Overview
This article offers valuable strategies for parents seeking to support the executive function skills of their children with autism. It highlights the significance of cognitive processes such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and emotional regulation. By understanding these essential components, parents can implement tailored strategies—like visual supports, consistent routines, and engaging activities—that can make a meaningful difference.
Imagine the joy of seeing your child manage daily challenges more effectively! By fostering these skills, you not only promote their growth but also enhance their independence. Together, let's explore how these approaches can empower your child and bring about positive change in their everyday life.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of autism, understanding executive function stands out as a vital element for nurturing success in daily life. This collection of cognitive processes—including skills like working memory, cognitive flexibility, and emotional regulation—plays a crucial role in how children with autism navigate their surroundings and interact with others.
As the number of children affected by autism continues to grow, it becomes increasingly important for parents and educators to recognize the challenges tied to executive function. By delving into the components of executive function and employing targeted strategies, caregivers can empower children to overcome obstacles, enrich their learning experiences, and flourish in their social interactions.
Through a comprehensive approach that encompasses tailored interventions and supportive routines, we can illuminate the path toward fostering independence and resilience in children with autism.
Define Executive Function and Its Importance in Autism
For parents of children with autism, understanding executive function autism is crucial. These cognitive processes—planning, working memory, attention, problem-solving, and emotional regulation—are essential for controlling behavior, managing time, and organizing tasks. For kids on the autism spectrum, executive function autism skills are particularly important as they influence their ability to navigate daily activities, engage in social interactions, and achieve academic success.
As AG pointed out, 'Each system is defined by various constructs that are assessed across separate units of analysis...' This highlights the complexity of assessing cognitive processes in executive function autism, especially cognitive control. When cognitive processes fall short, it can lead to challenges in managing routines, completing tasks, and adapting to changes. Therefore, it is vital for parents to understand these concepts to better support their children.
With a developmental disorder affecting approximately 80.80 per 10,000 children in the United States, recognizing the importance of cognitive processes becomes even more critical. Thankfully, various interventions and therapies are available to help manage these symptoms. By understanding these resources, parents can create an inclusive environment that fosters learning and development.
