Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and its treatment options is crucial for providing effective support and care for individuals on the spectrum. The wide-ranging nature of ASD means that treatment approaches must be diverse and individualized. This article explores the various treatment options available, including behavioral therapies, speech therapy, occupational therapy, medication management, and tailored interventions for children with ASD. It also delves into the challenges faced by adults on the autism spectrum and their neurodiverse partners. By understanding the importance of collaboration and building a supportive community, we can enhance the outcomes of ABA therapy and create a nurturing environment for individuals with autism and their families.
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Treatment Options
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a broad term used to describe a group of neurodevelopmental conditions. These conditions, varying greatly from person to person, manifest as unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behavior patterns. The wide-ranging nature of ASD means the treatment approach must be as diverse and individualized as the individuals themselves.
The treatment of ASD requires a personalized approach that takes into account the individual's unique strengths, weaknesses, and specific symptoms. A host of treatment options are available, including behavioral therapies, social skills training, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and medication management.

The effectiveness of these treatments can differ from person to person, and it's crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in ASD. These professionals can provide a comprehensive evaluation and develop a personalized treatment plan that ensures the most appropriate and effective treatment approach.
Behavioral therapies are an important intervention for ASD. These therapies focus on addressing specific behaviors and teaching new skills to individuals with ASD. Through structured and consistent interventions, they can aid individuals with ASD in learning essential life skills, improving communication and social interactions, and reducing challenging behaviors. However, assessing the efficacy of these therapies can be a complex process, hence the need for professional guidance.
Speech and language therapy is another crucial intervention for individuals with ASD. This therapy focuses on improving communication skills, such as speech production, language comprehension, and social interaction. Speech and language therapists help individuals with ASD develop effective communication skills, enhancing their ability to express themselves and improving their overall quality of life.
Occupational therapy has also shown to be beneficial for children with ASD, helping to improve their social skills, sensory processing abilities, and overall functional independence. Occupational therapists can assist children with ASD in developing and enhancing their fine motor skills, self-regulation, and daily living skills, while also addressing sensory sensitivities and challenges.
Various medication options are available to manage symptoms of ASD, addressing specific symptoms such as hyperactivity, aggression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and repetitive behaviors.
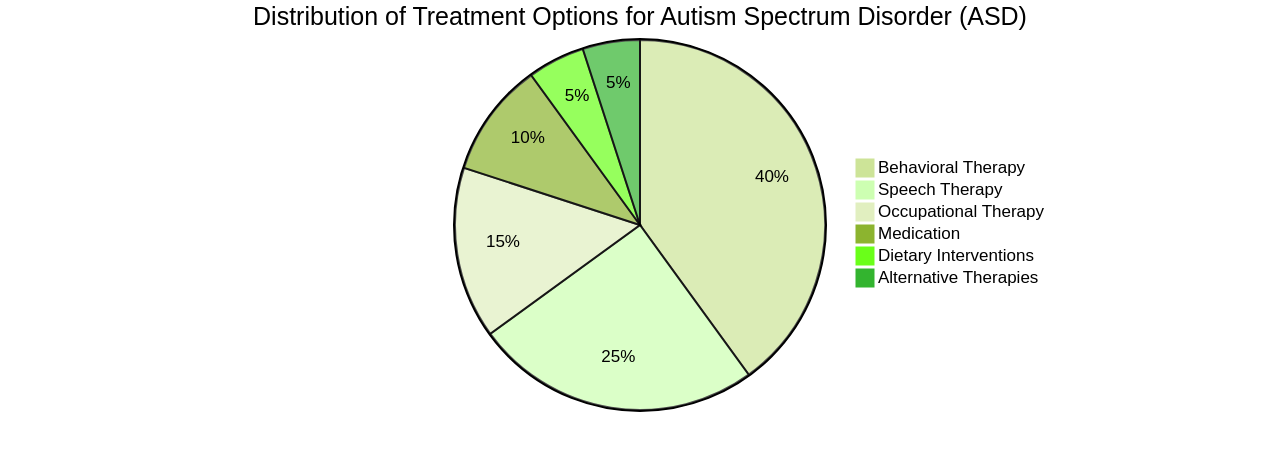
However, medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional experienced in treating individuals with ASD, as each person's needs and response to medication may vary.
In addition to professional therapies and medication, there are tailored interventions for children with ASD that can enhance their social skills. By providing personalized strategies and support, these interventions help children develop communication, social interaction, and adaptive skills. This can include individualized therapy sessions, social skills training programs, and the use of visual aids and schedules to promote structure and routine.
