Introduction
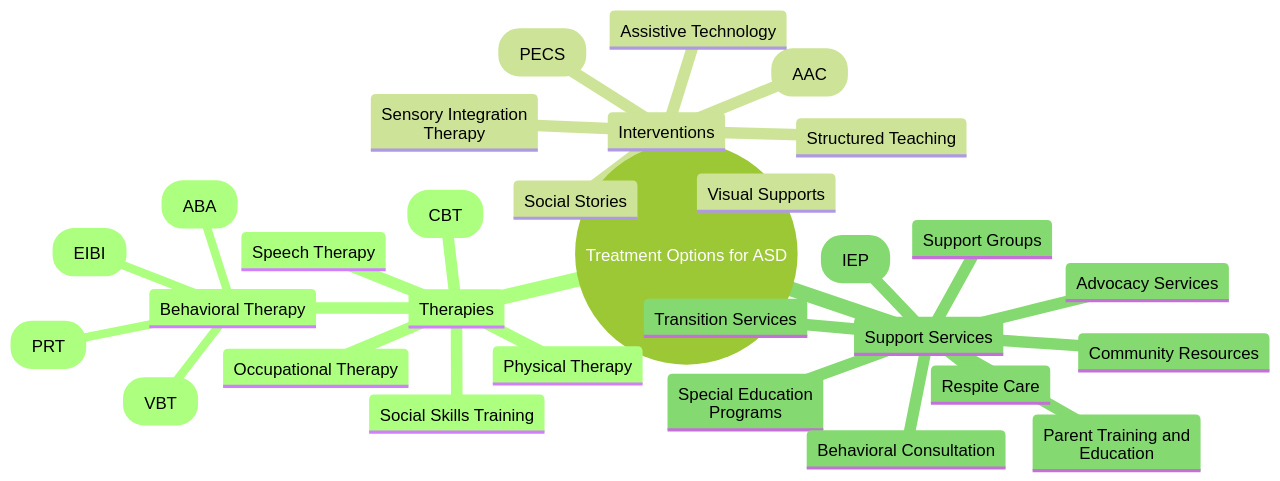
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and its treatment options is crucial for parents and professionals alike. ASD is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior in varying degrees. The spectrum nature of ASD means that each individual is impacted uniquely, requiring a wide range of treatment options. In this article, we will explore the various treatment options available, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, early intervention services, and other therapeutic approaches. We will also discuss the importance of evidence-based approaches and the need for personalized treatment plans. By gaining a deeper understanding of ASD and its treatment options, we can provide better support and care for individuals with autism
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Treatment Options
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition, influencing social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior in various degrees. Its spectrum nature means it impacts individuals uniquely, necessitating a broad range of treatment options, including behavioral therapies, educational interventions, family therapies, and medication.
An option recognized for its effectiveness is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. This approach targets enhancing specific behaviors and skills in individuals with ASD, using evidence-based techniques to promote positive behaviors and reduce challenging ones. It's highly individualized and tailored to meet the specific needs of each person with ASD, greatly enhancing their overall functioning and quality of life.

Recognizing the importance of early diagnosis and intervention for children with ASD is critical. Early intervention is a key component in achieving the most favorable outcomes for children with ASD. States are mandated to provide early intervention services until the age of 3, after which, services are provided by the school district. Behavioral therapies, especially those based on ABA, are among the most effective interventions for ASD. Other therapeutic options include occupational therapy, speech therapy, physical therapy, and pharmacological therapy.
However, it's crucial to acknowledge the need for evidence-based approaches and the risks associated with non-evidence-based therapies. Several types of evidence-based behavioral interventions are available, such as early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI), naturalistic developmental behavioral interventions (NDBIs), pivotal response training (PRT), discrete trial teaching, and the Lovaas model. While there are no FDA-approved medications that directly affect the core symptoms of ASD, some medications can help manage behavioral symptoms.