Consider real-world examples: difficulties in transitioning between activities or managing homework can illustrate the everyday challenges faced by individuals on the autism spectrum due to executive deficits. These experiences resonate deeply, reminding us of the importance of empathy and support for our children’s unique journeys.
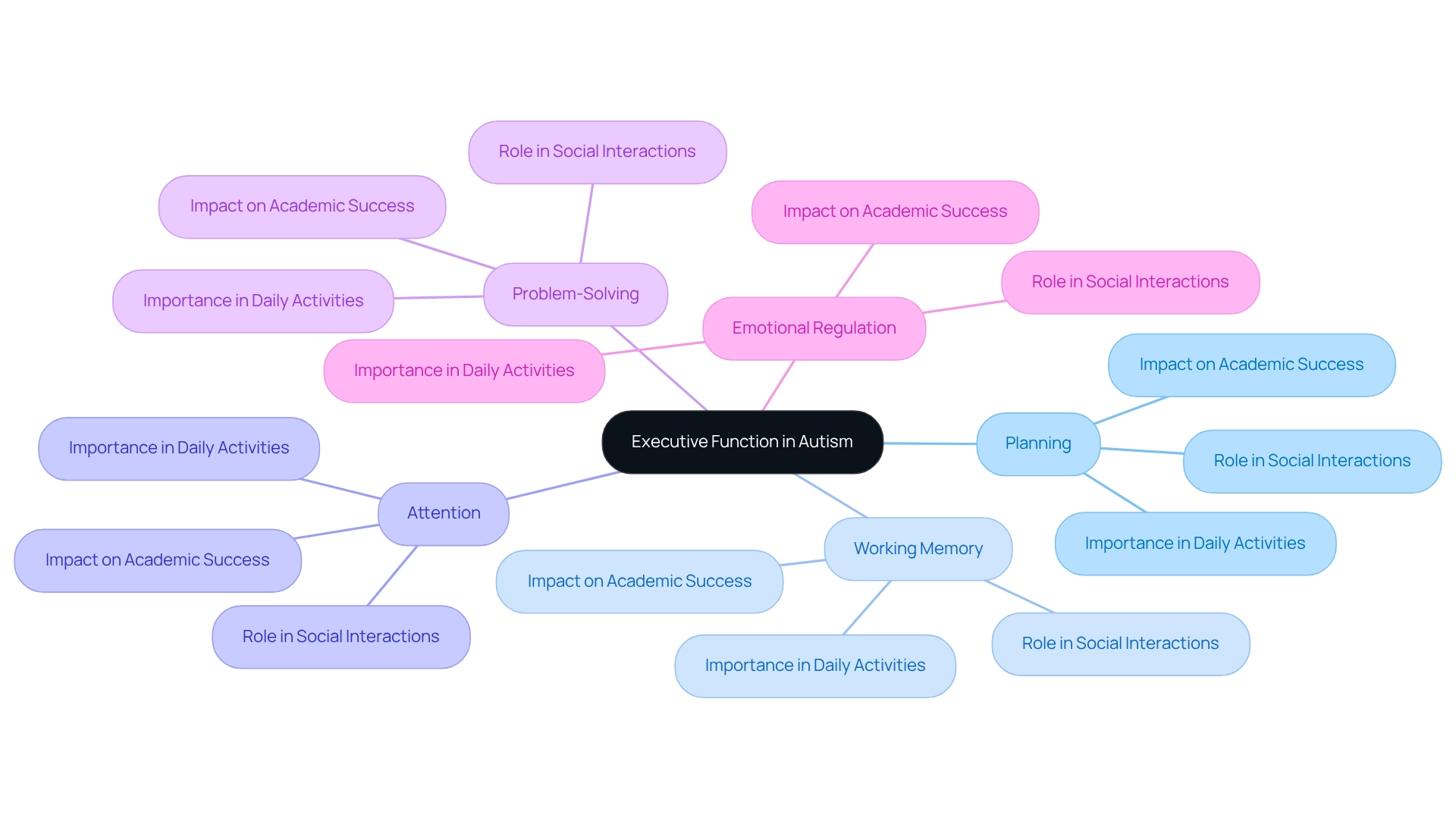
Explore Components of Executive Function in Autism
Executive function autism encompasses various vital elements essential for everyday activities, particularly for young individuals with developmental disorders. Understanding these components can empower parents to support their children more effectively.
- Working Memory: This refers to the ability to hold and manipulate information in mind over short periods. Many individuals with autism face significant challenges in executive function autism, particularly in working memory, which can hinder their ability to follow instructions and engage in complex tasks. Have you noticed this in your child?
- Cognitive Flexibility: This is the capacity to switch between thinking about different concepts or to consider multiple concepts simultaneously. Research indicates that individuals with autism often face cognitive flexibility challenges, which are a component of executive function autism, manifesting as difficulties in adjusting to changes in routine or transitioning focus between tasks. It’s important to recognize these struggles.
- Inhibitory Control: This involves the ability to suppress impulsive responses and think before acting. Individuals with executive function autism may experience difficulties with inhibitory control, leading to impulsive behaviors that can affect their social interactions and learning. Understanding this can help in guiding their behavior.
- Planning and Organization: These skills are crucial for setting goals, outlining steps to achieve them, and organizing tasks accordingly. Many individuals with autism face challenges related to executive function autism, which makes it difficult for them to plan and organize their activities, potentially impeding their academic and social success. How can we help them navigate this?
- Emotional Regulation: This is the ability to manage emotions appropriately in various situations. Individuals with executive function autism often face challenges with emotional regulation, which can lead to increased anxiety or frustration in difficult situations. Supporting them in this area is vital.
By grasping these elements, parents can identify specific obstacles their children may encounter and apply targeted strategies. Recent research highlights the importance of tailored interventions addressing working memory and cognitive flexibility, suggesting that effective assessment practices related to executive function autism can significantly improve outcomes for young autistic children. Notably, 1 in 186 individuals in China are estimated to be on the spectrum, underscoring the global relevance of these challenges. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention emphasizes the need to recognize disparities in autism rates by gender and race to ensure equitable support for all individuals on the autism spectrum.
