Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Level 2, frequently referred to as moderate autism, is crucial due to the significant challenges it presents in social interaction and communication. Children diagnosed with this level manifest repetitive behaviors and often struggle with routine alterations. A tailored approach is necessary for effective support and intervention, considering that each child's experience with autism is unique.
In this article, we will explore the unique needs and behaviors associated with Autism Spectrum Level 2 and the importance of understanding and supporting children with this diagnosis. We will discuss the role of organizations like Autism Speaks in providing resources and support for families navigating the autism journey. Additionally, we will delve into strategies for managing repetitive behaviors and interventions that can aid in the social and communication development of children with moderate autism. By understanding and addressing these needs, we can create a supportive environment for children on the autism spectrum level 2 to thrive
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Level 2
Understanding Autism Spectrum Level 2, frequently referred to as moderate autism, is crucial due to the significant challenges it presents in social interaction and communication. Children diagnosed with this level manifest repetitive behaviors and often struggle with routine alterations. A tailored approach is necessary for effective support and intervention, considering that each child's experience with autism is unique.

Moderate autism demands substantial assistance and understanding, given the distinct needs and behaviors associated with it. Recognizing these needs is the initial step in establishing an effective support system. Children with this level of autism may exhibit repetitive behaviors and find adaptations to changes challenging. However, remembering that each child is unique and their experiences with autism can vary significantly is essential.
Autism Speaks, a leading organization, plays an instrumental role in this context. They offer resources, support, and valuable information for families navigating the autism journey. They provide various screening tools and questionnaires for early detection and diagnosis of autism, in addition to comprehensive information on signs, symptoms, and causes of autism, including critical statistics and facts about the condition.
Autism Speaks also facilitates interventions and access to vital services for individuals with autism, such as insurance coverage and caregiver skills training. Their dedicated Autism Response Team (ART) offers personalized support and connects individuals with autism and their families to resources and information. This team forms a critical link for families seeking the most effective ways to manage and support their child's development.
Beyond providing resources, Autism Speaks organizes fundraising events like walks and campaigns to raise funds for research and support programs. Their mission embodies the promotion of autism awareness, provision of resources, and fostering a supportive community for families affected by autism.
Strategies for managing repetitive behaviors in children with moderate autism can help reduce and redirect these behaviors, promoting more adaptive and functional behaviors. Implementing visual schedules and routines, providing structured and predictable environments, using visual supports and social stories, and teaching alternative behaviors or coping strategies can be beneficial. Consulting with professionals, such as behavior analysts or therapists specializing in autism, can help develop a personalized plan addressing the child's specific needs.
Interventions for children with moderate autism can involve a variety of strategies, including behavioral therapies like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), focusing on shaping behavior through positive reinforcement. Speech and language therapy can improve communication skills, while occupational therapy can address sensory issues and promote independence in daily activities. Social skills training and social stories can aid in developing appropriate social interactions and relationships.
Implementing strategies for enhancing social skills like encouraging activities that promote communication, providing clear and consistent instructions, using visual aids, and offering positive reinforcement for appropriate social behaviors can significantly improve social interaction in children with moderate autism. Creating a supportive and inclusive environment that fosters understanding and acceptance can contribute to the social development of these children.
Understanding the unique needs of children with Autism Spectrum Level 2 requires considering various strategies and approaches. Seeking guidance from professionals experienced in working with individuals on the autism spectrum can provide helpful tips and techniques for creating a supportive and structured environment, developing effective communication skills, and implementing appropriate behavioral interventions.
Personalized approaches based on each child's unique needs and strengths can enhance social skills in children with moderate autism. Using visual aids, social stories, sensory integration techniques, and structured routines can help children navigate social situations and develop their social communication skills. Providing opportunities for structured, supportive social interaction and peer play can also contribute to their social development.
Improving communication skills in children with moderate autism may involve structured social skills training through techniques like visual supports, social stories, and role-playing. Speech therapy can also be beneficial in helping these children develop their communication skills.
In conclusion, understanding Autism Spectrum Level 2 and the unique needs and behaviors associated with it is crucial. With the right resources, support, and a personalized approach, managing and supporting the development of children with this level of autism becomes a journey of understanding and growth
2. The Role of Parent Advocates in ABA Therapy
In the sphere of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, the role of advocates is both influential and indispensable. These advocates act as a crucial bridge, linking the child undergoing therapy, the team of therapists, and the broader support network. Their responsibility is to understand the child's unique needs and communicate them effectively to the therapy team, ensuring that the child receives the necessary support and resources tailored to their individual needs.