Understanding ASD requires a non-linear approach. Currently, ASD is categorized into levels 1, 2, and 3, with level 3 being the most severe. However, this linear model often overlooks the diversity of experiences within autism and leads to unfair comparisons. A pie chart or wheel model can better encapsulate the diverse traits and experiences of individuals with autism. This model recognizes that symptoms may evolve over time, allowing for a more dynamic understanding of autism. It's important to remember that there is no "easy" or "good" autism, and each individual's experience is unique and complex. The pie chart model provides a visual representation of the various traits and their varying degrees of impact on individuals with autism. It offers a more nuanced understanding of the condition, emphasizing the strengths, abilities, and capacities of autistic individuals. While the pie chart model simplifies the complexity of autism, it provides a clearer visual of the diverse types and shapes that autism can take
2. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy: An Overview
Applied Behavior Analysis, or ABA therapy, is a scientifically validated method that focuses on understanding and modifying behavior in response to changes in the environment. The goal of ABA therapy is not only to promote specific behaviors such as social skills, communication, and academic abilities but also to develop adaptive learning skills like fine motor dexterity, hygiene, grooming, domestic capabilities, punctuality, and job competence.
One of the key areas that ABA therapy targets is social skills enhancement. It employs techniques to improve social interactions and relationships, although the specific techniques may vary depending on the individual's needs and the context.
Communication development is another crucial aspect of ABA therapy. While no explicit strategies are mentioned in the context, the therapy generally employs various techniques to improve communication skills, such as verbal behavior training and picture exchange communication system.
ABA therapy also plays a significant role in academic improvement. The therapy uses strategies based on learning principles to bring about positive changes in behavior, breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps, providing systematic reinforcement, and utilizing visual supports. The collaboration between therapists, educators, and parents is crucial to create a consistent and supportive learning environment.
Fine motor skills, which involve the use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, are important for tasks such as writing, drawing, and using utensils. ABA therapy uses specific techniques and activities, such as manipulating small objects, using scissors, and practicing handwriting, to improve these skills.
Hygiene and grooming skills, which are essential for daily living, are also addressed in ABA therapy. The therapy focuses on teaching individuals specific behaviors and helping them understand the consequences of their actions, thus enabling them to learn and develop hygiene and grooming skills.
ABA therapy can also be a useful tool for teaching domestic capabilities. It provides structured and consistent instruction, helping individuals acquire and strengthen skills related to daily living activities, such as cooking, cleaning, and personal hygiene.
Promoting punctuality is another area where ABA therapy can be effective. By using behavioral strategies and techniques, such as reinforcement, prompting, and shaping, individuals can develop and maintain punctuality skills.
Job competence is also enhanced through ABA therapy. By providing appropriate training to therapists, focusing on improving their skills and knowledge in implementing ABA therapy techniques, the therapy can lead to better outcomes for children with autism.
ABA therapy is implemented in real-world situations with the aim of increasing helpful behaviors and decreasing harmful ones. This approach helps individuals with autism generalize their skills to real-life situations and achieve better outcomes.
The effectiveness of ABA therapy is backed by various research designs, including single-case experimental designs, consecutive controlled case series studies, and group designs like randomized controlled trials. These designs ensure both internal and external validity in the research studies.
The article also discusses a study aiming to understand whether children who receive a personalized treatment dose based on data-driven approaches achieve better outcomes. The study uses the Vineland-3 comprehensive interview form to assess function throughout ABA treatment and analyzes the relationships between Vineland scores and variables such as hours of service, modality of supervision (in-person vs. telehealth), and COVID-19-induced changes.
The findings suggest that there are statistically and clinically significant improvements in function for children with ASD, regardless of the number of hours of service received. The study also identifies significant associations between the modality of supervision and Vineland scores. These findings challenge the notion of a linear dose-response relationship in ABA therapy and underscore the importance of tailoring treatment dosage to individual client needs.