By promoting an understanding of executive function autism skills, parents can better assist their children in managing everyday challenges and enhancing their overall growth. Additionally, findings from the case study titled 'Implications for Assessment Practices' suggest that while the CCTT serves as a beneficial resource for evaluating cognitive flexibility, verbal fluency tasks may require modifications to more accurately reflect the cognitive capabilities of young individuals with autism. This evidence reinforces the importance of understanding cognitive processes in the context of developmental disorders.
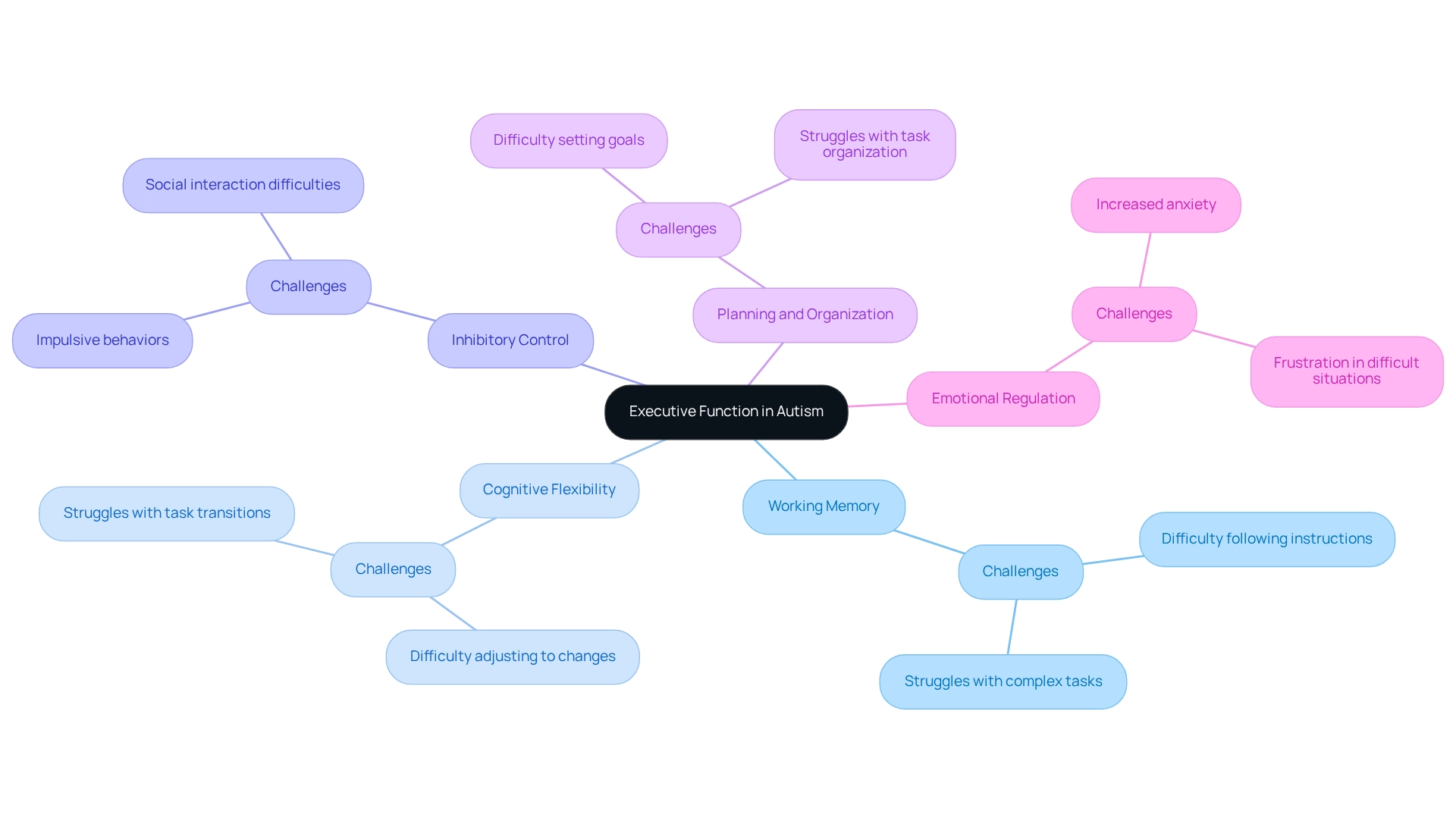
Implement Strategies to Support Executive Function Skills
Supporting executive function autism skills in children is a journey that requires understanding and compassion. Here are some strategies that can make a meaningful difference:
- Utilize Visual Supports: Visual schedules and checklists can significantly aid children in understanding and managing their daily tasks. These essential tools foster independence, acting as bridges to a more fulfilling life for individuals with autism.
