Overview
Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD) can be overwhelming for parents, as they involve significant delays in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Common types include Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's Syndrome. Understanding these disorders is crucial, and this article aims to provide you with insights into their symptoms, diagnostic processes, and therapeutic strategies. By emphasizing the importance of early intervention and tailored support, we hope to empower you in enhancing your child's development and quality of life.
Navigating the challenges associated with PDD can feel daunting, but you are not alone. Many parents have walked this path and found ways to support their children effectively. We encourage you to explore the symptoms and seek guidance from professionals who can help you understand your child's unique needs. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in your child's future.
As you read through this article, think about your own experiences and the challenges you may face. What questions do you have? What resources would be helpful for you? We invite you to share your thoughts in the comments or through our newsletter, as connecting with others can provide a sense of community and support. Together, we can foster a nurturing environment for our children to thrive.
Introduction
Understanding pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) is essential for parents navigating the complexities of their child's development. Conditions like Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's Syndrome impact many children, and recognizing symptoms while implementing effective strategies can truly make a difference. Yet, the path from identifying early signs to accessing appropriate interventions often raises difficult questions:
- How can parents effectively advocate for their child's needs in a system that can feel overwhelming?
This article explores vital concepts, symptoms, and strategies to empower families on this important journey.
Define Pervasive Developmental Disorders: Key Concepts and Terminology
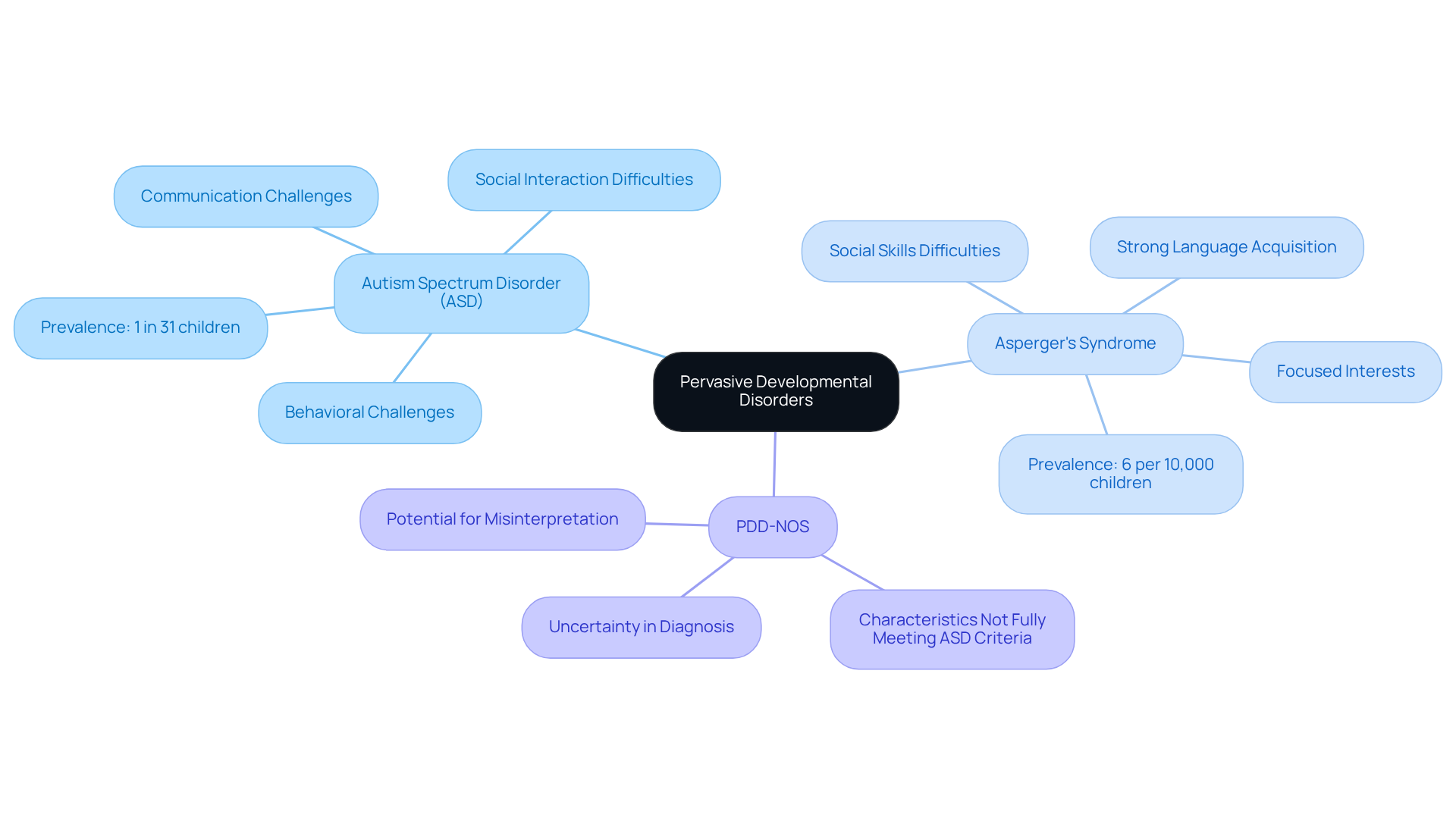
Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD) are defined as pervasive developmentally delayed conditions that include a variety of disorders marked by delays in social and interaction skills. Among these, the most recognized include Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Asperger's Syndrome, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS). Understanding these terms is essential for parents seeking clarity and support.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that impacts communication, behavior, and social interaction. It’s important to recognize the unique challenges that come with ASD, as each child navigates their journey in different ways.
Asperger's Syndrome, once considered a separate diagnosis, is now part of the ASD spectrum. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside focused interests and repetitive behaviors. Parents may notice their child’s distinct way of engaging with the world, which can be both fascinating and challenging.
PDD-NOS is a diagnosis given when a child shows some, but not all, characteristics of autism or other pervasive developmentally delayed conditions. This can leave parents feeling uncertain, but knowing this term helps in understanding their child's unique profile.
Familiarity with these terms not only aids in recognizing the nuances of each disorder but also fosters effective communication with professionals in the field. We encourage you to share your experiences and questions, as connecting with others can provide valuable support and insight.
Identify Symptoms and Early Signs of Pervasive Developmental Disorders
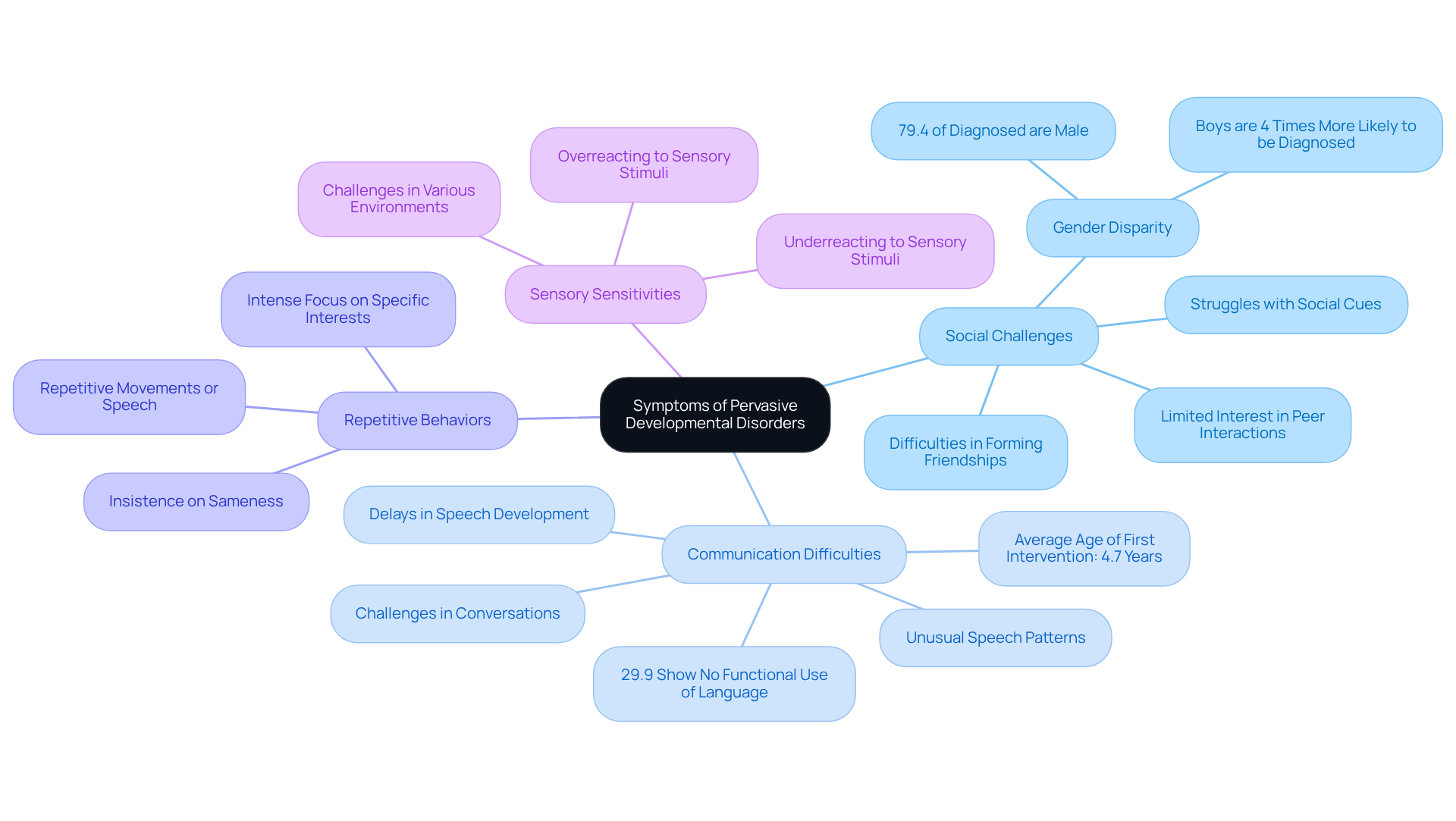
Identifying the early signs of pervasive developmentally delayed disorders (PDD) is crucial for facilitating timely intervention. As a parent, understanding these signs can be the first step toward ensuring your child's well-being. Common symptoms include:
- Social Challenges: Children may struggle to understand social cues, show limited interest in peer interactions, or face difficulties in forming friendships. Research shows that boys are almost four times more prone to being diagnosed with autism compared to girls, with 79.4% of those diagnosed with PDD being male. This highlights the importance of being aware of social development in your child.