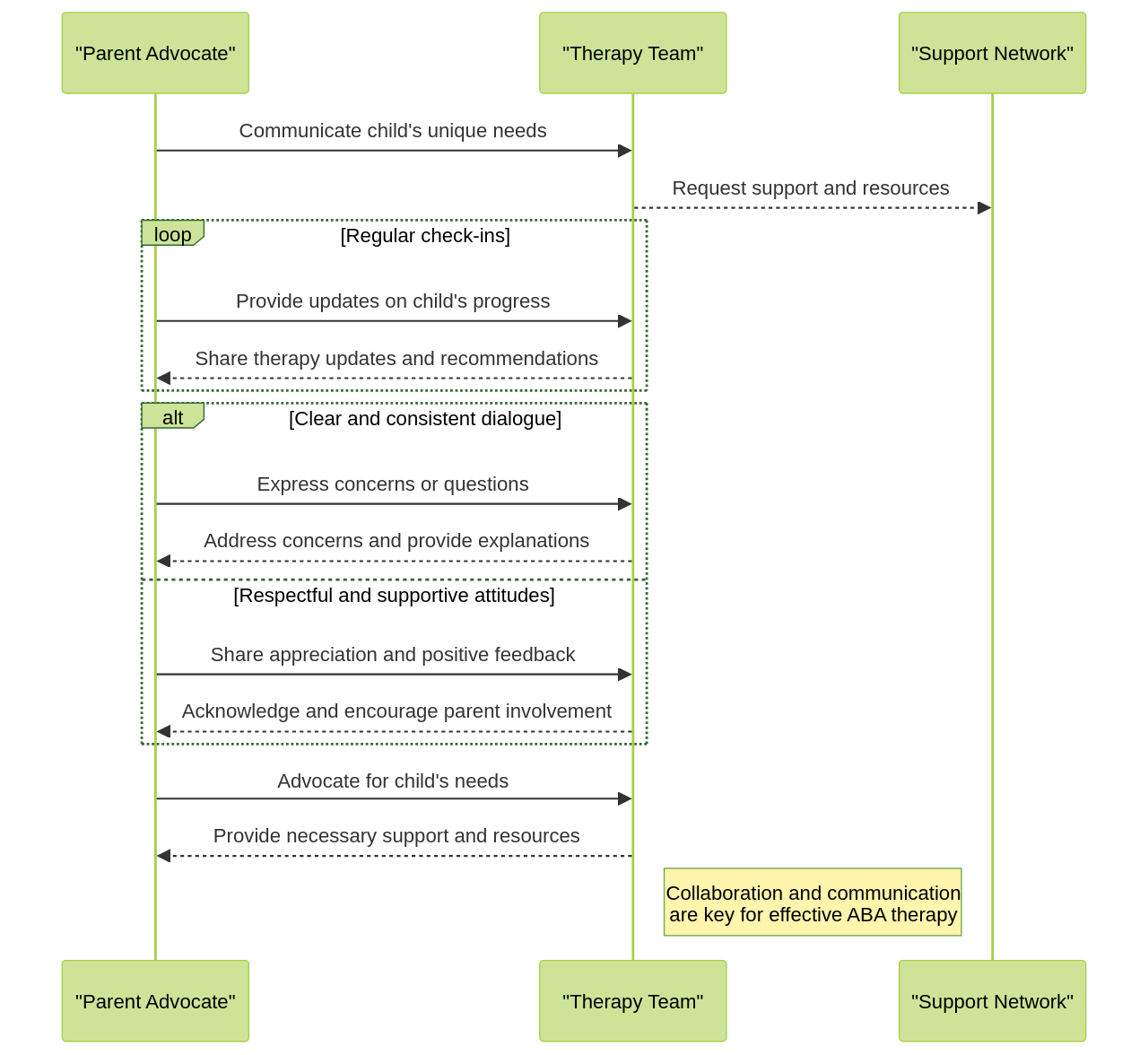
Clear and consistent dialogue is key to this process. Regular check-ins and meetings provide a platform for open dialogue and problem-solving. Establishing clear roles and responsibilities can help streamline communication and avoid misunderstandings. A respectful and supportive attitude towards each other strengthens the working relationship and ultimately benefits the child.