It's also important to address repetitive behaviors in individuals with ASD by implementing effective strategies. These strategies can include providing structured routines and schedules, using visual supports, incorporating sensory breaks and activities, teaching alternative behaviors and coping skills, and utilizing positive reinforcement and rewards.
Moreover, addressing the challenges faced by adults on the autism spectrum and their neurodiverse partners is essential. Issues like the absence of healthy relationships, guilt, alexithymia, and even porn addiction may arise. The concept of "Cassandra syndrome", referring to the emotional deprivation experienced by neurotypical partners of individuals with autism, also comes into play. These partners often grapple with unmet emotional needs, low self-esteem, and feelings of anger, guilt, anxiety, and depression. They may feel overlooked, disregarded, or rejected by their autistic partners. Communication difficulties, sensory sensitivities, and the tendency for individuals with autism to engage in lengthy monologues about their special interests further complicate matters.
Therefore, understanding, support, and resources are imperative for both individuals on the autism spectrum and their neurodiverse partners. These resources may include networks such as the Interactive Autism Network (IAN) research project. This journey requires patience, persistence, and the utilization of all available resources to ensure the well-being of individuals with ASD and their partners.
2. Exploring Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy for Autism
"Applied Behavior Analysis, also known as ABA, is a recognized 'gold standard' treatment for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), backed by extensive research. The core tenet of ABA therapy is the use of positive reinforcement to encourage beneficial behaviors while reducing behaviors that may be detrimental or hinder learning.
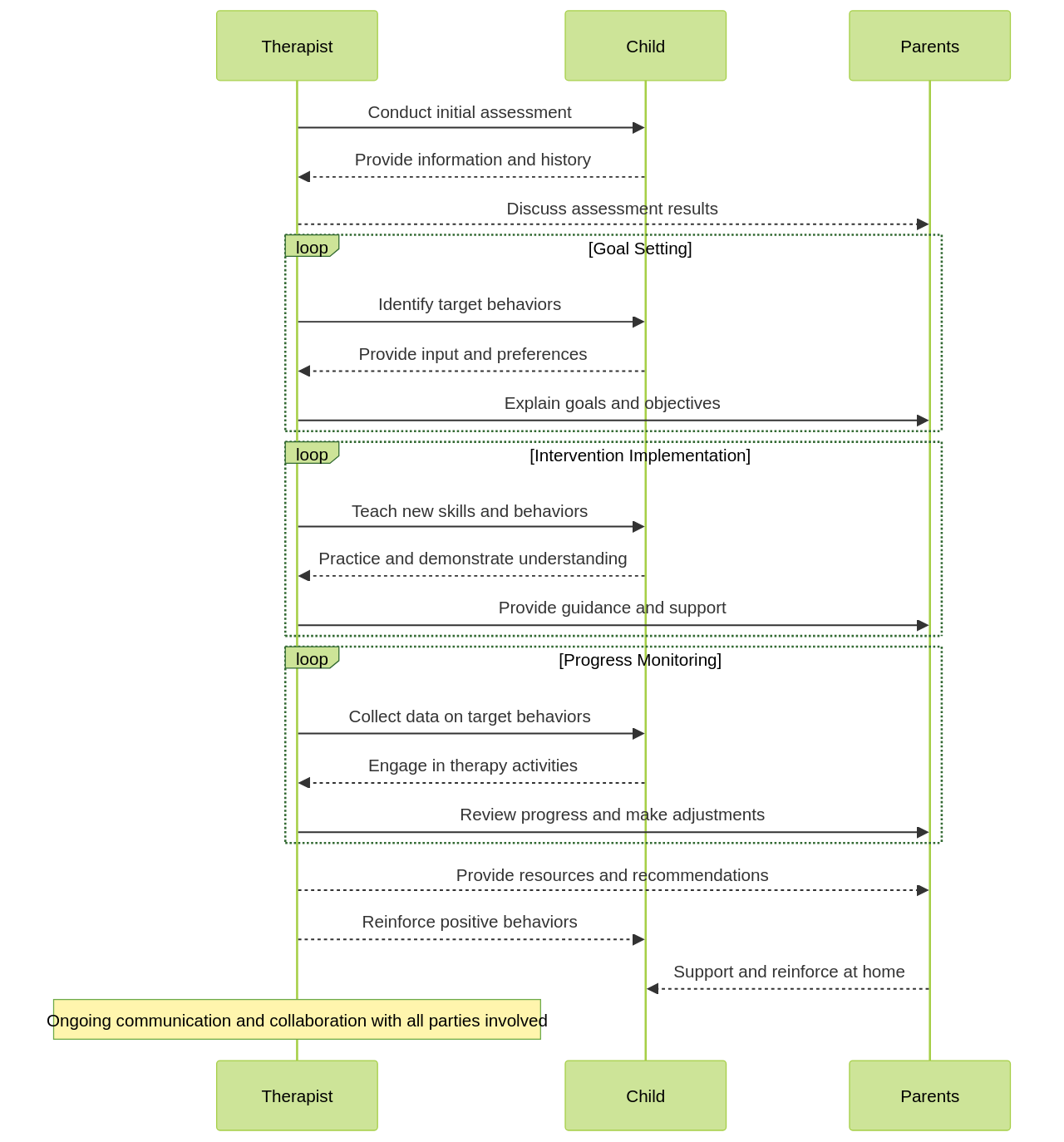
This therapy can be highly customized, allowing therapists to adjust their strategies to match the child's specific skills, needs, interests, preferences, and family context.