- Communication Difficulties: Delays in speech development, challenges in initiating or maintaining conversations, and unusual speech patterns are prevalent. Approximately 29.9% of kids diagnosed with PDD demonstrate no functional use of language, underscoring the significance of early detection. The average age of first intervention for autism in the U.S. is 4.7 years, emphasizing the need for timely support.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Many young individuals engage in repetitive movements or speech, demonstrate an insistence on sameness, or exhibit intense focus on specific interests. These behaviors can significantly impact their daily functioning and social interactions, making understanding and support vital.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Children may overreact or underreact to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures. This sensitivity can lead to challenges in various environments, affecting their ability to engage with peers and participate in activities.
As parents, it's essential to closely observe your child's behavior and developmental milestones, noting any deviations from typical patterns. The occurrence of pervasive developmentally delayed conditions, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), impacts approximately 1 in every 36 young individuals in the U.S., making early action even more essential. Early intervention can profoundly influence a young person's ability to thrive, as timely support can enhance social skills and communication abilities, ultimately improving their quality of life. For further insights, resources like the interactive dashboard "Autism by the Numbers" provide valuable data on autism across all 50 states. Remember, you are not alone on this journey; seeking support can make a significant difference.
Navigate the Diagnostic Process: Evaluation and Assessment for Pervasive Developmental Disorders
Navigating the diagnostic process for pervasive developmentally delayed disorders (PDD) can feel overwhelming for parents, but understanding the essential steps can empower you to advocate effectively for your child.
