Introduction
Understanding Level 2 Autism and providing effective support for individuals on the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for parent advocates. Level 2 Autism is characterized by challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors.
This article will explore various aspects of Level 2 Autism, including developing effective communication strategies, supporting social skills development, addressing sensory sensitivities, and collaborating with professionals. By understanding these areas and implementing appropriate strategies, parent advocates can empower and enhance the well-being of their children with Level 2 Autism.
Understanding Level 2 Autism
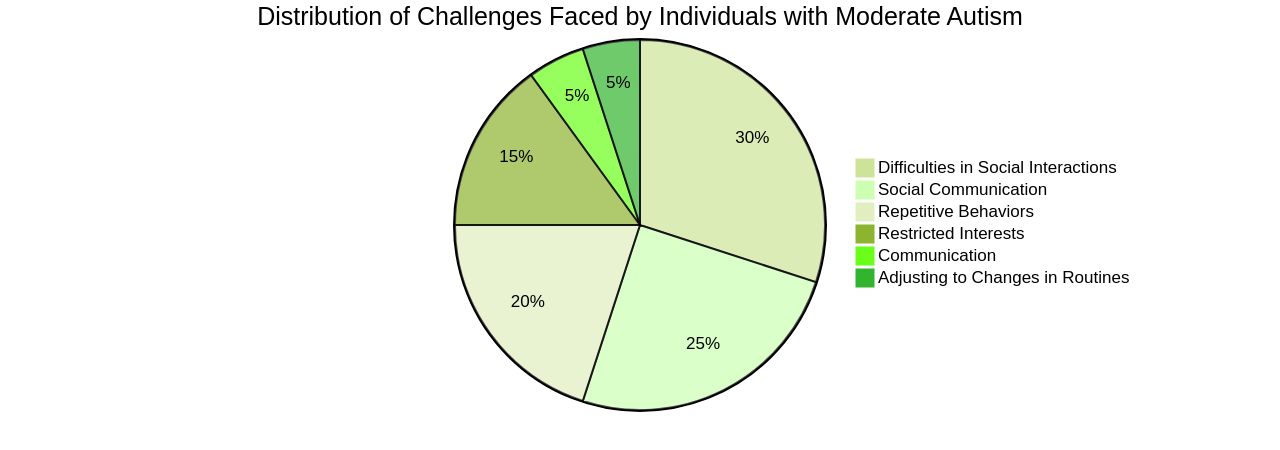
Moderate autism, or Level 2 Autism, is a category within the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), characterized by prominent challenges in social communication, along with restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. Individuals at this level often require considerable support for daily living and face difficulties in areas such as social interactions, communication, and adjusting to changes in routines. They may encounter misinterpretations of their behaviors as threatening or defiant, leading to unfortunate incidents such as police stops or arrests.
This is particularly true for young Black individuals with disabilities, including autism. The unique needs of these individuals are paramount for those advocating for parents, as it guides the provision of effective support. Technology has proven to be an invaluable tool in aiding communication for non-speaking autistic individuals.
For instance, a 10-year-old boy began communicating by pointing to images on an electronic tablet, a moment his father, an autism advocate, described as the 'biggest' of his life. Therapy can help uncover common abilities in autism, such as a strong sense of justice and fairness, and an increased capacity for feeling emotions. However, societal stigma has led to 'masking' where autistic individuals adopt specific behaviors to blend in with non-autistic individuals.
This often starts at a young age and evolves as a survival mechanism in response to criticism. While significant funds have been invested in autism research, more needs to be done to maintain funding for existing programs and expand efforts to address the challenges of those living with intense behaviors. The reauthorization of the Autism CARES Act aims to expand its influence and ability to support the entire autism community adequately.
Developing Effective Communication Strategies
As a supportive ally, it is important to facilitate effective communication for individuals with Level 2 Autism. A key part of this role involves introducing visual supports such as schedules and social narratives.
These tools can greatly enhance understanding and streamline communication. Alternative communication techniques, like picture exchange communication systems (PECS) or assistive communication devices, are also encouraged.