ABA therapy aims to enhance a variety of skills in children with autism, including social interaction, communication, reading, academics, and adaptive living skills. The latter category includes fine motor dexterity, hygiene, grooming, domestic capabilities, punctuality, and job competence.
The influential work of Ole Ivar Lovaas, a pioneer in the field, in the late 1980s showed that early, intensive ABA therapy of up to 40 hours per week led to children becoming indistinguishable from their peers after several years. This pivotal study has been replicated, reinforcing the understanding that intensive ABA therapy leads to superior treatment outcomes compared to less intense therapy models.
The intensity of the treatment is a critical factor. Comprehensive treatment involving 25-40 hours per week of therapy is associated with better outcomes. In contrast, focused treatment, requiring 10-24 hours per week, is more suitable for older children or those who have already undergone early intensive ABA therapy.
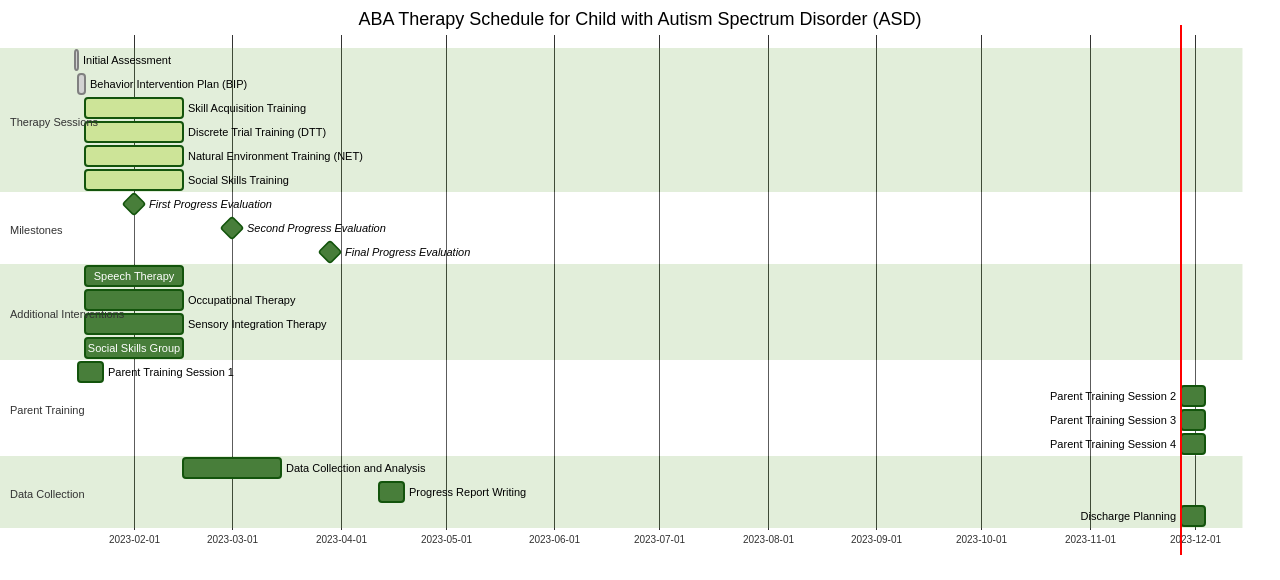
ABA therapy is not a monolith; it includes various techniques like discrete trial teaching (DTT), natural environment teaching (NET), and functional communication training (FCT). It's not just about "table time" or extended hours in front of a table.