-
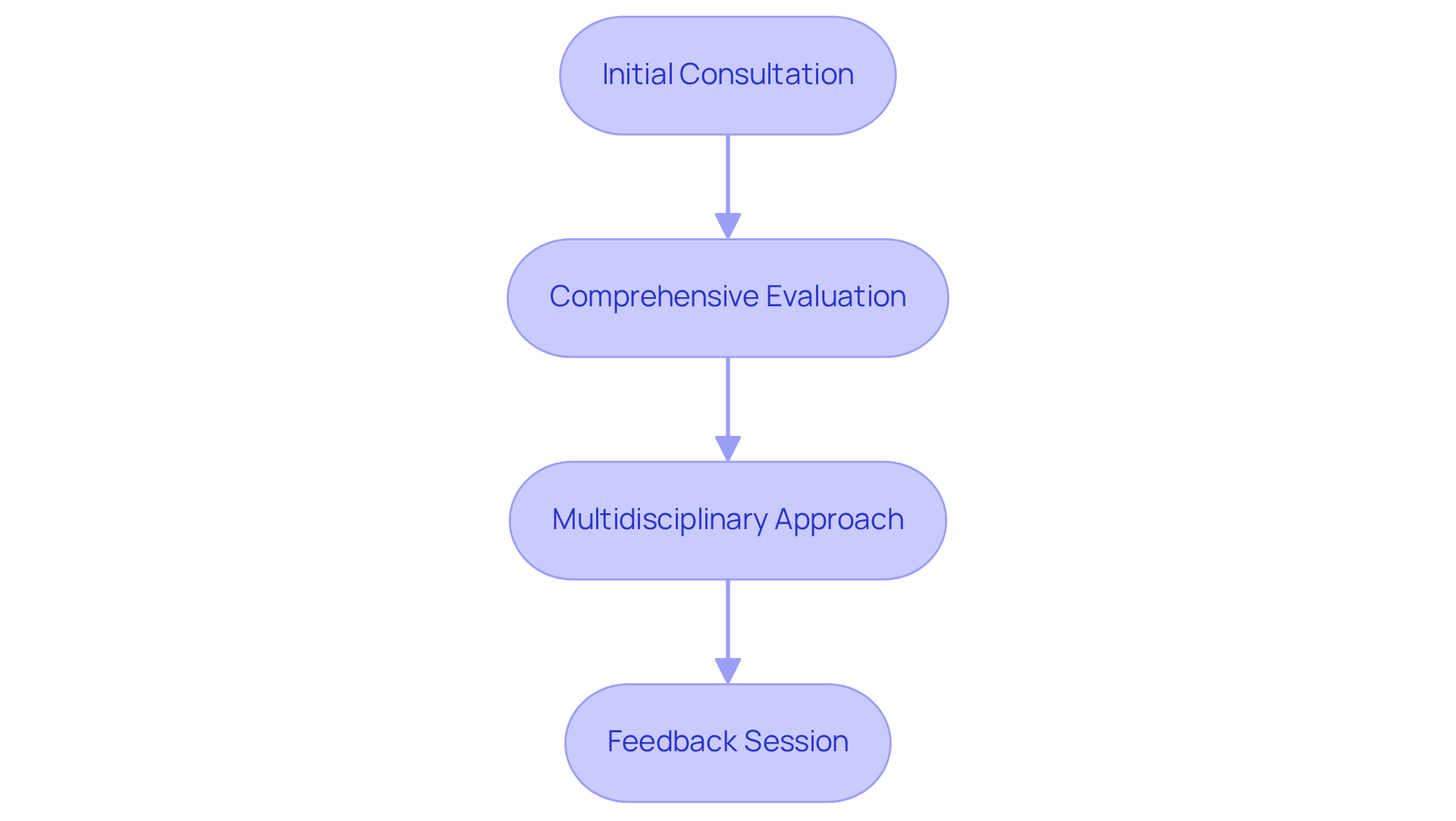
Initial Consultation: Begin by sharing your concerns with a pediatrician or psychologist who specializes in developmental disorders. This initial conversation is vital, as it lays the groundwork for further evaluation. Experts agree that addressing concerns early can significantly influence the diagnostic journey for children who are pervasive developmentally delayed, underscoring the importance of prompt discussions.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation: A thorough assessment typically involves standardized tests, behavioral evaluations, and developmental history questionnaires. These tools gather detailed information about your child's behavior and developmental milestones. Research shows that the median age for the earliest recorded evaluation for pervasive developmentally delayed is around 41 months, highlighting the necessity of timely assessments.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Often, a collaborative team of professionals—psychologists, speech therapists, and occupational therapists—works together to provide a holistic evaluation of your child. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of their development are considered. Families who engage a team of specialists frequently report gaining deeper insights into their child's needs, offering a more comprehensive understanding of their situation.