Overall, the study provides insights into optimizing ABA therapy and highlights the need for further research in this area. The potential of technology-driven innovation and data analytics tools to personalize ABA therapy and improve outcomes is emphasized, along with the impact of COVID-19 on telehealth utilization and its effects on treatment response
3. Role of Parent Advocates in ABA Therapy
Parent advocates are pivotal in the execution of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, serving as a vital link between the child, the therapist, and the broader support network. Their role encompasses understanding the unique needs of the child, communicating these to the therapist, and ensuring that the therapy aligns with these needs.
To enhance communication between parent advocates and ABA therapists, it is essential to establish regular communication channels, clearly define roles and responsibilities, practice active listening, share relevant information, and approach communication with respect and empathy. This effective communication is crucial to the successful implementation of therapy and support services.
Moreover, parent advocates are instrumental in reinforcing the strategies and behaviors learned during therapy sessions at home. This reinforcement ensures continuity and efficacy of the therapy. Parent advocates can support and reinforce ABA therapy strategies at home by actively participating in the therapy sessions, learning the techniques used by the therapists, and implementing them consistently in the home environment.
The importance of early intervention is underscored in enhancing socialization, communication, behavior, academic success, and family dynamics for children with autism. To better understand and meet their child's unique needs in ABA therapy, parent advocates can employ several strategies. These include actively participating in their child's therapy sessions, communicating openly and regularly with the ABA therapist, seeking out resources and educational materials specific to their child's diagnosis and ABA therapy, and connecting with other parents who have children in ABA therapy.
The necessity of clinical integrity in ABA therapy is also emphasized. In the context of resources such as PEC cards, the right picture symbols for individuals with autism can have a significant impact on their learning and growth. Parent advocates can find resources and support through various channels, including online platforms, organizations or associations focused on ABA therapy, local support groups, and workshops.
Parent advocates not only serve as the primary point of communication between various stakeholders but also ensure that the therapy is personalized to the child's unique needs. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the continuity of the therapy by reinforcing learned behaviors at home. Therefore, the role of parent advocates is indispensable in the successful implementation of ABA therapy. The article also emphasizes the importance of clinical integrity and the use of appropriate resources in the therapy process
4. Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Children with Autism
Addressing challenging behaviors in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a comprehensive understanding of the child's unique needs and an arsenal of effective strategies. ABA therapy, a widely used approach for treating autism, offers an array of methodologies tailored to each child's specific needs.
Among these methodologies are positive reinforcement techniques, which involve giving rewards or incentives for desired behaviors, such as praise, tokens, or other preferred items. This approach encourages individuals with autism to continue exhibiting those behaviors, thereby reducing challenging behaviors. Additionally, antecedent-based intervention is another technique that involves identifying and modifying triggers for challenging behaviors. However, understanding the root causes of these difficulties is also crucial. For example, children with ASD often have difficulties with expressive language and understanding non-verbal cues, which can lead to frustration and problematic behaviors. They may also struggle in social situations, like understanding others' perspectives and following social rules. Moreover, these children may find it challenging to deal with unstructured time and may become overwhelmed by sensory information.
These behavioral difficulties are symptoms of underlying challenges, not the child's fault. Hence, it is vital for parents and caregivers to look beyond surface behaviors and identify unaddressed needs. A behavior diary can be a useful tool for identifying patterns and triggers.
Strategies for managing these difficulties include using clear and concise language, employing visual supports such as visual schedules, creating social stories, and providing a structured and predictable environment. This can help reduce anxiety and minimize challenging behaviors. However, as one expert notes, "Unfortunately, due to a number of factors such as service availability and staff shortages, individuals may not receive the amount or quality of treatment they need". This underscores the importance of parents and caregivers working closely with professionals, like therapists and educators, who can provide guidance and support in implementing these strategies.