Furthermore, these advocates extend their role beyond therapy sessions. They are instrumental in applying and reinforcing the strategies and skills learnt during therapy within the home environment. By actively participating in the therapy process, collaborating with the therapists, and implementing the strategies at home, advocates can support and reinforce the skills learned during ABA therapy sessions. Consistent reinforcement aids in cementing the skills learnt and contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of the therapy.
Respecting the privacy of these individuals and challenging negative stereotypes is of the utmost importance. Advocates also play a key role in sharing valuable information and resources with caregivers, parents, and professionals involved in the care of the child. To this end, parent advocates can connect with other parents in similar situations, creating a supportive network and sharing resources and information.
The experiences and insights gained from this process can be shared within the community, fostering a supportive environment for these individuals. Participatory research can serve as a valuable tool in understanding and addressing the needs of these individuals, further enhancing the effectiveness of the therapy.
Advocates also have the potential to improve the lives of individuals with autism by advocating for their needs and rights, understanding the challenges they face in accessing support and services, and listening to and learning from their experiences. This not only bolsters the therapy process but also contributes to creating a better world for the autistic community
3. Effective Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors
Managing challenging behaviors in children with autism, particularly those at level 2 on the spectrum, can be an arduous task. One resourceful approach to this challenge is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, which uses a range of efficient methodologies. ABA therapy concentrates on identifying the root causes of challenging behaviors and applying evidence-based interventions to manage them.
One effective ABA strategy is positive reinforcement. This technique rewards desirable behavior, motivating its repetition. By offering rewards or incentives, such as verbal praise or tokens, children are encouraged to maintain these behaviors. The key to successful reinforcement lies in its individualization to the child's specific needs and preferences, along with an emphasis on consistency and immediate reinforcement.
Another impactful strategy is Functional Communication Training (FCT). FCT aims at equipping children with alternative communication skills to replace problematic behaviors used for communication. This training allows children to express their needs effectively and constructively, which can lead to a significant improvement in their communication skills.
It's vital to understand that these strategies are not universal solutions. They need to be tailored according to the unique needs and strengths of each child. By comprehending each child's specific challenges, therapists can create individualized treatment plans that cater to their needs. This personalized approach ensures the therapy strategies are effective and relevant, leading to better outcomes.
Consistency in applying these strategies is equally crucial. To maintain this consistency, a clear and well-defined plan should be in place. This plan should outline specific behavior targets, intervention strategies, data collection procedures, and reinforcement systems. The strategies should be implemented not only during therapy sessions but also integrated into the child's daily routines. This integration ensures a consistent approach to managing behaviors, which is key to long-term success.
ABA therapy strategies require patience and effort but have the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for children on the autism spectrum and their families. With consistent application and a commitment to understanding and meeting each child's unique needs, children can navigate their world with greater ease and confidence. It's essential to collaborate with a qualified ABA therapist who can assess the child's behaviors and develop a personalized intervention plan. The goal is to provide targeted interventions that help children develop essential skills and overcome barriers associated with autism.
There are resources and support available for parents and professionals to effectively manage challenging behaviors in children with autism using ABA therapy. These resources offer guidance and strategies for addressing specific behaviors and promoting positive behavior changes. Seeking out these resources and support systems ensures the necessary tools and knowledge are available for managing challenging behaviors effectively. Through these resources and consistent application of ABA therapy strategies, we can help children on the autism spectrum lead a better quality of life
4. Navigating Support Services for Children on the Autism Spectrum Level 2
For families with children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder Level 2, an abundance of support services exist, covering therapeutic interventions, educational assistance, and community-based programs.