Supportive Allies empower those with Level 2 Autism by helping them express their needs and preferences more effectively. Recognizing and leveraging the unique strengths that come with autism, such as excellent memory, attention to detail, and a strong sense of justice, is a crucial part of this process.
Autism is not solely defined by its challenges but also by the unique strategies individuals with autism develop to adapt and thrive. These strategies, often referred to as 'compensation,' include masking, where autistic individuals adopt certain behaviors to blend in with the neurotypical world.
Adapting communication styles to suit individuals with autism is also essential. This includes setting clear expectations for eye contact, asking direct questions, and rephrasing those questions to facilitate understanding. Special interests can play a significant role in an autistic person's life, providing a framework for their identity and a means to connect with others. In addition to these, resources such as www.asd.media offer unlimited digital access for $5-7 per month or $130 per year. They provide a wealth of information and tools to further enhance communication and understanding. By emphasizing a strengths-based approach and understanding the unique challenges and abilities of individuals with autism, we can foster more effective communication, leading to better outcomes for those living with Level 2 Autism.
Supporting Social Skills Development
Navigating social interactions can be a daunting task for individuals with Level 2 Autism. However, tailored support can empower them to enhance their social skills and foster meaningful connections. By orchestrating structured social experiences, such as playdates or social skills groups, parent advocates can create a nurturing environment for these individuals to learn and grow.
Understanding social cues and maintaining appropriate social behavior can be a hurdle for these individuals. With the right guidance, however, they can learn to interpret these cues and adapt their behavior accordingly. Incorporating assistive technology can further enhance this learning process, as it offers an innovative way to impart social skills.
In addition to this, the use of social scripts and role-playing scenarios can prove effective in preparing these individuals to confidently navigate diverse social situations. These methods can empower them to anticipate and respond to various social cues, thereby increasing their comfort and confidence in social settings. It's also important to focus on the enjoyment aspect of social learning, as this can greatly influence an individual's motivation to engage in social interactions.
By creating a positive, rewarding social learning environment, we can encourage them to actively participate and develop their social skills. Moreover, the involvement of parents in these programs is instrumental. Not only do they provide consistent support outside of sessions, but they also contribute to reducing parenting stress through empowerment, knowledge, and social support.
Lastly, it's crucial to remember that every individual's journey with autism is unique. Therefore, the support provided should be personalized, taking into account their specific needs and preferences. This approach ensures that the support is not only effective but also meaningful for the individual.
Addressing Sensory Sensitivities
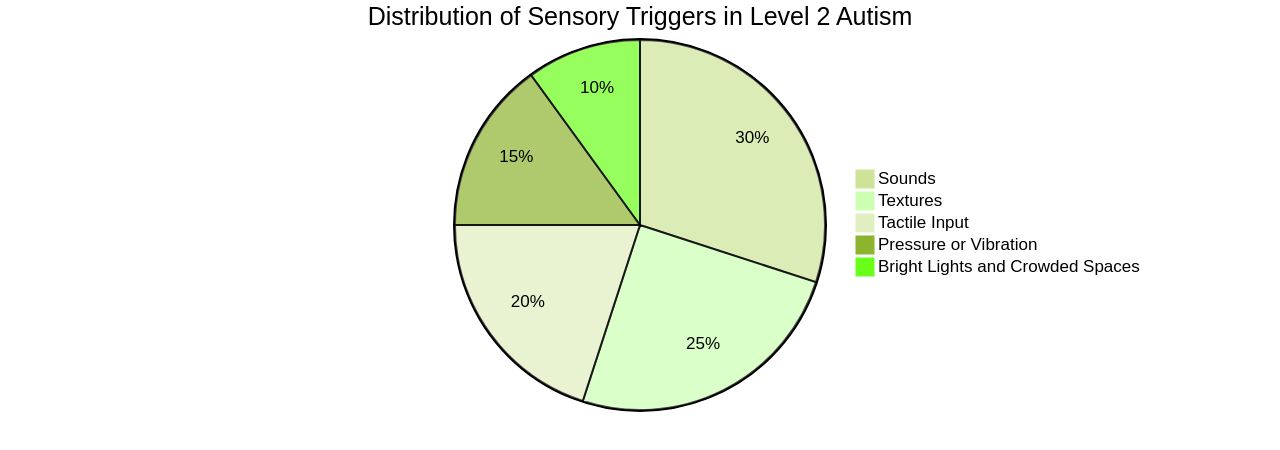
Level 2 Autism often brings with it sensory sensitivities that can disrupt daily routines. To enhance the quality of life for their children, parents can take proactive steps to identify and mitigate these sensory triggers.