The article also discusses the challenges faced by families dealing with severe challenging behavior and offers practical strategies to ensure everyone's safety. This includes proactive strategies, such as modifying the child's schedule, creating a safe space within the home, and using protective equipment. The article emphasizes the importance of creating a safety plan for the family to follow in case of a behavioral crisis and the need for increased availability of behavioral services.
In the end, remember that managing challenging behaviors requires patience, consistency, and professional support when needed. Taking advantage of the effective strategies provided by ABA therapy and working closely with professionals can help parents and caregivers provide the necessary support and guidance to children with autism
5. Navigating Support Services for Children with Autism
The journey that parents embark on to unlock and utilize support services for their children with autism can often feel maze-like. Covering a broad spectrum, these services range from medical to therapeutic, educational, and community support. One of the most crucial steps in this journey is understanding what services are available, how to access them, and their potential benefits for the child.
For families with newly diagnosed children within the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a wealth of resources and support avenues are available. The Autism Society of Oregon (ASO), for instance, serves as a wellspring of information and support. Additional lifelines for families navigating the intricate landscape of special healthcare needs include the Oregon Family to Family Health Information Center.
The Swindells Resource Center is another pillar of information and support for families grappling with developmental differences. In addition, there are government bodies like the Office of Developmental Disabilities Services (ODDS) and the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) program, each offering unique forms of support.
The educational sphere also offers assistance in the form of early intervention programs and special education services. Local support groups provide a network of shared experiences and understanding, underlining the power of community. The Autism Society of Oregon goes a step further, sponsoring social groups and clubs, along with summer camps and online social groups for autistic children and teens.
In another context, the article discusses the benefits of CBD pastes and concentrates. Seen as some of the most potent CBD oil products available, a small portion placed on the tongue can deliver effects within 10 to 15 minutes, lasting up to 12 hours. Despite the strong flavor which may deter beginners, their high concentration and long-lasting effects offer good value for money. These products can be found in both online and physical CBD oil stores.
The article concludes with some practical advice for parents of children and teens on the autism spectrum. This includes strategies for handling social rejection, preventing meltdowns, and managing defiant teens. All these resources and tips together form a comprehensive guide to help parents navigate the complexities of autism support services.
A practical guide to navigate these support services could include researching and gathering information about available support services in the area, such as therapy centers, support groups, and educational programs specifically designed for children with autism. Parents may find seeking recommendations from other parents or professionals with experience in autism support services helpful. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions. Contacting local organizations or associations that specialize in autism to inquire about available resources and services can guide parents in accessing appropriate support for their children.
Creating a support network by connecting with other parents who have children with autism can also be beneficial. Online forums, support groups, and social media platforms can help in finding and connecting with other families who are going through similar experiences. Staying informed about the latest research and developments in autism support services can help parents make informed decisions regarding the best approaches and interventions for their children.
Remember, every child with autism is unique, so it's important to tailor the support services to their specific needs. Regularly assess and adjust the services as necessary to ensure they are effectively meeting your child's needs
6. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Autism
Understanding and enhancing social skills is a key component in the journey of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) management. Children with ASD often struggle with interpreting social cues, expressing their emotions, and interacting effectively with their peers. With the implementation of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, these challenges can be addressed through techniques such as role-playing, social narratives, and video modeling, which can significantly improve these skills.
When it comes to sensory processing disorder (SPD), occupational therapists bring their expertise to the table. They employ group activities as an effective method to help children with SPD understand and navigate social situations more comfortably. The use of play-based learning, interpretation of non-verbal communication, establishment of visual boundaries, organization of low-motor activities, and attention direction towards other children are all strategies that can bolster social skills. The Star Institute is a notable entity in the field of SPD treatment and research.
In adults with less severe ASD or Asperger's syndrome, the road to improving their social skills can be marked by gradual progress. It's important to understand personal motivations and goals when deciding to work on social skills. Clear values and informed decisions about the pursuit of social skills improvement can be beneficial. Many individuals with ASD have successfully adapted to social norms and learned to navigate the complexities of socializing. Effective strategies can include seeking mentorship, practicing in real-world scenarios, and joining social skills training groups. The use of scripts or rote memorization can also aid in social interactions. It's important to recognize the positive aspects of ASD and adjust expectations accordingly.