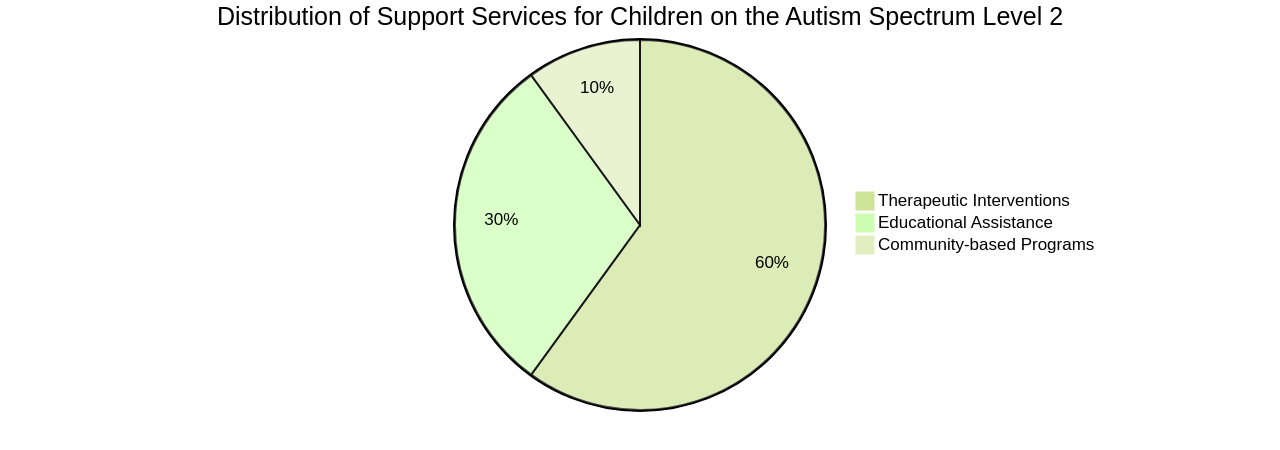
The journey through these services may seem daunting for parents, but it's essential to remember that you're not alone. Many professionals and families who have navigated this path before are ready to lend a helping hand.
A significant transition for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is the move from high school to further education. This process can be overwhelming, but there are various avenues to explore, each tailored to individual needs. These range from specialized post-secondary experiences and life skills programs to certificate programs, technical schools, community colleges, and four-year universities.
For students who are independent and possess cognitive and adaptive skills, a college degree may be a viable option with the right accommodations in place. Students who may need more support but possess academic skills can consider colleges with specific autism support programs. These bridge the gap between the student and the school faculty, providing an environment conducive to learning.
Community colleges can serve as a stepping stone for those who want to pursue college education. These institutions often accommodate students who might find adjusting to college expectations challenging. For students who may not be candidates for a college degree due to cognitive functioning, certificate or technical schools can be an appropriate choice. These schools offer focused instruction and can accommodate organizational and time management challenges.
Non-degree seeking students with higher levels of support can consider special programs focusing on independent living skills. Some individuals might find supported or customized work experiences more suitable, often with the help of their local department of vocational rehabilitation.
Various organizations, such as the Autism Society Oregon, offer a wealth of resources and information to help parents understand and access these services. They host workshops, webinars, and social events, providing a community of support. Other resources like the Oregon Family to Family Health Information Center and the Swindells Resource Center provide information and support for families with special health care needs and developmental differences, respectively.
The Office of Developmental Disabilities Services (ODDS) offers support plans and access to services for children and adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Federal programs like the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) provide income and medical insurance for eligible children with disabilities and their families. Medicaid is also available for eligible children.
Educational supports can be accessed through county early intervention programs, early childhood special education programs, and special education services in school districts. The Autism Society Oregon sponsors social groups and clubs for kids and teens with autism, offering opportunities for social interaction and friendship.
In addition to these resources, parents can visit the website https://www.asd.media. This website provides various resources and articles related to promoting social skills in children with autism. You can find valuable information and tutorials on enhancing social skills step-by-step. Subscription options may also be available on the website to access unlimited digital content for a fee.
Parents can also find advice from other parents of children with autism spectrum level 2 on various online platforms and support groups. These platforms provide a space for parents to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek advice from others who have gone through similar situations. Many parents find it helpful to connect with others who understand their challenges and can offer guidance and support based on their own experiences.
Remember that seeking help and taking one step at a time is not just okay, but encouraged. The support is out there, ready to assist you on this journey
5. Enhancing Social Skills Development: Techniques and Approaches
ABA therapy's focus on social skills development for children with level 2 autism spectrum disorder is crucial. It's a process that nurtures their emotional and social intelligence, both critical for forging successful relationships and navigating various professional roles.
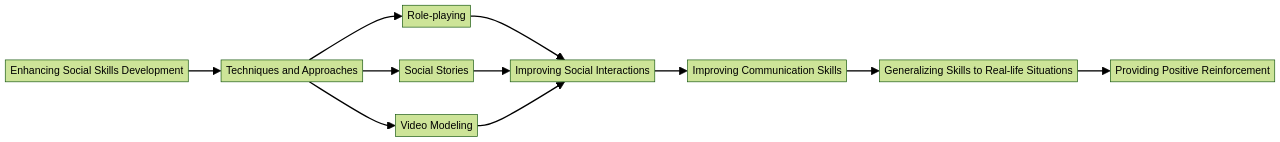
A variety of techniques are employed to achieve this, such as role-playing, social stories, and video modeling.
