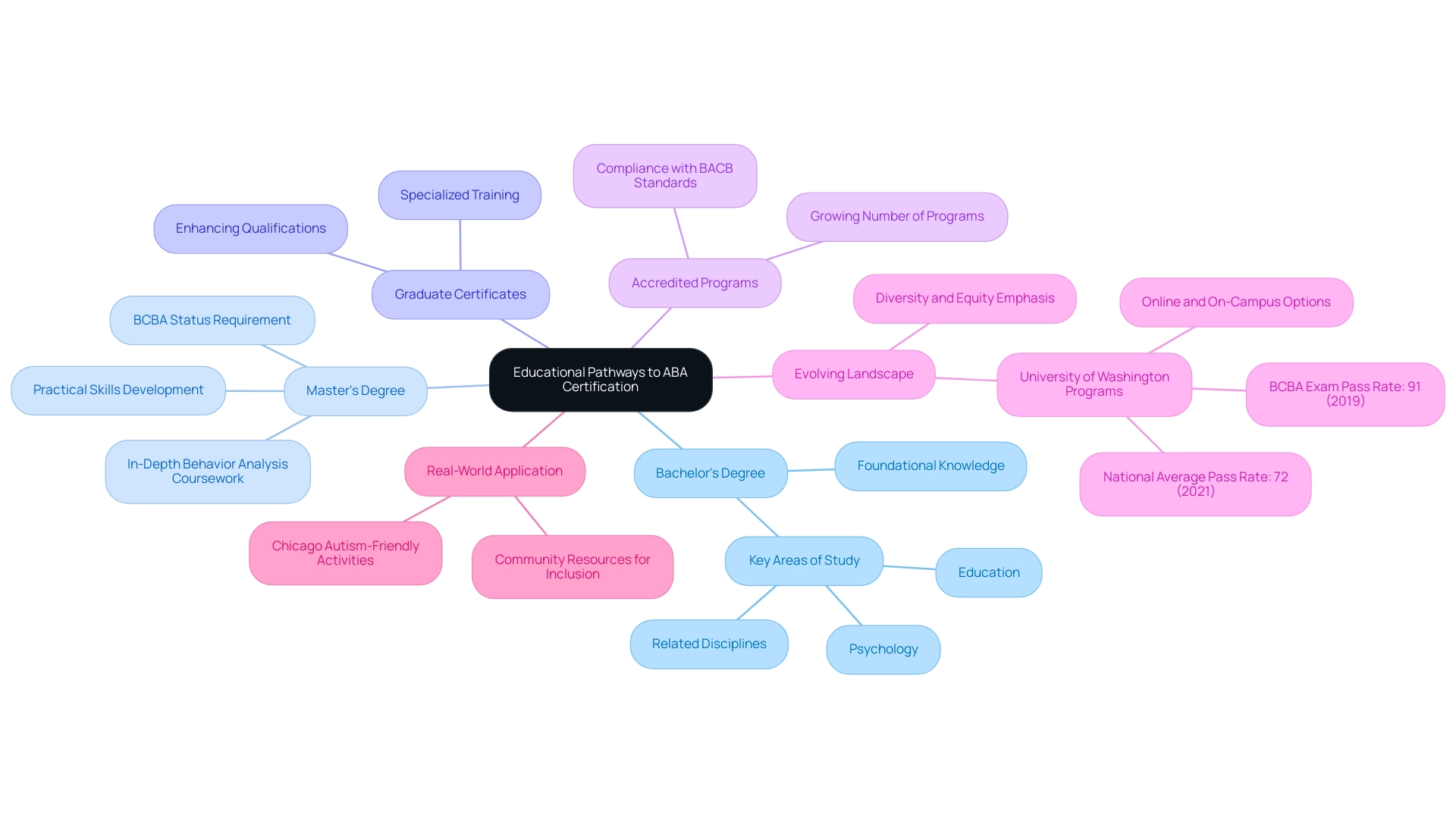
To embark on the journey of obtaining qualifications in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), individuals often need to follow specific educational pathways that align with the standards set by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB). Understanding these routes can be crucial for parents and aspiring behavior analysts alike.
- Bachelor's Degree: This foundational step is typically pursued in areas such as psychology, education, or related disciplines. A bachelor's degree lays the groundwork, providing essential knowledge and skills vital for grasping behavioral principles.