Parents can play a significant role in reinforcing these strategies in both home and social environments. This provides children with autism plenty of opportunities to practice and enhance their social skills. Structured and consistent social skills training, teaching appropriate social behaviors, and strategies for initiating and maintaining conversations can be beneficial. Visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules, can be helpful in reinforcing social skills and promoting social understanding.
Role-playing activities are effective in enhancing social skills in individuals with autism. By engaging in role-playing scenarios, individuals with autism can practice and develop important social skills such as communication, perspective-taking, and problem-solving. These activities provide a safe and structured environment for individuals with autism to learn and practice social interactions, which can then be transferred to real-life situations.
Social stories can be an effective tool for teaching social skills to children with autism. They provide a structured way to present information about social situations and appropriate behaviors, using clear and concise language.
Parents can facilitate social skills development by advocating for their child's needs and ensuring that appropriate interventions and supports are in place. By actively engaging with professionals, educators, and therapists, parents can help create a supportive environment that promotes social skill development. This may involve attending meetings, sharing information and resources, and collaborating with professionals to develop effective strategies for their child. Additionally, parents can provide ongoing support and reinforcement at home, reinforcing social skills learned in therapy sessions and providing opportunities for social interaction in a safe and structured manner.
Incorporating social skills training in ABA therapy can be an effective practice for children with autism. By combining the principles of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) with targeted social skills interventions, therapists can help children develop and enhance their social interaction skills. ABA therapy focuses on identifying and modifying behaviors through positive reinforcement, prompting, and modeling. By incorporating social skills training into ABA therapy, therapists can teach children important skills such as turn-taking, initiating and maintaining conversations, understanding nonverbal cues, and perspective-taking.
Parents looking for resources and support to enhance social skills development in children with autism can find helpful information on websites like www.asd.media. These websites provide articles and guides on effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism. Additionally, they may offer digital access to resources and subscriptions that provide ongoing support and guidance for parents in this area
7. Building a Supportive and Inclusive Community for Parents and Professionals
Building a nurturing and inclusive community is a crucial component of improving the outcomes of treatment for children on the autism spectrum. Such a community serves as a vital link between parents and professionals, fostering an environment where experiences can be shared, collective learning can occur, and reciprocal support can be provided. This community encourages teamwork, continual learning, and progress, which in turn promotes favorable outcomes for children with autism.
However, this community isn't merely about support - it's about diversity and inclusivity. It's about acknowledging that families from all walks of life bring unique perspectives and experiences that can enrich our understanding of autism and its treatment. As researchers and professionals, it's crucial to approach our work with humility and understand that these families and communities are the experts. As Kristin A. Buss and Frances M. Lobo insightfully said, "We need to realize they are the experts and that we must learn from them."
Additionally, this community should also be a place where parents, especially those from diverse backgrounds, can find empowerment. Many parents who are also academics, for instance, encounter challenges in balancing their roles as scholars and parents due to the lack of support and understanding from institutions. However, they have found ways to build communities, create non-traditional family arrangements, and advocate for themselves. They demand recognition for their complex lives and the assets and knowledge they bring to their work. This is a testament to the power and resilience of parents, and it is something that our community should strive to support and learn from.
Parent advocates play a pivotal role in creating and nurturing such a community. They can help bridge the gap between researchers and families, ensuring that the voices of parents are heard, and their experiences are recognized. They can contribute to creating a community that is not just supportive but also diverse, inclusive, and empowering. They can help ensure that our community is a place where everyone is valued, everyone is heard, and everyone can learn and grow.