A common misconception is that a smaller dosage of ABA therapy is sufficient. However, Lovaas' research showed that only 2% of children achieved normal intellectual and educational functioning with 10 hours of therapy per week. Therefore, for a young child diagnosed with ASD, best practices recommend 25 to 40 hours per week of intensive comprehensive ABA.
In essence, ABA therapy should embody scientific rigor and structure. The intensity and dosage of ABA therapy are crucial in achieving positive outcomes for individuals with ASD. The recommendations and treatment options available should be grounded in this scientific rigor."
3. Role of Parents in ABA Therapy: Challenges and Strategies
Parental involvement in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial. Parents, as primary caregivers, often ensure the principles of ABA are carried out at home, outside the structured therapy sessions. This involves implementing strategies and ensuring consistency, which are both vital for the therapy's effectiveness.
ABA therapy aims to help children with ASD modify their thinking and behavior patterns. It is grounded in the principles of observable and measurable behavior, with the goal of shaping behaviors through positive reinforcements. Parents, who spend a significant amount of time with their children, play a crucial role in maintaining these principles outside the therapy sessions. This requires consistency and persistence, which are key factors in achieving long-term behavior changes.
Here are some suggestions to maintain consistency in ABA therapy at home:
- Establish a schedule: Create a consistent daily routine for therapy sessions at home. Set specific times for therapy activities and adhere to them as much as possible.
- Create a dedicated therapy area: Designate a specific area in your home for ABA therapy. This will help create a structured environment and minimize distractions.
- Communicate with the therapist: Regularly communicate with the ABA therapist to discuss goals, progress, and any challenges you may be facing. They can provide guidance and support to ensure consistency.
- Involve family members: Encourage other family members to participate in therapy sessions. This will help reinforce skills learned during therapy and promote consistency across different settings.
- Use visual aids: Visual schedules and prompts can be helpful in maintaining consistency. Use visual aids to outline the therapy activities and provide clear instructions for your child.
- Provide positive reinforcement: Consistently use positive reinforcement techniques, such as praise and rewards, to encourage desired behaviors during therapy sessions. This will help motivate your child and reinforce consistency.
Parents seeking support resources for ABA therapy can find valuable information and guidance from reputable sources. These resources can provide insights on navigating the challenges and improving outcomes in ABA therapy implementation. Additionally, subscribing to trusted platforms can provide ongoing support and access to industry insights tailored to overcoming specific challenges in ABA therapy.
Parents should also prioritize managing emotional stress while their child is undergoing ABA therapy. ABA therapy can be challenging for both the child and the parent, so it is crucial for parents to take care of their own emotional well-being. Some strategies that can help parents manage emotional stress in ABA therapy include seeking support from other parents who have gone through similar experiences, practicing self-care activities such as exercise or meditation, and seeking professional help from therapists or counselors who specialize in working with parents of children with special needs.
When it comes to balancing responsibilities as a parent in ABA therapy, it is important to prioritize your child's therapy while also managing your other obligations. It may be helpful to communicate with your ABA therapist or provider to discuss scheduling options that work best for you and your family.
To ensure effective communication with the ABA therapy team as a parent, it is important to establish clear lines of communication and maintain regular contact with the team. This can be done through various means such as phone calls, emails, or in-person meetings. Additionally, actively participating in therapy sessions and asking questions to stay informed about the progress and goals of the therapy are crucial.
Parents in ABA therapy can benefit from practicing self-care to manage stress and maintain their well-being. Prioritizing self-care, seeking support, taking breaks, practicing mindfulness, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are some of the self-care tips for parents in ABA therapy.
When participating in ABA therapy as a parent, it is important to set realistic expectations. This involves understanding that progress may take time and that every child's journey is unique. It is important to communicate openly with the ABA therapist and collaborate on setting achievable goals for your child.
Parent support groups can play a valuable role in ABA therapy. These groups provide parents with a platform to connect with others who are going through similar experiences and facing similar challenges. They can share information, resources, and strategies for navigating the complexities of ABA therapy.
In essence, the role of parents in their child's ABA therapy is multifaceted and critical. It involves various responsibilities, ranging from implementing behavior plans to collaborating with their child's therapy team. By doing so, they can significantly contribute to their child's progress and well-being.