- Master's Degree: For those aiming to achieve Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) status, a master's degree is necessary. This advanced degree delves into behavior analysis coursework, equipping candidates with in-depth knowledge and practical skills essential for effective practice in the field.
- Graduate Certificates: These shorter programs serve as valuable supplements to existing degrees, offering specialized training in ABA. They can enhance a candidate's qualifications and prepare them for the credentialing process.
As we look ahead to 2025, the landscape of ABA education is evolving, with a notable emphasis on diversity and equity in programs. Institutions like the University of Washington are leading the way, offering both online and on-campus ABA programs. Notably, this institution reported a BCBA exam pass rate of 91% in 2019, significantly higher than the national average of 72% in 2021. This showcases the effectiveness of their educational pathways and highlights the importance of ensuring that all individuals have access to quality education in ABA.
In addition to formal education, it is essential to explore accredited programs that comply with BACB standards to guarantee eligibility for qualification. Currently, many accredited programs are available across the United States, reflecting a growing commitment to quality education in the field. This trend is supported by the increasing number of individuals pursuing ABA certification, with 15,266 candidates tested for Registered Behavior Technician (RBT) certification, achieving a pass rate of 46%.
Moreover, statistics indicate that the number of accredited ABA programs in the U.S. is on the rise, further enhancing opportunities for aspiring behavior analysts.
Case studies from Chicago illustrate the significance of community resources and activities designed for children with autism. These initiatives enhance their social experiences and support their sensory needs, fostering inclusion while highlighting the practical application of ABA techniques in real-world settings. As one anonymous source noted, "It’s my understanding that similar pay mechanisms do not exist in many other jurisdictions, in which case accrediting programs is not going to help protect them." This underscores the challenges encountered in the sector and the importance of robust educational pathways.
In summary, navigating the path to applied behavior analysis certification involves understanding the educational requirements and exploring accredited programs that meet professional standards. By staying informed about current trends and leveraging available resources, aspiring behavior analysts can effectively prepare for a rewarding career in this meaningful field.
Exploring Certification Options: BCBA, RBT, and Beyond
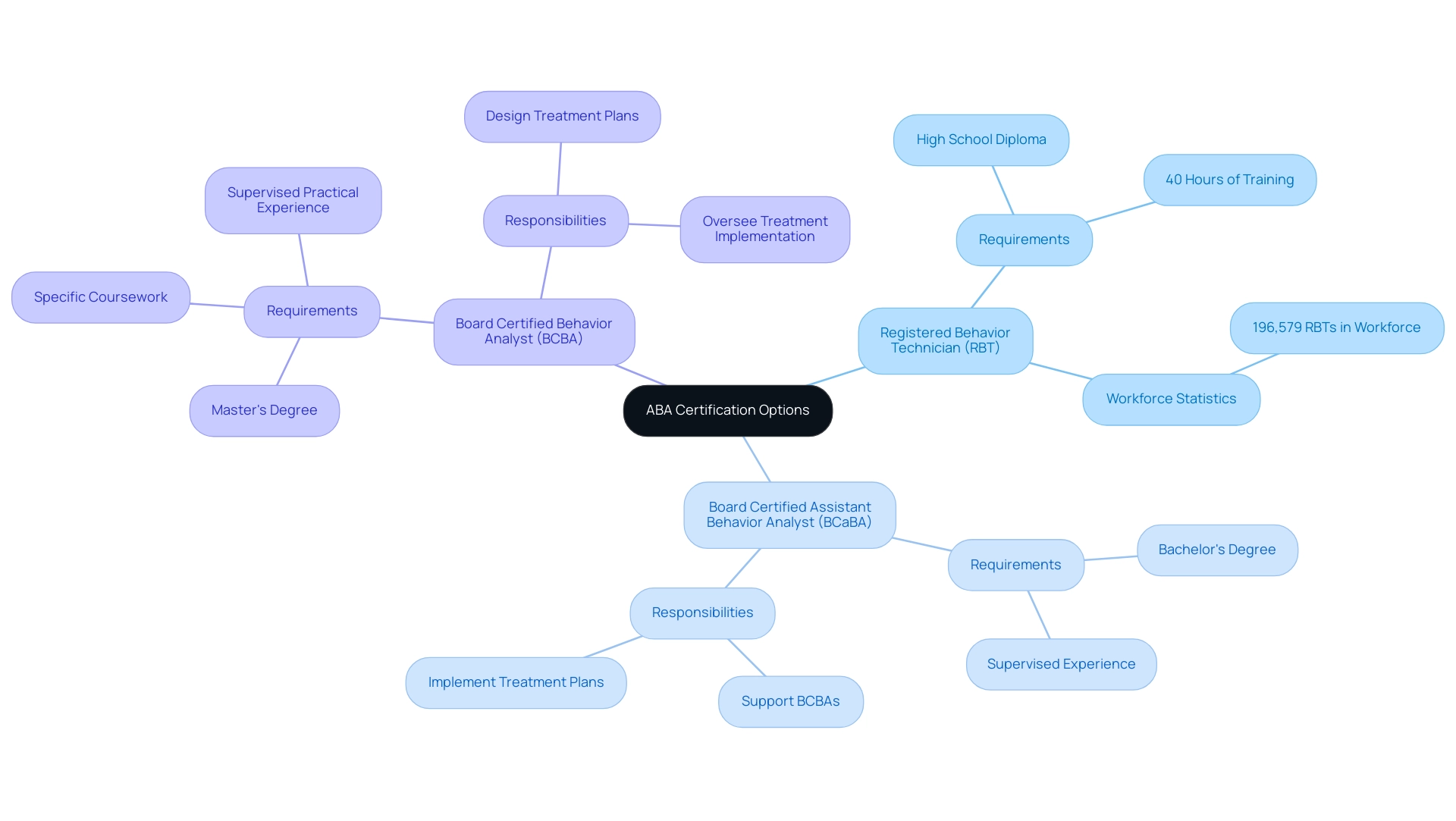
In the field of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), there are several certification options available, each catering to different levels of expertise and responsibility. Understanding these paths can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to recognize the unique roles they play in shaping effective support for individuals and families.