To build a supportive and inclusive community for autism spectrum treatment, several key factors need to be prioritized. Firstly, education and awareness are paramount. By educating the community about autism, its challenges, and the importance of support, understanding and empathy can be fostered. Providing accessible and inclusive resources and services for individuals on the autism spectrum and their families is also essential. These resources can include specialized therapy programs, support groups, and community events tailored to their needs. Finally, collaboration and partnerships with local organizations, healthcare providers, and schools can create a network of support, ensuring that individuals with autism receive comprehensive care and opportunities for growth.
Strategies to create a collaborative and inclusive community in autism therapy may involve promoting communication and cooperation among therapists, parents, and individuals with autism. Encouraging open and respectful dialogue, fostering a sense of belonging, and involving all stakeholders in decision-making processes can contribute to the creation of an inclusive community. Providing training and education to all members of the community can help increase understanding and empathy towards individuals with autism and their unique needs.
One approach to foster collaboration and learning in the autism treatment community could be to establish online platforms or forums where professionals, researchers, and parents can connect and share their experiences, knowledge, and resources. This would allow for cross-collaboration and the exchange of best practices. Organizing conferences, workshops, or webinars focused on autism treatment and intervention methods can provide opportunities for professionals to come together, learn from each other, and discuss advancements in the field.
Parents can actively participate in a supportive autism community by connecting with local support groups, attending workshops and seminars focused on autism, engaging in online communities, staying informed about the latest research and developments in autism, seeking professional guidance, and sharing their personal experiences and insights.
Parent advocates empower parents to navigate autism support services and provide guidance and resources to help them overcome the challenges they may face. By sharing their own experiences and knowledge, parent advocates help create a network of support, connect families with appropriate services and therapies, and foster a sense of community among parents of children with autism.
A possible solution to create a platform for parents and professionals to share experiences in autism treatment could be to develop an online forum or social media group specifically dedicated to this purpose. This platform could provide a space for parents and professionals to connect, ask questions, share resources, and exchange personal experiences related to autism treatment.
Providing resources, information, and guidance to empower parents to navigate autism support services, connect with other parents who are facing similar challenges, and share their experiences can help create a supportive community. Offering unlimited digital access to relevant content and articles can further support parents in their journey of raising a child with autism.
To provide mutual support in an inclusive community for autism spectrum treatment, it is important to create a supportive and understanding environment. This can be achieved by fostering open communication, promoting acceptance and empathy, and providing resources and information on autism spectrum treatment. Encouraging collaboration and creating opportunities for individuals to share their experiences and insights can also facilitate mutual support within the community. It is essential to ensure that all members of the community feel valued and included, and that their individual needs and perspectives are respected
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and its treatment options is crucial for parents and professionals alike. ASD is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior in varying degrees. The spectrum nature of ASD means that each individual is impacted uniquely, requiring a wide range of treatment options. In this article, we have explored various treatment options available, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, early intervention services, and other therapeutic approaches. We have also discussed the importance of evidence-based approaches and the need for personalized treatment plans.
The main points discussed in this article include the effectiveness of ABA therapy in enhancing specific behaviors and skills in individuals with ASD, the role of parent advocates in ensuring effective communication and reinforcement of strategies at home, strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with autism, navigating support services for children with autism, enhancing social skills development in children with autism, and building a supportive and inclusive community for parents and professionals.
The broader significance of this article's topic is that it provides valuable information and guidance to parents and professionals involved in the care of individuals with autism. By gaining a deeper understanding of ASD and its treatment options, we can provide better support and care for individuals with autism. This article emphasizes the importance of evidence-based approaches, early intervention services, effective communication between parents and professionals, and building a supportive community.
In conclusion, by understanding ASD treatment options and implementing evidence-based strategies such as ABA therapy, parents can play an active role in supporting their child's development. It is essential to seek out appropriate resources and support services while also advocating for the unique needs of each individual. By working together as a community that values diversity, inclusivity, collaboration, and continuous learning, we can ensure better outcomes for individuals with autism. Start now to gain more knowledge about ASD treatment options by visiting asd.media