4. Managing Time and Responsibilities While Supporting Child's ABA Therapy
The journey of supporting a child with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) through Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a significant commitment for parents. It often feels like a balancing act, juggling therapy sessions, work, personal time, and the needs of other children. However, effective time management strategies can act as a guiding light in this journey.
Creating a structured schedule is a powerful first step. This should include specific time blocks for therapy sessions, meals, playtime, rest, and other daily activities. Such a schedule helps manage tasks more efficiently, ensuring a balance between work, personal time, and therapy. It also provides predictability and structure for both the parent and the child, enhancing their sense of security and the child's learning experience.
Prioritizing tasks is another key strategy. Collaborating with the ABA therapist to establish clear goals and objectives for the therapy can help in this regard. This collaboration allows parents to focus on the areas that need to be addressed first, breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps. It reduces the feeling of being overwhelmed and helps parents stay organized.
Delegation is a powerful tool in time management. Assigning tasks to family members or hired help can lighten the load, freeing up time for parents to focus on their child's therapy. It can be tasks like meal preparation, household chores, or running errands. This not only helps manage time efficiently but also ensures that all tasks are taken care of.
Self-care is a crucial aspect of this journey. Parents often tend to overlook their own needs while caring for their child undergoing therapy. However, taking care of oneself is not a luxury, but a necessity. Self-care activities can help parents manage stress, prevent burnout, maintain a positive outlook, and replenish their energy, enabling them to provide better support to their child.
Family dynamics often shift when raising a child with ASD, especially with siblings. It's important to acknowledge and validate the feelings of siblings who might sometimes feel overlooked or misunderstood. Open conversations about autism, using simple and age-appropriate language, can help siblings understand their brother or sister's unique needs. Moreover, allocating special one-on-one time with each child can help in building stronger relationships and ensuring that each child feels valued and loved.
When choosing an ABA provider, it's important to look for certain "green flags" that indicate ethical and effective practices. These include individualized programming, respecting the child's assent and withdrawal, balanced BCBA caseloads, parent training and support, naturalistic teaching strategies, and BCBA-owned agencies. Such indicators can help parents ensure that they are choosing a provider who prioritizes ethical and effective practices.
Remember, seeking support from relevant organizations or communities specializing in autism support services can provide valuable resources, guidance, and support. Online platforms or forums dedicated to autism support services can offer a space for parents to connect with others going through similar experiences. It's perfectly okay to ask for help and take breaks when needed. This journey is a marathon, not a sprint, and maintaining a healthy balance is key for the well-being of the entire family.
5. Effective Strategies for Handling Challenging Behaviors in Children with Autism
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often exhibit behaviors that can be difficult to navigate, which can lead to stress for parents. It's crucial to understand that these behaviors are a reflection of the child's struggles with communication, sensory processing, and social interaction, rather than a fault of the child. This comprehension can foster empathy and patience in dealing with such situations.
The challenges posed by these behaviors extend beyond communication. Children with ASD can find it hard to understand others' perspectives, adhere to social norms, and manage unstructured time. Changes in routine can lead to confusion or frustration, and sensory processing issues, such as sensitivity to loud noises or touch, can instigate problematic behaviors.
Recognizing these behaviors as a form of communication is key. These behaviors often signal unmet needs. It's essential to delve beneath the surface behaviors to identify and address these underlying needs. As one insightful quote in this article states, "It's vital to look beyond the surface behaviors and discover the unaddressed needs the child is trying to communicate, rather than reacting to the behavior or resisting 'punishing'."
Addressing these behavioral challenges can involve various strategies. Visual aids, social stories, and supportive therapies can be of great help. Maintaining consistency in routines and expectations can provide a sense of security and predictability for the child. Positive reinforcement, such as praise that suits the child's unique needs, can be an effective form of encouragement. For instance, visual aids like "stress scales" can assist children in understanding and expressing their emotions.
The Challenging Behaviors Tool Kit provided by Autism Speaks is one such resource that can be beneficial. The tool kit offers strategies and resources to address challenging behaviors associated with autism, including positive strategies for behavior support, crisis management, and long-term solutions. It also includes a glossary and quick tips for caregivers. The Autism Response Team, available through Autism Speaks, can provide personalized support and connect individuals with autism and their families to information and resources.
Remember, managing challenging behaviors is a process that requires patience, consistency, and positivity. Progress may be slow, but every step forward is an achievement. Seeking professional help from psychologists or psychiatrists is recommended for handling difficult situations and accessing additional support.