Role-playing proves to be a highly effective technique in ABA therapy for teaching social skills. It allows children to engage in simulated social situations, giving them an avenue to practice and learn appropriate behaviors and responses. This technique provides an environment where they can repeat, reinforce, and generalize social skills safely and under control, thereby contributing to the improvement of their social interactions and communication skills.
Another integral part of ABA therapy is the use of social stories. These are short narratives that describe different social scenarios, offering specific guidelines on how to behave and respond in these situations. By integrating social stories into the therapy, children with autism can learn appropriate social behaviors and improve their communication skills. This approach helps them recognize social cues, develop empathy, and navigate social interactions more successfully.
Video modeling is another method that proves effective. Here, children learn by watching videos of desired social behaviors and then imitating them. This approach, combined with other evidence-based strategies like peer-mediated interventions and naturalistic teaching strategies, can enhance the effectiveness of social skills instruction in ABA therapy. These strategies help children understand and practice appropriate social behaviors in a structured and supportive environment.
However, the learning doesn't stop at the therapy session. It's crucial to extend these skills to real-life situations, allowing for the generalization of skills. This practice aids children in gradually improving their social competence. While progress may seem slow at times, it's essential to remember that each child with autism spectrum disorder is unique, with their own quirks and idiosyncrasies. Even if they don't become the most socially adept, they can significantly enhance their social skills.
In this journey, it's also important to respect the feelings of these children. Some may have mixed emotions about enhancing their social skills, as it could seem like a departure from their true selves. Acknowledging these feelings can help them reconcile with the idea of social skill improvement and align it with their personal goals and values.
Support can come in various forms, such as social skills training groups, mentors, and counselors who provide guidance and encouragement. These supports help children with autism spectrum disorder navigate the complexities of social situations and improve their social skills without suppressing their unique traits.
Finally, celebrating small victories and providing positive reinforcement is vital. Positive feedback techniques involve providing praise, rewards, or other forms of positive reinforcement when a child with autism demonstrates desired social behaviors. This reinforcement encourages the child to continue practicing and improving their social skills. The road to social competence may be long and challenging, but with patience, understanding, and consistent practice, children on the autism spectrum level 2 can learn to navigate the social world more effectively
6. Building a Supportive Community: Sharing Experiences and Learning from Each Other
Building a support system is a vital part of managing the challenges associated with Autism Spectrum Level 2. The sharing of experiences and mutual learning can provide valuable insights and emotional support. ASD Media is dedicated to fostering such a community, where parents and professionals can come together, share their experiences, and learn from each other.
This community shares similarities with the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC), a professional membership organization that promotes high-quality early learning for children from birth to age 8. It links early childhood practice, policy, and research, serving as a resource for those who care for, educate, and work on behalf of young children. NAEYC offers a platform called "Hello," where members can engage in discussions, build connections, and discuss important early learning issues. It serves as a space for open discussion forums and interest forums on topics such as early childhood science, outdoor play, and supporting families with diverse languages.
Participation within this community can provide parents with a sense of belonging and empowerment, knowing they are not alone in their journey. This is akin to another forum dedicated to providing support for individuals dealing with a teen or adult child with a personality disorder. It offers resources, guidelines, and FAQs for parents seeking help and information. This forum has specific sections for parents to discuss their experiences and seek support from others in similar situations. Parents can discuss various topics in the discussion section, including dealing with name-calling, safe places, venting, and communication issues.
ASD Media's community is a similar platform, where users can share their stories, seek support, and discuss their experiences with others who understand. We foster a safe and supportive environment for all users, ensuring that everyone feels heard, understood, and empowered.
Joining the ASD Media community is simple. Visit their website at www.asd.media and follow the registration process to become a part of this supportive network. Here, you can connect with parents and professionals, engaging with the community through articles and discussions related to autism support services, social skills in children with autism, and other relevant topics.
Sharing your experiences within the ASD Media community can be done by commenting on articles and participating in discussions. Engaging with the community offers access to valuable resources and information related to autism spectrum disorder, and the opportunity to connect with others facing similar challenges. This can provide a sense of support and understanding.