For instance, the creation of sensory-friendly spaces at home can provide a safe haven for these children. Noise-cancelling headphones or ear defenders can be used to drown out overwhelming sounds, and providing sensory breaks when needed can help manage overstimulation.
It's important to note that each child may have unique sensory needs, and these can be identified through tailored assessments, as shown in a study that adapted a 39-item informant-based survey from the Autism Education Trust. This survey required participants to describe their environment and select the statement that best described it.
This aids in understanding the sensory issues the child might face and how to adjust their environment to meet these needs. The prevalence of autism in children is 2.78%, and boys are more than three times as likely as girls to be diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder.
This reveals the pressing need for such supportive measures. Furthermore, the development of diagnostic tools, such as the EarliPoinT Evaluation, has revolutionized the early diagnosis of autism, allowing for the formulation of individualized treatment plans, leading to better outcomes for children with autism. In this journey, parents play a crucial role. They can help their children avoid sensory overloads by creating a sensory-friendly environment, adjusting to their child's sensory needs, and providing the necessary support. Understanding and addressing these sensory sensitivities is a significant step towards improving the well-being and comfort of individuals with Level 2 Autism.
Collaborating with Professionals
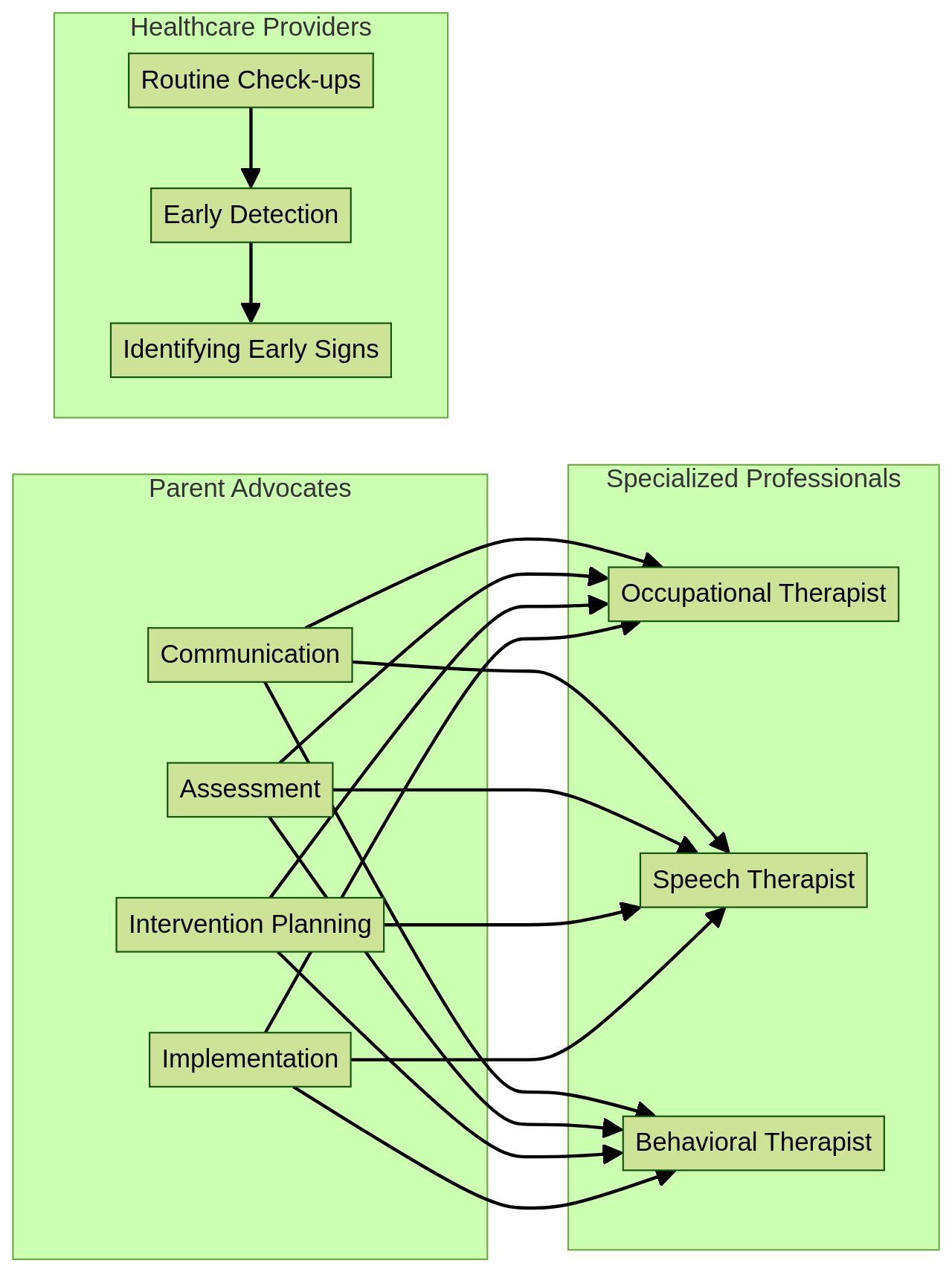
Parent advocates play a pivotal role in supporting individuals with Level 2 Autism by collaborating with specialized professionals like occupational therapists, speech therapists, and behavioral therapists. These experts can offer specific strategies and interventions that cater to the unique needs of the child. Research studies have shown the efficacy of such collaborations.
For instance, a study at the University of Maryland invited professionals who work with autistic adults to participate in focus groups and interviews. The aim was to gain insights that could enhance the support system for individuals with autism. News from the health sector also underscores the importance of early detection of autism and the role of healthcare providers in identifying early signs during routine check-ups.