In managing challenging behaviors in children with autism, implementing appropriate strategies and interventions is crucial. This can involve creating a structured and predictable environment, using visual supports and schedules, implementing positive reinforcement techniques, and providing clear and consistent expectations. Working closely with professionals such as therapists, behavior analysts, and educators specializing in autism to develop individualized behavior plans and interventions tailored to the specific needs of each child can be beneficial.
Understanding what triggers challenging behaviors in children with autism is a key aspect of providing effective support and intervention. By identifying and understanding these triggers, caregivers and professionals can develop strategies to prevent or manage challenging behaviors. This involves careful observation and analysis of the child's environment, interactions, and sensory experiences. Recognizing patterns and common triggers can help implement strategies to create a more supportive and predictable environment for the child with autism.
Positive reinforcement plays a crucial role in managing challenging behaviors in children with autism. This involves providing rewards or incentives to encourage and reinforce desired behaviors. This approach focuses on recognizing and rewarding positive actions, which can help children with autism develop new skills, improve social interactions, and decrease the occurrence of challenging behaviors.
Parents dealing with challenging behaviors in children with autism can find support and resources through various channels. Organizations and websites specialize in providing information, guidance, and strategies for managing challenging behaviors in children with autism. Support groups and parent advocacy groups can offer a sense of community and provide opportunities to connect with others who may be facing similar challenges.
One effective strategy for building patience and consistency when managing challenging behaviors in children with autism is to establish a structured and predictable routine. This can reduce anxiety and frustration, provide clear and consistent expectations, and use positive reinforcement and rewards to encourage desired behaviors.
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, is a widely used approach for encouraging positive behaviors in children with autism. It focuses on systematically applying interventions to teach and reinforce desired behaviors, while also reducing behaviors that may be harmful or interfering with learning.
One effective strategy for managing challenging behaviors in children with autism is to celebrate small victories. By acknowledging and celebrating even small improvements or successes, it can help reinforce positive behaviors and motivate the child to continue making progress. This can also help build the child's self-esteem and confidence, which can further contribute to managing challenging behaviors.
6. Enhancing Social Skills Development through ABA Therapy
"Children with autism and ADHD often encounter difficulties when navigating social interactions. To help tackle these challenges, strategies such as structured teaching methods, visual supports and social narratives have proven to be effective. By providing a predictable and structured environment, along with clear instructions, these strategies break down complex social skills into smaller, manageable steps.
Structured teaching methods are particularly beneficial when dealing with autism. They allow for a predictable environment and clear instructions, which helps children understand social expectations and navigate social situations. Visual supports like visual schedules and social stories can be highly effective in this regard.
Role-playing techniques also offer a unique and effective approach to improving social skills. By engaging in pretend play scenarios, children can practice their social interaction skills in a safe and controlled environment. This method allows children to learn how to initiate conversations, take turns, understand social cues, and navigate social situations. It also aids in developing appropriate behavior, empathy, and problem-solving skills.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has also shown to be beneficial for children with autism in developing social skills. This form of therapy uses specific techniques and interventions to teach individuals how to engage in appropriate social interactions. Through the use of positive reinforcement and structured learning, ABA therapy can help children learn and practice social skills in a controlled and supportive environment.
Parents can support their child's social skills development in ABA therapy by creating opportunities for their child to interact with peers and practice social skills in a wide range of settings. This could include playdates, structured activities, or joining social skills groups. Parents can also provide consistent reinforcement and positive feedback when their child demonstrates appropriate social behavior.
Social stories, a narrative-based intervention, provide individuals with autism with specific information about social situations. By incorporating these into ABA therapy, therapists can help children with autism improve their social communication and interaction abilities.
Video modelling, another effective tool, uses videos to demonstrate appropriate social behaviors and interactions, allowing children with autism to observe and learn these skills in a visual and structured manner.
In the case of children with Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD), social interaction skills are pivotal. Occupational therapists can assist these children in honing their social skills through group activities. The author's experience working with children in social skills groups underscores the importance of identifying shared interests and nurturing them within the group.
The Star Institute is an excellent resource for SPD treatment and research. It provides a wealth of information and strategies for building social skills, such as recognizing the importance of play, understanding non-verbal communication, using visual boundaries, planning low motor activities, drawing attention to other children, and participating in social skills groups."