-
Feedback Session: After evaluations, you will participate in a feedback session where findings are discussed, and recommendations for intervention strategies are provided. This session is crucial for understanding the next steps in supporting your child's development. Pediatricians often stress that clear communication during this time enables parents to make informed choices about their child's care.
By grasping this organized procedure, you can advocate effectively for your child, ensuring they receive the essential support and tailored measures that meet their unique needs. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to guide you along the way.
Implement Therapeutic Interventions: Strategies for Managing Symptoms and Supporting Development
Applying therapeutic approaches can significantly enhance the quality of life for young individuals who are pervasive developmentally delayed. It’s essential to explore effective strategies that can make a real difference in their lives.
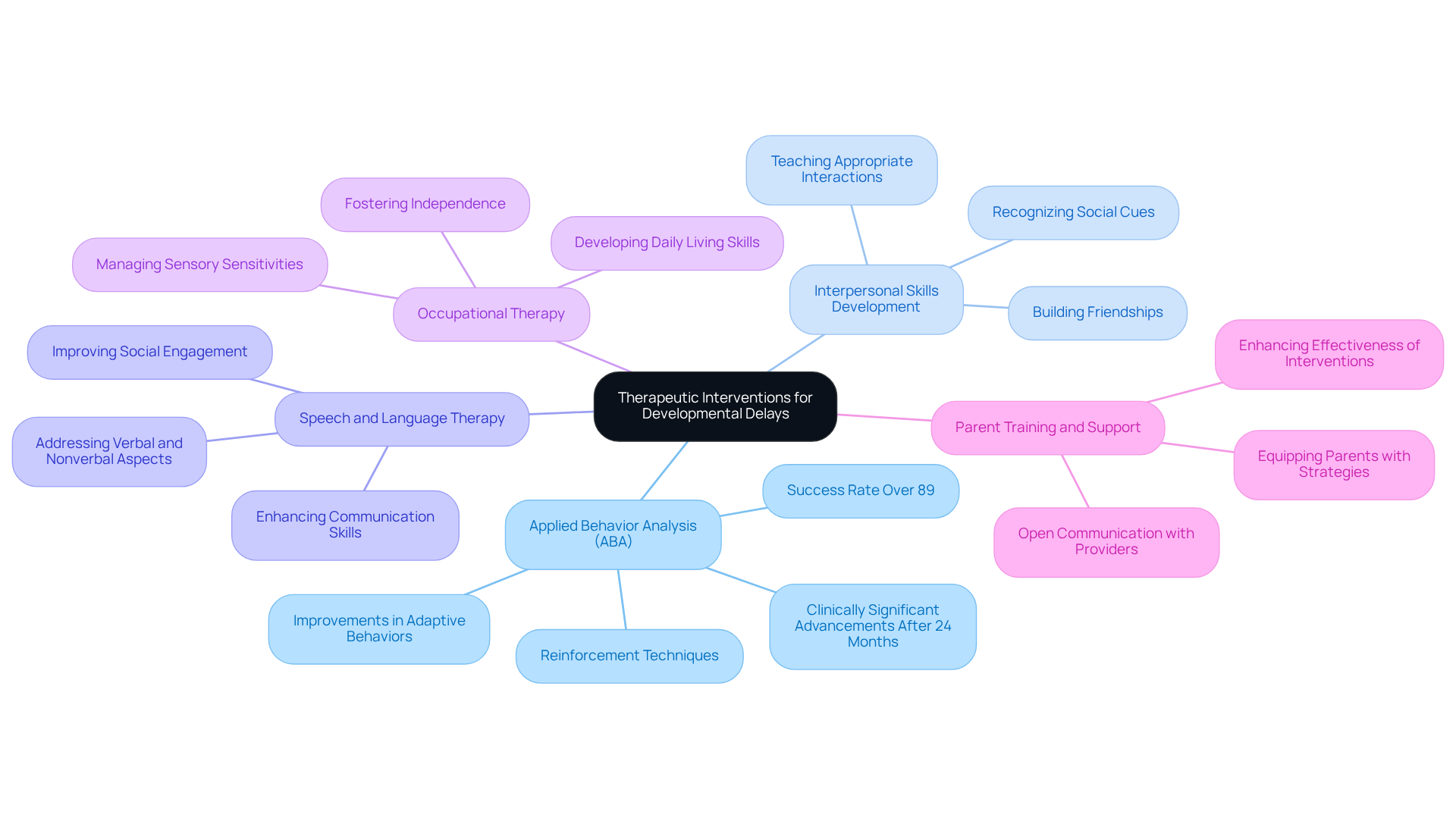
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out as a powerful, evidence-based approach. This method uses reinforcement techniques to encourage positive behaviors while minimizing challenging ones. Research shows that ABA therapy can lead to remarkable improvements in adaptive behaviors and interpersonal skills. In fact, studies indicate that after just 24 months of intervention, many young people experience clinically significant advancements. An impressive success rate of over 89% in treating autism spectrum disorder highlights its effectiveness.