- Registered Behavior Technician (RBT): This entry-level credential is designed for individuals looking to start their careers in ABA. To qualify, candidates must possess a high school diploma and complete 40 hours of training focused on the principles of ABA. As of 2024, the workforce includes approximately 196,579 RBTs, highlighting the growing demand for this foundational role. This is a fantastic opportunity for those eager to make a difference in the lives of others.
- Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analyst (BCaBA): This credential requires candidates to have a bachelor's degree along with supervised experience in the field. BCaBAs play a crucial role in supporting Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) and implementing treatment plans under their supervision. Their contributions are vital in ensuring that clients receive the best possible care.
- Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA): The BCBA credential is more advanced, requiring a master's degree, specific coursework in the analysis of conduct, and supervised practical experience. BCBAs are responsible for designing and overseeing treatment plans, making them integral to the success of ABA interventions. Their expertise is essential in guiding effective strategies that foster positive change.
Each credential serves a unique function within the ABA framework, enabling professionals to specialize and contribute effectively to their domain. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone considering a career in ABA and looking to obtain an applied behavior analysis certification, as it helps in making informed decisions about educational and professional pathways.
As Imed Bouchrika, PhD, Co-Founder and Chief Data Scientist, states, "Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a rapidly growing domain that helps individuals improve behaviors and life skills through evidence-based techniques." This growth is reflected in the increasing number of RBTs in the workforce, showcasing the expanding opportunities in this field.
Additionally, the case study titled "Naturalistic Teaching in ABA: Techniques, Benefits, and Strategies for Autism" illustrates how ABA methods can enhance communication and social skills for children with autism through real-life interactions. Furthermore, the technique of chaining in ABA, which breaks down complex tasks into smaller steps, is crucial for skill acquisition and independence. Recent discussions, such as the article from March 18, 2025, define 'Chaining ABA' as a method that aids in this process, emphasizing its relevance in current practices.
Including these elements not only enhances the content but also offers a thorough understanding of the qualifications and their influence on the domain of ABA. If you’re considering a career in this rewarding field, remember that each step you take towards certification is a step towards making a significant impact in the lives of those you serve.