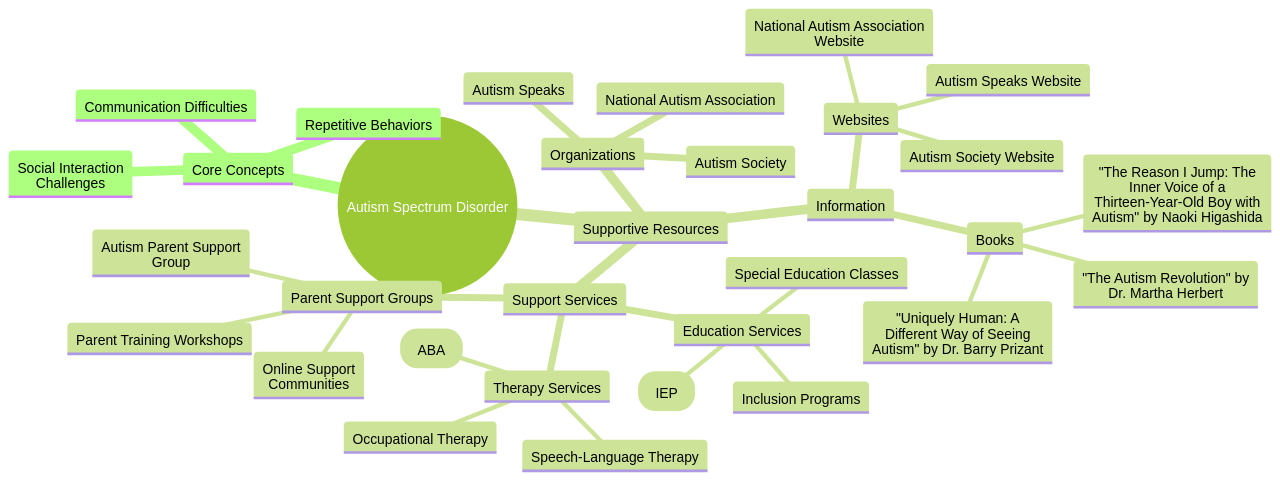
7. Navigating Support Services for Children with Autism: Resources and Tips
Navigating the complex terrain of support services for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can seem daunting. However, it is imperative to remember that there is a wealth of resources available at your fingertips. Among these resources is ASD Media, a comprehensive platform dedicated to providing a wealth of information on ASD treatments such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. This platform extends its support to parents and professionals involved in ASD care, offering guidance on how to empower themselves and navigate the challenges associated with autism support services.
As parents embark on this journey, they must be proactive in exploring their options, engaging in active inquiries, and assertively advocating for their child's needs. Personal stories, like the one shared by the author about their child Keegan, highlight the importance of early intervention and the need for unwavering advocacy in securing the right services.
This process can present its unique challenges, such as long waiting lists and the task of evaluating the quality of care provided by professionals. Establishing a trust-based relationship with therapists is essential, but it's equally crucial to realize that a child with ASD's progress may not follow a predictable path. There is no universal guide to raising a child with ASD; each journey is unique.
A myriad of resources and support systems are available for families grappling with a new ASD diagnosis. The Autism Society of Oregon (ASO) and the Oregon Family to Family Health Information Center provide excellent starting points for families seeking information and resources. The Swindells Resource Center offers support for families with developmental differences, while county mental health agencies provide services like counseling, respite services, and support groups.
Programs like the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) provide income and medical insurance for eligible children with disabilities. Educational supports, such as early intervention programs and early childhood special education, are also available. Parents can connect with their child's school district to access these special education supports. Organizations like FACT Oregon and Washington PAVE can assist with school-based supports.
In addition, there are summer camps and social groups for children with autism and their families, as well as resources for parents and teens. While the journey can feel overwhelming, it is important to remember that you are not alone. The support you need is out there, and with persistent effort and advocacy, you can secure the necessary resources for your child's unique needs.
ASD Media, with its vast repository of resources, can provide parents with the necessary tools to navigate these challenges. By visiting the ASD Media website, parents can find valuable information and guidance on understanding and accessing support services. ASD Media's resources aim to empower parents in navigating the challenges of autism support services and unlocking the potential for their children. With unlimited digital access, parents can stay informed and equipped to advocate effectively for their child's needs. ASD Media is committed to providing valuable information and support to parents on their journey of advocating for their child.