Another vital strategy is Interpersonal Skills Development. Tailored programs focus on teaching young individuals how to interact appropriately with peers, recognize social cues, and build friendships. These initiatives have yielded positive outcomes, with children demonstrating improved interactions and newfound confidence in group settings.
Speech and Language Therapy also plays a crucial role. Customized interventions aim to enhance communication skills, addressing both verbal and nonverbal aspects. This therapy is key in helping young individuals articulate their thoughts and understand others, ultimately enriching their social engagement.
Let’s not overlook the importance of Occupational Therapy. This approach aids youngsters in developing essential daily living skills and managing sensory sensitivities, which is vital for fostering independence. By focusing on practical abilities, occupational therapy empowers young individuals to navigate daily challenges more effectively.
Finally, Parent Training and Support is indispensable. Equipping parents with strategies to manage behaviors and support their child's development is essential. Research underscores that parent education significantly enhances the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions, enabling families to create supportive environments tailored to their child's unique needs. Open communication and collaboration between parents and ABA providers can lead to even better therapy outcomes.
By embracing these strategies, parents can nurture a supportive atmosphere that fosters their child's growth and development, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being. Together, we can make a meaningful impact on their journey.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD) is crucial for nurturing the well-being of affected children. By recognizing the nuances of these conditions—such as Autism Spectrum Disorder, Asperger's Syndrome, and PDD-NOS—parents can navigate the complexities of their child's developmental journey with greater ease. This knowledge not only facilitates effective communication with professionals but also empowers families to seek the necessary support and interventions.
The article highlights the significance of early identification of symptoms, including:
- Social challenges
- Communication difficulties
- Repetitive behaviors
By remaining vigilant and proactive, parents can initiate timely interventions that greatly enhance their child's development. Furthermore, understanding the diagnostic process and employing a multidisciplinary approach ensures that children receive comprehensive evaluations tailored to their unique needs. The article also underscores the effectiveness of various therapeutic strategies, such as:
- Applied Behavior Analysis
- Speech therapy
- Parent training
All of which contribute to improved outcomes for children with PDD.
Ultimately, the journey of supporting a child with Pervasive Developmental Disorders can be challenging, yet it is also filled with opportunities for growth and connection. By advocating for early intervention and embracing effective therapeutic strategies, parents can cultivate a nurturing environment that promotes their child's development and quality of life. Engaging with available resources and communities can further empower families on this path, reinforcing the message that they are not alone in their efforts to foster their child's potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD)?
Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDD) are developmental conditions characterized by delays in social and interaction skills. They include disorders such as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Asperger's Syndrome, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS).
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. Each child with ASD faces unique challenges as they navigate their development.
How is Asperger's Syndrome related to Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Asperger's Syndrome, which was once considered a separate diagnosis, is now classified as part of the Autism Spectrum Disorder. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with focused interests and repetitive behaviors.
What does Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS) mean?
PDD-NOS is a diagnosis given to children who exhibit some, but not all, characteristics of autism or other pervasive developmental delays. This diagnosis can create uncertainty for parents, but it helps in understanding their child's unique profile.
Why is it important for parents to understand these terms?
Familiarity with the terms related to PDD helps parents recognize the nuances of each disorder and fosters effective communication with professionals in the field, aiding in their child's support and care.