Gaining Practical Experience: Internships and Supervised Practice
Gaining practical experience is a cornerstone of achieving applied behavior analysis certification, and it’s a journey that can feel overwhelming. Here are essential steps to help you secure internships and supervised practice:
- Research Opportunities: Actively seek internships at clinics, schools, or organizations specializing in ABA services. The growing demand for ABA therapists—especially in states like Georgia, where job growth for BCBAs is projected to exceed the national average—highlights the importance of finding the right placement. Additionally, statistics indicate that Bachelor's-level therapists could experience a 25% growth by 2029, underscoring the increasing opportunities in this rewarding profession.
- Network: Establish connections with professionals in the industry by attending conferences, workshops, and engaging in online forums. Networking is crucial; it opens doors to internship opportunities and provides valuable insights into the field. Many successful ABA professionals emphasize that building relationships can lead to mentorship and job offers. As Laura NG, Clinical Operations Manager, wisely states, "Learn the best strategies for communicating with parents in ABA therapy to build trust, encourage collaboration, and support their autistic child’s progress."
- Document Experience: Maintain meticulous records of your hours and the nature of your work. This documentation is essential for fulfilling qualification requirements and showcasing your dedication to the field.
Internships not only meet prerequisite requirements but also significantly enhance your skills and broaden your professional network. As the landscape of ABA therapy evolves, securing practical experience through internships while pursuing applied behavior analysis certification will position you favorably in a competitive job market. The demand for qualified professionals continues to rise, and a career as a BCBA allows individuals to make a meaningful impact by helping those with behavioral challenges improve their skills and quality of life.
Preparing for the Certification Exam: Tips and Strategies
To maximize your chances of success, preparing for the applied behavior analysis certification exam requires a well-structured and strategic approach. Let's explore some key steps together:
- Understand the Exam Format: Start by familiarizing yourself with the exam's structure, including the types of questions you will encounter. This knowledge will empower you to navigate the exam more effectively.
- Create a Study Schedule: Develop a detailed study plan that allocates specific times for each topic. Consistency is crucial; by setting aside dedicated study periods, you will reinforce your learning and stay on track.
- Utilize Study Resources: Embrace a variety of study materials, such as textbooks, online courses, and practice exams. These resources are designed to deepen your understanding and prepare you for the questions you'll face in the applied behavior analysis certification. Recent advancements in technology have transformed exam preparation, providing interactive study tools and practice exams that can significantly enhance your readiness. As highlighted in the case study titled "The Role of Technological Advancements in Exam Preparation," leveraging technology allows candidates to access diverse interactive materials, enriching their preparation experience.
- Join Study Groups: Collaborating with peers can be incredibly beneficial. Forming study groups enables you to discuss complex concepts, quiz each other, and share insights. Real-life examples show that candidates who engage in group study often report higher levels of understanding and retention of material.
- Expert Strategies for Exam Preparation: According to industry experts, implementing targeted strategies can greatly enhance your exam preparation for the applied behavior analysis certification. For instance, focusing on high-yield topics and practicing with timed quizzes can help simulate the exam environment, boosting your confidence. Laura NG, MA BCBA Clinical Operations Manager, states, "By implementing key strategies, candidates can enhance their exam preparation and increase their chances of passing the BCBA exam."
- Stay Informed on Pass Rates: Understanding the statistics surrounding the exam can provide motivation. For example, the pass rate for the BCBA exam in 2019 was 67%. Knowing this can help you set realistic goals and expectations for your preparation, reinforcing the importance of a strategic approach.
By following these strategies and maintaining a consistent study routine, you will enhance your chances of success on exam day. Remember, preparation is not just about hard work; it's about working smart and utilizing the resources available to you.
Maintaining Your Certification: Continuing Education and Renewal
Upholding your ABA certification is not just a requirement; it’s a commitment to your professional growth and the well-being of those you serve. To ensure you remain knowledgeable and effective in your practice, it’s crucial to meet specific continuing education requirements:
- Complete CEUs: For Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs), completing a total of 32 Continuing Education Units (CEUs) every two years is essential. This includes four CEUs focused on ethics and three CEUs in supervision, reflecting the evolving standards of our profession.
- Stay Informed: Actively engaging in workshops, webinars, and conferences is vital for keeping up with the latest developments in ABA practices. Connecting with BACB-approved providers not only enriches your professional knowledge and skills but also helps you fulfill the CEU requirements for your applied behavior analysis certification.