8. Building a Supportive Community: The Importance of Collaboration in the Field of ABA Therapy
The success of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy significantly hinges on creating a supportive community and fostering collaboration. This unity among parents, therapists, educators, and other professionals, all working together, can greatly enhance the outcomes for children diagnosed with autism. This collective synergy of knowledge, experiences, and strategies not only enriches the therapeutic process but also serves as a robust support system for parents.
Recognizing ethical and effective practices in ABA providers is key in this collaborative environment. These "green flags" include the prioritization of individualized programs tailored to each learner's unique strengths, needs, and interests, and the respect for learners' assent and right to withdraw from therapy. Maintaining well-balanced caseloads for Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) assures effective case oversight and supervision. Other indicators of ethical practices are the emphasis on parent training and support, the integration of naturalistic teaching strategies, and having the agency owned by BCBAs who align with the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB)'s code of ethics.
However, it is equally crucial to be aware of the "red flags" that may signal potentially harmful or outdated practices in ABA therapy. These include an undue focus on reducing self-stimulatory behavior or enforcing sustained eye contact without considering the individual's comfort and sensory issues. Providers aiming to "recover" or "cure" autistic individuals also raise red flags. As Ashleigh from the ABA Resource Center aptly puts it, "Many autistic individuals consider autism a significant part of who they are. Regardless of the goal of therapy, it should never be to recover or cure a child."
Other warning signs include forced compliance without allowing for autonomy, recommending an unusually high number of therapy hours without substantiating the need, relying solely on food as a primary reinforcer, and refusing to collaborate with other providers. These signs indicate that the provider's practices may not align with modern, ethical standards in ABA therapy.
ASD Media, dedicated to cultivating this sense of community and collaboration, offers a platform for growth within the ABA therapy industry. This platform connects parents, therapists, and educators, providing a space where these individuals can share information, resources, and support related to autism. It aims to empower parents in navigating autism support services and promote collaboration among therapists and educators to better serve children with autism.
By keeping an eye out for green and red flags, parents and professionals can ensure they are engaging with ethical, effective, and supportive ABA providers. In this way, ASD Media contributes to building a collaborative community for children with autism, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive, integrated approach to therapy and the value of a supportive network.
The collaboration between parents and professionals in autism therapy can bring numerous benefits. By working together, parents and professionals can share valuable insights and knowledge about the child's needs and progress. Parents can play an active role in implementing therapy strategies at home, enhancing the child's progress and generalizing skills across different settings. This collaboration also helps build a strong support system for the child and the family, with parents feeling empowered and supported by the professionals, and professionals gaining a deeper understanding of the child's unique needs and strengths through the parents' input.
In the ABA therapy industry, fostering collaboration can be achieved through the establishment of professional networks or organizations where practitioners and experts can come together to share best practices, research findings, and collaborate on projects. Regular conferences, workshops, and training sessions can also facilitate collaboration by bringing professionals together to exchange ideas and build relationships.
In conclusion, a collaborative approach is considered one of the best practices for success in ABA therapy. By involving multiple stakeholders, such as therapists, parents, and educators, in the therapy process, a more comprehensive and effective treatment plan can be developed. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone is working towards the same goals and that interventions are consistent across different settings. The success stories from individuals who have benefited from a collaborative approach in ABA therapy highlight the positive outcomes that can be achieved when all parties work together.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and its treatment options is crucial for providing effective support and care for individuals on the spectrum. The wide-ranging nature of ASD means that treatment approaches must be diverse and individualized. This article has explored various treatment options available, including behavioral therapies, speech therapy, occupational therapy, medication management, and tailored interventions for children with ASD. It has also delved into the challenges faced by adults on the autism spectrum and their neurodiverse partners.
The main points covered in this article include the importance of personalized treatment plans that take into account the unique needs and strengths of individuals with ASD. It emphasized the effectiveness of behavioral therapies, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and medication management in improving communication skills, social interactions, and overall quality of life. The article also highlighted the role of parents in ABA therapy, providing strategies for maintaining consistency at home and managing emotional stress.
The broader significance of this article's topic lies in the need for collaboration and building a supportive community. By understanding the importance of working together as parents, therapists, educators, and professionals in the field of ABA therapy, we can enhance the outcomes of treatment and create a nurturing environment for individuals with autism and their families.
In conclusion, by embracing a collaborative approach to ASD treatment and creating a supportive community, we can empower parents, provide effective support services for children with autism, and promote positive outcomes. Let's work together to enhance the lives of individuals with ASD. Start now by accessing valuable resources on ASD Media.