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) has backed research into making early autism screening a part of routine health care, which can have a significant impact on children and families. Parent advocates can learn from the experiences of autistic adults who often report being turned away by practitioners due to a lack of understanding of their specific needs. With additional training and willingness to learn, these advocates can help bridge the gap between caregivers and the medical community.
Moreover, the Autism Society has emphasized the importance of increasing research to assist individuals with Autism, and addressing premature mortality among this group. Legal advocacy can also be a powerful tool to address injustices experienced by those with Autism. In conclusion, by working with professionals and leveraging available resources, parent advocates can greatly enhance the quality of life for children with Level 2 Autism, helping them to thrive in an environment that understands and caters to their unique needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Level 2 Autism and providing effective support for individuals on the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for parent advocates. This article has explored key areas such as developing effective communication strategies, supporting social skills development, addressing sensory sensitivities, and collaborating with professionals. To facilitate communication, advocate for visual supports and alternative communication techniques.
Emphasize strengths-based approaches to foster effective communication. Support social skills development through structured experiences and involve parents in programs. Personalize support to meet specific needs.
Address sensory sensitivities by creating sensory-friendly spaces and using tools like noise-cancelling headphones. Collaborate with professionals like occupational therapists and speech therapists. Bridge the gap between caregivers and the medical community by learning from autistic adults' experiences.
By working with professionals and leveraging resources, parent advocates can greatly enhance the quality of life for children with Level 2 Autism. Empower parents to navigate challenges effectively and ensure their children's well-being on the autism spectrum. Together, we can create an environment that understands and caters to their unique needs.