- Renew Certification: Don’t forget to submit your CEU documentation along with your renewal application before the deadline. This step is crucial for maintaining your applied behavior analysis certification and demonstrates your dedication to professional growth.
The significance of continuing education cannot be overstated; it directly impacts the quality of services you provide to your clients. A recent case study titled "Why, What and How? Making the Case for Diversity in ABA" highlighted the necessity for ABA practices to adapt to a diversifying population. It underscores that inclusive therapy approaches lead to more effective outcomes for a broader range of children.
As the field of analysis continues to evolve, BCBAs and BCaBAs who prioritize ongoing education play a vital role in advancing the discipline. They ensure they are equipped to meet the diverse needs of their clients. As emphasized by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board, "As the domain evolves, BCBAs and BCaBAs who stay updated on advancements contribute to the progress of analysis of conduct." For the latest information on CEU requirements, please refer to the Behavior Analyst Certification Board site. Your journey in this field is important, and staying informed is a key part of that journey.
Ethics in Applied Behavior Analysis: Upholding Professional Standards
Ethics are foundational to the practice of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), guiding professionals in delivering effective and compassionate care. The key ethical principles that practitioners must uphold include:
- Do No Harm: The primary obligation of ABA practitioners is to prioritize the well-being of clients in all interventions, ensuring that no harm comes from the services provided.
- Informed Consent: It is vital that clients fully understand the nature of the services offered, their rights, and the potential risks involved. This principle not only fosters transparency but also empowers clients to make informed decisions about their treatment.
- Confidentiality: Protecting client information is paramount. Practitioners must maintain strict confidentiality to safeguard the privacy of individuals receiving ABA services.
Adhering to these ethical standards is essential for building trust between practitioners and clients, which in turn enhances the effectiveness of service delivery. Recent statistics indicate that ethical violations in ABA practice have been a growing concern, with a significant number of reported breaches in 2025. This underscores the importance of informed consent, as it serves as a cornerstone for ethical practice and highlights the need for ongoing education and vigilance in maintaining these standards.
For instance, a case study titled "Evidence-Based Practice in ABA Therapy" demonstrates how integrating client values and preferences into treatment planning leads to better outcomes. By adhering to ethical principles, behavior analysts can provide high-quality, client-centered care that promotes positive results for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Insights from ABA professionals emphasize that informed consent is not merely a procedural formality but a vital component of ethical practice. As Jay Reeves, author of 'The Most Powerful Attorney in the World,' observes, 'The committee dismissed 158 files, abated two files, and continued two files,' highlighting the ongoing scrutiny and significance of ethical practices in the profession. This ensures that clients are active participants in their treatment, fostering a collaborative environment that respects their autonomy and dignity.
Furthermore, contemporary developments, such as those discussed in the article "Revolutionizing Strategies: Technology-Assisted Learning for Autism," highlight the evolving landscape of ABA therapy and the critical role of ethical practices and informed consent. As the area evolves, the commitment to ethical standards will remain a guiding principle for practitioners dedicated to improving the lives of those they serve.
Career Opportunities in ABA: Making a Difference in Lives
A career in applied behavior analysis certification opens a world of opportunities to create meaningful change in the lives of individuals with autism and other developmental disorders. The roles within this area are diverse and impactful, offering a chance to make a real difference:
- Behavior Specialist: These compassionate professionals work directly with clients, implementing customized modification strategies that foster positive development and enhance quality of life.
- Consultant: Consultants provide invaluable expertise to schools and organizations, guiding the integration of ABA practices to support students and staff effectively.
- Researcher: Researchers contribute to the advancement of the field through rigorous studies and publications, helping shape evidence-based practices that improve outcomes for clients.
- Educator: Educators play a crucial role in training the next generation of analysts, imparting essential knowledge and skills in academic settings.
The demand for Board Certified Analysts (BCBAs) has surged dramatically, reflecting a staggering 1,942% increase in applied behavior analysis certification from 2010 to 2018, as noted by the Analyst Certification Board. This remarkable growth underscores the increasing recognition of ABA's effectiveness in treating autism. As we look towards 2025, the job market for ABA professionals continues to thrive, with projections indicating a 22% growth rate for BCBAs in Georgia alone, surpassing the national average.
This robust job growth is fueled by the rising number of autism diagnoses and legislative mandates for ABA services, paving a fulfilling career pathway for those seeking applied behavior analysis certification in the field.