Participation in the ASD Media community also allows for the sharing of your own knowledge and insights, contributing to the collective understanding of autism and potentially helping others in the process.
Share your experiences and insights within the ASD Media community!
For parents of children with autism, ASD Media offers online forums and social media groups dedicated to autism support, providing a space to share experiences, ask questions, and support one another.
In the ASD Media community, a sense of belonging is fostered by creating an inclusive environment in which individuals with autism feel valued and accepted. This is achieved through strategies such as promoting social skills in children with autism, providing a troubleshooting guide for challenges they may face, and using effective communication techniques. Furthermore, a sense of community is fostered through shared experiences, providing resources and support, and encouraging participation in community activities
7. Staying Updated: Importance of Continuous Learning in ABA Therapy
In the dynamic and ever-evolving realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, it's crucial for both parents and practitioners to stay informed about the latest advancements. This dedication to continuous learning and keeping in touch with the most recent updates ensures the highest quality of support for children within Autism Spectrum Disorder Level 2.
Organizations such as the Association for Behavior Analysis International (ABAI) are instrumental in this endeavor. As a nonprofit entity, ABAI strives to contribute to societal welfare through the development, improvement, and advocacy of behavior analysis science. They offer a myriad of resources, including research opportunities and continuing education (CE) credits recognized by esteemed organizations like the American Psychological Association (APA) and the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB).
Being a member of ABAI offers numerous perks, such as access to higher education resources, learning center videos, and journals. Members are also gifted with 10 complimentary virtual CE credits and are welcomed to a host of events like the Annual Autism Conference, the Annual Convention, and the Theory Philosophy Conference. These gatherings serve as platforms for discussing the latest in ABA research and practice, providing invaluable insights for parents and practitioners alike.
Beyond ABAI, resources like the "Behaviorbabe" website, managed by Dr. Amanda N. Kelly, are also worth exploring. This website is a repository of ABA-related information offering resources for students, parents, providers, and practitioners interested in behavior analysis. It provides a plethora of free resources, including podcasts and articles, with a membership option for extended content.
The mission of Behaviorbabe is to nurture a non-judgmental and supportive community aimed at collectively driving change. It covers an extensive range of topics such as treatment planning, advocacy, fire safety, ethics, and sustainability.
Staying updated with the most recent developments in ABA therapy is fundamental for delivering optimal support to children on the autism spectrum level 2.
Stay informed with the latest advancements in ABA therapy through ASD Media's newsletter!
To achieve this, it's recommended to refer to credible sources like academic journals, professional conferences, and publications by recognized experts. Subscribing to newsletters, such as the one offered by ASD Media, and joining online communities dedicated to ABA therapy can also help stay informed about new developments, techniques, and resources in the field.
Moreover, routinely visiting reputable websites or online platforms that focus on autism and ABA therapy, as well as attending conferences, workshops, and seminars related to ABA therapy, can provide valuable opportunities to learn from experts, network with professionals, and stay up-to-date with the latest advancements.
In essence, resources like ABAI and Behaviorbabe, along with academic journals, newsletters, and online communities, are integral to this continuous learning journey, offering a wealth of information and a supportive community for parents and practitioners
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Level 2 and the unique needs and behaviors associated with it is crucial. With the right resources, support, and a personalized approach, managing and supporting the development of children with this level of autism becomes a journey of understanding and growth. Organizations like Autism Speaks play a significant role in providing valuable resources, support, and interventions for families navigating the autism journey. Strategies for managing repetitive behaviors and interventions such as ABA therapy can aid in the social and communication development of children with moderate autism. By understanding and addressing these needs, we can create a supportive environment for children on the autism spectrum level 2 to thrive.
It is important to recognize that each child's experience with autism is unique, and tailored approaches are necessary to provide effective support. Building a supportive community where parents and professionals can share their experiences, learn from each other, and access valuable resources is essential for managing the challenges associated with Autism Spectrum Level 2. Continuous learning through organizations like ABAI and resources like Behaviorbabe ensures that parents and practitioners stay updated on the latest advancements in ABA therapy, enabling them to provide the highest quality support for children with moderate autism. By staying informed, connecting with others, and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can create an inclusive environment that fosters understanding, acceptance, and growth for individuals on the autism spectrum level 2.