- Establish Consistent Routines: Structured daily routines enhance predictability, alleviating anxiety and improving task completion rates. It's important to regularly assess and modify these routines based on feedback from the young individual. As ASD Media states, "Routines are not fixed; they should be periodically assessed and modified according to the individual's feedback and developmental changes."
- Break Tasks into Manageable Steps: Dividing larger tasks into smaller, more manageable steps helps prevent feelings of overwhelm and fosters a sense of accomplishment.
- Incorporate Engaging Activities: Games that promote working memory and cognitive flexibility—like memory games or puzzles—can be both enjoyable and beneficial for skill development.
- Model Problem-Solving Techniques: Demonstrating how to tackle issues and make choices inspires young individuals to express their thought processes, enhancing their cognitive abilities.
- Provide Positive Reinforcement: Acknowledging successful use of organizational skills through praise and rewards motivates young individuals to continue practicing these essential abilities.
Research indicates that structured physical activity can also serve as an effective intervention, promoting cognitive and behavioral improvements in children with ASD. This reinforces the idea that a holistic approach, including physical activity, is vital for supporting executive function autism skills and overall well-being. By embracing these strategies, we can nurture the growth and independence of children with autism, fostering a brighter future for them.
Conclusion
Understanding executive function is essential for supporting children with autism as they navigate daily life and strive for success in both academic and social environments. This collection of cognitive processes—including working memory, cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, planning and organization, and emotional regulation—plays a pivotal role in how these children manage their routines and engage with their surroundings. Recognizing the challenges linked to executive function is crucial for parents and educators, empowering them to implement targeted strategies that nurture resilience and independence.
By employing practical strategies such as:
- visual supports
- consistent routines
- breaking tasks into manageable steps
caregivers can create an environment that fosters learning and development. Engaging activities that promote executive function skills, combined with positive reinforcement, further encourage children to practice and enhance their cognitive abilities. The integration of structured physical activity underscores the importance of a holistic approach to supporting children with autism.
As the prevalence of autism continues to rise, the need for tailored interventions becomes increasingly critical. By focusing on executive function and its components, caregivers can better assist children in overcoming obstacles and enriching their learning experiences. Ultimately, fostering an understanding of these cognitive processes not only enhances the daily lives of children with autism but also paves the way for their long-term success and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is executive function in the context of autism?
Executive function refers to cognitive processes such as planning, working memory, attention, problem-solving, and emotional regulation, which are essential for controlling behavior, managing time, and organizing tasks.
Why is understanding executive function important for parents of children with autism?
Understanding executive function is crucial for parents as it influences their child's ability to navigate daily activities, engage in social interactions, and achieve academic success.
What challenges can arise from deficits in executive function for children with autism?
Deficits in executive function can lead to difficulties in managing routines, completing tasks, and adapting to changes, which can affect daily life and learning experiences.
How prevalent is autism, and why is executive function important in this context?
Autism affects approximately 80.80 per 10,000 children in the United States, making it critical to recognize the importance of cognitive processes like executive function to better support affected individuals.
What types of interventions are available to support executive function in children with autism?
Various interventions and therapies are available to help manage executive function symptoms, enabling parents to create an inclusive environment that fosters learning and development.
Can you provide examples of everyday challenges related to executive function for individuals with autism?
Everyday challenges may include difficulties in transitioning between activities or managing homework, which illustrate the impact of executive function deficits on daily life.