Real-life examples abound, showcasing analysts who are making significant differences in their clients' lives. Their work not only transforms individual outcomes but also contributes to a broader societal understanding and acceptance of autism. With high career satisfaction reported among behavior analysts, this profession offers not just a job, but a rewarding vocation dedicated to nurturing growth and development in those who need it most.
Furthermore, ASD Media provides expert assistance in enhancing child development through tailored ABA therapy, emphasizing the importance of skilled professionals in this crucial area. The median annual salary for substance abuse, behavioral disorder, or mental health counselors was $47,660 as of May 2020, providing additional context about the financial prospects within the field of ABA. The demand for BCBAs is further supported by statistical data indicating a strong job market, ensuring that those who pursue an applied behavior analysis certification can expect a fulfilling and impactful professional journey in ABA.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) reveals its profound impact on individuals facing behavioral challenges. By mastering core principles such as positive and negative reinforcement, practitioners can develop effective intervention strategies that lead to meaningful changes in clients' lives. The importance of education, from foundational degrees to specialized certification programs, cannot be overstated, as these pathways equip future behavior analysts with the necessary skills to navigate this dynamic field.
The various certification options, including RBT, BCaBA, and BCBA, highlight the diverse opportunities available within ABA. Each certification plays a crucial role in addressing specific needs and responsibilities, allowing professionals to specialize and contribute effectively to the community. Gaining practical experience through internships and supervised practice further enhances the readiness of aspiring behavior analysts, ensuring they can meet the growing demand for qualified professionals in this sector.
Moreover, the commitment to ethical standards is fundamental in ABA practice. Upholding principles such as informed consent and confidentiality fosters trust and empowers clients, ultimately leading to better therapeutic outcomes. As the field evolves, continuous education and adherence to ethical practices remain paramount for practitioners dedicated to improving the lives of those they serve.
In conclusion, a career in ABA not only offers the potential for personal fulfillment but also the opportunity to make a significant difference in the lives of individuals with autism and other developmental disorders. With a robust job market and a growing recognition of the effectiveness of ABA, those who pursue this path can expect a rewarding journey that combines professional growth with the chance to foster positive change in their communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientific discipline focused on understanding and modifying behaviors using systematic techniques.
What are the core principles of ABA?
The core principles of ABA include: 1. Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging preferred actions through rewards. 2. Negative Reinforcement: Strengthening actions by removing aversive stimuli. 3. Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence (ABC) Model: Understanding the relationship between triggers, actions, and outcomes. 4. Data Collection: Systematic recording of behavior for informed decision-making.
How does positive reinforcement work in ABA?
Positive reinforcement involves providing rewards or incentives to encourage preferred actions, which has been shown to significantly enhance adaptive behaviors.
What is negative reinforcement in the context of ABA?
Negative reinforcement strengthens behaviors by removing unpleasant stimuli after a desired action is performed, increasing the likelihood of that action being repeated.
Can you explain the ABC Model in ABA?
The ABC Model stands for Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence and helps practitioners understand the dynamics of behavior by identifying triggers (antecedents), the behavior itself, and the resulting consequences.
Why is data collection important in ABA?
Data collection is vital for tracking progress, evaluating the effectiveness of interventions, and making necessary adjustments to ensure the best outcomes for clients.
What recent developments are being emphasized in ABA training?
Recent developments advocate for comprehensive training for parents and professionals to enhance the effectiveness of ABA therapy, particularly addressing high rates of discontinuation and low dosing of interventions.
What educational pathways are necessary for obtaining qualifications in ABA?
The educational pathways include: 1. Bachelor's Degree in psychology, education, or related fields. 2. Master's Degree for Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) status. 3. Graduate Certificates for specialized training in ABA.
How has the landscape of ABA education evolved?
There is a growing emphasis on diversity and equity in ABA programs, with institutions offering both online and on-campus options, and an increase in accredited programs across the U.S.
What is the significance of accredited programs in ABA?
Accredited programs ensure compliance with Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) standards, which is essential for eligibility for ABA certification.
What challenges exist in the field of ABA education and certification?
Challenges include ensuring access to quality education and addressing discrepancies in pay mechanisms across jurisdictions, which can impact the effectiveness of educational programs.




